L5 Heritability
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
What is heritability?
The proportion of variation in a trait that can be attributed to genetic factors.
What are behaviour genetics
a group of methods that studies families to examine variation among individuals on a characteristic to infer genetic contribution
Purpose of family studies
assess the biological relatives of an individual affected with a MD
Purpose of twin studies
to compare the proportion of MZ twins in which a MD occurs in both twins vs proportion of DZ twins
Purpose of adoption studies
to examine whether an individual born to a parent with an MD develops it if adopted by unaffected families
What did Gottesman’s (1991) family study on schizophrenia find
high genetic component – 48% concordance rate MZ twins
A different in concordance rate between non-identical twins and non-twin siblings suggests the role of ? (Gottesman didn’t measure)
environmental influence
What did Polderman et al.’s (2015) review of twin studies conclude about heritability?
MZ twins consistently show higher concordance rates than DZ twins for various conditions, supporting high heritability.
What 3 MH conditions did Polderman et al. find high concordance between MZ than DZ twins (suggesting high heritability) (3 others)
depressive episode, conduct disorder, alcohol
2 reasons why there might be an overestimation of genetic contribution in family/twin studies
shared environmental factors and non-genetic psychological factors affect MZ more than DZ twins
What did Heston’s (1966) adoption study on schizophrenia find?
10.6% of adoptees born to mothers with schizophrenia later developed the disorder, compared to 0% in controls.
How many adoptees (out of 47) born to schizophrenic mothers developed the disorder later in life, according to Heston
5
Why are adoption studies useful in genetic research?
They help separate genetic influences from environmental effects.
What is a limitation of adoption studies?
Adoption is rare, and obtaining pre-adoption clinical information can be difficult due to ethical concerns.
2 advanced ways to study brain and genes
brain imaging and genetic association studies
3 things measured by brain imaging in MD heritability
differences in brain structure, function and connectivity in individuals with MH conditions
What is the role of genetic association studies in mental health research?
To identify gene variants that may contribute to the risk of developing a mental disorder.
Case control vs family-based genetic association study design
comparing an individual with MH condition to individuals without that MD or an unaffected sibling
2 functions of hippocampus
transfer of STM to LTM and encoding emotional context of events from amygdala
3 brain areas associated with depression
hippocampus, hypothalamus, prefrontal cortex
2 brain areas associated with psychosis
amygdala and thalamus
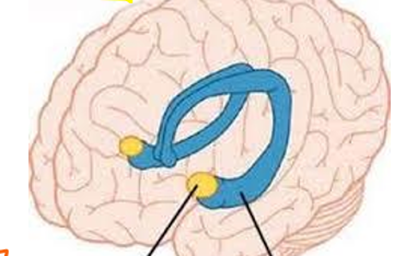
Label yellow and blue area
yellow = amygdala, blue = hippocampus
Role of amygdala
generate emotional responses
3 functions of hypothalamus
regulates hormones, head of HPA system and regulates non-conscious processes
Role of prefrontal cortex
executive functioning e.g. planning, decision making and regulating social behaviour
What brain activity is linked with visual hallucinations
reduced activity of hippocampus
What MH condition is increased hippocampus-amygdala connectivity linked to and why
paranoid schizophrenia - due to heightened sense of fear/threat
Is there greater or lower hippocampal volume in early onset / recurring depression
lower
What auditory function are temporal lobes important for and what schizophrenia symptom is it associate with
important for speech processing, affects auditory hallucinations
What are polymorphic genes + what do they contribute to in genetic association studies
different variants or forms of a gene + account for individual differences in MH conditions
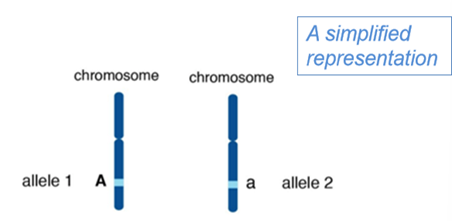
Explain what it means if a gene has different variants
more than 1 allele occupies that gene’s position in the chromosome
Explain a ‘risk allele’
when one allele in a gene variant is identified as being more common in individuals with a certain MH condition
What is polygenic
when many genes are involved
Do gene variants contribute to mental health risk
many polymorphisms increase risk for various MH conditions but involve small effects
How many gene variants were found to be associated with schizophrenia + % of statistical variance?
128 variants, explaining 23% of statistical variance
How many gene variants associated with major depression
102
What are the three mental disorder clusters shared by polymorphisms identified by Lee et al. (2019)?
Mood & psychotic disorders, disorders with compulsive behaviors, and early-onset neurodevelopmental disorders.
What is a limitation of brain imaging and genetic association studies if variables cannot be manipulated?
They cannot determine causal effects, only correlational and may be influenced by environmental factors.
What is a key population validity limitation of genetic research in mental health?
The majority of genetic data comes from individuals of European ancestry, limiting generalizability.
What is epigenetic studies
examining how gene expression is affected by experience
What did Caspi et al. gene X environment study about the serotonin transporter gene (5-HTT)?
2 out of 3 variants of the 5-HTT gene increased depression risk, but only in individuals who had experienced multiple stressful life events.
What is behavioural epigenetics?
the study of how experience leads to epigenetic changes that may affect behaviour like MH
What is epigenetic modification
when environmental influence alters gene/phenotypic expression but the genotype itself does not change – switches genes ON or OFF
What gene was suppressed by early life stressed mice
‘dopamine expression’ gene