VT 111 Lec. 2 Tissues & Body Membranes
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Tissues
Are a collection of cells that are similar and that function together for a similar purpose.
Used to build organs in animals
Classification of tissues based on:
Structure of the cells
composition of the non cellular substance surrounding the cells (the matrix)
Function of the cells
Histology
The study of tissues
Cytology
The study of cells
Types of Embryonic Tissues
Ectoderm: skin and adnexal structures (supporting appendages (structures/organs) near primary organs or systems), nervous system
Endoderm: lining of G.I. tract, hollow organs (bladder)
Mesoderm: bone, blood vessels, muscle, parenchyma of internal organs
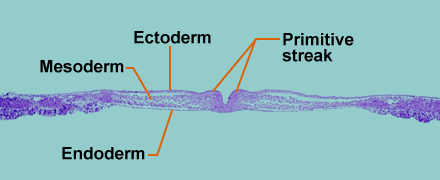
Embryonic Tissues
Tissues in the embryo that begin to form soon after fertilization
Day 13 or 14 in humans
15 hrs in chickens
Embryologic tissues are germinal layers because they can become different types of structures in the adult
Types of Post Embryonic (Adult) Tissues
Epithelial → covers & lines
Connective (CT) → provides support
Muscular → enables movement
Nervous → controls work
Post Embryonic (Adult) Tissues
All tissues formed from the germinal tissues
Once the adult tissue is formed, its structural and functional fate is determined
Adult tissues are said to be differentiated (range of cell types with distinct structures/functions)
Separate tissues have individual functions, but they all work together for survival of the organism.
Biopsy
The process of removing tissues for analysis from a patient
Epithelium: Where it’s Located
Protective covering of the surface of the body
Both inner and outer surfaces
External surface made from ectoderm
Internal surfaces made from endoderm
Characteristics of Epithelium
Composed entirely of cells, lateral surfaces connected to neighboring cells by junctional complexes → very little extracellular matrix, if at all
Some lack nerves but most are innervated → provide sensory input
Specialized connections: tight junctions, desmosomes, gap junctions
No blood supply, lacks blood vessels (avascular)
Has polarity: apical vs. basal surface
Basement membrane that separates it from underlying connective tissue
Basal surface (side of the cell that faces the underlying connective tissue
Apical (side of the cell that faces the lumen (body cavity)
Forms in sheets, covering or lining a structure
Retains high mitotic rate among undifferentiated stem cells even in adult animals
Functions of Epithelium
Protect, covers & lines underlying structures
skin, mucous membrane protects against abrasion
Act as a barrier
epithelium prevents movement of substances through the epithelial layer, prevent entry of microorganisms
Absorption/exchange/filter biochemical substances
exchange of respiratory gases, movement of nutrients, renal filter
Excretion – substances that leave the body
Urine, feces, sweat
Secretion – substances that stay in the body
mucous glands, sweat, etc.
Provides sensory input
Smell, taste, sight
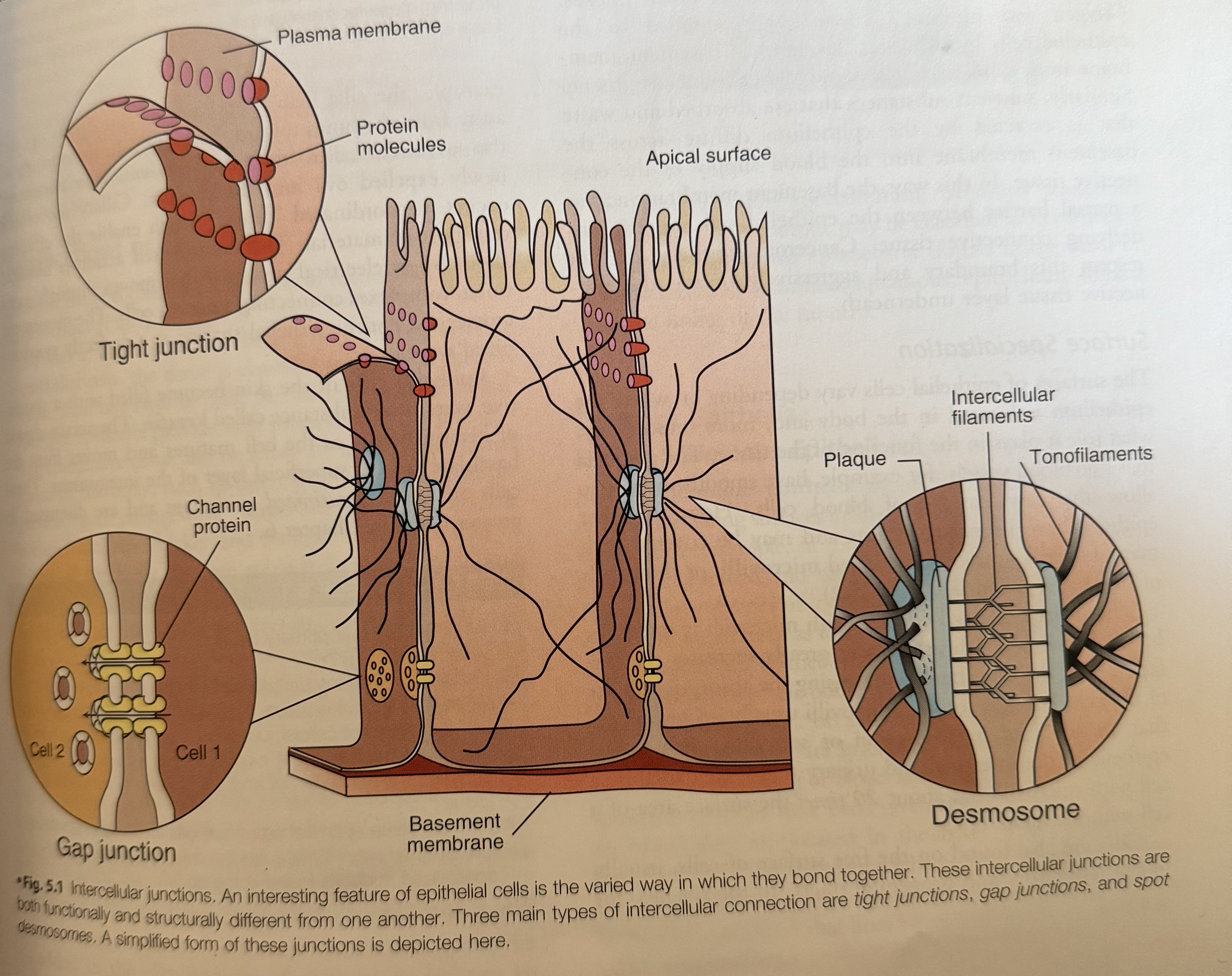
Cellular Attachments
Plasma membranes
Tight junctions
Desmosomes
Gap junctions
Basement membrane/Basal lamina
Plasma Membranes
Join to form specialized attachments
Junctional complexes → provide strength
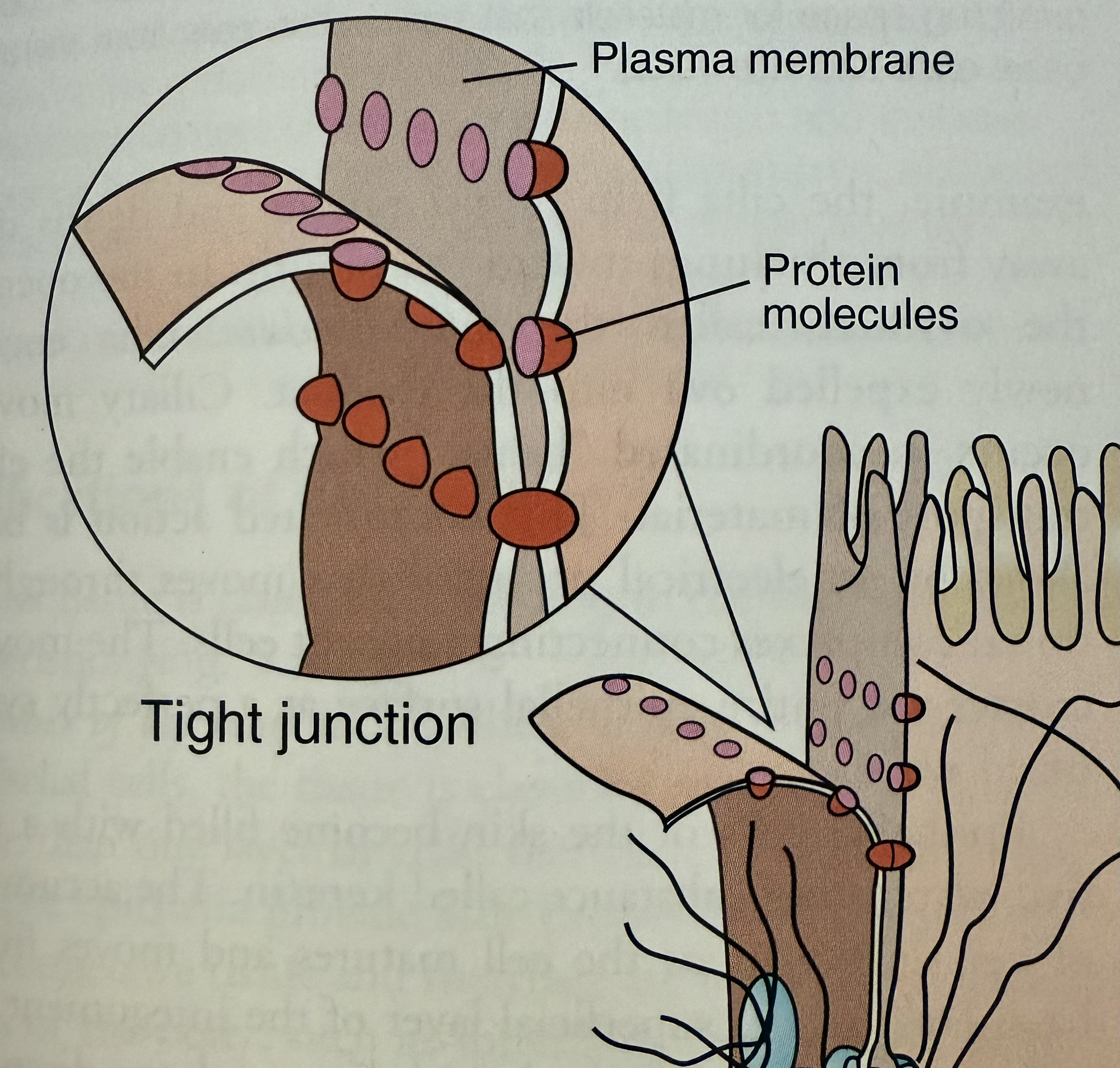
Tight Junctions
Formed by fusion of outermost layers of plasma membranes of adjoining cells
No leaks i.e tissues of the bladder or digestive tract
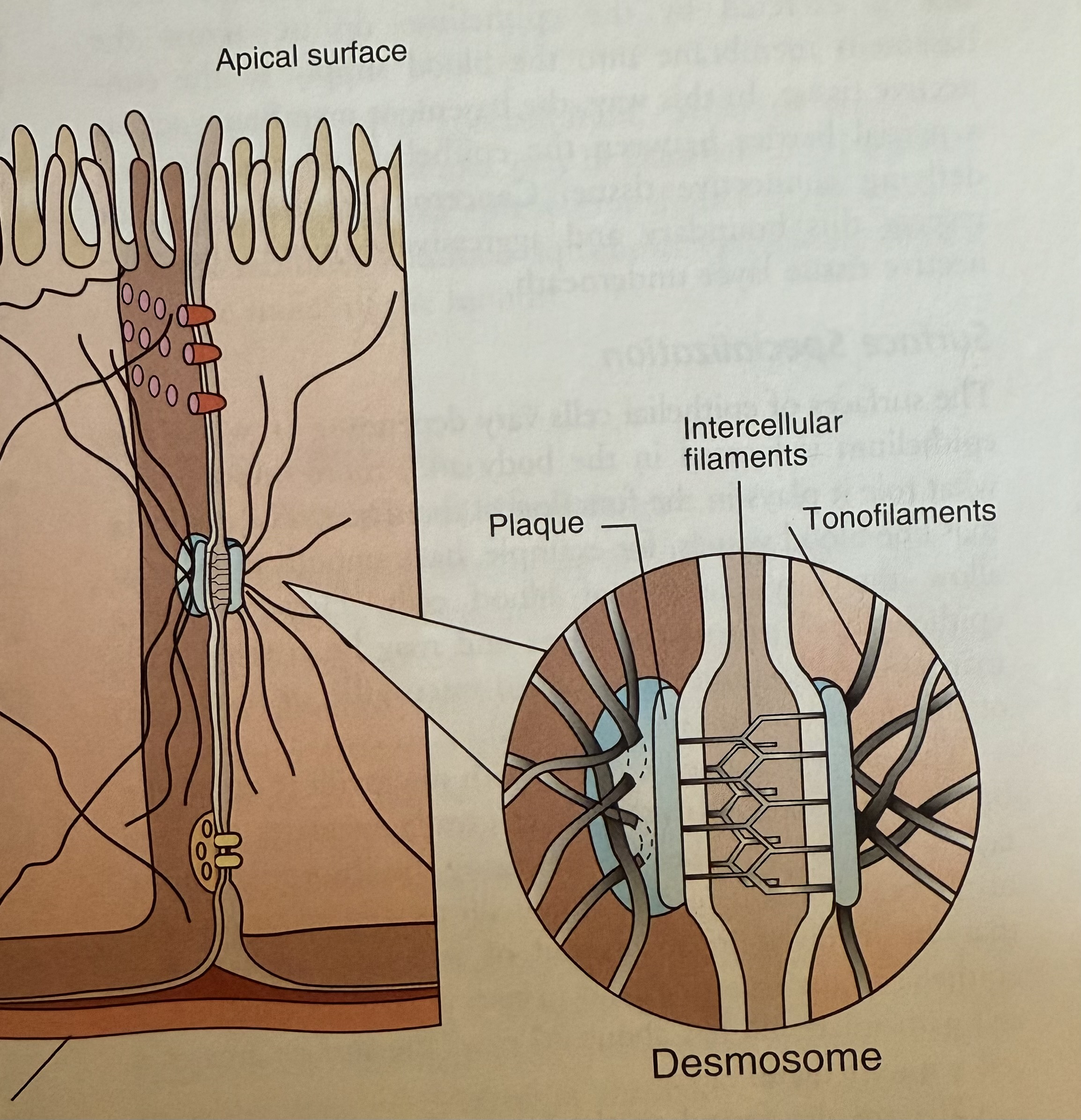
Desmosomes
Connect plasma membranes of adjacent cells
Strong mechanical coupling formed by filaments that interlock
Plaque (thickening)
Tonofilaments – intermediate filaments that extend from the plaque into the cytoplasm of each cell like anchors
Found in tissues that undergo repeated tension & stretching
i.e skin, heart, uterus
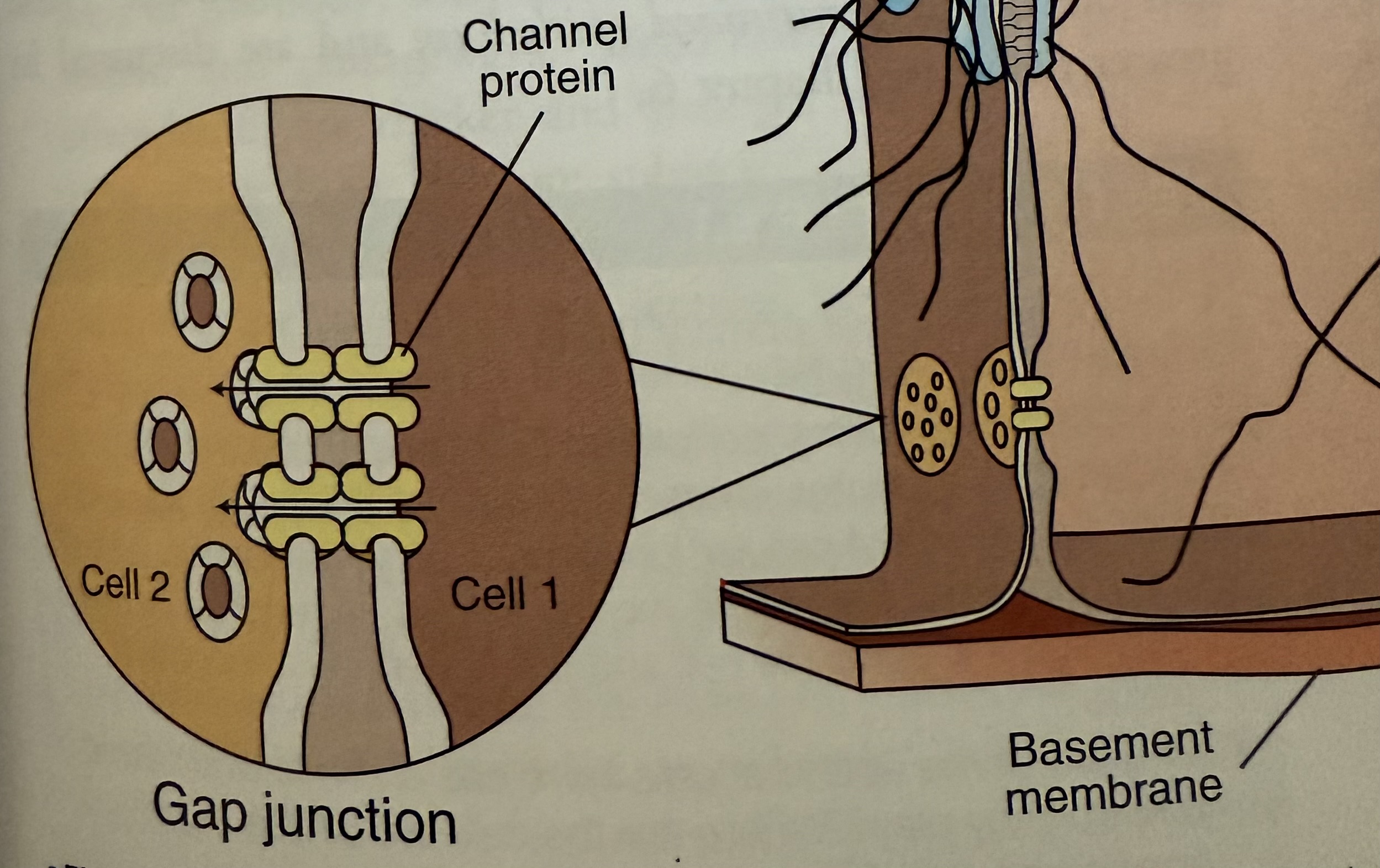
Gap Junctions
Cells linked by tubular channel proteins (transmembrane proteins)
Aka Connexons
Extend from cytoplasm of one cell to the next
Allow exchange and passage of ions and nutrients
Role in cardiac and smooth muscle cells is to have the ability to quickly transport electrical signals between cells
Basement Membrane = Basal Lamina
Foundation of the epithelial cell
Nonliving network of fibers
Cements cells to underlying connective tissue
Varies in thickness
Helps prevent cells from being torn off
Partial barrier to underlying connective tissue
Surface Specialization
Surfaces vary depending on their location and their role in the function of the tissue
Smooth
Epithelia that line blood vessels is smooth to allow easy passage of blood cells
Microvilli – fingerlike projections
Brush border – surface of a cell covered with microvilli; greatly increases surface area → increases absorptive ability; microvilli tend to occur on cells involved in absorption or secretion
Cilia
Found on the free surfaces of cells and helps propel mucus and debris
Ex. Respiratory tract or urogenital tracts
Keratin
Waterproof
Accumulation of keratin occurs when mature cells move from the basal layer to the superficial layer; keratinized epithelium
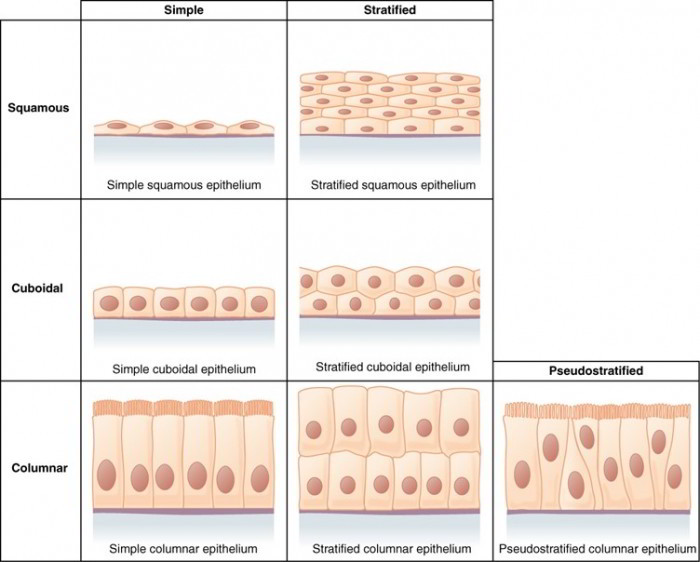
Classification of Epithelium
# of layers of cells
Simple: single layer of cells (little protection to CT)
Stratified: multiple layers of cells (stronger)
Pseudostratified columnar: looks stratified but isn’t. Some cells tall, some short, all cells attached at basement membrane
Shape of cell:
Classified by the shape of the cell on the luminal surface
Squamous = flat
Cuboidal = like a box
Columnar = taller than it is wide
Presence of surface specializations
“cilia”, “keratinized” to indicate increased level of specialization
Types of Epithelia
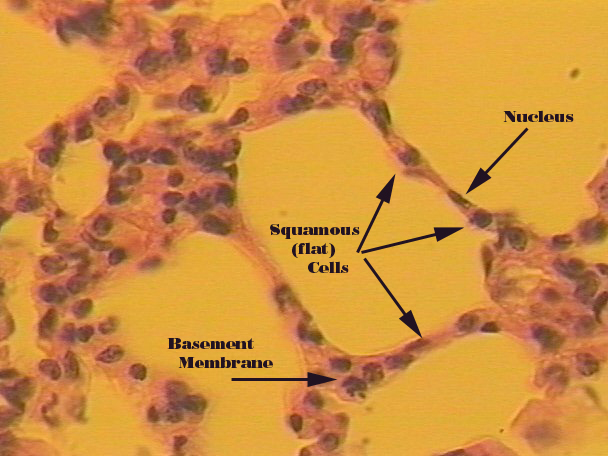
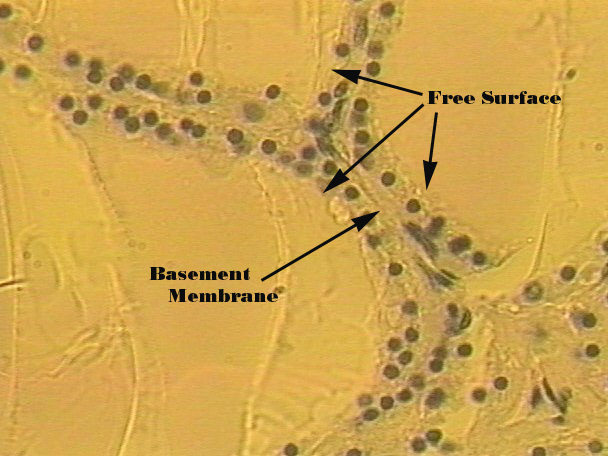
Simple Squamous
Delicate, thin: inner lining of lung alveoli
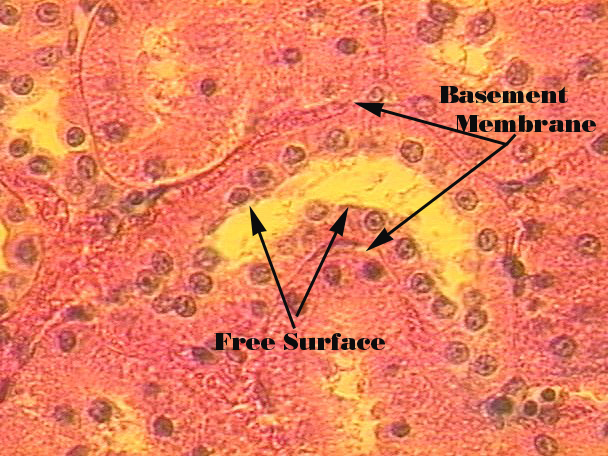
Simple Cubodial
Central nuclei aligned in a row: ducts of liver, pancreas, salivary gland
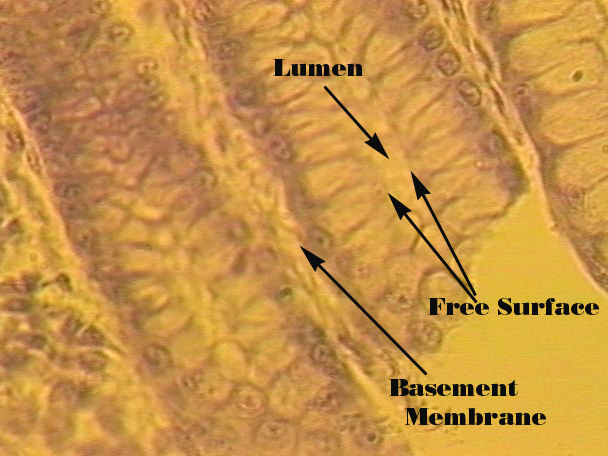
Simple Columnar
Elongated cells; nuclei at base of cell: lining of GI tract
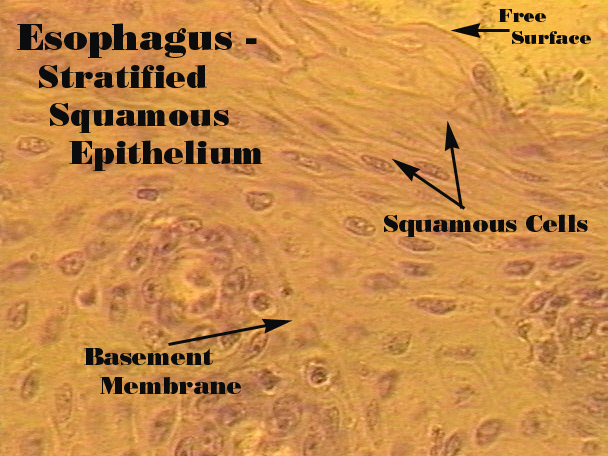
Stratified Squamous
Layers of cells: lining of the mouth or skin
Stratified Cuboidal
Generally 2 layers: sweat glands
Stratified Columnar
Rare: urethra
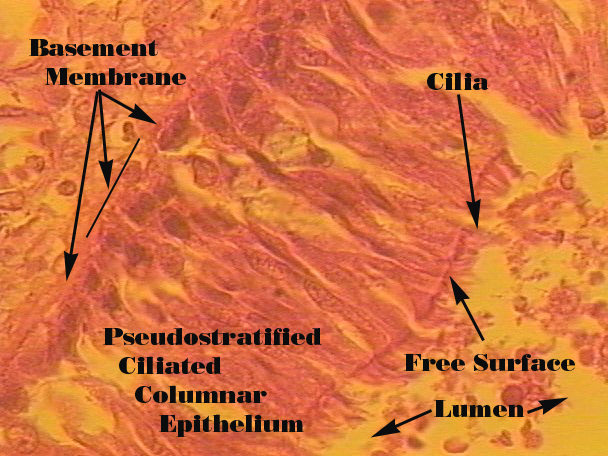
Pseudostratified Columnar
Cells of different heights; ciliated: trachea
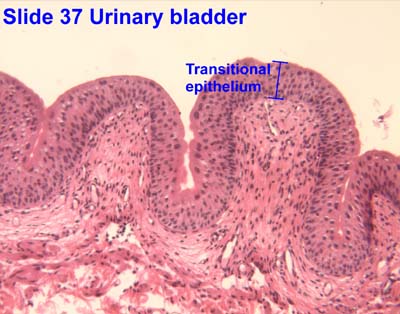
Transitional
Ability to stretch: bladder
Squamous Epithelium
Simple Epithelium
Delicate and thin
Flat and smooth
Found lining surfaces involved in passage of either gas or liquid
Mesothelium – epithelium of the serous membranes
Endothelium – epithelium that lines blood and lymphatic vessels
Stratified Epithelium
Multilayered
Protect underlying tissues
Occurs in areas of body subject to mechanical and chemical stresses
Mouth, esophagus, vagina
Outer layer continually being worn off
Replaced at equal rate from cells in deeper layer
Cuboidal Epithelium
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Single layer of cube-shaped cells
Nuclei aligned in single row
Found in areas where secretion and absorption occur
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Generally occurs in two layers
Protects underlying tissues
Found primarily along large excretory ducts
Sweat glands, mammary glands, salivary glands
Columnar Epithelium
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Cells are elongated, closely packed together
Nuclei aligned in a row at base of cell
Some cells associated with absorption and secretion
Some ciliated on apical surfaces – simple ciliated columnar epithelia
Absorptive cells – covered in microvilli
Goblet cells – manufacture and store lubricating mucus onto luminal surfaces of epithelia
Columnar Epithelium Continued…
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
Rare type of epithelia
In select parts of respiratory, digestive, and reproductive systems
Along some excretory ducts
Function in secretion and protection
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
Not truly stratified; rather simple
Nuclei at varying levels. not all cells reach luminal surface
Attach to basement membrane
Most are ciliated
In respiratory tract and portions of male reproductive tract
Transitional Epithelium
Description:
Basal layer of cuboidal or columnar cells
Superficial layer of squamous cells
Leak-proof membrane
Found in regions required to expand and contract as part of their normal function
Ureters, urethra, bladde
Connective Tissue (CT)
Derived from mesoderm
Vascularized structural-type of tissue; found throughout body
Most abundant and varied tissue
Several types of CT
Bone, blood, fibrous tissue, cartilage, fat
Most (except fat) have more extracellular matrix than cells
Classification scheme based on
Protein fiber type and orientation
Type of ground substance in the matrix
The fluid of the extracellular matrix
Types of Cells
➡
Fibrocytes
Maintain the general matrix of collagen
-blast type cells
cells that create the matrix
-clast type cells
cells that break the matrix down for remodeling
-cytes
cells that are maintenance type of
cells; cytes can convert back to blasts if
needed
Specialized Cells
➡
Chondrocytes
cells of the cartilage
Osteocytes
Cells of the bone
Adipocytes
Fat cells
Mast Cells
contain histamine, vasoactive chemicals
Leukocytes
White blood cells
Erythrocytes
Red blood cells
Macrophages
Phagocytic cells
Undifferentiated stem cells
Another type of specialized cell
Characteristics of Connective Tissue
Unique single feature is that it consists of a living cellular component and a non-living matrix.
Wide variety in ground substances, # and type of cells, and type of fibers allow for the many different kinds of CT
The matrix is a combination of 3 basic components:
Protein fibers (collagen, elastin, reticular)
Ground substance (from liquid to gel to solid)
Water
Carbohydrates, simple sugars, ions, complex CHO’s
Hyaluronic acid, glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans
Minerals
Cells can be fixed (adipose) or wandering (WBC, macrophage)
Ground Substances
Medium through which the cells exchange nutrients and waste with blood
Amorphous homogeneous material that ranges from liquid to gel to solid (glycoproteins)
Shock-absorbing cushion that envelopes and protects delicate cells
Effective obstacle for invading microorganisms (microbes)
Extracellular Fibers
Collagenous fibers
Reticular fibers
Elastic fibers
Collagenous Fibers
Most common; strong (immense tensile strength), thick strands of protein collagen
Organized into bundles
Varying density and arrangement of fibers
Loose CT surrounds organs
Dense CT around tendons & ligaments
Reticular Fibers
Thin, delicate, branched networks of collagen
Provide support for highly cellular organs
Endocrine glands, lymph nodes, spleen, bone marrow, liver
Also found around nerves, blood vessels, muscle fibers, and capillaries
Elastic Fibers
Composed primarily of the protein elastin
Branched to form complex networks
Coiled microfibrils that can stretch & contract
Occur in tissues subjected to stretching
Vocal cords, lungs, skin, walls of blood vessels
Major Cell Types
Fixed cells
Transient Cells
Fixed Cells
Remains in connective tissue
Involved in production and maintenance of the matrix
Fibroblast – manufacture & secrete fibers & ground substances of their matrix
Chondroblast
Osteoblast
Adipocyte – begin by looking like fibroblasts, but as they mature, fill with lipid & swell
Reticular cell – involved in immune response
Transient Cells
Passes in and out of connective tissue = diapedesis
Involved in repair and protection of tissue
Leukocyte – involved in immune response to kill invaders; can move through the walls of blood vessels through diapedesis
Mast cell – contain histamines and heparin; involved in inflammatory response,
Macrophage – involved in immune response to infection; phagocytes that engulf microbes, dead cells, and debris
Function of Connective Tissue
Packaging, separating
Capsules around organs, holding layers to separate other tissues
Connecting tissues to one another
Tendons, ligaments
Support, movement
Bones, cartilage
Storage
Nutrients, fat, minerals
Cushioning, insulating
Adipose tissue
Transportation/diffusion
Blood acts as a transport medium
ECF acts as a diffusion matrix for cells
Protection
Cells of the immune system, bones protect underlying structures, et
Types of Connective Tissue
➡
Loose CT
Packaging around organs attaches skin to underlying tissues
Areolar
Adipose
Reticular tissues
Dense CT
Dense regular CT
Protein fibers oriented in one direction
tendons, ligaments, etc.
Elastic CT
Contains collagen, elastin
vocal folds, nuchal ligament, external ear
elastic type: walls of arteries
Dense irregular CT
Random oriented fibers (collagen)
Dermis, fibrous covering of organs
Cartalige
Chondrocytes
Classification depends on different types of ground substance
Multiple functions
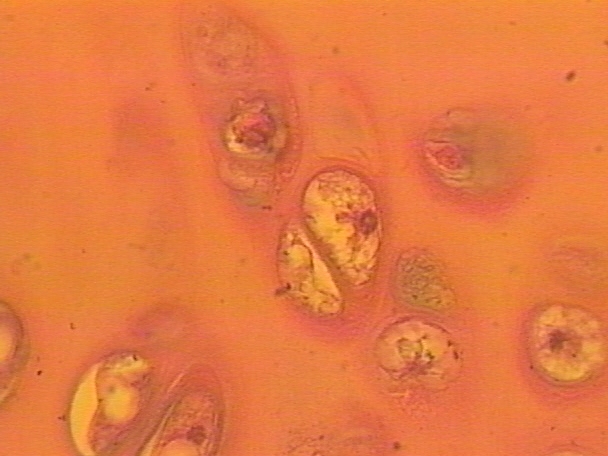
Hyaline Cartalige
Most common cartilage
Most rigid cartilage
Composed of closely packed collagen fibers and enclosed within a perichondrium
Smooth, high amount of proteoglycans and collagen
Articulating surfaces
Ends and growth plates of long bones, ribs, trachea, costal cartilage of ribs connecting to sternum
Fetal skeleton
Fibrocartilage
Usually found merged with hyaline cartilage and dense connective tissue
Contains thick bundles of hyaline cartilage
No perichondrium
More collagen than proteoglycans
Slightly compressible, but very tough
Takes a great deal of pressure
Menisci of knee
Between bones in pelvis
Intervertebral discs
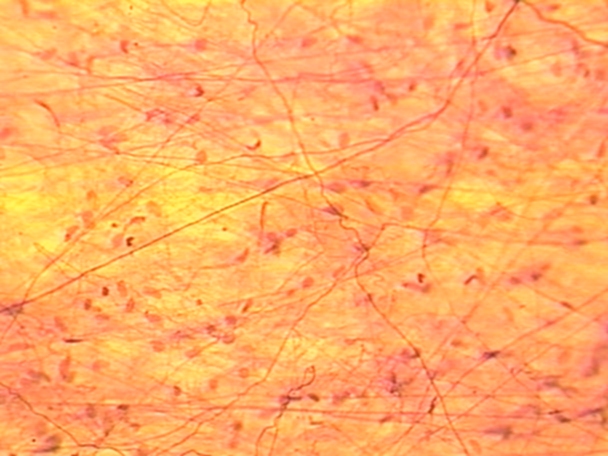
Areolar Tissue
Loose connective tissue; most common type of CT; found everywhere in the body
Tangle of random fibers and cells suspended in thick ground substance
Predominant cell is fibroblast
Functions
Surrounds and supports
Provides nutrients
Present in all mucous membranes
Pathological state
Loose CT fills with excessive body fluid -> Edema, pitting edema
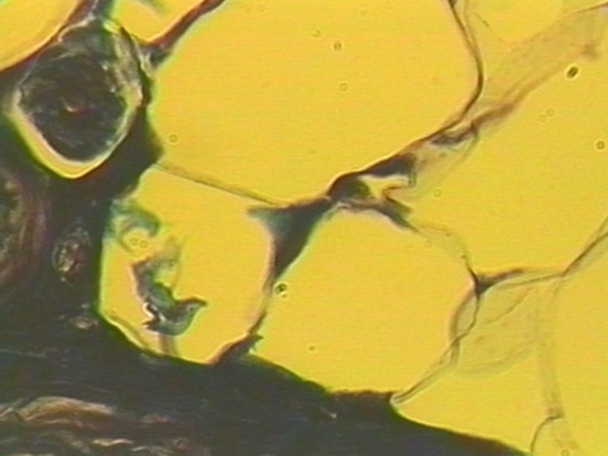
Adipose Tissue = Fat
Loose connective tissue
Areolar tissue in which adipocytes (fat cells) predominate
Located throughout body
Highly vascular
Very little extracellular matrix
2 main types
White adipose in the deep layers of the skin
Brown adipose found in newborn animals and those that hibernate
Functions
Energy storehouse
Thermal insulator
Mechanical shock absorber
Reticular Tissue
Loose connective tissue
Thin, 3D network of loosely arranged reticular fibers and fibroblasts suspended in ground substance
Forms framework for organs = Stroma
Spleen, lymph nodes, bone marrow
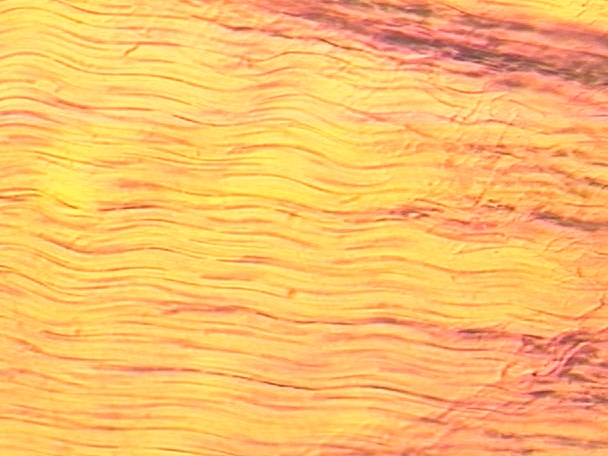
Dense Regular CT
Tightly packed parallel collagen fibers
Fibroblasts form rows
Immense tensile strength in one direction (fibers lie in the direction in which the force is exerted on them)
Relatively avascular; slow to heal
Locations
Tendons and ligaments
Sheets of fascia
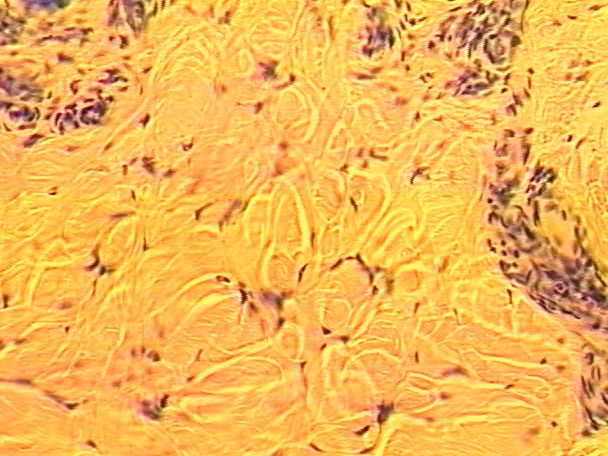
Dense Irregular CT
Thicker bundles of collagen than in dense regular
Fibers interwoven into single sheet; can withstand forces from different directions
Locations
Dermis of skin
Fibrous covering of organs
Kidney, testes, liver, spleen
Tough capsule of joints
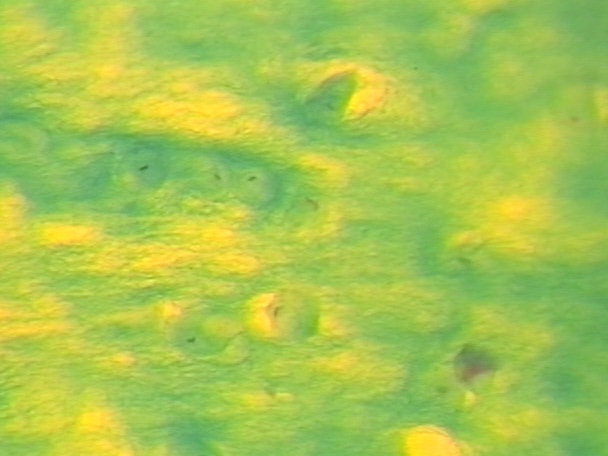
Elastic CT
Composed primarily of elastic fibers in dense, branching bundles; along with collagen and proteoglycans
Parallel or interwoven pattern with fibroblasts and collagen
Flexible
Withstands repeated bending
Locations
Spaces between vertebrae
Body regions that require stretching
Ligaments
Walls of arteries, stomach, bronchi, bladder, heart
Epiglottis of larynx
External ears of animal
Specialized CT
Cartilage
Based on type of fiber in matrix
Osseous connective tissue = bone
Calcium phosphate salts
Blood
Cells
Plasma is the extracellular fluid matrix
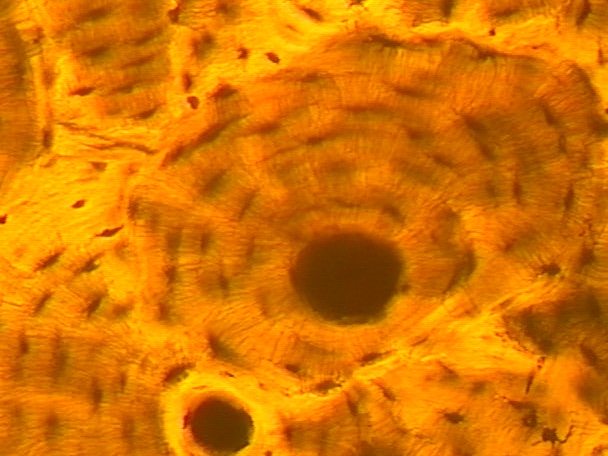
Bone CT
Hardest and most rigid connective tissue
Specialized matrix
Organic collagen fibers
Inorganic calcium salts
Well vascularized
Central haversian canal – vascular supply & nerve supply
Canaliculi
Locations
Skeletal fram
Blood CT
Matrix
Ground substance = plasma
Fibrous component = protein
Cells
Erythrocytes = RBCs
Leukocytes = WBCs
Thrombocytes = platelet
Cartilage = Gristle
More rigid than dense connective tissue
More flexible than bone
No innervation – can withstand a great deal of compression; avascular
Cells
Chondrocytes in lacunae
Matrix
Firm gel ground substance, tissue fluid, collagen, & elastic fibers
Locations
Joints, ear, nose, vocal cords
Framework for bone formation
Muscle Tissue
Primary characteristic: all muscle tissue is contractile
Muscle only does work when it contracts
Classification based on structure and function
Striated, non striated
Voluntary, involuntary
Muscle Tissue Continued…
3 different types
cardiac, smooth, skeletal
Characteristics:
Contractile
Allows movement
Cells are long and either tubular or spindle shaped
Cells contain bundles of contractile proteins: actin and myosin
Can be multinucleate
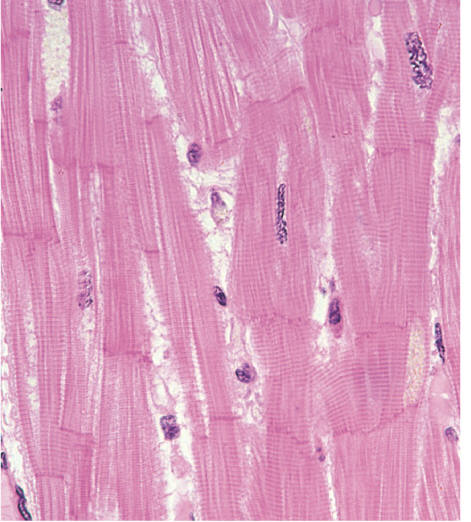
Cardiac Muscle
Only in the heart
Involuntary
Specialized pacemaker cells
Striated
Cells are "split“, terminate in “intercalated disks”
Way for cells to connect to one another
Disks pass excitation from one cell to the next
Mononucleate
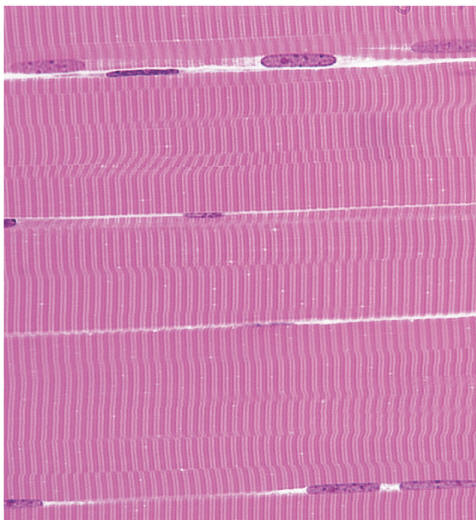
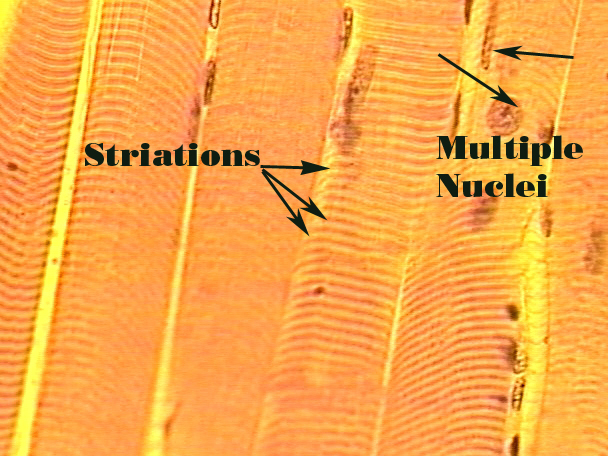
Skeletal Muscles
Striated cells
Can be very large!!!!
Voluntary- innervated by nerve cells
Multinucleate, do not branch
Arranged like fibers surrounded by loose
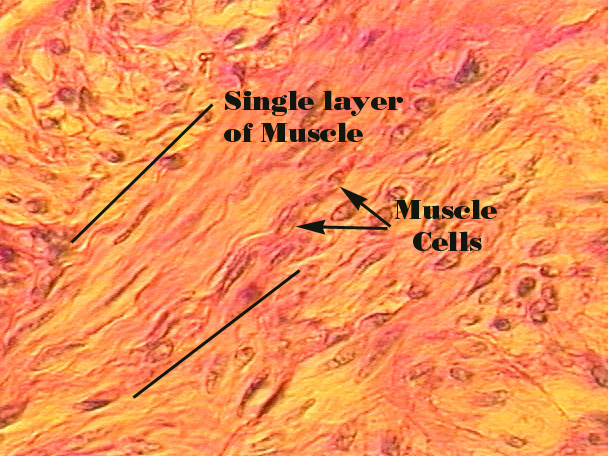
Smooth Muscle
Mononucleate
Non-striated
Involuntary
Cells are spindle shaped
Slow, sustained contractions
Found in walls of hollow organs
bladder, uterus, intestines
Nervous Tissue
Brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves
Only cells of the body that are normally excitable and conductive
Even longer cells!
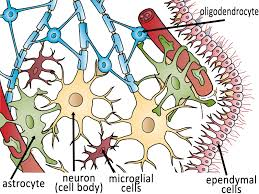
Different types of nerve and support cells
Neurons
Neuroglial cells (supporting) – more numerous
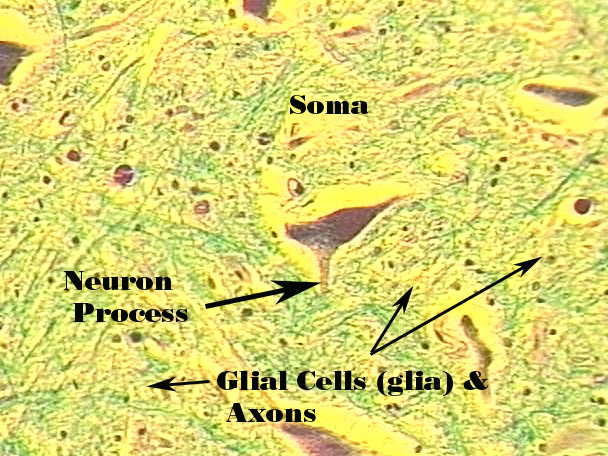
Neurons - longest cells in the body
Composed of 3 main parts:
Cell body – perikaryon; contain nucleus & controls cell metabolism
Short cytoplasmic extensions – dendrites; receive impulses from other cells
Long single extension – axon; conducts impulses away from the cell
Nervous Tissue Continued…
Neurons: transport electrical signals
Neuroglia: support cells of the nervous system
Feed the cells, maintain homeostasis of the extracellular fluid
Insulative
Protective
Membranes
Thin, protective layers of tissue linked together that line body cavities, separate organs, and cover surfaces
Multicellular epithelial sheet bound to underlying connective tissue proper to form membranes; this epithelium bathed in mucous or in the case of the bladder, urine.
4 common types
Mucous membranes
Serous membranes
Cutaneous membranes
Synovial membranes
Mucous Membranes = Mucosae
Line organs with connections to outside environment
Composition
Stratified squamous or simple columnar epithelium; covers a layer of CT called lamina propria
CT layer, submucosa connects mucosa to underlying structures
Generally produce large quantities of mucus
May contain goblet cells or multicellular glands
Mucus = water, electrolytes, and the protein mucin
Rich supply of antibodies helpful in trapping invaders/debris
Some mucosae can also absorb
Epithelial layer in the intestine transfers nutrients to CT
Controls what goes in and out of the body by forming a barrier