Uark Kral General Microbiology Chapter 4 Multiple Choice Questions
1/175
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
176 Terms
Innate immunity includes all of the following EXCEPT
inflammation
phagocytosis
activation of complement
production of interferon
production of antibody
production of antibody
Normal microbiota provide protection from infection in each of the following ways EXCEPT
they change the pH of the environment
they produce antibacterial chemicals
they produce lysozyme
they make the chemical environment unsuitable for nonresident bacteria
they compete with pathogens for nutrients
they produce lysozyme
Macrophages arise from which of the following?
neutrophils
basophils
lymphocytes
monocytes
eosinophils
monocytes
Which of the following exhibits the highest phagocytic activity?
basophils
neutrophils
eosinophils
macrophages
erythrocytes
macrophages
All of the following are effects of histamine EXCEPT
redness
pain
fever
vasodilation
swelling
fever
A child falls and suffers a deep cut on her leg. The cut went through her skin and she is bleeding. Which of the following defense mechanisms will participate in eliminating contaminating microbes?
lysosome
normal skin flora
acidic skin secretions
phagocytosis in the inflammatory response
mucociliary escalator
phagocytosis in the inflammatory response
All of the following pertain to fever EXCEPT that it
can be initiated by specific types of pathogens
stimulates T lymphocyte activity
intensifies the effect of antiviral interferons
accelerates microbial growth by increasing iron absorption from the digestive tract
is caused by interleukin-1 and TNF-alpha coming into contact with the hypothalamus
accelerates microbial growth by increasing iron absorption from the digestive tract.
Each of the following is an effect of complement activation EXCEPT
increased blood vessel permeability
increased phagocytic activity
bacterial cell lysis
interference with viral replication
opsonization
interference with viral replication
The ID50 is
the dose that will cause an infection in 50 percent of the test population
a measure of pathogenicity.the dose that will kill some of the test population
the dose that will cause an infection in some of the test population
the dose that will kill 50 percent of the test population
the dose that will cause an infection in 50 percent of the test population
Most pathogens that gain access through the skin
enter through hair follicles and sweat ducts
must be injected
can penetrate intact skin
must adhere first while their invasive factors allow them to penetrate
just infect the skin itself
just infect the skin itself
The most frequently used portal of entry for pathogens is the
skin
mucous membranes of the respiratory tract
mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract
parenteral route
All of these portals are used equally
mucous membranes of the respiratory tract
Which is NOT specifically employed by pathogens to avoid destruction by phagocytosis?
forming biofilms
possessing ability to remain dormant within a phagocyte
producing a capsule
possessing ability to replicate within a phagolysosome
producing superantigens
producing superantigens
The best description of direct damage by a pathogen is
capsule components of pathogens kill cells
poisonous substances secreted by viruses kill cells
host cells destroyed when pathogens metabolize and multiply
protein synthesis is interrupted by toxins
superantigens cause cytokine release which then cause symptoms of disease
host cells destroyed when pathogens metabolize and multiply
All of the following bacteria release endotoxin EXCEPT
Neisseria meningitidis
Salmonella Typhi
Proteus vulgaris
Clostridium botulinum
Haemophilus influenzae
Clostridium botulinum
Twenty-five people developed symptoms of nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea three to six hours after attending a church picnic where they ate a ham and green bean casserole with cream sauce. The most likely cause of this case of food intoxication is
botulinum toxin
erythrogenic toxin
cholera toxin
aflatoxin
staphylococcal enterotoxin
staphylococcal enterotoxin
Lysogenic bacteriophages contribute to bacterial virulence because bacteriophages
produce toxins
kill the bacteria, causing release of endotoxins
give new gene sequences to the host bacteria
carry plasmids
kill human cells
give new gene sequences to the host bacteria
All of the following organisms produce exotoxins EXCEPT
Staphylococcus aureus
Clostridium tetani
Corynebacterium diphtheriae
Clostridium botulinum
Salmonella typhi
Salmonella typhi
Botulism is caused by ingestion of a proteinaceous exotoxin; therefore, it can easily be prevented by
administering antibiotics to patients
preventing fecal contamination of food
boiling food prior to consumption
filtering food
not eating canned food
boiling food prior to consumption
Endotoxins are
molecules that bind nerve cells
excreted from the cell
A-B toxins
part of the gram-negative cell wall
associated with gram-positive bacteria
part of the gram-negative cell wall
The presence of which of the following indicates a current infection rather than a previous infection or vaccination?
IgM
IgE
IgG
IgD
IgA
IgM
In the figure, which areas represent antigen-binding sites?
a and c
b and d
c and d
b and c
a and b
a and b
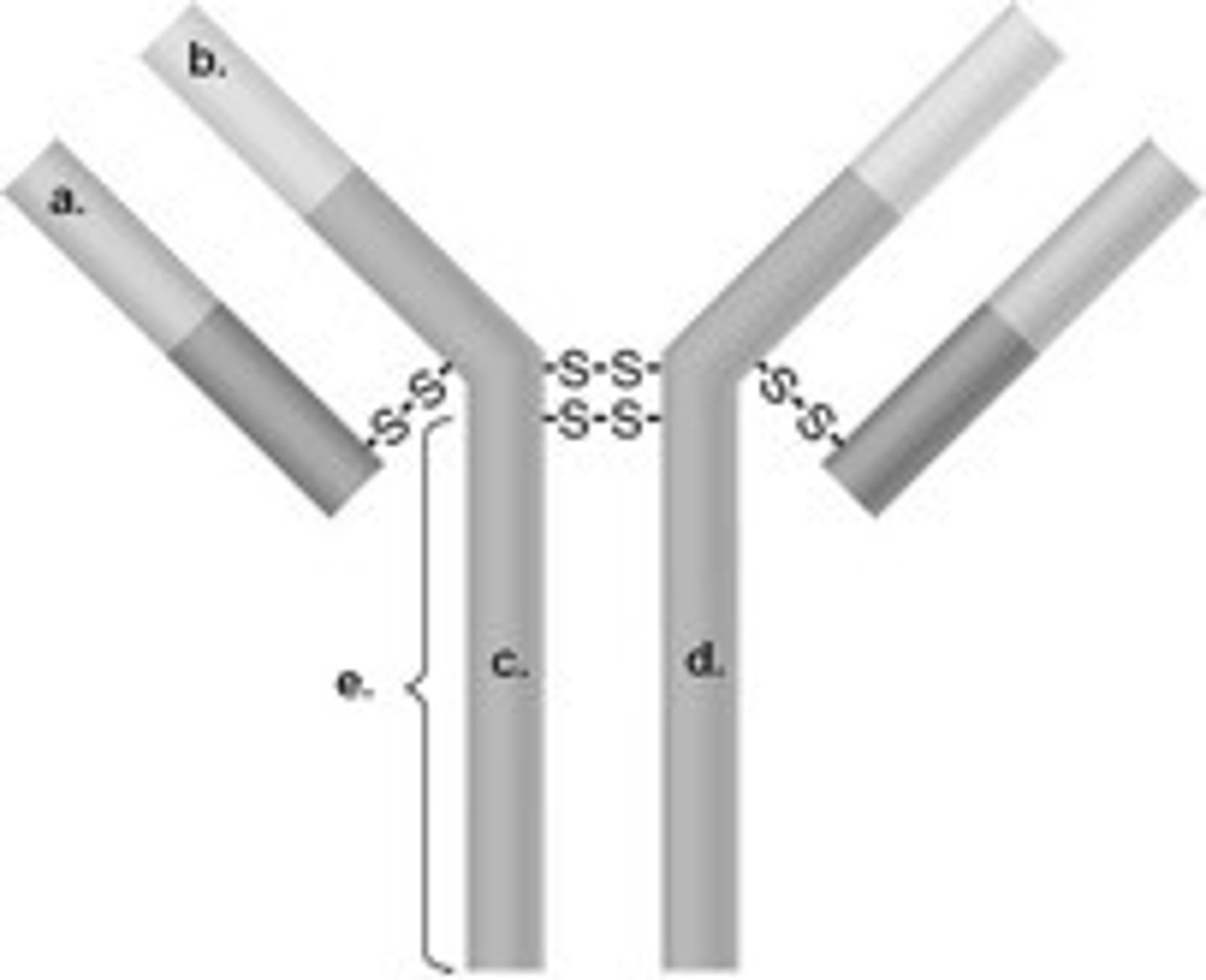
Which of the following is the best definition of antigen?
something foreign in the body
a pathogen
a protein that combines with antibodies
a chemical that combines with antibodies
a chemical that elicits an antibody response and can combine with these antibodies
a chemical that elicits an antibody response and can combine with these antibodies
The most abundant class of antibodies in serum is
IgD
IgG
IgA
IgE
IgM
IgG
Large antibodies that agglutinate antigens are
IgA
IgD
IgG
IgE
IgM
IgM
In addition to IgG, the antibodies that can fix complement are
IgE
IgD
IgM
IgA
None of the above answers is correct
IgM
The antibodies found almost entirely and only on the surface of B cells (not secreted from them), and which always exist as monomers, are
IgD
IgE
IgA
IgM
IgG
IgD
The antibodies found in mucus, saliva, and tears are
IgD
IgM
IgA
IgE
IgG
IgA
Which of the following is the best definition of epitope?
specific regions on antigens that interact with T-cell receptors
specific regions on antigens that interact with haptens
specific regions on antigens that interact with perforins
specific regions on antigens that interact with antibodies
specific regions on antigens that interact with MHC class molecules
specific regions on antigens that interact with antibodies
Plasma cells are activated by a(n)
antigen
B cell
memory cell
T cell
APC
antigen
When an antibody binds to a toxin, the resulting action is referred to as
opsonization
ADCC
neutralization
apoptosis
agglutination
neutralization
Which of the following destroys virus-infected cells?
TH
Treg
dendritic cells
B cells
CTL
CTL (cytotoxic lytic cells)
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of cellular immunity?
Cells mature in the thymus gland
B cells make antibodies
T cells interact with epitopes in MHC molecules
The cells originate in bone marrow
Response to abnormal cells
B cells make antibodies
What type of immunity results from recovery from mumps?
innate immunity
naturally acquired active immunity
naturally acquired passive immunity
artificially acquired active immunity
artificially acquired passive immunity
naturally acquired active immunity
Desensitization involves injection of
antigens
histamine
antihistamine
IgG antibodies
IgE antibodies.
antigens
All of the following are considered examples of type I hypersensitivity EXCEPT
severe reactions to insect venom
transplant rejections
pollen allergies
dust allergies
asthma
transplant rejections
Anaphylaxis is the term for reactions caused when certain antigens combine with
macrophages
histamine
IgG antibodies
IgE antibodies
complement
IgE antibodies
Hemolytic disease of the newborn can result from an
Rh- mother and an A fetus
AB mother with an O fetus
Rh+ mother with an Rh- fetus
AB mother with a B fetus
Rh- mother with an Rh+ fetus
Rh- mother with an Rh+ fetus
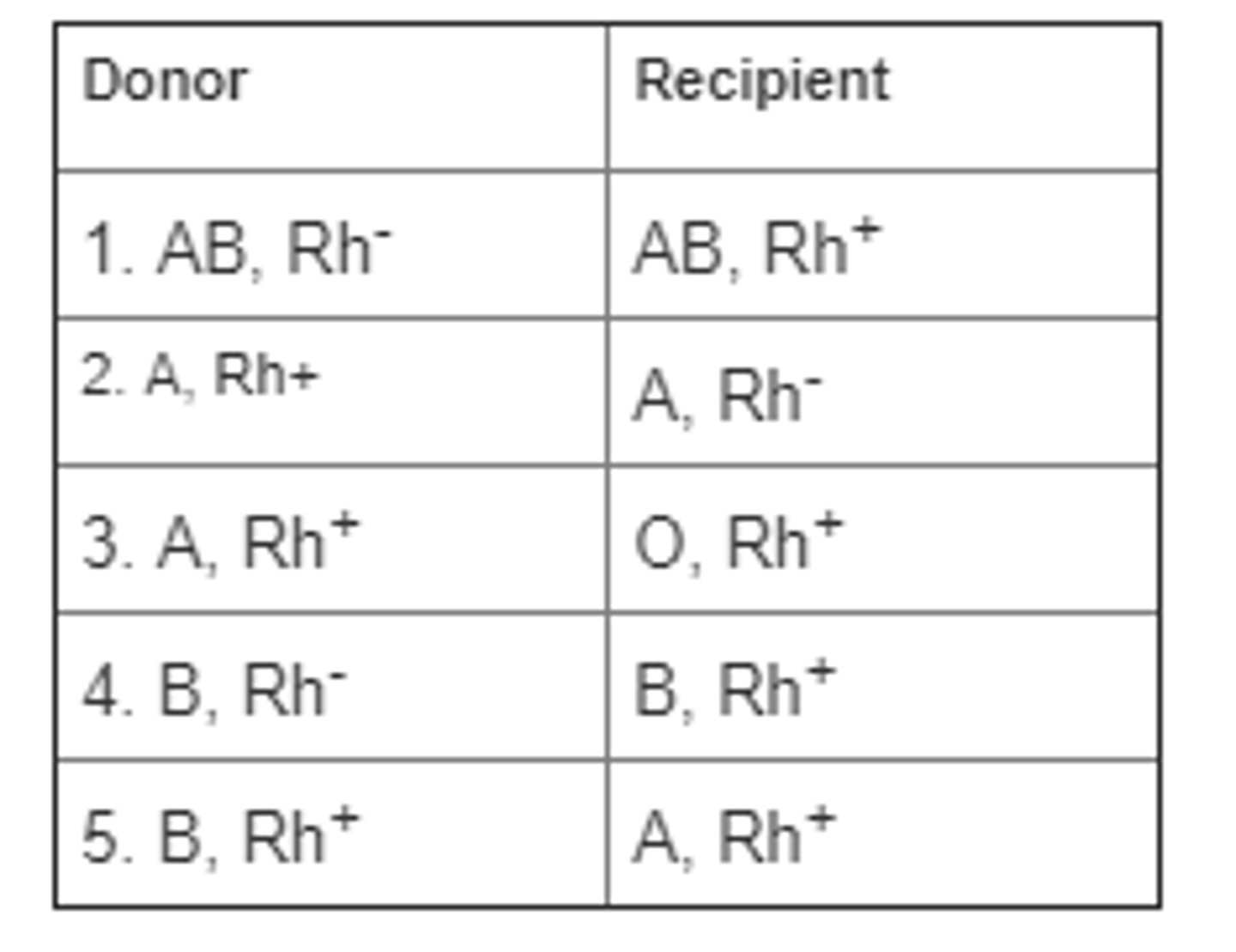
Which blood transfusions in the table are incompatible?
1, 2, and 3
2, 3, and 5
3 and 4
1 and 2
2 and 5
2, 3, and 5
Which of the following statements about type I reactions is FALSE?
The symptoms occur soon after exposure to an antigen
Antibodies bind to mast cells and basophils
The symptoms are due to histamine
They involve IgE antibodies
They involve helper T cells
They involve helper T cells
The chemical mediators of anaphylaxis are
the proteins of the complement system
antigen-antibody complexes
antibodies
antigens
found in basophils and mast cells
found in basophils and mast cells
Which of the following statements is true?
a. Interferon is an antiviral protein
b. Interferon causes phagocytosis
c. Interferon causes bacteriocidal activity by macrophages
d. Interferon acts against specific viruses and bacteria
e. All of the above are true.
a. Interferon is an antiviral protein
Which of the following is not a function of inflammation?
a. To destroy an injurious agent
b. To remove an injurious agent
c. To wall off an injurious agent
d. To repair tissue damage
e. To produce antibodies.
e. To produce antibodies.
One result of fever is
a. Decreased availability of iron
b. Increased availability of iron
c. Slower tissue repair
d. Increased nickel concentration
e. None of the above.
a. Decreased availability of iron
The first line of defense does not include
a. Skin
b. Tears
c. Interferon
d. Mucous membranes
e. It includes all of the above.
c. Interferon
Cells that are involved in the humoral allergic response are
a. Basophils and erythrocytes
b. Neutrophils and basophils
c. Neutrophils and erythrocytes
d. Basophils and mast cells
e. Mast cells and neutrophils.
d. Basophils and mast cells
The major phagocytic cells in the body are
a. Macrophages and neutrophils
b. Neutrophils and erythrocytes
c. Erythrocytes and basophils
d. Macrophages and basophils
e. Macrophages, neutrophils, erythrocytes and basophils.
a. Macrophages and neutrophils
What type of immunity results from vaccination?
a. Innate immunity
b. Natural active immunity
c. Natural passive immunity
d. Artificial active immunity
e. Artificial passive immunity.
d. Artificial active immunity
The structure in the phagocytic cell that contains inactive digestive enzymes is the
a. Phagosome
b. Lysosome
c. Lysozyme
d. Phagolysosome
e. Residual body.
b. Lysosome
A human's resistance to canine distemper is an example of
a. Innate immunity
b. Natural active immunity
c. Natural passive immunity
d. Artificial active immunity
e. Artificial passive immunity.
a. Innate immunity
The killing mechanism of the phagocytic cell includes reaction of
a. Hydrogen peroxide, lysozyme, and chloride ion
b. Superoxide, chloride ion and myeloperoxidase
c. Lysozyme, myeloperoxidase, and chloride ion
d. Chloride ion, myeloperoxidase and hydrogen peroxide
e. Hydrogen peroxide, chloride ion, lysozyme and myeloperoxidase.
d. Chloride ion, myeloperoxidase and hydrogen peroxide
Chronic granulomatous disease
a. Is a mild, non-fatal disease
b. Is due to a defect in phagocytic killing
c. Is where granulocyte number is reduced in the body
d. Can be cured with artificial passive immunity
e. None of the above.
b. Is due to a defect in phagocytic killing
In the fever process due to a Gram negative bacterium
a. Interleukin I causes endotoxin to travel to the hypothalamus
b. The phagocytic cell releases prostaglandins
c. The hypothalamus releases prostaglandins which go to the phagocytic cell
d .Endotoxin release by the bacterium causes interleukin I production
e. None of the above.
d .Endotoxin release by the bacterium causes interleukin I production
In the humoral immune response
a. Penicillin can act as an antigen
b. Penicillin can act as a hapten
c. Catechol can act as an antigen
d. Catechol can act as a hapten
e. Penicillin and catechol can both act as antigens.
b. Penicillin can act as a hapten
Antibodies
a. And antibiotics are the same things
b. Can be antigens
c. Are sometimes made of proteins and sometimes made of polysaccharide
d. Are part of the cellular immune system
e. None of the above.
b. Can be antigens
The immunoglobulin that fixes complement, but does NOT pass the placenta is
a. IgG
b. IgM
c. IgA
d. IgD
e. IgE.
b. IgM
Hydrogen cyanide (HCN)
a. Always acts as a hapten
b. Is not an antigen because it is not foreign since H, C and N are normal constituents of the body
c. Can be an antigen in high concentration
d. Can cause immunity in small doses
e. Is simply too small to be an antigen.
e. Is simply too small to be an antigen.
The microorganism that can survive inside of a phagocytic cell is
a. Mycoplasma pneumoniae
b. Clostridium botulinum
c. Mycobacterium tuberculosis
d. Chlamydia trachomatis
e. All of the above.
c. Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Which of the following is not a characteristic of B cells?
a. They originate in the bone marrow of humans
b. They have antibodies on their surfaces
c. They are responsible for a memory response
d. They are precursors to plasma cells
e. They recognize antigens presented by T cells.
e. They recognize antigens presented by T cells.
What type of immunity is not due to antibodies?
a. Innate immunity
b. Natural active immunity
c. Natural passive immunity
d. Artificial active immunity
e. Artificial passive immunity.
a. Innate immunity
Which of the following is not normally used in a vaccine?
a. Toxoid
b. Parts of bacterial cells
c. Live, attenuated bacteria
d. Inactivated viruses
e. Antibodies
e. Antibodies
Natural passive immunity is facilitated by
a. IgG and IgM
b. IgM and IgA
c. IgA and IgG
d. IgD and IgM
e. IgE and IgD.
c. IgA and IgG
The mechanism that humans use to raise body temperature is
a. Ingestion of interleukin-1
b. Ingestion of prostaglandin
c. Ingestion of interleukin-1 and prostaglandin
d. Chills
e. Sweating.
d. Chills
Desensitization with an allergy shot works by
a. Inducing synthesis of blocking IgE
b. Altering the antigen before it is injected
c. Blocking complement activation
d. Inducing synthesis of blocking IgG.
e. Blocking the histamine receptor sites.
d .Inducing synthesis of blocking IgG.
Which statement is correct?
a. Haptens are antigens
b. Haptens can induce antibody production in a person with the "proper" genetics
c. Haptens can never induce antibody production
d. Haptens are too large to be antigens
e. Haptens induce cell-mediated immunity only.
c. Haptens can never induce antibody production
Requirements for inducing antibody production include
a. Antigenic fragments, B cells, T helper cells and cytokines
b. Basophils, T helper cells and antigenic fragments
c. Mast cells, haptens, B cells and cytokines
d. Mast cells, basophils and cytokines
e. None of the above.
a. Antigenic fragments, B cells, T helper cells and cytokines
The anamnestic response is facilitated by
a. T helper cells
b. Memory B cells
c. Memory T cells
d. Cytokines
e. Macrophages.
e. Macrophages.
Transfusion of a normal A+ blood type person with type A- blood should result in
a. Immediate attack of the A- blood by antibodies
b. Eventual production of antibodies against the A- blood
c. Activation of complement which will lyse the A- blood
d. Inflammation
e. None of the above.
e. None of the above.
Antisera
a. Were not used much in the 20th century, but are commonly used today
b. Are used mainly for bacterial infections
c. Are derived mainly from chicken eggs and pigs
d. Are most frequently used for prevention of disease following exposure
e. All of the above apply to antisera.
d. Are most frequently used for prevention of disease following exposure
Which of the following is true in humans?
a. Stem cells are differentiated into B cells in the adult red bone marrow and T cells in the thymus
b. Stem cells are differentiated into B cells in the fetal liver and T cells in the thymus
c. Stem cells are differentiated into B cells in the adult red bone marrow and T cells in the fetal liver
d. Stem cells are differentiated into B cells in the adult red bone marrow and T cells in the hypothalamus
e. None of the above.
a. Stem cells are differentiated into B cells in the adult red bone marrow and T cells in the thymus
Which statement is correct?
a. Memory T cells and memory B cells are produced in humoral immunity
b. Memory T cells and memory B cells are produced in cellular immunity
c. Only memory T cells are produced in humoral immunity
d. Only memory T cells are produced in cellular immunity
e. Only memory B cells are produced in cellular immunity.
d. Only memory T cells are produced in cellular immunity
Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn
a. Afflicts all fetuses from a Rh- mother
b. Can be a problem if the father is Rh+
c. Is never fatal
d. Has to do with A and B blood type antigens in the fetus
e. None of the above.
b. Can be a problem if the father is Rh+
An example of immune-complex hypersensitivity is
a. Rheumatoid arthritis
b. Multiple sclerosis
c. Hemolytic disease of the newborn
d. Chronic granulomatous disease
e. All of the above.
a. Rheumatoid arthritis
Cyclosporine
a. Is an antibiotic, by definition
b. Is a chemically-synthesized chemotherapeutic agent
c.Is normally administered to a Rh- woman after she has given birth
d. Is an immunosuppressant
e. None of the above.
d. Is an immunosuppressant
Cancer cells are typically killed by a(an)
a. Antibody plus complement
b. Antibody plus a helper virus
c. Antibody plus a T helper cell
d. Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte
e. Antibody plus a Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte plus a helper virus.
d. Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte
HIV originated and has the largest presence in
a. North America
b. Latin America
c. Sub-Saharan Africa
d. Southeast Asia
e. Eastern Europe
c. Sub-Saharan Africa
The protective mechanism of antibodies includes all of the following except
a. Agglutination
b. Opsonization
c. Tissue repair
d. Neutralization
e. The protective mechanism includes all of the above.
c. Tissue repair
A term for the part of the antigen that binds to the antibody is
a. Epitope
b. Carrier molecule
c. Adjuvant
d. Immunoglobulin
e. Cytokine.
a. Epitope
The common factor between humoral immunity and cellular immunity that is the primary target of HIV is the
a. Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte
b. T suppressor cell
c. Polymorphonuclear neutrophil
d. T helper cell
e. Cytokine.
d. T helper cell
A person who has a genetic predisposition for an allergy to penicillin
a. Will have an anaphylactic response immediately following EVERY exposure to penicillin
b. Will have an anaphylactic response immediately following JUST the first exposure to penicillin
c. Will have an anaphylactic response immediately following EVERY subsequent exposure to penicillin, but not following the first exposure
d. Will never have an anaphylactic response after any exposure to penicillin
e. None of the above.
c. Will have an anaphylactic response immediately following EVERY subsequent exposure to penicillin, but not following the first exposure
Which statement is correct?
a.HIV can be transmitted by blood and sexual contact
b. HIV can be transmitted by sexual contact and mosquito bites
c. HIV can be transmitted by blood and kissing
d. HIV can be transmitted by blood, sexual contact, kissing and mosquito bites
e. None of the above.
a.HIV can be transmitted by blood and sexual contact
Which of the following is NOT a part of the first line of defense in non-specific host resistance?
a. Inflammation
b. Tears
c. Skin
d. Mucous membranes
e. All of the above are part of the first line of defense.
a. Inflammation
By paralyzing the cilia in the respiratory tract, cigarette smoke interferes with which of the following?
a. First line of defense
b. Second line of defense
c. Third line of defense
d. Immunity
e. Interferon
a. First line of defense
Which statement concerning fever is true?
a. Fever is harmful to the host and should always be treated with medication
b. Fever is beneficial to the host up to a point
c. Fever is beneficial because it results in the total destruction of all bacteria, viruses and toxins
d. Fever normally follows sweating
e. None of the above are true.
b. Fever is beneficial to the host up to a point
In the fever process, which chemical induces the hypothalamus to produce prostaglandins?
a. Interleukin I
b. Interferon
c. Complement
d. Interleukin II
e. Histamine
a. Interleukin I
Taking 10 showers a day may not be such a good idea because
a. Being "too" clean will embarrass your friends
b. Washing the oils off your skin is washing away some of your first line of defense
c. You may use up all of the hot water
d. You will wash away your B and T cells
e. None of the above.
b. Washing the oils off your skin is washing away some of your first line of defense
In the process of inflammation following a cut by a knife
a. Blood leaves the area around the cut so a clot can form
b. Phagocytic cells enter the blood vessels and are carried away
c. Tissue repair must occur before phagocytosis
d. Neutrophils leave the blood vessels and go after the bacteria
e. None of the above.
d. Neutrophils leave the blood vessels and go after the bacteria
Antigens
a. Are sometimes foreign to the host and reasonably large
b. Are always foreign to the host and reasonably large
c. Are the same as epitopes
d. By definition contain only one hapten
e. Are always antibodies.
b. Are always foreign to the host and reasonably large
A hapten
a. By itself causes the production of antibodies and binds to those antibodies
b. Cannot cause antibody production by itself
c. By itself causes the production of antibodies, but requires a carrier to bind to the antibodies
d. Is an antigen
e. None of the above.
b. Cannot cause antibody production by itself
A typical antibody
a. Can bind two epitopes
b. Is a protein.
c. Can be an antigen
d. All of the above
e. None of the above.
d. All of the above
Which is true about penicillin?
a. It can cause an allergic response the very first time it is introduced into a body
b. It can bind to a normal protein in some individuals, and the combination can induce antibody synthesis
c. It is not antigenic because it is not considered foreign by the host
d. All of the above are true
e. None of the above are true.
b. It can bind to a normal protein in some individuals, and the combination can induce antibody synthesis
The immunoglobulin that is most commonly found on the surface of B cells is
a. IgG
b. IgM
c. IgA
d. IgD
e. IgE.
d. IgD
The most important phagocytic cells in the body are
a. All of the leukocytes are equally important phagocytic cells
b. Neutrophils and macrophages
c. Neutrophils and lymphocytes
d. Macrophages and lymphocytes
e. Basophils and lymphocytes.
b. Neutrophils and macrophages
The structure in the phagocytic cell that stores the digestive enzymes is the
a. Phagosome
b. Endoplasmic reticulum
c. Residual body
d. Nucleus
e. Lysosome.
e. Lysosome.
In the human, stem cells differentiate into B cells in the
a. Red bone marrow of the adult
b. Bursa of fabricius
c. Thymus
d. Hypothalamus
e. Spleen.
a. Red bone marrow of the adult
In the activation of B cells to differentiate into plasma cells which produce antibodies, the antigen fragment is displayed on the B cell surface along with
a. IgG.
b. Helper T cell.
c. Major histocompatibility complex class II
d. Plasma cell.
e. Cytokines.
c. Major histocompatibility complex class II
What releases cytokines that activate the B cell to differentiate into plasma cells?
a. Extracellular antigens
b. Major histocompatibility complex class II
c. Gram negative bacterial cell
d. Helper T cell
e. Macrophage
d. Helper T cell
In the anamnestic response
a. More IgG is produced than in the primary response
b. Less IgG is produced than in the primary response
c. Only IgM is produced
d. The same amount of IgG is produced as in the primary response
e. None of the above.
a. More IgG is produced than in the primary response
Opsonization
a. Is where multiple antigens are tied together by antibodies
b. Enhances phagocytosis
c. Is simply neutralization
d. Requires complement
e. None of the above.
b. Enhances phagocytosis
Treatment following a venomous spider bite normally results in
a. Natural active immunity
b. Natural passive immunity
c. Artificial active immunity
d. Artificial passive immunity
e. Innate immunity.
d. Artificial passive immunity
Activation of complement requires the antigen to bind to
a. IgG or IgM
b. IgM or IgA
c. IgA or IgD
d. IgD or IgE
e. IgE or IgG.
a. IgG or IgM