L19 Mass extinction
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
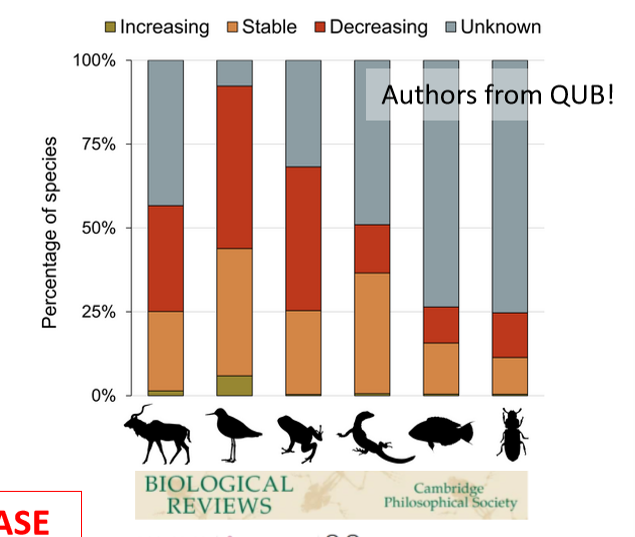
Earth’s sixth mass extinction event
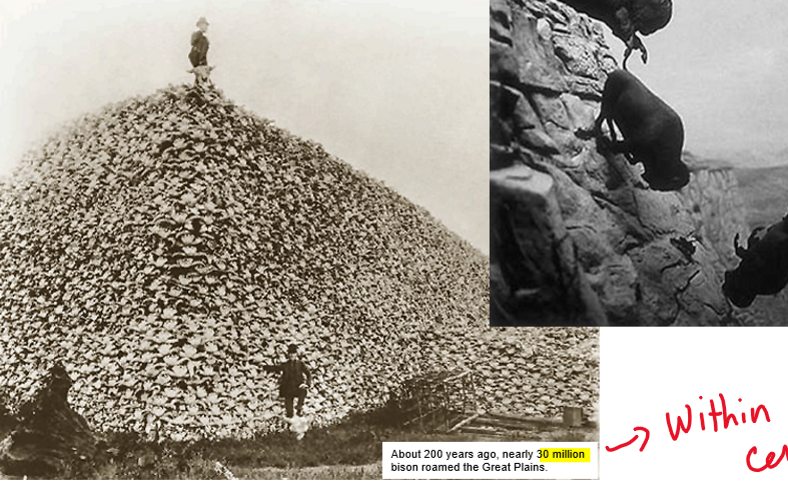
About 200 years ago there were nearly 30 million bison roaming planet earth.
1890
As few as 750 bison were left in North America due to extreme overhunting

Next great extinction: Climate change (Human activity indirect action)
2004
Climate change could drive million of the world’s species to extinction as soon as 2050, scientific studies says.
2023
Agriculture accounts of all land 40%
Global deforestation of globe 90%
Fresh water use 70%
Greenhouse emissions and global warming, frequent intense droughts, storms and floods
Linked greenhouse gases in Ireland are fossil fuels 62% and agriculture 38&.
These factors significantly alters habitats, leading species to extinction and loss of habitat and ecosystems worldwide.
What could the 6th mass extinction be?
Asteroids
Global nuclear war
Global warming
Eruption of super volcanoes
Geo-engineering disaster
Genetically engineered killer microbe
Artificial intelligence?
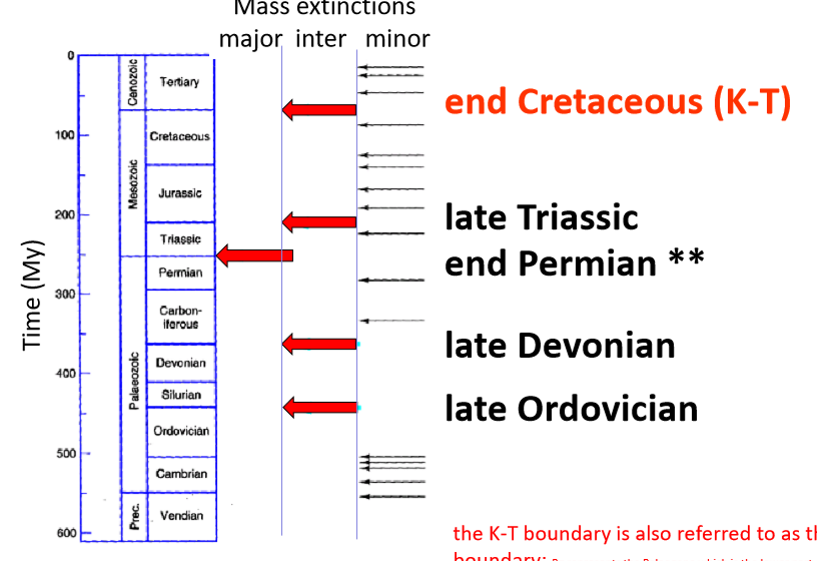
Mass extinctions major inter minor diagram

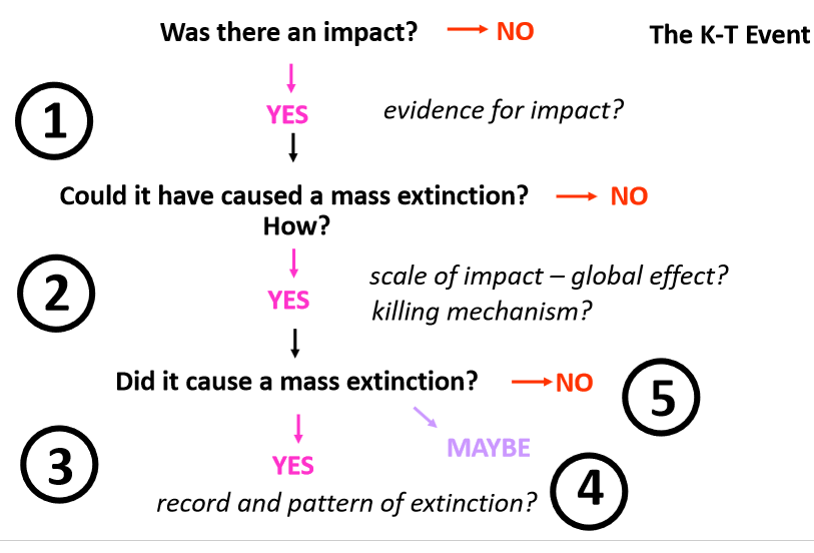
The K-T event
Key points to the catastrophic, extra-terrestrial cause of K-T event
external to Earth system
no reason to assume biotic stress in Earth system in advance of impact
sudden event
global effect from local source (impact): what is the killing mechanism

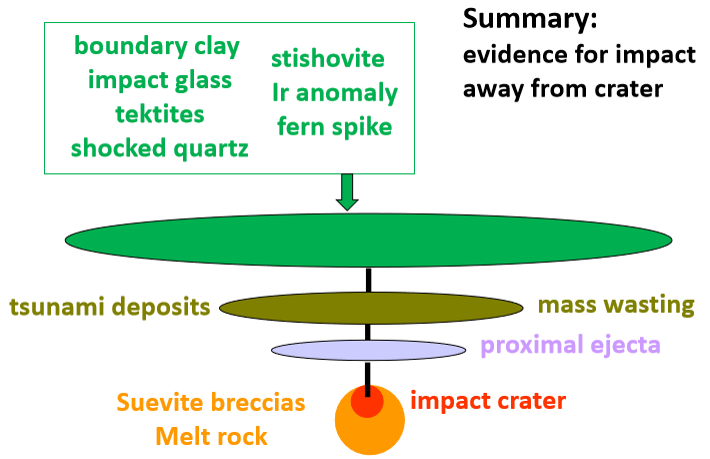
Summary of the K-T event
Evidence of the impact of the K-T event
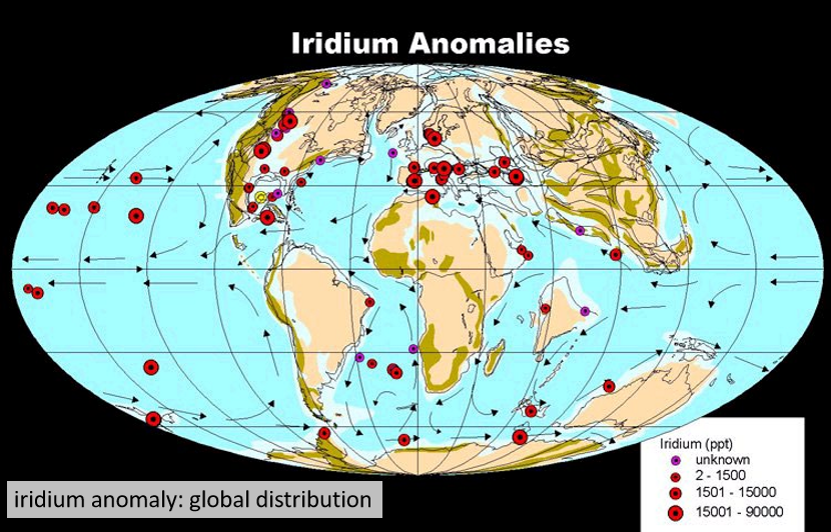
Iridium (Ir) anomaly
low abundance on Earth (core) but abundant in meteorites supplied continuously to Earth from space.
Accumulates sedimentary record in extremely low abundances
Anomaly refers to elevated abundances found in K-T boundary sections.
Iridium Anomalies map
K-T boundary clay layer in Contessa (Italian Appenines)
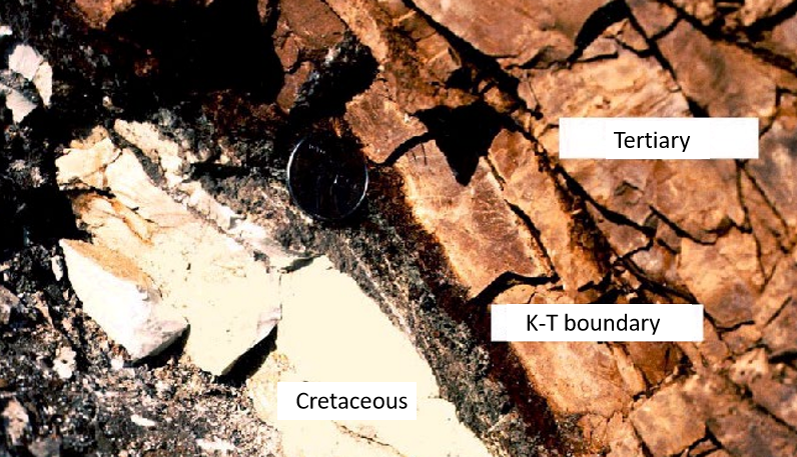
Boundary clay
Thin (in cms or less), fine-grained layer (clay & coal)
global distribution
usually distinct from lithologies above and below
hosts other evidence (Ir anomaly, tektites, Impact glass etc)

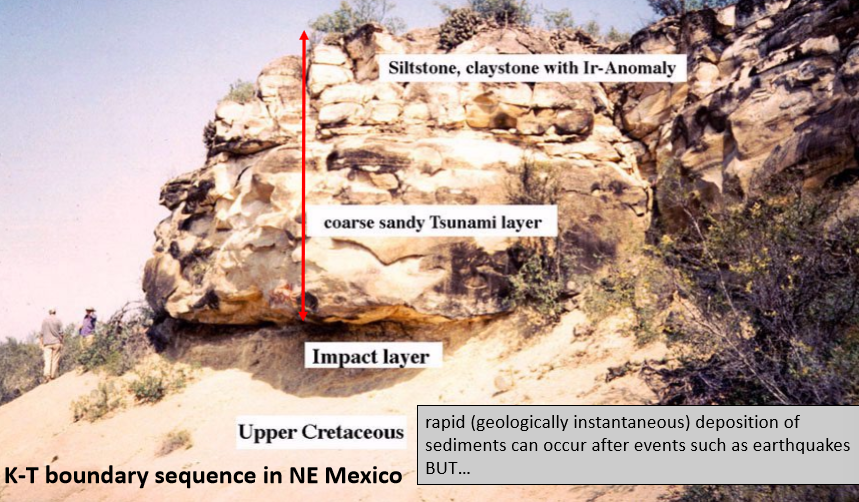
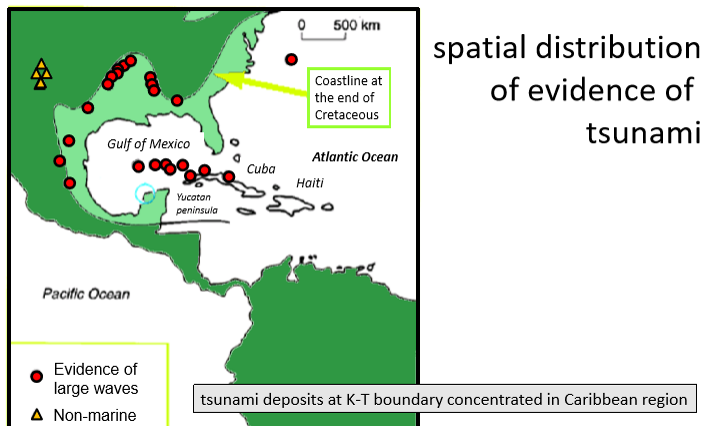
Tsunami deposits
rapid (geologically instantaneous) deposition of sediments can occur after events such as earth quakes HOWEVER
tsunami deposits at K-T boundary concentrated in Caribbean region
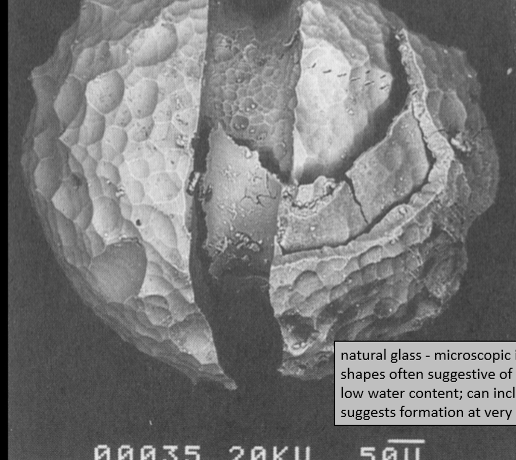
Tektites
natural glass → microscopic in size
shapes often, suggesting rapid cooling while moving
low water content; can include partially melted zircons
suggests formation of very high P + T
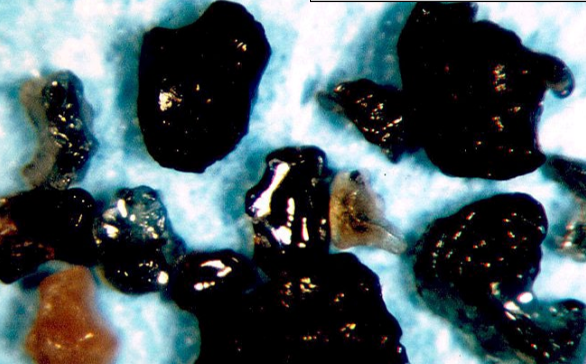
Impact glass
Rapid quenching of molten droplets
Found at the base of the K-T boundary sequence in the Gulf of Mexico region
Shocked quartz
unusual microstructure
cross-cutting shock lamellae
deformation of crystal structure
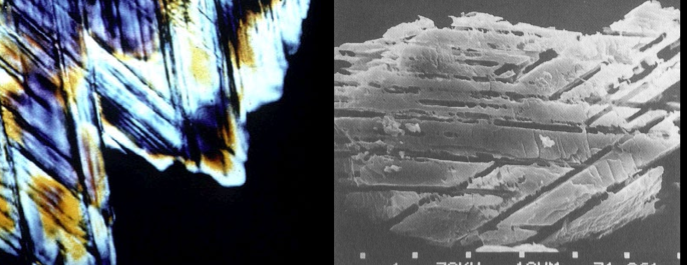
Stishovite
High temperature of polymorph of quartz


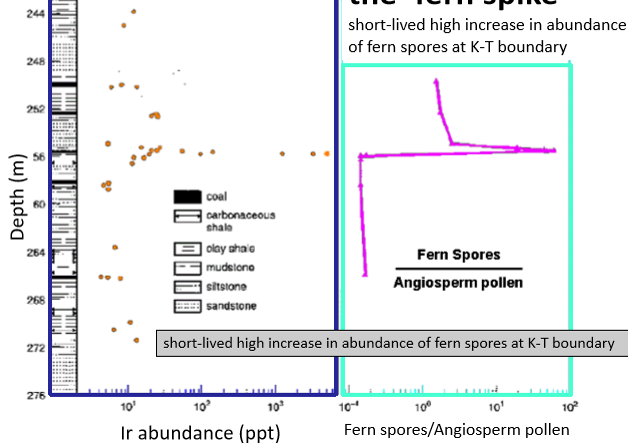
The ‘fern spike’
short-lived high increase in abundance of fern spores at K-T boundary
ferns adapted to low-light conditions
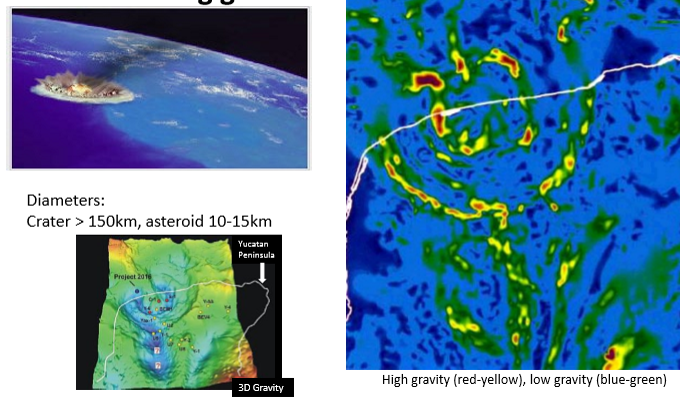
The Chicxulub crater aka ‘the smoking gun’
impactor estimated at 10km diameter, crater radius up to 80km.
Cores from crater reveal unusual lithologies
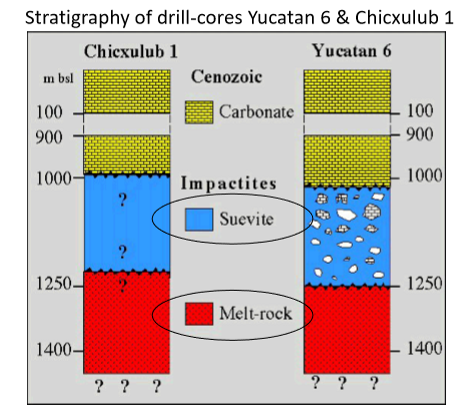
Suevite (suevite breccia)
Chicxulub melt rock from well Yucatan 6
melting and solidification in situ (‘in place’)
formed and deposited relatively close to impact crater

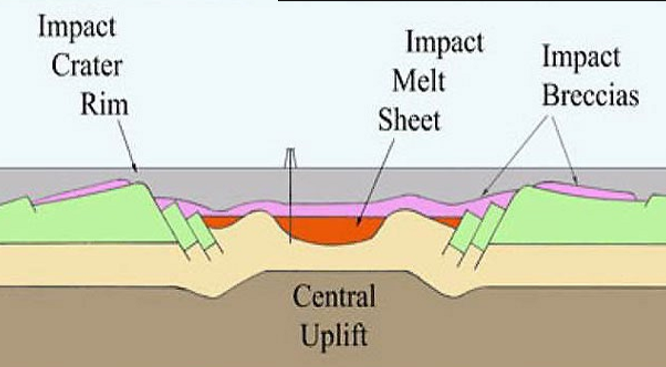
Crater morphology
Combination of melt rock and suevite (breccia) within and adjacent to impact crater
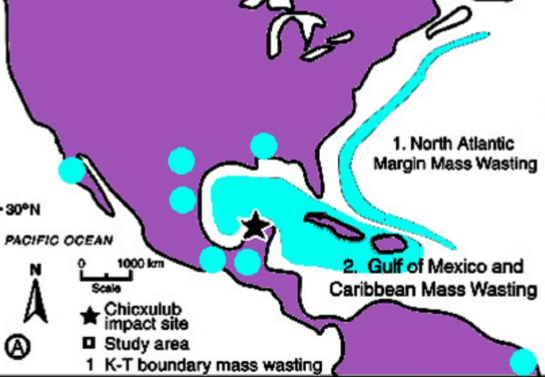
Mass wasting deposits → i.e. landslides
mainly in Caribbean and easter seaboard of South and North America.
Summary of evidence from impact away from crater
The K-T event: Could impact cause the mass extinction?
Evidence doesn’t prove it resulted in extinction
Although demonstrates the cause and effect (killing mechanisms)
Indirect killing mechanisms
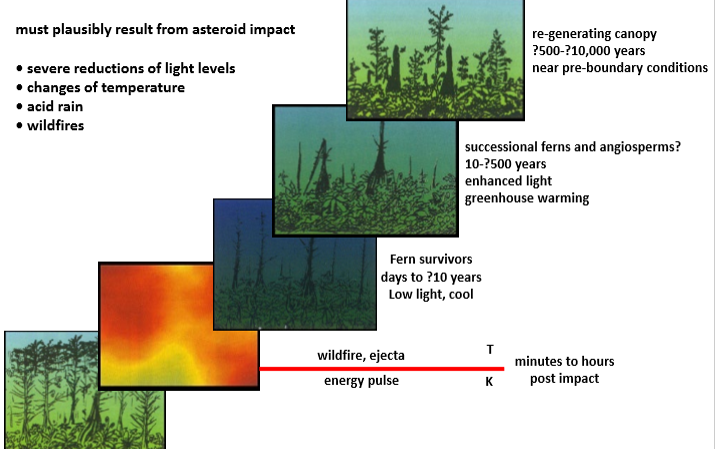
Plausible result from asteroid impact
sever reductions of light levels
changes of temperature
acid rain
wildfires
Lots of combos