Review of Translation, DNA Damage and DNA Repair
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
translation
a structurally different biopolymer (protein) is synthesized from RNA
Crick’s Adaptor hypothesis
Can folded RNA act directly as the template for protein synthesis? Seems unlikely: no clear way to discriminate chemically similar amino acids
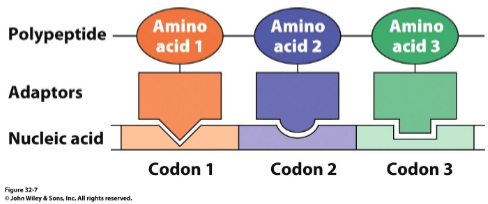
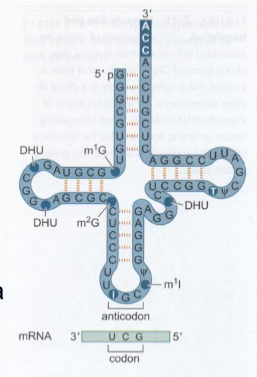
transfer RNAS (tRNAs)
RNA molecules
Self-folding by complementary base pairs gives a structure with several functional domains
clover shape
end with CCA - where amino acid attaches
~10% of cellular RNA abundance
Typically includes several modified, non-standard bases (inosine, ψ, pseudouridine, etc.)
Genetic Code
AUG codes for N-formylmethionine (fMet) in prokaryotes or methionine (Met) in eukaryotes - start code
three stop signals - important for non-natural proteins
redundant
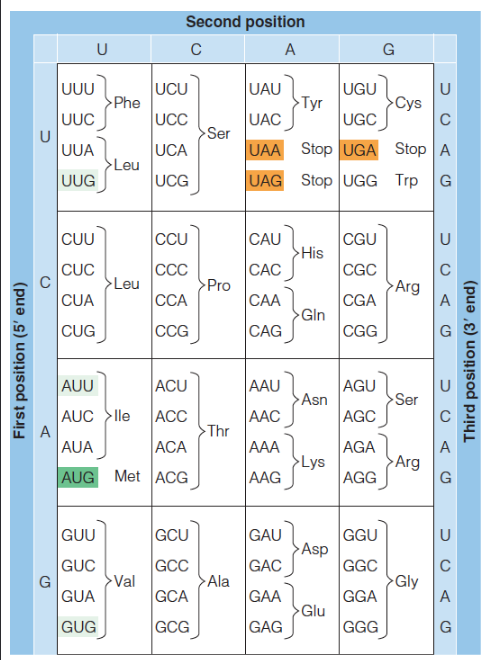
redundancy in genetic code
Trp - special and difficult amino acid → only one codon
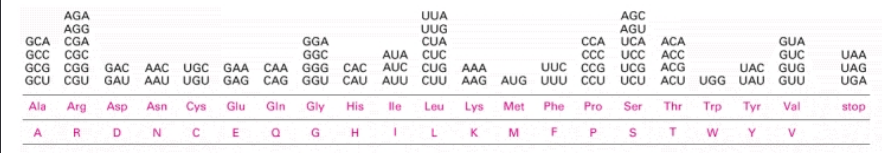
Ribosome
50S subunit
2 rRNAs
34 proteins
30S subunit
1 rRNA
21 proteins
binding site for mRNA (read 5' to 3')
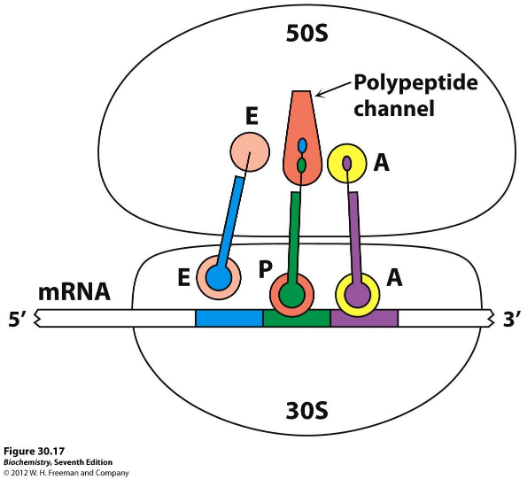
Translation elongation
binding of specific aa-tRNA to A (amino-acyl) site
Peptide bond formation at P (peptidyl) site; chain tranfer from p-tRNA to aa-tRNA
translocation of p-tRNA from A to P
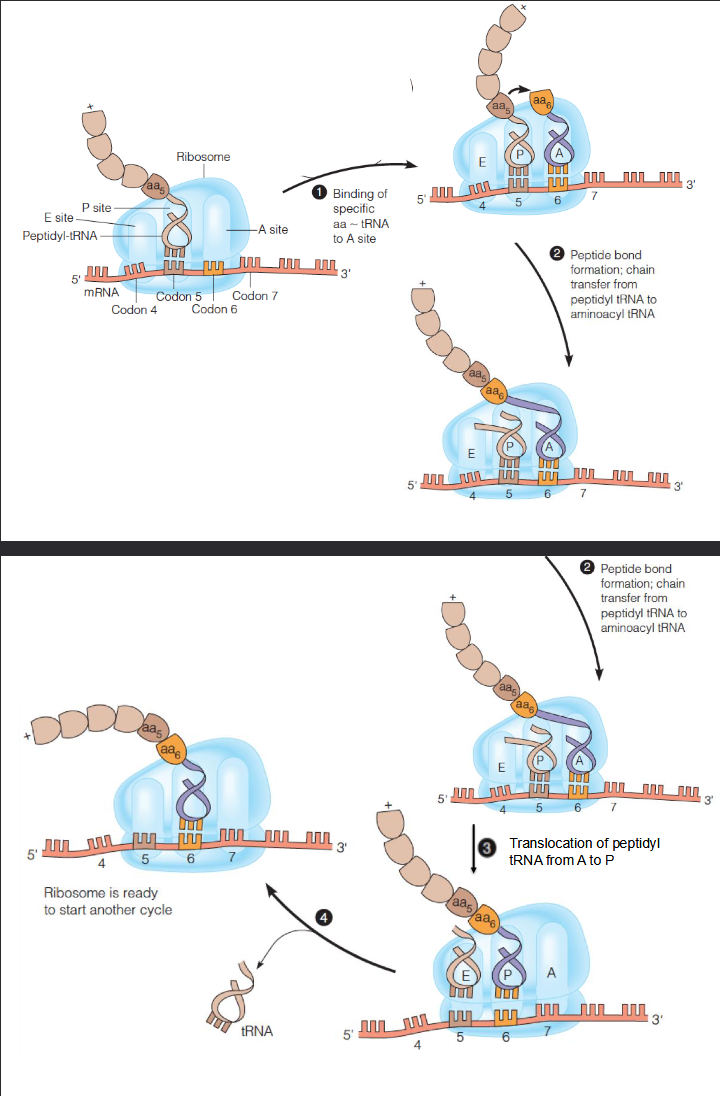
Elongation mechanism
Nucleophilic attack on the ester by the incoming amino end with tetrahedral intermediate
Occurs at the peptidyl transferase center (PTC)
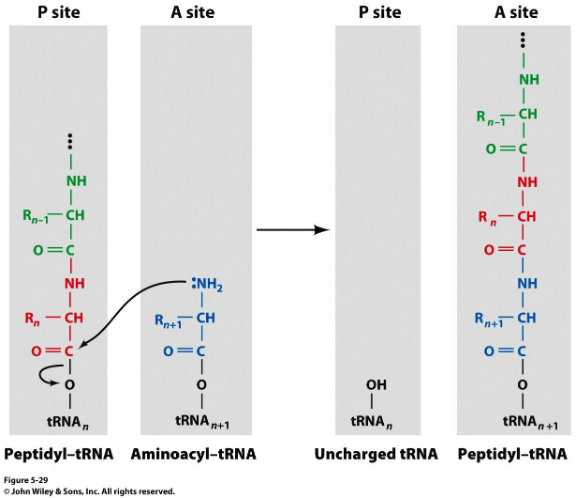
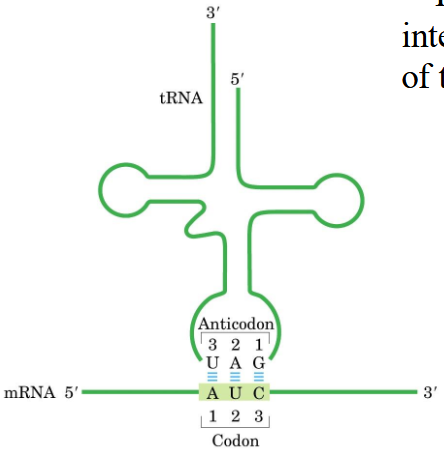
codon-anticodon interaction
The first base of codon interacts with the third base of the tRNA anticodon
Synthetase accuracy
essential for fidelity of translation
post-charged modifications can be made - nonnatural amino acids to make aritificial proteins and peptides
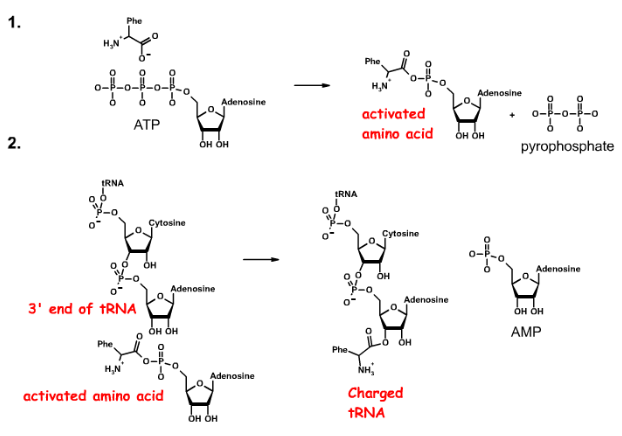
Synthetase mechanism
amino acid + ATP = activated amino acid (aminoacyladenylate) + PPi
3’ end tRNA + activated amino acid = charged tRNA + AMP
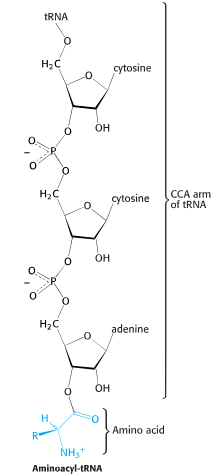
Aminoacyl-tRNA
3’ end of CCA
What can DNA be damaged by?
Temperature
Radical reactions
Nucleophiles
Electrophiles
Pi-stacking
Hydrogen bonding
Ionic interactions
monoclonal antibodies (MABs)
chemotherapeutic - bind only to cancer-cell-specific antigens and induce an immune response against the target cancer cell
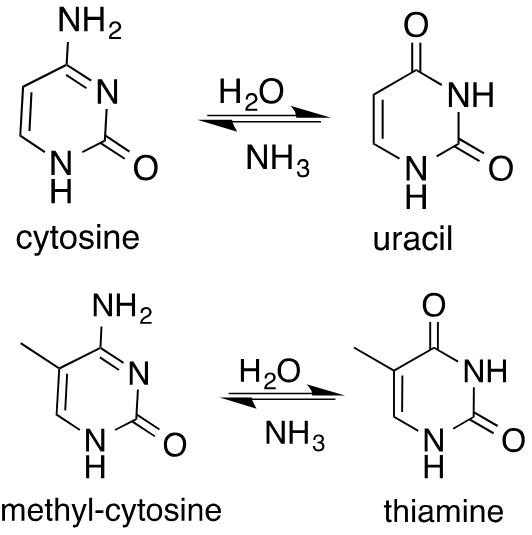
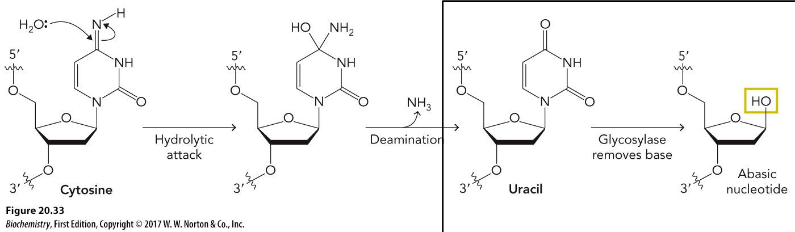
Why is uracil only in RNA?
deamination of cytosine makes uracil → if U not removed, it will pair with A in replication → next replication will pair T with A → overall: C to T mutation
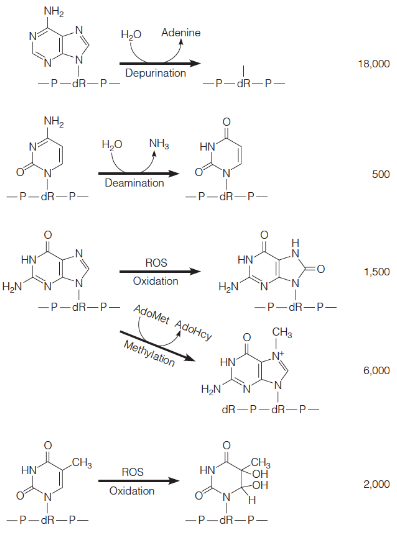
Endogenous DNA-damaging reactions
frequency in number of lesions per mammalian cell per day
depurination - A to abasic
deamination - C to U
oxidation - G and T
methylation - SAM/AdoMet → abasic site
mutations
Permanent change in DNA sequence
Can affect gene function
Can alter protein-coding sequence
missense - different amino acid
nonsense - stop codon
silent - no change
Repair Mechanisms
Recognize the error
Remove it
Repair the gap with DNA polymerase and DNA ligase
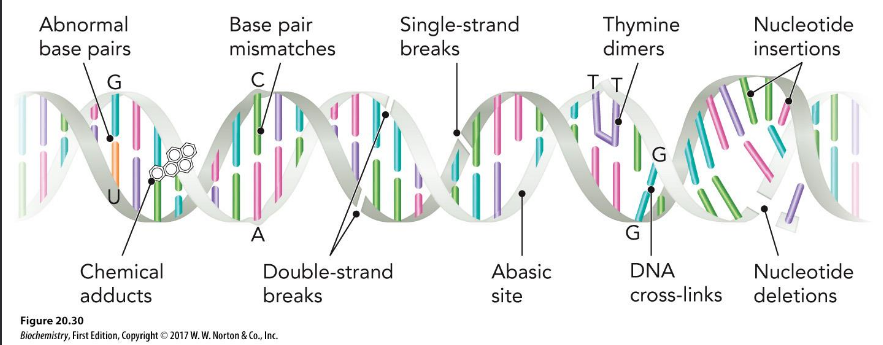
Common Mutations
abnormal basepairs
chemical adducts
base pair mismatches
doublestrand breaks
single strand breaks
abasic site
thymine dimers
DNA crosslinks
nucleotide insertions
nucleotide deletions
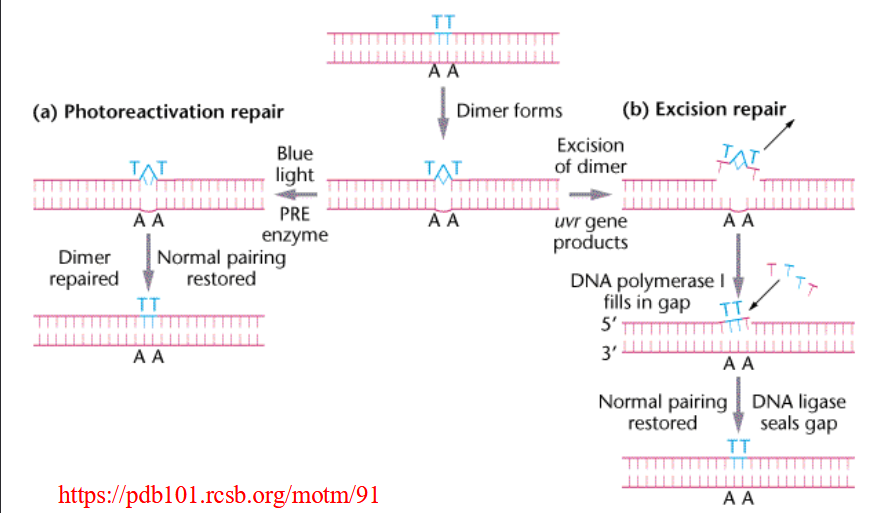
Direct repair pathway
mistake fixed w/o removing neculeotide
base-excision repair pathway
one nucleotide is removed and fixed
nucleotide excision repair pathway
stretch of DNA removed and fixed
Spontaneous deamination of C to U
Improper complimentary base pairing; Generates an abasic site by glycosylase base removal
UV radiation (photoproducts)
thymine dimer; creates DNA strain
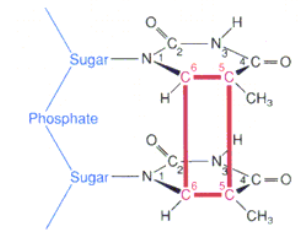
Repair of Thymine dimers
highly reversible reaction due to high strain - fixed by leaving sunlight
Environmental DNA-damaging agents
radiation
ionising
ultraviolet
DNA-methylating reagents
N-Methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine (MNNG)
DNA-cross-linking reagents
Cisplatin (chemotherapeutic)
Bulky electrophilic agents
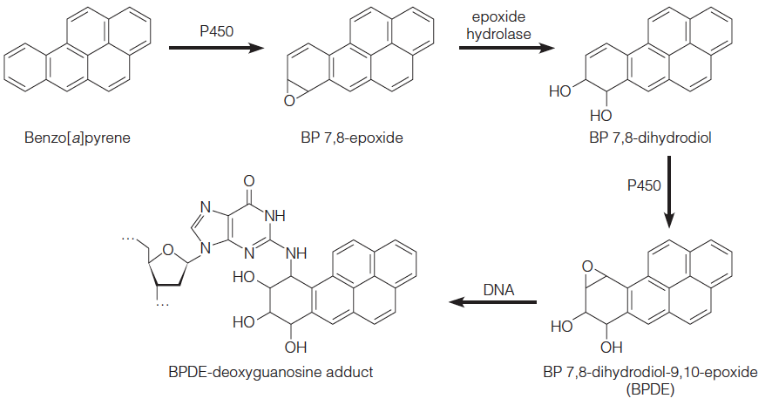
Benzo[a]pyrene (carcinogenic hydrocarbon in tobacco smoke)
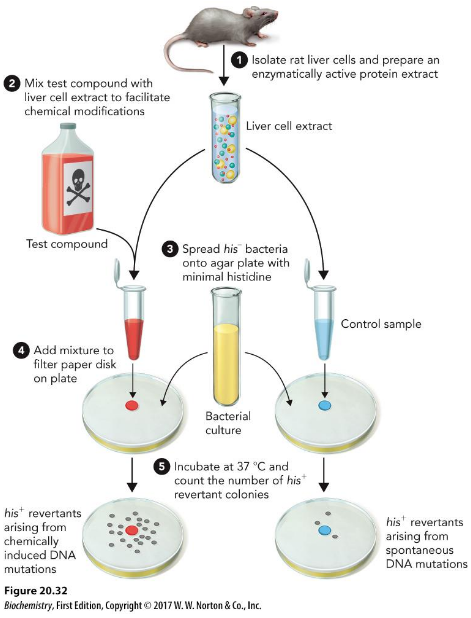
Ames test
Several strains of the bacterium Salmonella typhimurium carry mutations in genes involved in histidine synthesis. These strains are auxotrophic mutants, i.e. they require histidine for growth, but cannot produce it.
The method tests the capability of the tested substance in creating mutations so that the cells can grow on a histidine-free medium.
benzopyrene damage
adduct on G-2-exoamino via reactive epoxide
minor groove
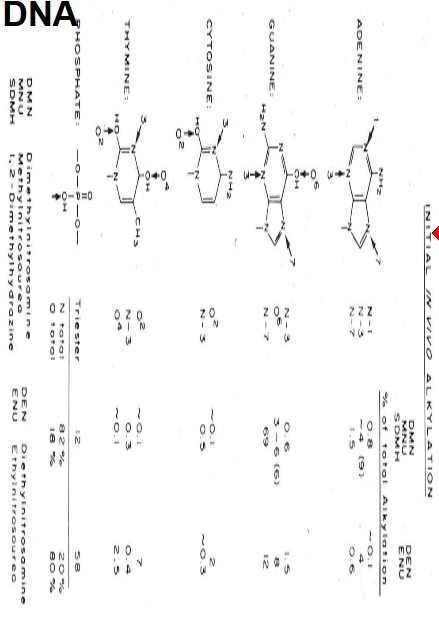
Sites of alkylation of DNA
69% of the time adds to G-N7