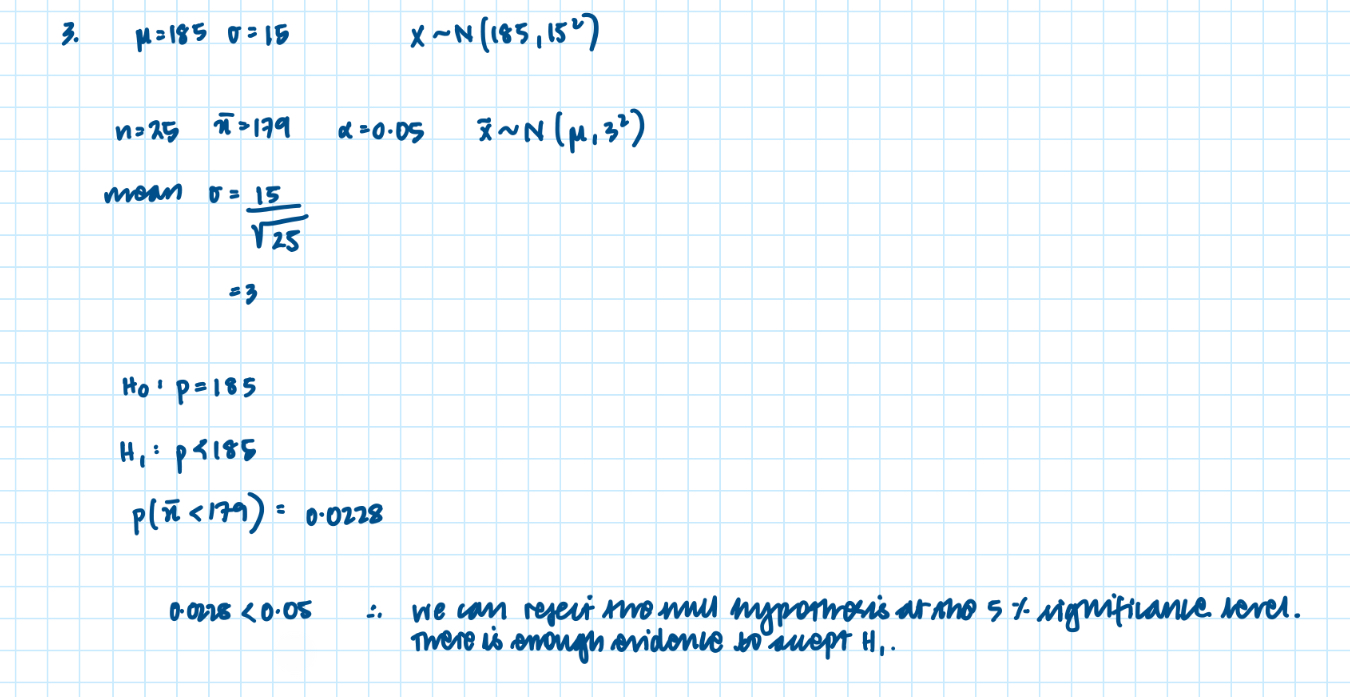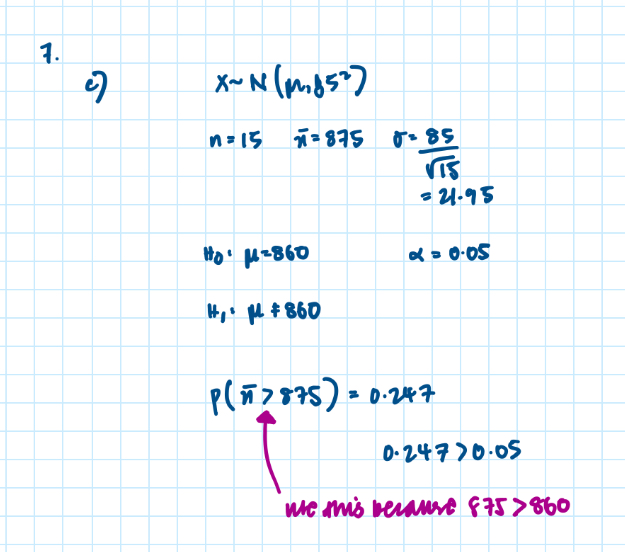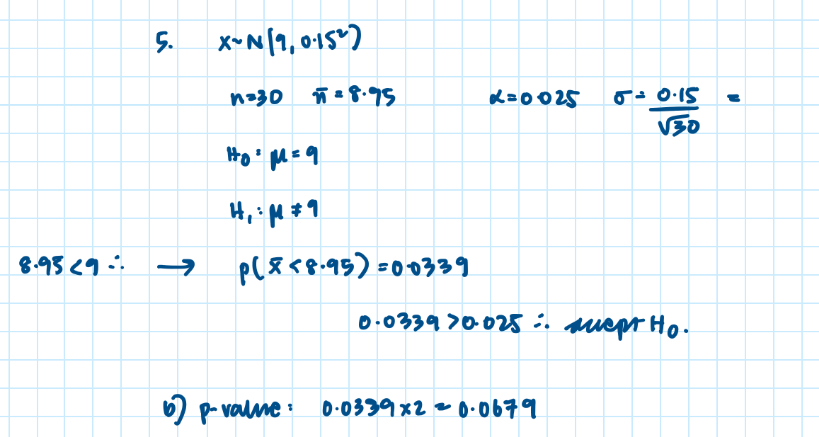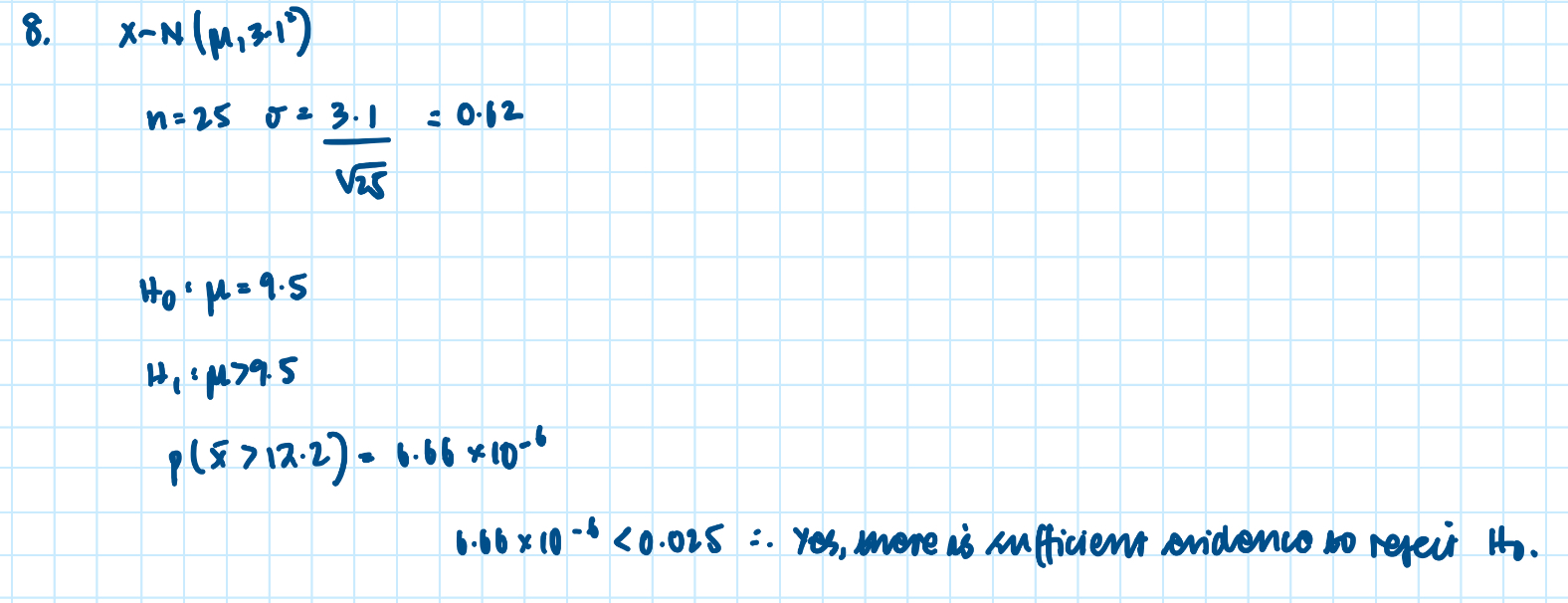The Normal Distribution:
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
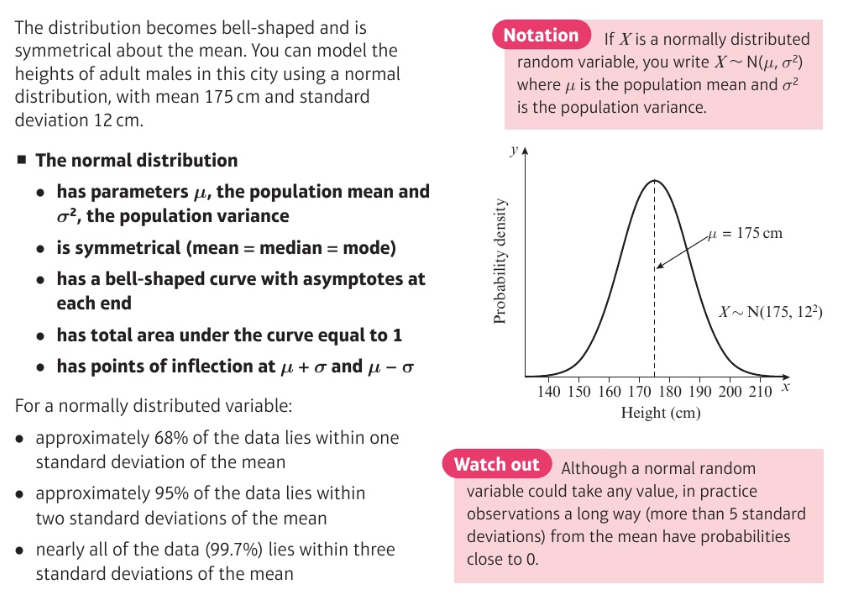
Overview of the normal distribution:
A continuous random variable can take any one of infinitely many values. A continuous random variable has a continuous probability distribution. This can be shown as a curve on a graph.
The area under a continuous probability distribution is equal to 1.
A discrete random variable can only take certain distinct values.
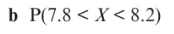
Finding probabilities using the normal distribution:
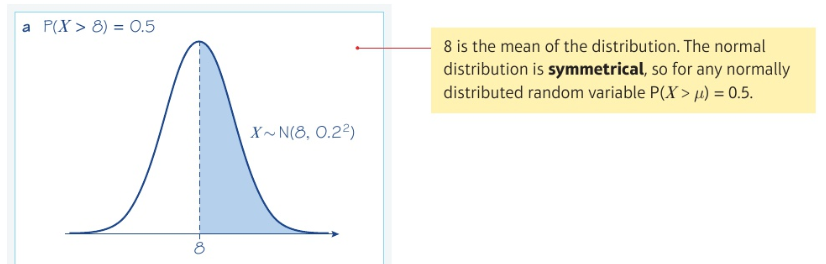
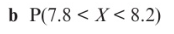
Finding probabilities using the normal distribution:


Using calculators to find probabilities for normal distributions:

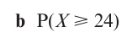
Using calculators to find probabilities for normal distributions:
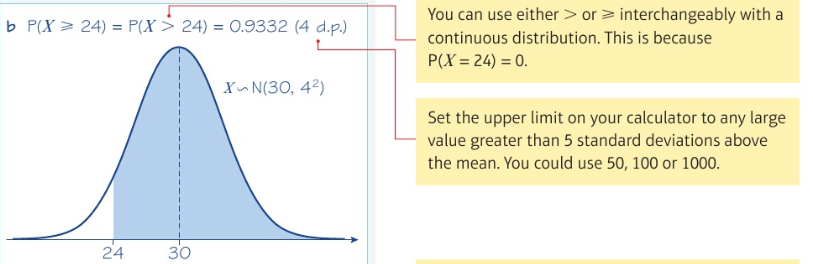
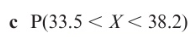
Using calculators to find probabilities for normal distributions:
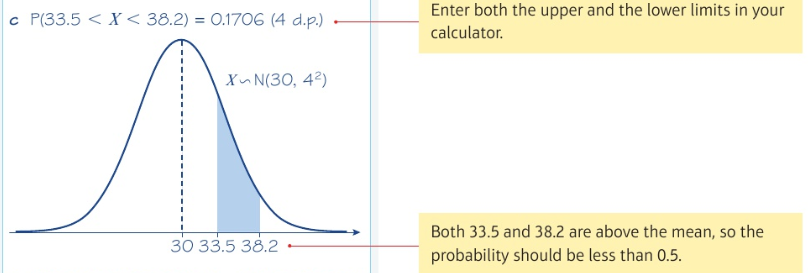
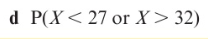
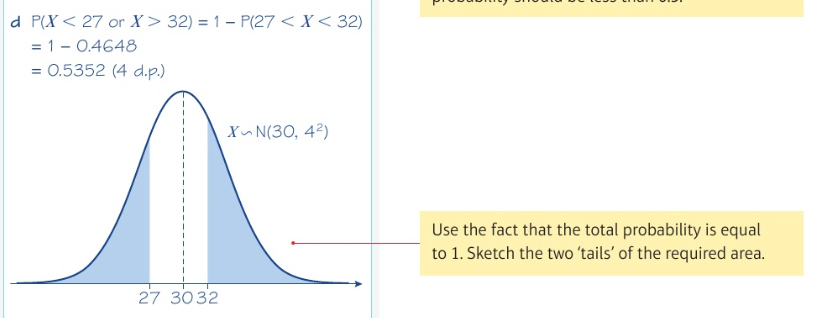
The inverse normal distribution function:


Examples of the inverse normal distribution function:
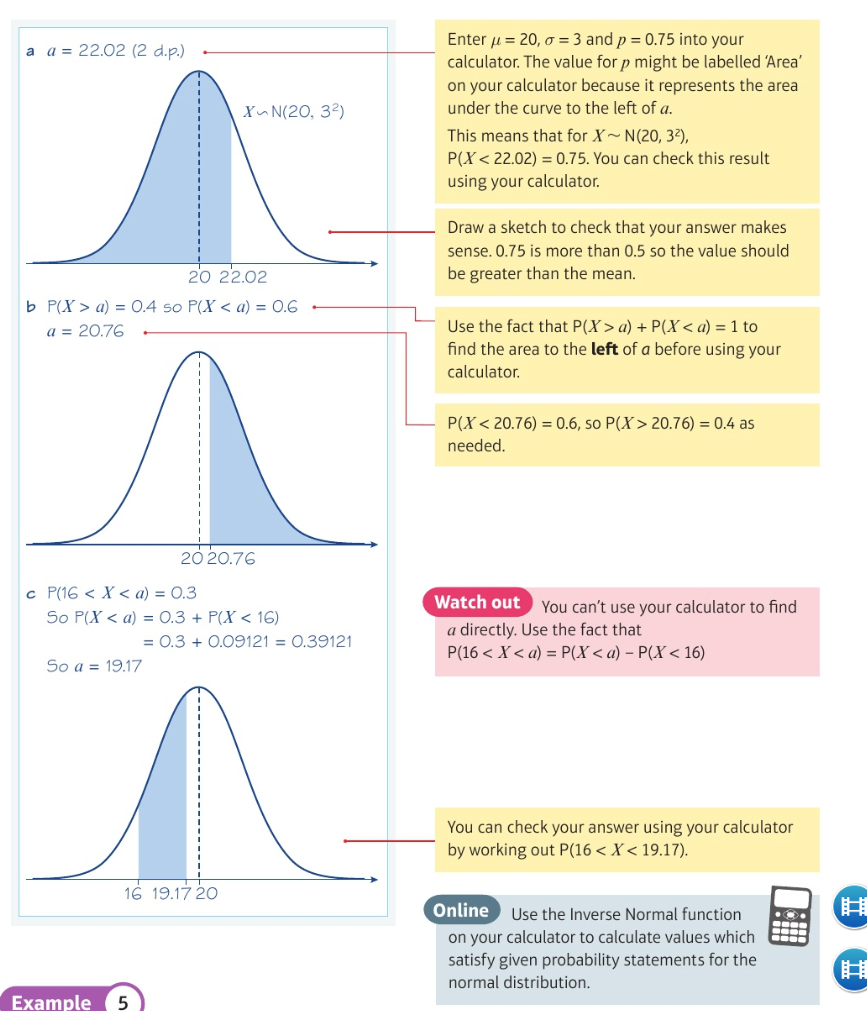

Examples of the inverse normal distribution function: (worded questions)
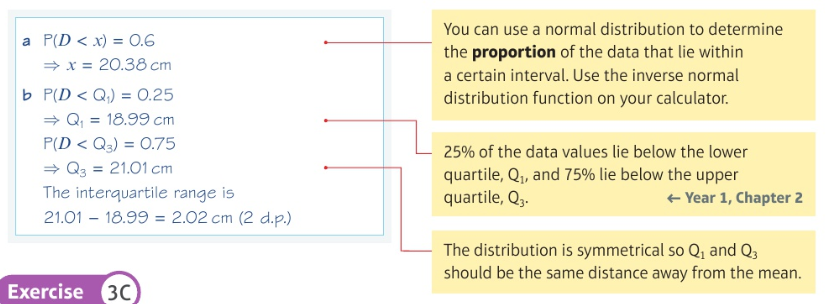
The standard normal distribution:
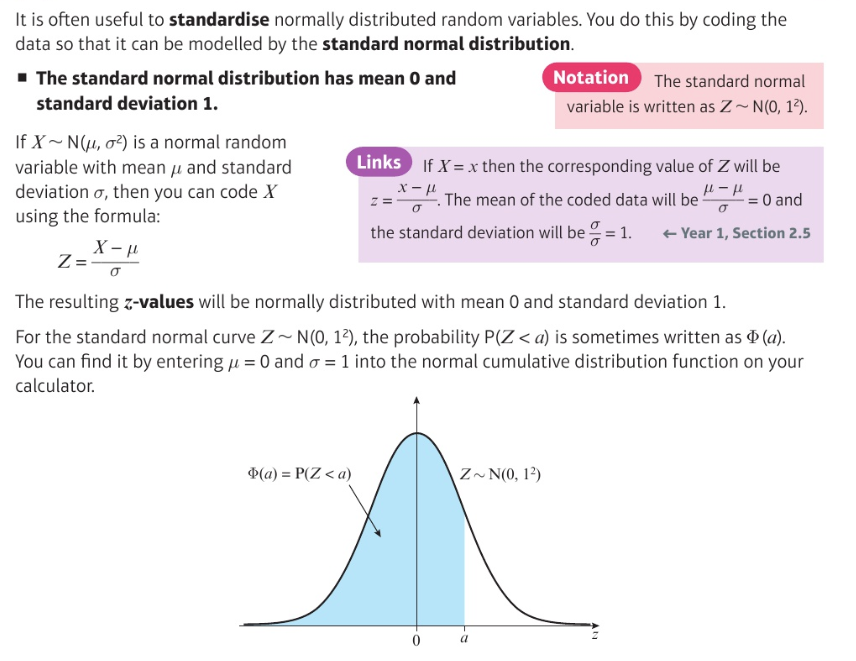

Using the standard normal distribution:
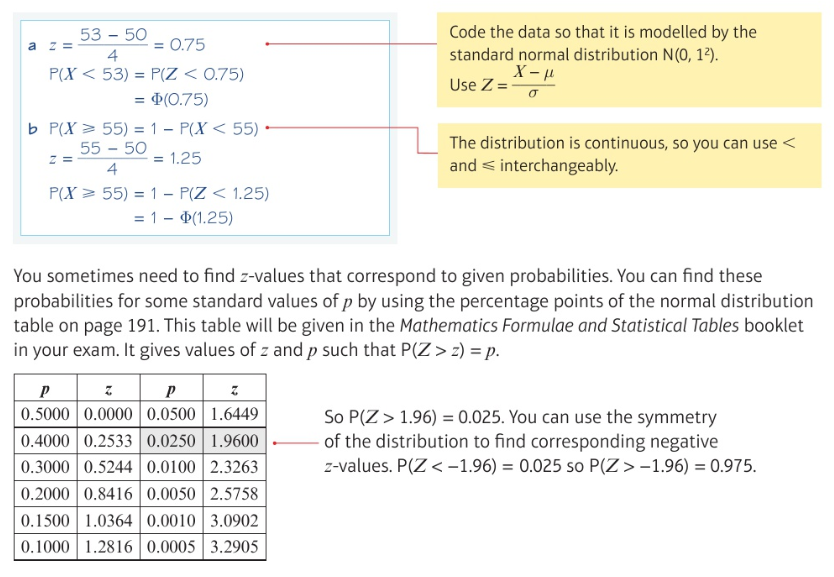

Using the standard normal distribution: (worded question)
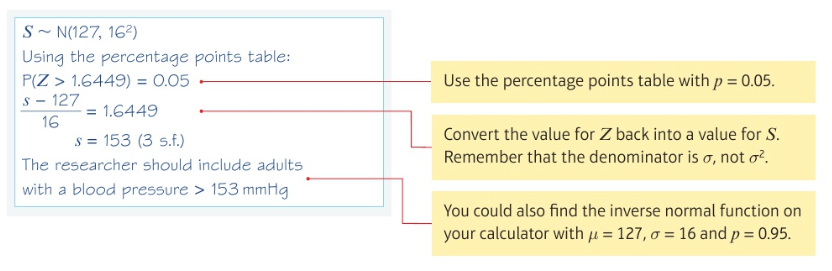
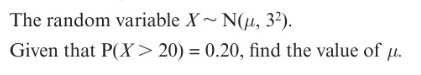
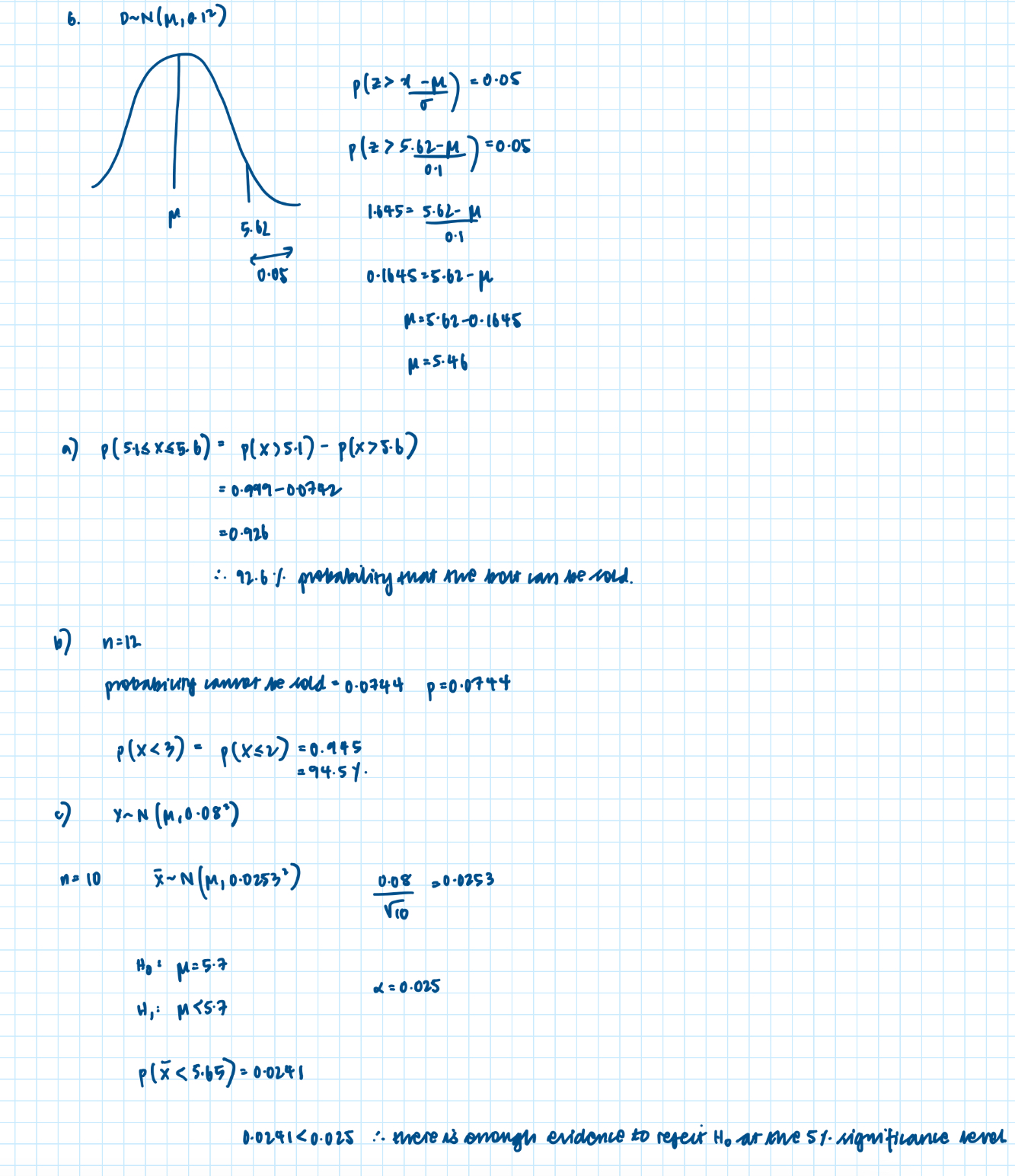
Finding an unknown mean or standard deviation for a normally distributed variable
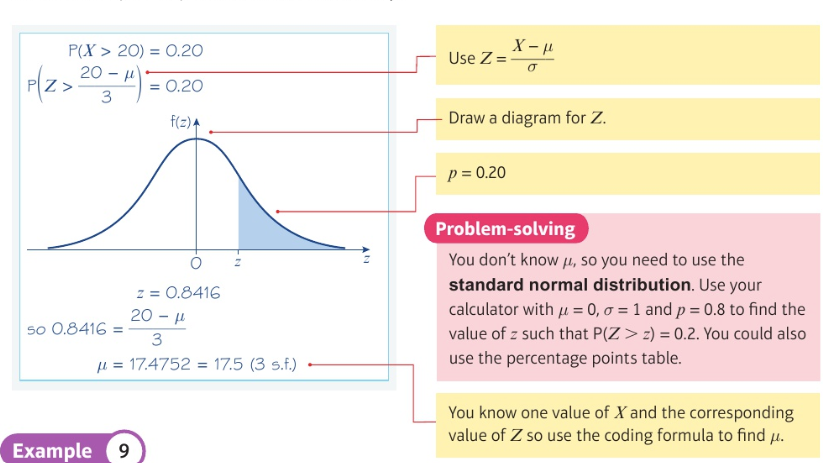

Finding an unknown mean or standard deviation for a normally distributed variable: (worded question)
b) X-N(50,52)
let a be the 90th percentile
P(X<a)=0.9
a=56.4cm (1dp)
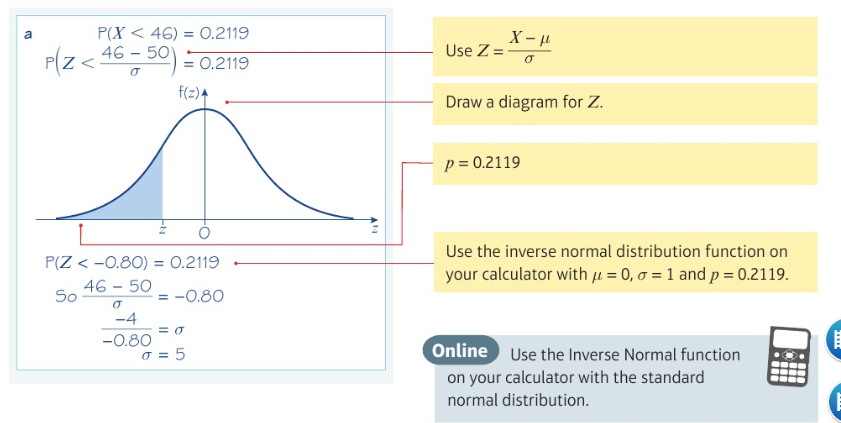
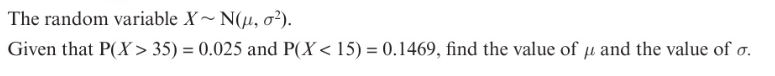
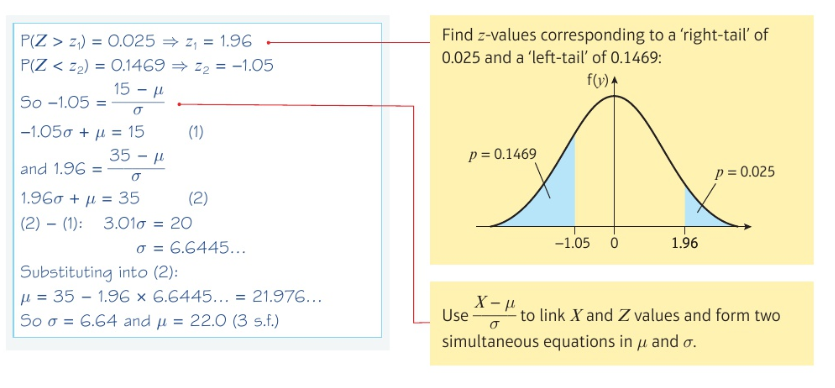
Using simultaneous questions to find the mean and standard deviation:
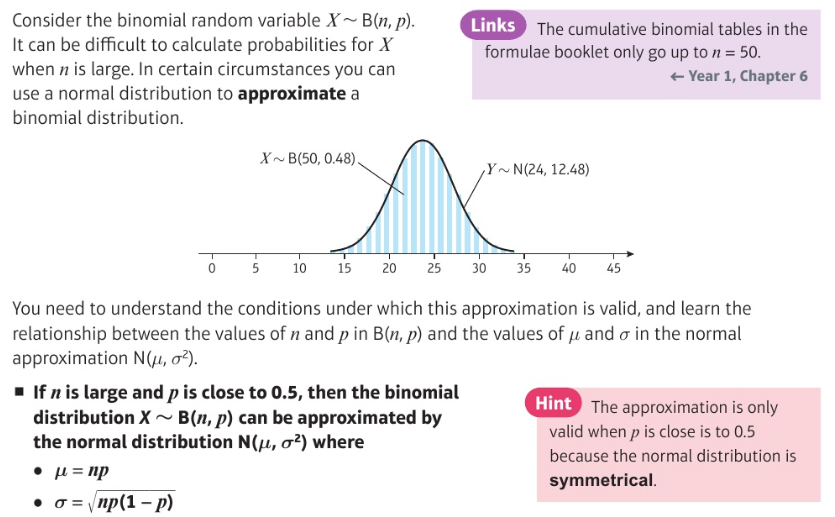
Approximating a binomial distribution:

Example of approximating a binomial distribution:

Applying a continuity correction:
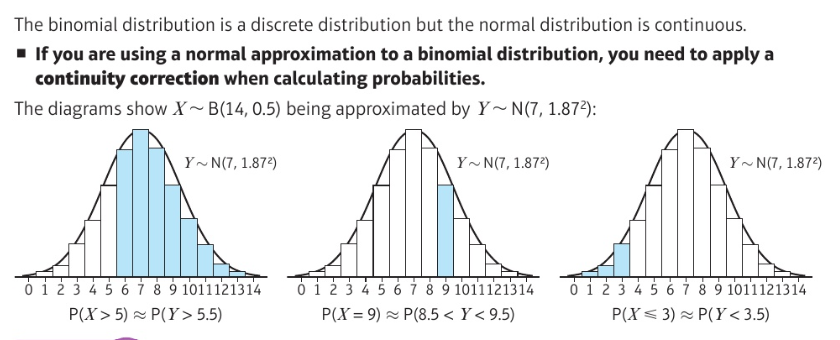
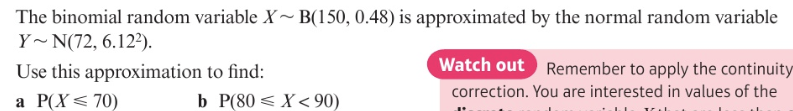
Example of applying a continuity correction:


Combining approximating a binomial and the continuity correction:
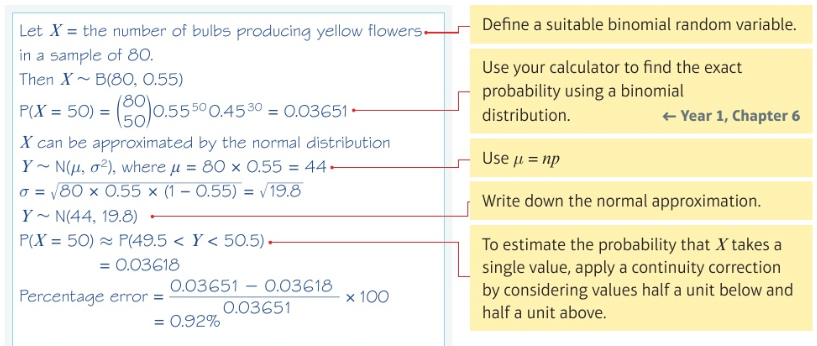
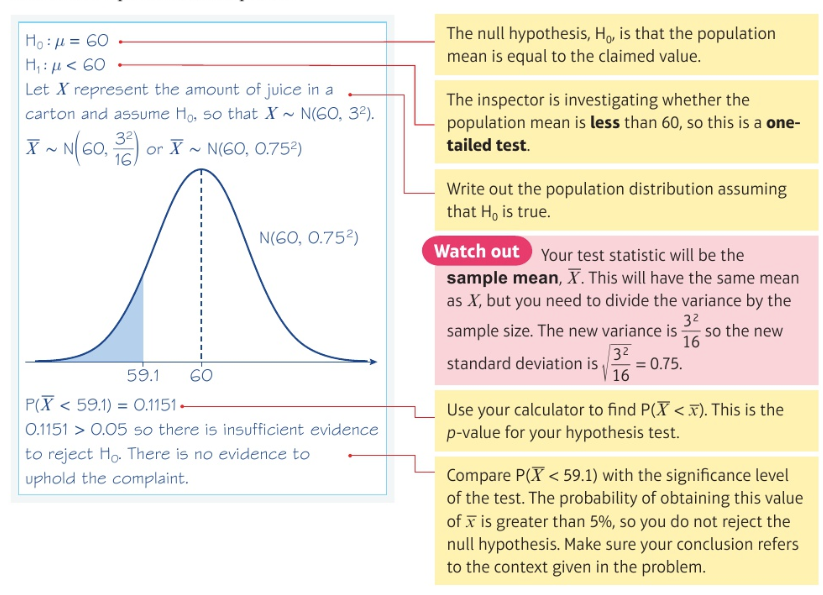
Hypothesis testing with the normal distribution:


Example of hypothesis testing with the normal distribution:
Finding the critical region / critical value for a hypothesis test for the mean of a normal distribution:


Example of finding the critical region for a hypothesis test for the mean of a normal distribution: (part 1)
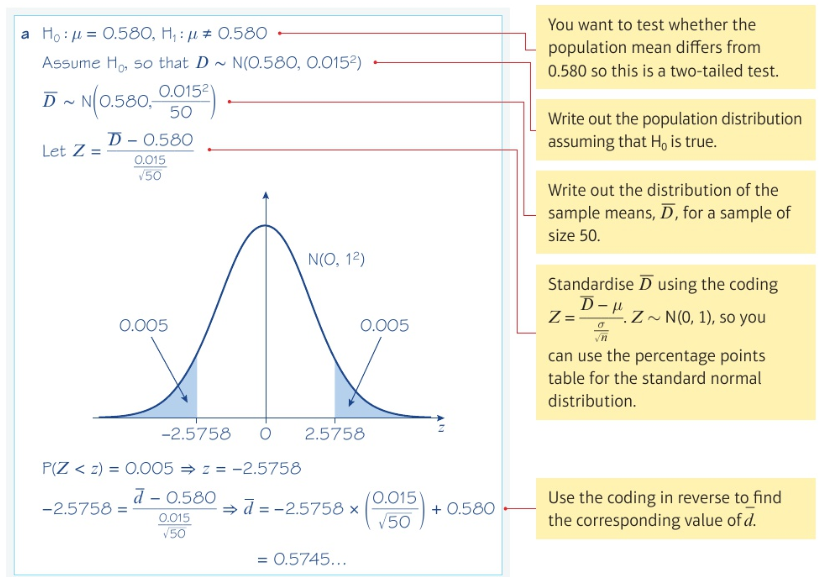
Example of finding the critical region for a hypothesis test for the mean of a normal distribution: (part 2)


Distribution of the sample mean: