Spinal Curves and IVF (Exam 1)
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Describe spinal curves.
- Normal anterior to posterior bending
- Adds 10x resistance to axial compressive loads
What are excessive curves called?
Kyphosis/hyperkyphotic - hunchback
- Aging, weightlifting
Lordosis/hyperlordotic - swayback
- Pregnancy, obesity
Scoliosis - lateral bend
Describe anterior spinal curves.
- AKA Lordotic or secondary curves
- Cervical and lumber
Describe posterior spinal curves.
- AKA Kyphotic or primary curves
- Thoracic, sacrum, and coccyx
Describe the embryonic period of spinal curvature.
- Primary curves present
- Cervical begins to appear toward the end due to muscle development
Describe the neonatal period of spinal curvature.
- 3-4 days infant begins head lift
- 3-4 months cervical lordosis can be observed
Describe the infant period of spinal curvature.
- 6-9 months infant crawls and sits up
- 9-18 months infant walks
- causes lumber to curve, and increase in size and density
What is the range and degree of curve of normal cervical spine?
- Tip of odontoid process of C2 to T2
- 35-45 degrees
What is the range and degree of curve of normal thoracic spine?
- Between T2 and T12
- 20-40 degrees
What is the range and degree of curve of normal lumbar spine?
- Between T12 - lumbosacral angle
- 50-60 degrees
What is the range normal sacrococcygeal spine?
- Lumbosacral angle to tip of coccyx
What is anklyosing spondylitis?
-Complete auto fusion of the spine due to inflammation
What are the two types of bone tissue?
- Cortical bone: dense outer shell
- Cancellous bone: inner spongy
What is bone density?
Measurement of minerals in bones (more minerals=more strength)
What three cells manage bones?
- Osteocytes: maintain bone and diffuse nutrients
- Osteoblasts: secrete bone matrix
- Osteoclasts: breaks down bone matrix
When do bones grow the most?
During puberty
What happens during the ages of 25 - 50 years?
Equal amounts of bone deposition and break down
When does bone break down exceed bone deposition?
Over the age of 50 or during menopause
What bone trends are seen in women?
- Low bone density than men
- Estrogen levels are linked to osteoblast activity
What is osteoporosis?
- Bones become brittle and fragile from loss of tissue
- Linked with hormones and lack of use
Prior to the age of 40, what type of bone supports most of the compressive load?
Cancellous/spongy bone (55%)
After the age of 40, what type of bone supports most of the compressive load?
Compact bone (65%)
What is Wolffs law?
bones grow or remodel in response to demands placed on them
How does spinal flexion affect the IVF?
Opens the IVF
Collateral flexion only one opens
Decreases lordosis, increases kyphosis
How does spinal extension and rotation affect the IVF?
Closes IVF
Ipsilateral flexion closes only one
Increases lordosis, decreases kyphosis
What forms a the roof of the IVF?
Inferior pedicle notch of superior vertebrae
What forms the floor of the IVF?
Superior pedicle notch of inferior vertebrae
What forms the posterior wall of IVF?
Articular processes
What forms the anterior wall of the IVF?
Cervical and Lumbar:
- Posterior of vertebral body above and below and the disk
Thoracic:
- Posterior of vertebral body above only and the disk
What trends are seen in the IVF as you go superior to posterior?
- IVF notch height increases
- Spinal nerve diameter is constant
- Spinal nerve is always in upper 1/3
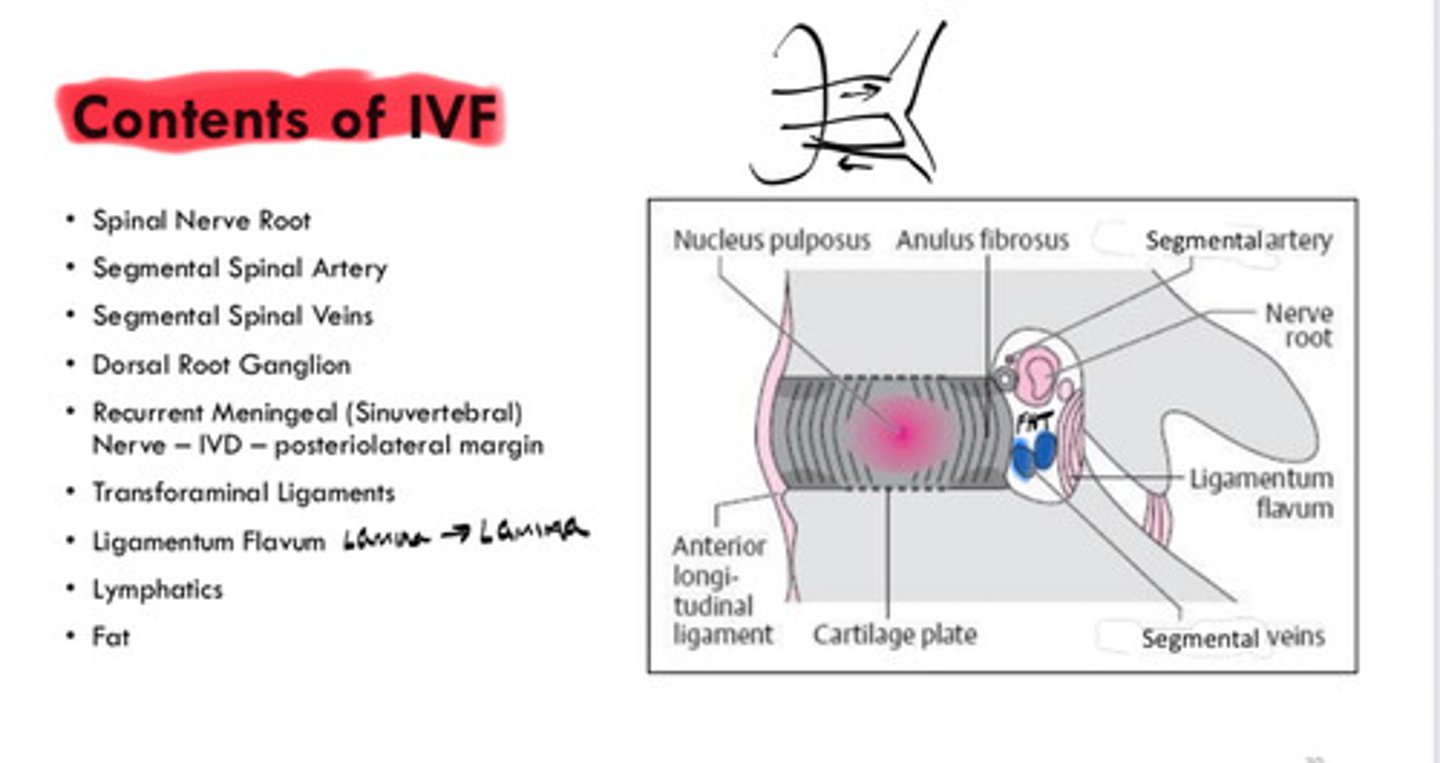
What is located in the IVF?
- Spinal nerve root
- Segmental spinal artery/veins
- Dorsal root ganglion
- Recurrent meningeal nerve
- Transforaminal ligaments
- Ligamentum flavum
- Lymphatics
- Fat
Describe the transforaminal ligaments.
- Protects nerves and vessels
- Normal structures
- Mainly in lumber
- Not present in every individual
What is the intervertebral motor unit?
2 adjacent vertebrae and their continuous structures
- Includes muscles, ligaments, and nerves