Node.js Interview Review
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
Describe the HTTP request/response lifecycle
HTTP is a request-response protocol. When you visit a URI, you (the client side) are making a request to an HTTP server to a server. The client opens a connection to the server and sends a request message.
An HTTP server listening on port waits for the client side to send a request, typically has a request can contains a request method (basic CRUD) and could have a body.
The server then send a response to the client, can consist of headers and response body if (successful or error).
What is Node.js?
Node.js is a runtime environment that's used for building serverside apps.
A runtime like Node.js is an environment where code is executed. It provides the necessary tools, libraries, and system interactions that allow programs to run efficiently.
What is Express.js?
Express is a "minimalist web framework for Node.js" that simplifies creating modern server-side web applications in Node.
Express apps:
- serve static assets like HTML, CSS, client-side JavaScript, and images
- expose RESTful APIs that clients can make requests to in order to retrieve data
- persist data to and retrieve data from databases
How does a simple express counter app work?
https://glitch.com/edit/#!/express-counterapp-nodemock?path=server.js:23:62
1. Look at the index.html, we see that when our app loads it has a counter set to 0.
2. On package.json we have some dependencies. One of it is express.
3. On server.js, require express.
4. Then create a new app by invoking express.
5. Define theCount as global scope variable
6. Serve up public assets via app.use(static('public'))
7. Make a simple get request to increment theCount
8. Using app.listen() create a way for your app to listen for HTTP request over a certain port (8080)
Describe the architecture of a basic Express app. How is it organized?
The key parts of a modern server-side web app:
- a way to listen for HTTP requests over a port
- a way to inspect and interact with HTTP request and response objects
- a way to route HTTP requests from clients to the right request handlers
- a way to serve static assets to client browsers (e.g., our route for /)
- a way to serve data to clients (e.g., our route for /the-count)
Tell me about a time when you've used Express Router. How was it helpful?
A router object is an isolated instance of middleware and routes. It's like a mini-app that creates a new router object so you specify how your endpoints respond by adding middleware and stating the HTTP method routes (basic CRUD).
You can use app.use() or router.use, router.get, etc.
https://expressjs.com/en/4x/api.html#router
https://glitch.com/edit/#!/todo-router-mi
https://expressjs.com/en/guide/routing.html
Routing refers to how your endpoints responds to client requests.
What's your experience with continuous deployment?
Continuous Integration is the practice of testing each change done to your codebase automatically and as early as possible.
https://css-tricks.com/continuous-integration-continuous-deployment/
What are the common HTTP methods?
The ones you'll most commonly use are GET, POST, PATCH, PUT, and DELETE (which correspond to the Express methods app.get(), app.post(), app.patch(), app.put(), and app.delete(), respectively.
GET is used to read or retrieve resources
POST is used to create new resources
PATCH is used to update part of an existing resource
PUT is used to replace an existing resource
DELETE is used to delete resources
The request method along with the request path are used to route the request to the right request handler, which is a function that knows how to supply the requested resource.
What is a response object?
The response object will contain at minimum an HTTP status code and some headers (for instance, for Content-Length). Unless you explicitly set a different status code, HTTP responses default to 200. If the response contains content, that content goes in the response body.
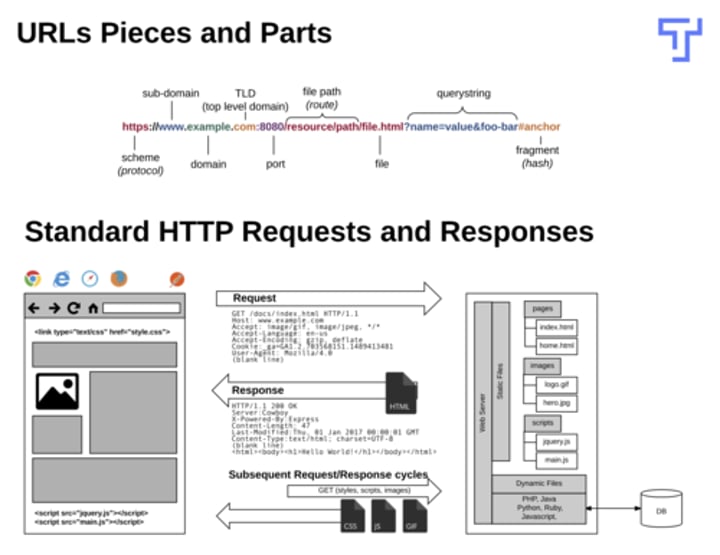
What are the URL Pieces and Parts?
Give an example of a conditional logic and status codes
https://glitch.com/edit/#!/rust-friction
What's your experience with continuous integration? How has it helped you?
Mocha & Chai
https://courses.thinkful.com/node-001v5/lesson/1.5
CI & Testing with Mongo/ose
https://courses.thinkful.com/node-001v5/lesson/2.3
https://css-tricks.com/continuous-integration-continuous-deployment/
Continuous Integration is the practice of testing each change done to your codebase automatically and as early as possible.
Describe how a Mongo database is structured.
https://courses.thinkful.com/node-001v5/unit/2
MongoDB, a non-relational, document-based database, and Mongoose, a library for creating Mongo-backed models that represent the data in our applications.
mongo db is organized by collections of documents
schema and model to instantiate = documents
How do JSON web tokens work?
JWT https://jwt.io/
JWTs are strings that can be used to identify a user and grant them access to an API. By supplying a valid JWT when you make a request to an API, the server can validate that you are a genuine, registered user.
it's a way for a user not to input the password everytime.
It's the access card that verifies your credential and also determines what you can access in a building.
jwt tokens have a header, payload, and signature. Your code should verify the token. If its valid, then you can use it to access a protected endpoint
What is the purpose of bcrypt in the authentication process?
Bcrypt https://github.com/dcodeIO/bcrypt.js
As you can see, we're using the bcryptjs library (which is a JavaScript implementation of bcrypt, a popular password hashing function) to handle hashing user passwords.
We call the bcrypt hash method with the raw password and an integer value indicating how many rounds of the salting algorithm should be used. The higher this number is, the more computationally difficult it is to compare two passwords. A value between 10 and 12 provides a nice balance between taking long enough so brute-force cracking is difficult, and being quick enough that your app is responsive to your users.
https://courses.thinkful.com/node-001v5/assignment/3.1.2
- define your strategy using const localStrategy = new LocalStrategy(); This is a promise
- then register the route on server.js through passport.use(localStrategy)
- then use passport.authenticate()
Create and require a Node module in a basic Express app.
https://glitch.com/edit/#!/code-export-require-destructure
Create a Mongoose Schema for a basic todo app.
https://glitch.com/edit/#!/code-create-todo-schema
Move a set of endpoints into a router and reconnect the app.
https://glitch.com/edit/#!/code-move-to-express-router
Request and Response Drills
https://courses.thinkful.com/node-001v5/project/1.1.5
Echo: https://glitch.com/edit/#!/echo-endpoint-barrett-trisha?path=server.js:4:3
MadLib:
What is middleware, and what does it do?
Is a function with req, res, next and does something. It's sandwiched between the require and app.listen.
What does chai.request(app).get('/api/folders').set('Authorization', `Bearer ${token}`) do?
In testing, to use chai http's live integration testing, you first need to make a request to the app or url.
When you pass in the app (from server.js) you are open the server from incoming request by listen(), chai automatically closes the server once testing is done with close().
The example is a get request on a protected endpoint
What are JS promises?
Have to do with asynchronous fn.
The Promise object represents the eventual completion (or failure) of an asynchronous operation, and its resulting value.
Compared to synchronous fn where the whole app stops as the request is fulfilled, promises has the ability to load other requests while attempting to resolve or reject other requests.
Junior - What is Node.js? Where can you use it?
Node.js is a web application framework built on Google Chrome's JavaScript Engine (V8 Engine).
Node.js comes with runtime environment on which a Javascript based script can be interpreted and executed (It is analogus to JVM to JAVA byte code). This runtime allows to execute a JavaScript code on any machine outside a browser. Because of this runtime of Node.js, JavaScript is now can be executed on server as well.
Node.js = Runtime Environment + JavaScript Library
Junior - Why use Node.js?
Node.js makes building scalable network programs easy. Some of its advantages include:
It is generally fast
It almost never blocks
It offers a unified programming language and data type
Everything is asynchronous
It yields great concurrency
Junior - What are the two types of API functions in Node.js?
The two types of API functions in Node.js are: a) Asynchronous, non-blocking functions b) Synchronous, blocking functions
Junior - What are the core modules of Node.js?
EventEmitter
Stream
FS
Net
Global Objects
Junior - How you can monitor a file for modifications in Node.js ?
We can take advantage of File System watch() function which watches the changes of the file.
Junior - Could we run an external process with Node.js?
Yes. Child process module enables us to access operating system functionaries or other apps. Scalability is baked into Node and child processes are the key factors to scale our application. You can use child process to run system commands, read large files without blocking event loop, decompose the application into various "nodes" (That's why it's called Node).
Child process module has following three major ways to create child processes -
spawn - child_process.spawn launches a new process with a given command.
exec - child_process.exec method runs a command in a shell/console and buffers the output.
fork - The child_process.fork method is a special case of the spawn() to create child processes.
Junior - What are the benefits of using Node.js?
Aynchronous and Event DrivenAll APIs of Node.js library are aynchronous that is non-blocking. It essentially means a Node.js based server never waits for a API to return data. Server moves to next API after calling it and a notification mechanism of Events of Node.js helps server to get response from the previous API call.
Very Fast Being built on Google Chrome's V8 JavaScript Engine, Node.js library is very fast in code execution.
Single Threaded but highly Scalable - Node.js uses a single threaded model with event looping. Event mechanism helps server to respond in a non-bloking ways and makes server highly scalable as opposed to traditional servers which create limited threads to handle requests. Node.js uses a single threaded program and same program can services much larger number of requests than traditional server like Apache HTTP Server.
No Buffering - Node.js applications never buffer any data. These applications simply output the data in chunks.
Junior - How to make Post request in Node.js?
var request = require('request');
request.post('http://www.example.com/action', {
form: {
key: 'value'
}
}, function(error, response, body) {
if (!error && response.statusCode == 200) {
console.log(body)
}
});
Junior - If Node.js is single threaded then how it handles concurrency?
Node provides a single thread to programmers so that code can be written easily and without bottleneck. Node internally uses multiple POSIX threads for various I/O operations such as File, DNS, Network calls etc.
When Node gets I/O request it creates or uses a thread to perform that I/O operation and once the operation is done, it pushes the result to the event queue. On each such event, event loop runs and checks the queue and if the execution stack of Node is empty then it adds the queue result to execution stack.
This is how Node manages concurrency.
Junior - Is Node.js single threaded?
Yes! Node uses a single threaded model with event looping.
Junior - What is a control flow function?
It is a generic piece of code which runs in between several asynchronous function calls is known as control flow function. Allows for, if, try/catch following await
Junior - What do you mean by Asynchronous API?
All APIs of Node.js library are aynchronous that is non-blocking. It essentially means a Node.js based server never waits for a API to return data. Server moves to next API after calling it and a notification mechanism of Events of Node.js helps server to get response from the previous API call.
Junior - What are event listeners?
Event Listeners are similar to call back functions but are associated with some event. For example when a server listens to http request on a given port a event will be generated and to specify http server has received and will invoke corresponding event listener. Basically, Event listener's are also call backs for a corresponding event.
Node.js has built in event's and built in event listeners. Node.js also provides functionality to create Custom events and Custom Event listeners.
Intermediate - What is the purpose of setTimeout function?
The setTimeout(cb, ms) global function is used to run callback cb after at least ms milliseconds. The actual delay depends on external factors like OS timer granularity and system load. A timer cannot span more than 24.8 days.
Intermediate - What is REPL in context of Node?
REPL stands for Read Eval Print Loop and it represents a computer environment like a window console or unix/linux shell where a command is entered and system responds with an output. Node.js or Node comes bundled with a REPL environment. It performs the following desired tasks.
Read - Reads user's input, parse the input into JavaScript data-structure and stores in memory.
Eval - Takes and evaluates the data structure
Print - Prints the result
Loop - Loops the above command until user press ctrl-c twice.
Intermediate - What is a callback function?
A function written in a client script that runs asynchronously.
Intermediate - What's the event loop?
The event loop is what allows Node.js to perform non-blocking I/O operations — despite the fact that JavaScript is single-threaded — by offloading operations to the system kernel whenever possible.
Every I/O requires a callback - once they are done they are pushed onto the event loop for execution. Since most modern kernels are multi-threaded, they can handle multiple operations executing in the background. When one of these operations completes, the kernel tells Node.js so that the appropriate callback may be added to the poll queue to eventually be executed.
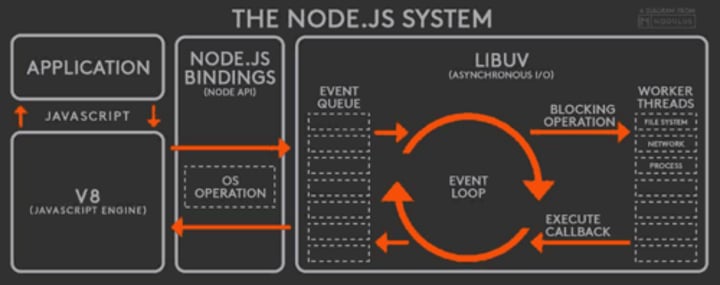
Intermediate - What is a blocking code?
If application has to wait for some I/O operation in order to complete its execution any further then the code responsible for waiting is known as blocking code.
Intermediate - How Node prevents blocking code?
By providing callback function. Callback function gets called whenever corresponding event triggered.
Intermediate - What is stream and what are types of streams available in Node.js?
Streams are a collection of data that might not be available all at once and don't have to fit in memory. Streams provide chunks of data in a continuous manner. It is useful to read a large set of data and process it.
There is four fundamental type of streams:
Readable.
Writeable.
Duplex.
Transform.
Readable streams as the name suggest used in reading a large chunk of data from a source. Writable streams are used in writing a large chunk of data to the destination.
Duplex streams are both readable and writable ( Eg socket). Transform stream is the duplex stream which is used in modifying the data (eg zip creation).
Intermediate - What is Event Emmitter?
All objects that emit events are members of EventEmitter class. These objects expose an eventEmitter.on() function that allows one or more functions to be attached to named events emitted by the object.
When the EventEmitter object emits an event, all of the functions attached to that specific event are called synchronously.
const EventEmitter = require('events');
class MyEmitter extends EventEmitter {}
const myEmitter = new MyEmitter();
myEmitter.on('event', () => {
console.log('an event occurred!');
});
myEmitter.emit('event');
Intermediate - What is purpose of Buffer class in Node?
Buffer class is a global class and can be accessed in application without importing buffer module. A Buffer is a kind of an array of integers and corresponds to a raw memory allocation outside the V8 heap. A Buffer cannot be resized.
Intermediate - When should I use EventEmitter?
Whenever it makes sense for code to subscribe to something rather than get a callback from something. The typical use case would be that there's multiple blocks of code in your application that may need to do something when an event happens.
Intermediate - What is difference between synchronous and asynchronous method of fs module?
Every method in fs module has synchronous as well as asynchronous form. Asynchronous methods takes a last parameter as completion function callback and first parameter of the callback function is error. It is preferred to use asynchronous method instead of synchronous method as former never block the program execution where the latter one does.
Intermediate - What is the preferred method of resolving unhandled exceptions in Node.js?
Unhandled exceptions in Node.js can be caught at the Process level by attaching a handler for uncaughtException event.
process.on('uncaughtException', function(err) {
console.log('Caught exception: ' + err);
});
However, uncaughtException is a very crude mechanism for exception handling and may be removed from Node.js in the future. An exception that has bubbled all the way up to the Process level means that your application, and Node.js may be in an undefined state, and the only sensible approach would be to restart everything.
The preferred way is to add another layer between your application and the Node.js process which is called the domain.
Domains provide a way to handle multiple different I/O operations as a single group. So, by having your application, or part of it, running in a separate domain, you can safely handle exceptions at the domain level, before they reach the Process level.
Intermediate - What is Chaining in Node?
Chanining is a mechanism to connect output of one stream to another stream and create a chain of multiple stream operations. It is normally used with piping operations.
Intermediate - What are the global objects of Node.js?
These objects are available in all modules:
process - The process object is a global that provides information about, and control over, the current Node.js process.
console - Used to print to stdout and stderr.
buffer - Used to handle binary data.
Intermediate - How does Node.js Work?
A Node.js application creates a single thread on its invocation. Whenever Node.js receives a request, it first completes its processing before moving on to the next request.
Node.js works asynchronously by using the event loop and callback functions, to handle multiple requests coming in parallel. An Event Loop is a functionality which handles and processes all your external events and just converts them to a callback function. It invokes all the event handlers at a proper time. Thus, lots of work is done on the back-end, while processing a single request, so that the new incoming request doesn't have to wait if the processing is not complete.
While processing a request, Node.js attaches a callback function to it and moves it to the back-end. Now, whenever its response is ready, an event is called which triggers the associated callback function to send this response.
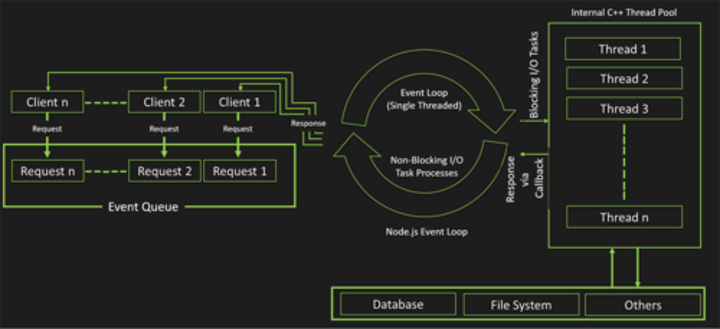
Intermediate - How does Node.js handle child threads?
Node.js, in its essence, is a single thread process. It does not expose child threads and thread management methods to the developer. Technically, Node.js does spawn child threads for certain tasks such as asynchronous I/O, but these run behind the scenes and do not execute any application JavaScript code, nor block the main event loop.
If threading support is desired in a Node.js application, there are tools available to enable it, such as the ChildProcess module.
Junior - How to debug in Node
Using the native Node debugger, you can set a breakpoint using 'debugger' and step into and over call stack and event loop. Using the node inspector, you can connect to a node process using Chrome dev tools.
Pass --inspect when running node.
What is an API
An interface that hides details of an implementation.
What is an API used for?
Perform tasks.
Retrieving data.
Manipulating data.
What is the difference between http-request and http-response
http-request - sent when requesting a network based resource.
Contains:
- URL path
- Method
- Headers
- Body
http-response - received from a http-request
Contains:
- Status code (200 - OK, 404 - Not found, 301 - Redirect, 500 - Error)
- Headers
- Body
What is a REST collection?
A group of elements with the same representation
/posts
/users
/tasks
What are the endpoints for a REST collection?
GET - List collection elements
POST - Insert an element to the collection
PUT - Replace the entire element list
DELETE - Delete the element list
What are the endpoints for a REST element?
GET - Get a single element
GET /tasks/123
PUT - Replace an element
PUT /tasks/123
DELETE - Delete an element
DELETE /tasks/123
What are some rules of thumb with RESTful apis?
- Same result should occur whether you run a command once or 10 times
- Use verbs when provding an endpoint that does a task.
What does REST stand for?
Representations State Transfer
What is REST
An architectural style for building APIs.
(Stands for 'Representational State Transfer'. We decide that HTTP verbs and URLs mean something.
What are the rules of REST architecture?
REST servers are stateless.
REST uses client to handle UI concerns and server to handle data storage concerns.
REST responses must be labeled as cacheable or not.
REST should use uniform interface, it all resources are accessed using HTTP. Resource endpoints do NOT need to mimic the data on the server. IE, /agenda may access data from 'events' and 'tasks'
REST should uses a layered system. Components of an API can transform content of messages or utilize middleware to check security for example.
What is Piping in Node?
Piping is a mechanism to connect output of one stream to another stream. It is normally used
to get data from one stream and to pass output of that stream to another stream. There is no
limit on piping operations.
Name some of the events fired by streams.
Each type of Stream is an EventEmitter instance and throws several events at different
instance of times. For example, some of the commonly used events are:
data - This event is fired when there is data is available to read.
end - This event is fired when there is no more data to read.
error - This event is fired when there is any error receiving or writing data.
finish - This event is fired when all data has been flushed to underlying system
What is the purpose of __filename variable?
The __filename represents the filename of the code being executed. This is the resolved
absolute path of this code file. For a main program this is not necessarily the same filename
used in the command line. The value inside a module is the path to that module file.
What is the purpose of __dirname variable?
The __dirname represents the name of the directory that the currently executing script resides
in.
How can you listen on port 80 with Node?
Run the application on any port above 1024, then put a reverse proxy like nginx
(http://nginx.org/) in front of it.
What tools can be used to assure consistent code style?
JSLint, ESLint
What's a stub? Name a use case
Stubs are functions/programs that simulate the behaviours of components/modules. Stubs
provide canned answers to function calls made during test cases. Also, you can assert on with
what these stubs were called.
A use-case can be a file read, when you do not want to read an actual file:
Does Node.js support multi-core platforms? And is it capable of
utilizing all the cores?
Yes, Node.js would run on a multi-core system without any issue. But it is by default a singlethreaded
application, so it can't completely utilize the multi-core system.
However, Node.js can facilitate deployment on multi-core systems where it does use the
additional hardware. It packages with a Cluster module which is capable of starting multiple
Node.js worker processes that will share the same port.
Is Node.js entirely based on a single-thread?
Yes, it's true that Node.js processes all requests on a single thread. But it's just a part of the
theory behind Node.js design. In fact, more than the single thread mechanism, it makes use of
events and callbacks to handle a large no. of requests asynchronously.
Moreover, Node.js has an optimized design which utilizes both JavaScript and C++ to
guarantee maximum performance. JavaScript executes at the server-side by Google Chrome v8
engine. And the C++ lib UV library takes care of the non-sequential I/O via background
workers.
To explain it practically, let's assume there are 100s of requests lined up in Node.js queue. As
per design, the main thread of Node.js event loop will receive all of them and forwards to
background workers for execution. Once the workers finish processing requests, the registered
callbacks get notified on event loop thread to pass the result back to the user.
When to not use Node.js?
CPU intensive operations
Why to use Buffers instead of binary strings to handle binary
data ?
Pure JavaScript does not able to handle straight binary data very well. Since Node.js servers
have to deal with TCP streams for reading and writing of data, binary strings will become
problematic to work with as it is very slow and has a tendency to break. That's why it is always
advisable to use Buffers instead of binary strings to handle binary data.
How to gracefully Shutdown Node.js Server?
We can gracefully shutdown Node.js server by using the generic signal called SIGTERM or
SIGINT which is used for program termination. We need to call SIGTERM or SIGINT which will
terminate the program and clean up the resources utilized by the program.
What are the timing features of Node.js?
setTimeout/clearTimeout - can be used to schedule code execution after a
designated amount of milliseconds
setInterval/clearInterval - can be used to execute a block of code multiple times
setImmediate/clearImmediate - will execute code at the end of the current event
loop cycle
process.nextTick - used to schedule a callback function to be invoked in the next
iteration of the Event Loop
Explain usage of NODE_ENV
Node encourages the convention of using a variable called NODE_ENV to flag whether we're in
production right now. . This determination allows components to provide better diagnostics
during development, for example by disabling caching or emitting verbose log statements.
Setting NODE_ENV to production makes your application 3 times faster.
How would you handle errors for async code in Node.js?
it is better to use a reputable promise library or async-await
instead which enables a much more compact and familiar code syntax like try-catch.
Consider following code snippet:
{
console.time("loop");
for (var i = 0; i < 1000000; i += 1) {
// Do nothing
}
console.timeEnd("loop");
}
The time required to run this code in Google Chrome is considerably more than the time
required to run it in Node.js Explain why this is so, even though both use the v8 JavaScript
Engine.
Within a web browser such as Chrome, declaring the variable i outside of any function's scope
makes it global and therefore binds it as a property of the window object. As a result, running
this code in a web browser requires repeatedly resolving the property i within the heavily
populated window namespace in each iteration of the for loop.
In Node.js, however, declaring any variable outside of any function's scope binds it only to the
module's own scope (not the window object) which therefore makes it much easier and faster
to resolve.
How would you scale Node application
1. cloning using Cluster module.
2. decomposing the application into smaller services - i.e micro services.
How to solve "Process out of Memory Exception" in Node.js
To solve the process out of memory exception in Node.js we need to increase the max-oldspace-size.
By default the max size of max-old-space-size is 512 mb which you can increase
by the command:
node --max-old-space-size=1024 file.js
Explain what is Reactor Pattern in Node.js?
Reactor Pattern is an idea of non-blocking I/O operations in Node.js. This pattern provides a
handler(in case of Node.js, a callback function) that is associated with each I/O operation. When
an I/O request is generated, it is submitted to a demultiplexer.
Explain some Error Handling approaches in Node.js you know
about. Which one will you use?
Error return value - doesn't work asynchronously
Error throwing - well-establish pattern, in which a function does its thing and if an
error situation arises, it simply bails out throwing an error. Can leave you in an unstable
state. It requires extra work to catch them. Also wrapping the async calls in try/catch
won't help because the errors happen asynchronously. To fix this, we need domains.
Domains provide an asynchronous try...catch.
var validateObject = function (obj) {
if (typeof obj !== 'object') {
throw new Error('Invalid object');
}
};
try {
validateObject('123');
}
catch (err) {
console.log('Thrown: ' + err.message);
Error callback - returning an error via a callback is the most common error handling
pattern in Node.js. Handling error callbacks can become a mess (callback hell or the
pyramid of doom).
var validateObject = function (obj, callback) {
if (typeof obj !== 'object') {
return callback(new Error('Invalid object'));
}
return callback();
};
validateObject('123', function (err) {
console.log('Callback: ' + err.message);
});
Error emitting - when emitting errors, the errors are broadcast to any interested
subscribers and handled within the same process tick, in the order subscribed.
var Events = require('events');
var emitter = new Events.EventEmitter();
var validateObject = function (a) {
if (typeof a !== 'object') {
emitter.emit('error', new Error('Invalid object'));
}
};
emitter.on('error', function (err) {
console.log('Emitted: ' + err.message);
});
validateObject('123');
Promises for async error handling
Try...catch with async/await - ES7 Async/await allows us as developers to write
asynchronous JS code that look synchronous.
Why should you separate Express 'app' and 'server'?
Keeping the API declaration separated from the network related configuration (port, protocol,
etc) allows testing the API in-process, without performing network calls, with all the benefits
that it brings to the table: fast testing execution and getting coverage metrics of the code. It
also allows deploying the same API under flexible and different network conditions. Bonus:
better separation of concerns and cleaner code.
How do you catch an error from await?
await someFunction().catch((error)=>console.log(error));
What is the difference between res.send and res.end?
res.send - Properly formats a response header and other headers along with content.
res.end - Does not include content header
What is the difference between ./ and __dirname?
In Node.js, __dirname is always the directory in which the currently executing script resides (see this). So if you typed __dirname into /d1/d2/myscript.js, the value would be /d1/d2.