BOC Immunology
1/238
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
239 Terms
b (lupus erythematosus)
1) Antinuclear antibody tests are performed to help diagnose?
a) acute leukemia
b) lupus erythematosus
c) hemolytic anemia
d) Crohn disease
c (Crithida lucilia)
2. In the anti-double-stranded DNA procedure, the antigen most commonly utilized is:
a. rat stomach tissue
b. mouse kidney tissue
c. Crithida lucilia
d. Toxoplasma gondii
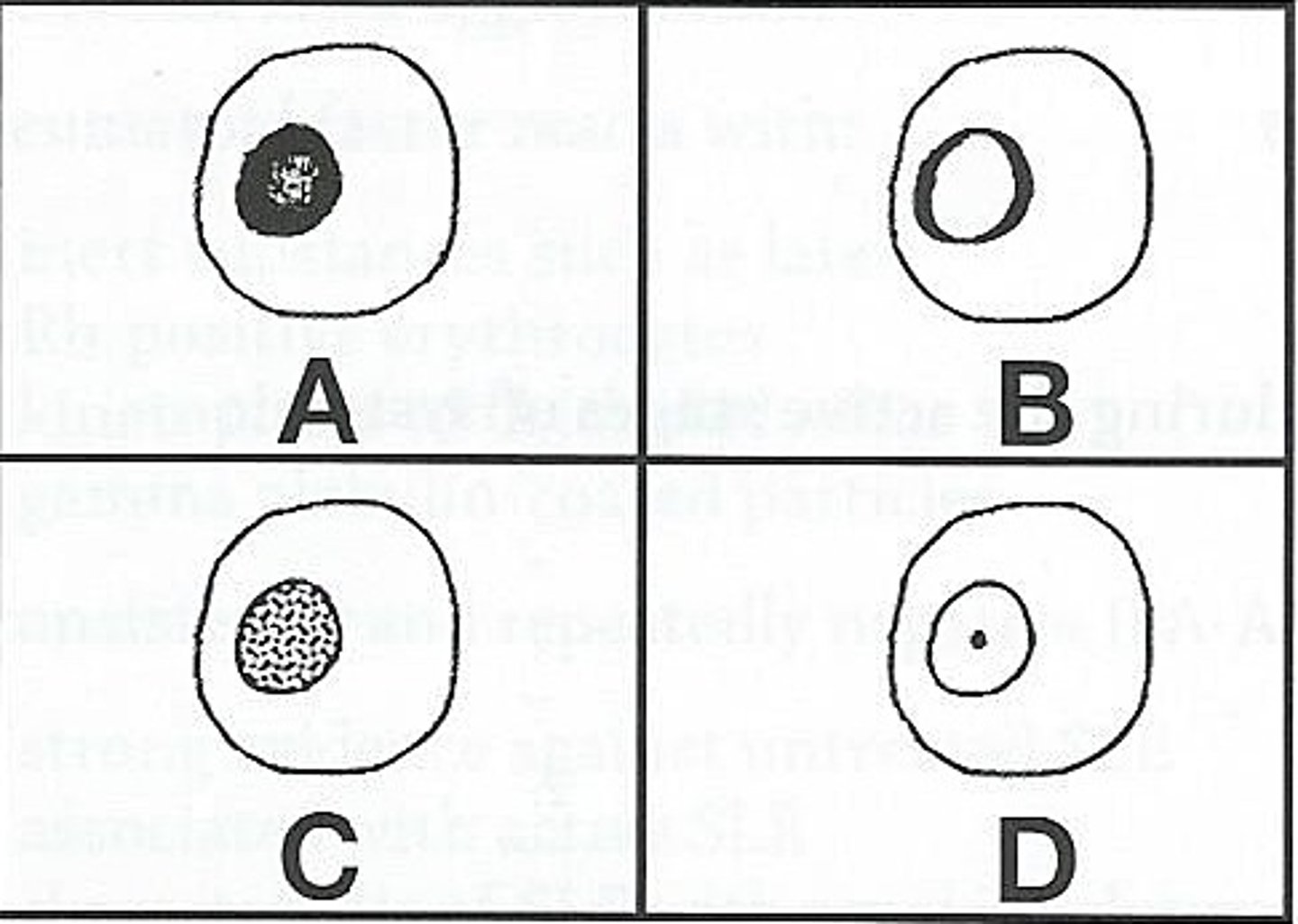
c (diagram C)
3) Which of the ANA patterns shown above would be associated with high titers of antibodies to the Sm antigen?
a) diagram A
b) diagram B
c) diagram C
d) diagram D
b (5°C +/- 2°)
4) Sera to be tested for IFA-ANA 6 days after drawing is best stored at?
a) room temperature
b) 5°C +/- 2°
c) -70°C in a constant temperature freezer
d) -20°C in a frost-free self-defrosting freezer
a (rim)
5) Antibodies directed at native DNA are most frequently associated with which pattern of fluorescence in the IFA-ANA test?
a) rim
b) diffuse
c) speckled
d) centromere
b (expected for anti-DNA antibodies)
6) The technologist observes apparent homogenous staining of the nucleus of interphase cells while performing an IFA-ANA, as well as staining of the chromosomes in mitotic cells. This result is:
a) indicative of 2 antibodies, which should be separately reported after titration
b) expected for anti-DNA antibodies
c) inconsistent; the test should be reported with new reagent
d) expected for anti-centromere antibodies
a (anti-dsDNA titer 1:80, and a high titer of antibodies to Sm)
7) The result of an anti-nuclear antibody test was a titer of 1:320 with a peripheral pattern. Which of the following sets of results best correlate with these results?
a) anti-dsDNA titer 1:80, and a high titer of antibodies to Sm
b) antimitochondrial antibody titer 1:160, and antibodies to RNP
c) anti-Scl-70, and antibodies to single-stranded DNA
d) high titers of anti-SS-A and anti-SS-B
a (high titers of DNA antibody)
8) Systemic lupus erythematosus patients often have which of the following test results?
a) high titers of DNA antibody
b) decreased serum immunoglobulin levels
c) high titers of anti-smooth muscle antibodies
d) high titers of antimitochondrial antibody
c (marked decrease in serum CH50)
9. Systemic lupus erythematosus patients with active disease often have which of the following test results?
a. high titers of antimicrosomal antibodies
b. high titers of anti-smooth muscle antibodies
c. marked decrease in serum CH50
d. decreased serum immunoglobulin levels
c (complement (C3))
10. Which of the following is decreased in serum during the active stages of systemic lupus erythematosus?
a. anti-nuclear antibody
b. immune complexes
c. complement (C3)
d. anti-DNA
c (CREST syndrome)
11. A positive ANA with the pattern of anticentromere antibodies is most frequently seen in patients with:
a. rheumatoid arthritis
b. systemic lupus erythematosus
c. CREST syndrome
d. Sjӧgren syndrome
DNA
12. In the indirect fluorescent anti-nuclear antibody test, a homogenous pattern indicates the presence of antibody to:
a. RNP
b. Sm
c. RNA
d. DNA
b (Sm)
13. In the indirect fluorescent anti-nuclear antibody test, a speckled pattern may indicate the presence of antibody to:
a. histone
b. Sm
c. RNA
d. DNA
c (lupus erythematosus)
14) A patient has the following test results:
The above results could be seen in patients with:
a) rheumatic fever
b) rheumatoid arthritis
c) lupus erythematosus
d) glomerulonephritis

a (mixed connective tissue disease)
15. Autoantibodies in the absence of Sm are found in patients with:
a. mixed connective tissue disease
b. systemic lupus erythematosus
c. Crohn disease
d. multiple myeloma
a (nephelometry)
16) Which of the following is the most sensitive and appropriate method for the detection of rheumatoid factor?
a) nephelometry
b) immunofixation electrophoresis
c) immunofluorescence
d) manual latex agglutination
d (gamma globulin-coated particles)
17) Rheumatoid factor reacts with:
a) inert substances such as latex
b) Rh-pos erythrocytes
c) kinetoplasts of Crithidia luciliae
d) gamma globulin-coated particles
a (strong evidence against untreated SLE)
18) A consistently and repeatedly negative IFA-ANA is:
a) strong evidence against untreated SLE
b) associated with active SLE
c) characteristic of SLE with renal involvement
d) associated with lupus inhibitor
a (hyperglobulinemia)
19) Positive rheumatoid factor is generally associated with:
a) hyperglobulinemia
b) anemia
c) decreased erythrocyte sedimentation rate
d) azotemia
a (results are consistent with active infection with rubella)
20) The following results are from rubella titer performed on acute and convalescent sera using 2-fold serial dilution:
Date tested: 1/23/04
Acute serum titer: 1:8
Convalescent serum titer: 1:32
After evaluating the above results, best interpretation is:
a) results are consistent with active infection with rubella
b) variation in the acute serum titers invalidates these results
c) test should be repeated by a different technologist
d) patient was not infected with rubella
a (Fc fragment of IgG)
21) Rheumatoid factors are immunoglobulins with specificitiy for allotypic determinants located on the:
a) Fc fragment of IgG
b) Fab fragment of IgG
c) J chain of IgM
d) secretory of component of IgA
a (positive test for the detection of IgM class antibodies)
22) Rheumatoid factor in patients serum may cause a false:
a) positive test for the detection of IgM class antibodies
b) negative test for the detection of IgM class antibodies
c) positive test for the detection of IgG class antibodies
d) negative test for the detection of IgG class antibodies
c (autoantibodies with specificity for the Fc portion of the immunoglobulin (IgG) molecule)
23) Rheumatoid factors are defined as:
a) antigens found in the sera of patients with rheumatoid arthritis
b) identical to the rheumatoid arthritis precipitin
c) autoantibodies with specificity for the Fc portion of the immunoglobulin (IgG) molecule
d) capable of forming circulating immune complexes only when IgM-type autoantibody is present
c (deposition of immune complexes)
24. Tissue injury in systemic rheumatic disorders such as systemic lupus erythematosus is thought to be caused by:
a. Cytotoxic T cells
b. IgE activity
c. deposition of immune complexes
d. cytolytic antibodies
d (C1q)
25. False-positive rheumatoid factor in agglutination and nephelometric methods can be due to elevated levels of:
a. cryoglobulin
b. histidine-rich-glycoprotein
c. aspartame
d. C1q
a (C-reactive protein)
26. An acute phase protein that binds to the membrane of certain microorganisms and activates the complements system is:
a. C-reactive protein
b. tumor necrosis factor alpha
c. neutrophils
d. kinins
d (thyroid disease)
27) High titers of antimicrosomal antibodies are most often found in:
a) rheumatoid arthritis
b) systemic lupus erythematosus
c) chronic hepatitis
d) thyroid disease
c (Addison disease)
28. Which of the following is an organ-specific autoimmune disease?
a. myasthenia gravis
b. rheumatoid arthritis
c. Addison disease
d. progressive systemic sclerosis
b (anti-smooth muscle)
29) In chronic active hepatitis, high titers of which of the following antibodies are seen?
a) antimitochondrial
b) anti-smooth muscle
c) anti-DNA
d) anti-parietal cell
a (antimitochondrial)
30. In primary biliary cirrhosis, which of the following antibodies is seen in high titers?
a. antimitochondrial
b. anti-smooth muscle
c. anti-DNA
d. anti-parietal cell
d (nucleolar)
31) Anti-RNA antibodies are often present in individuals having an anti-nuclear antibody immunoflurorescent pattern that is:
a) speckled
b) rim
c) diffuse
d) nucleolar
a (speckled)
32) Anti-extractable nuclear antigens are most likely associated with which of the following anti-nuclear antibody immunofluorescent patterns?
a) speckled
b) rim
c) diffuse
d) nucleolar
c (screen for Sm and RNP antibodies)
33) In an anti-nuclear antibody indirect immunofluorescent test, a sample of patient serum shows a postive, speckled pattern. Which would be the most appropriate additional test to perform?
a) antimitochondrial antibody
b) immunoglobulin quantitation
c) screen for Sm and RNP antibodies
d) anti-DNA antibody using C luciliae
d (Goodpasture disease)
34. Anti-glomerular basement membrane antibody is most often associated with this condition:
a. systemic lupus erythematosus
b. celiac disease
c. chronic active hepatitis
d. Goodpasture disease
d (high-level ribonucleoprotein (RNP) antibody)
35. A 25-year-old woman is seen by a physician because of Raynaud phenomenon, myalgias, arthralgias and difficulty in swallowing. There is no evidence of renal disease. An ANA titer is 1:5120 with a speckled pattern with mitotic. Which of the following are also likely to be found in this patient?
a. high-level nDNA antibody and a low CH50 level
b. high-level Sm antibody
c. high-level rheumatoid factor
d. high-level ribonucleoprotein (RNP) antibody
d (anti-parietal cell)
36. In pernicious anemia, which of the following antibodies is characteristically detected?
a. antimitochondrial
b. anti-smooth muscle
c. anti-DNA
d. anti-parietal cell
b (IgG2 and IgG4)
37. Anti-phospholipid antibodies associated with autoimmune disorders tend to have immunoglobulin (IgG) that belongs to which of the following subclasses?
a. IgG1 and IgG3
b. IgG2 and IgG4
c. IgG1 and IgG4
d. IgG2 and IgG3
c (P-ANCA)
38. The IIF staining pattern on ethanol-fixed leukocytes slides shows a perinuclear or nuclear staining pattern. This pattern is typically due to:
a. C-ANCA
b. LKM
c. P-ANCA
d. GBM
c (antibody used in the assay)
39. The specificity of an immunoassay is determined by the:
a. label used on the antigen
b. method used to separate the bound from free antigen
c. antibody used in the assay
d. concentration of unlabeled antigen
a (positive specimens correctly identified)
40. In assessing the usefulness of a new laboratory test, sensitivity is defined as the percentage of:
a. positive specimens correctly identified
b. false-positive specimens
c. negative specimens correctly identified
d. false-negative specimens
c (goat anti-human immunoglobulin)
41. In the indirect immunofluorescence method of antibody detection in patient serum, the labeled antibody is:
a) human anti-goat immunoglobulin
b) rheumatoid factor
c) goat anti-human immunoglobulin
d) complement
a (the reaction is reversible)
42. Which of the following describes an antigen-antibody reaction?
a) the reaction is reversible
b) the reaction is the same as a chemical reaction
c) a lattice is formed at prozone
d) a lattice is formed at postpone
c (fluorescein isothiocyanate)
43. The most common label in direct fluorescent antibody technique (DFA) is:
a) alkaline phosphatase
b) horseradish peroxidase
c) fluorescein isothiocyanate
d) calcofluor white
c (indirect fluorescence)
44. A substrate if first exposed to a patients serum, then after washing, anti-human immunoglobulin labeled with a fluorochrome is added. The procedure described is:
a) fluorescent quenching
b) direct fluorescence
c) indirect fluorescence
d) fluorescence inhibition
d (strength of a reacting antibody)
45. Avidity may be defined as the:
a) degree of hemolysis
b) titer of an antigen
c) dilution of an antibody
d) strength of a reacting antibody
b (rise in titer of the patients serum)
46. In the interpretation of aggutination tests for febrile diseases, which of the following is of the greatest diagnostic importance?
a) anamnestic reactions caused by the heterologous antigens
b) rise in titer of the patient's serum
c) history of previous vaccination
d) naturally occurring antibodies prevalent where the disease is endemic
d (increase sensitivity of the antigen)
47. Cholesterol is added to the antigen used in flocculation tests for syphilis to:
a) destroy tissue impurities present in the alcoholic beef heart extract
b) sensitize the sheep RBCs
c) decrease specificity of the antigen
d) increase sensitivity of the antigen
c (avidity)
48. The strength of a visible reaction is known as:
a) prozone reaction
b) absorption
c) avidity
d) elution
a (precipitin lines cross, forming double spurs)
49. Which of the following describes an antigen-antibody precipitation reaction of non-indentity?
a) precipitin lines cross, forming double spurs
b) precipitin lines fuse, forming single spur
c) no precipitin lines are formed
d) precipitin lines fuse, forming a single arc
c (ELISA)
50. Which test has the greatest sensitivity for antigen detection?
a) precipitin
b) agglutination
c) ELISA
d) complement fixation
d (dissolve the precipitate after formation)
51. Excess antigen in precipitation gel reactions will:
a) have no effect on the precipitate reaction
b) not dissolve precipitate after formation
c) enhance the precipitate reaction
d) dissolve the precipitate after formation
b (antigen excess)
52. Soluble immune complexes are formed under the condition of:
a) antigen deficiency
b) antigen excess
c) antibody excess
d) complement
b (precipitation)
53. The visible serological reaction between soluble antigen and its specific antibody is:
a) sensitization
b) precipitation
c) agglutination
d) opsonization
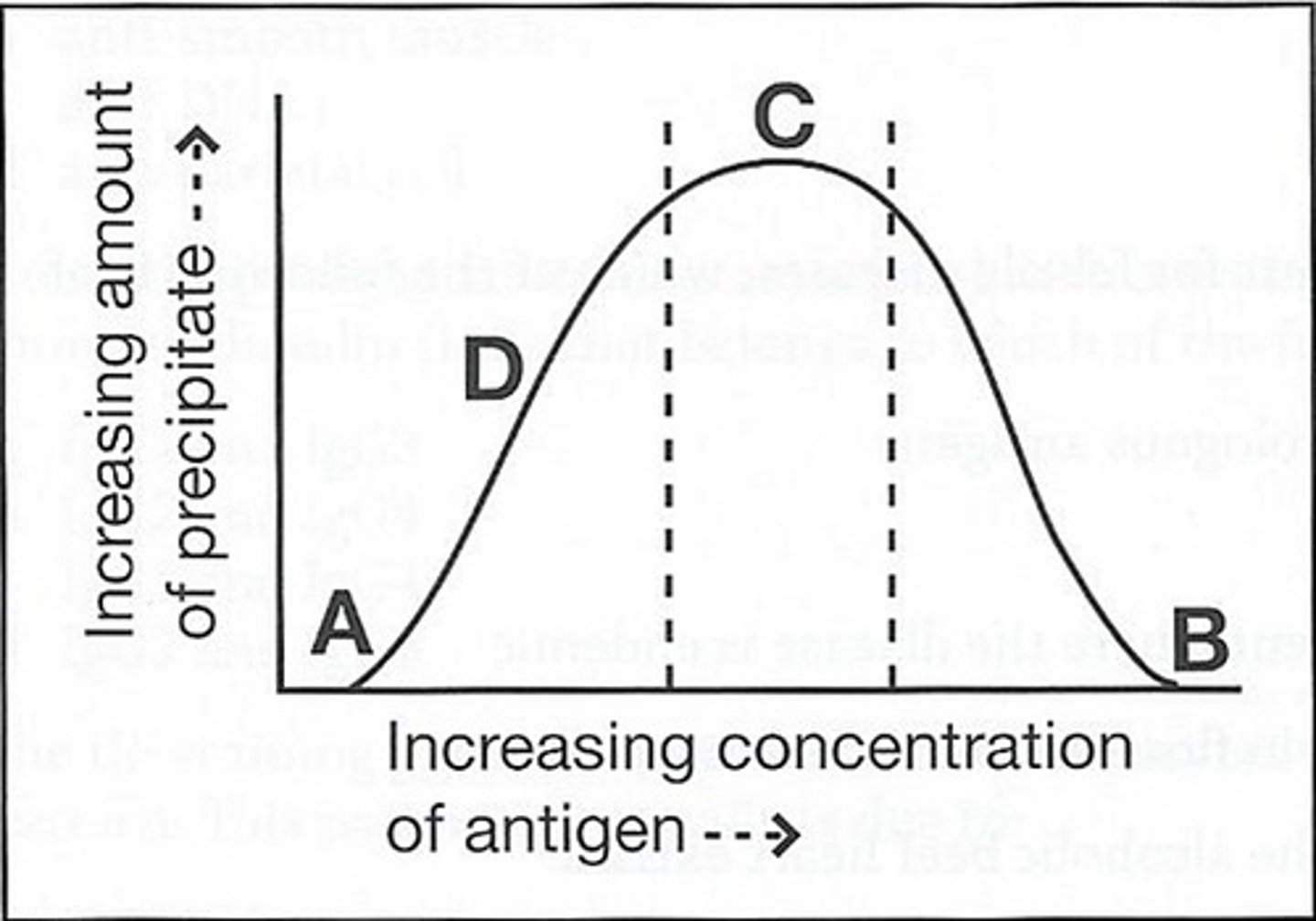
c (C)
54) The curve below obtained by adding increasing amounts of a soluble antigen to fixed volumes of monospecific antisera:
The area on the curve for equivalence precipitate is:
a. A
b. B
c. C
d. D
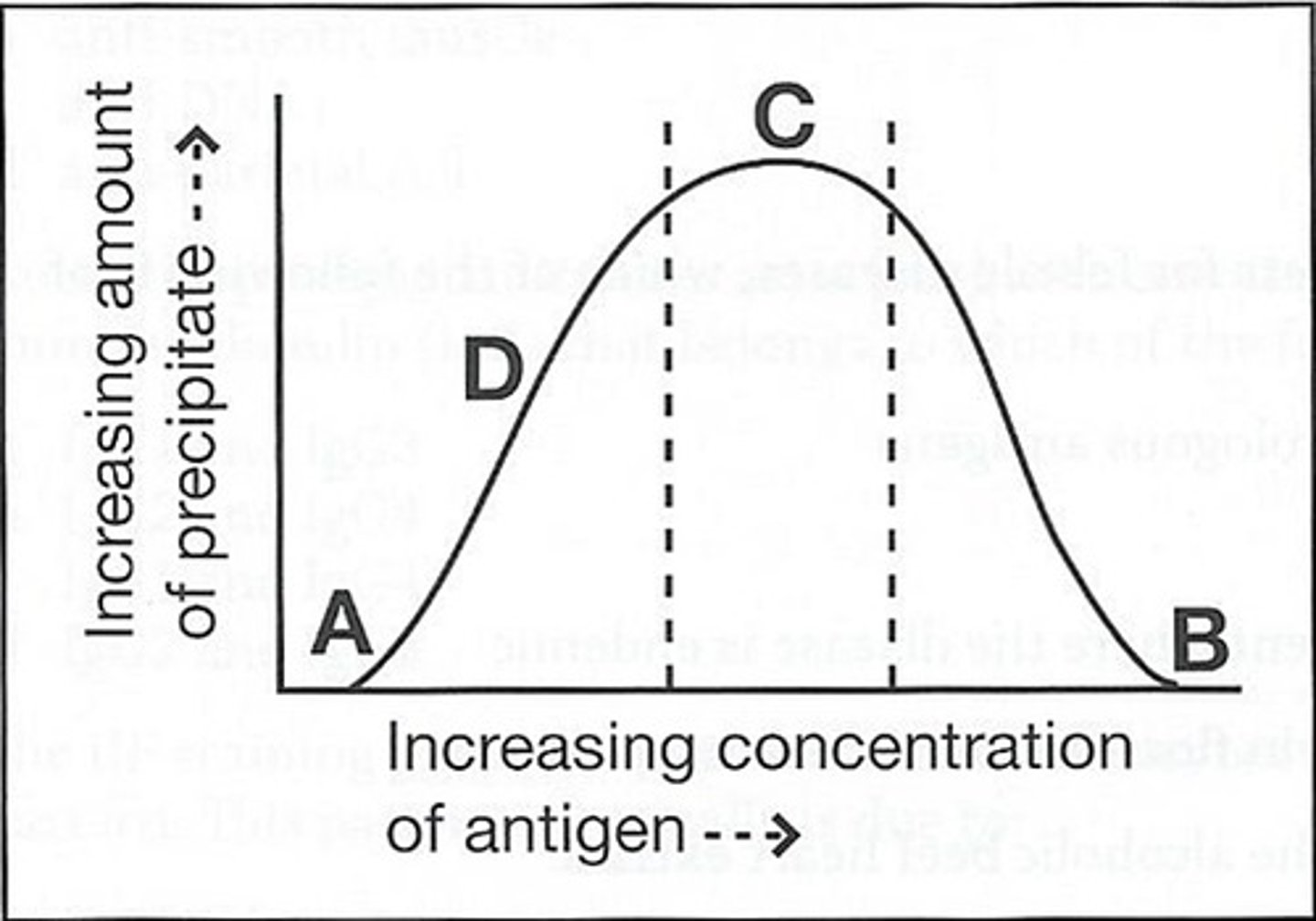
b (B)
55) The curve below obtained by adding increasing amounts of a soluble antigen to fixed volumes of monospecific antisera:
The area on the curve where no precipitate formed due to antigen is:
a. A
b. B
c. C
d. D
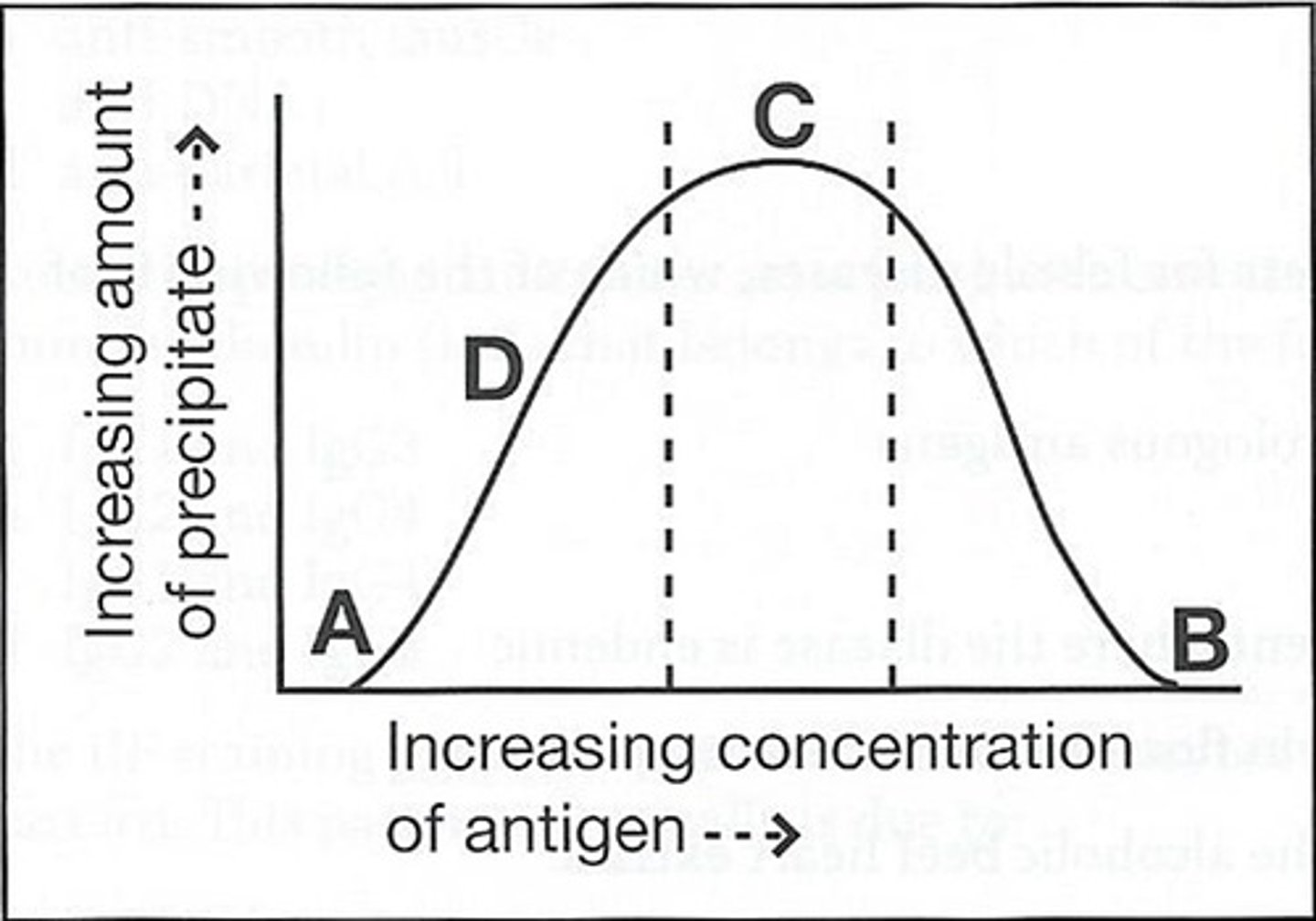
a (A)
56) The curve below obtained by adding increasing amounts of a soluble antigen to fixed volumes of monospecific antisera:
The area on the curve for prozone is:
a. A
b. B
c. C
d. D
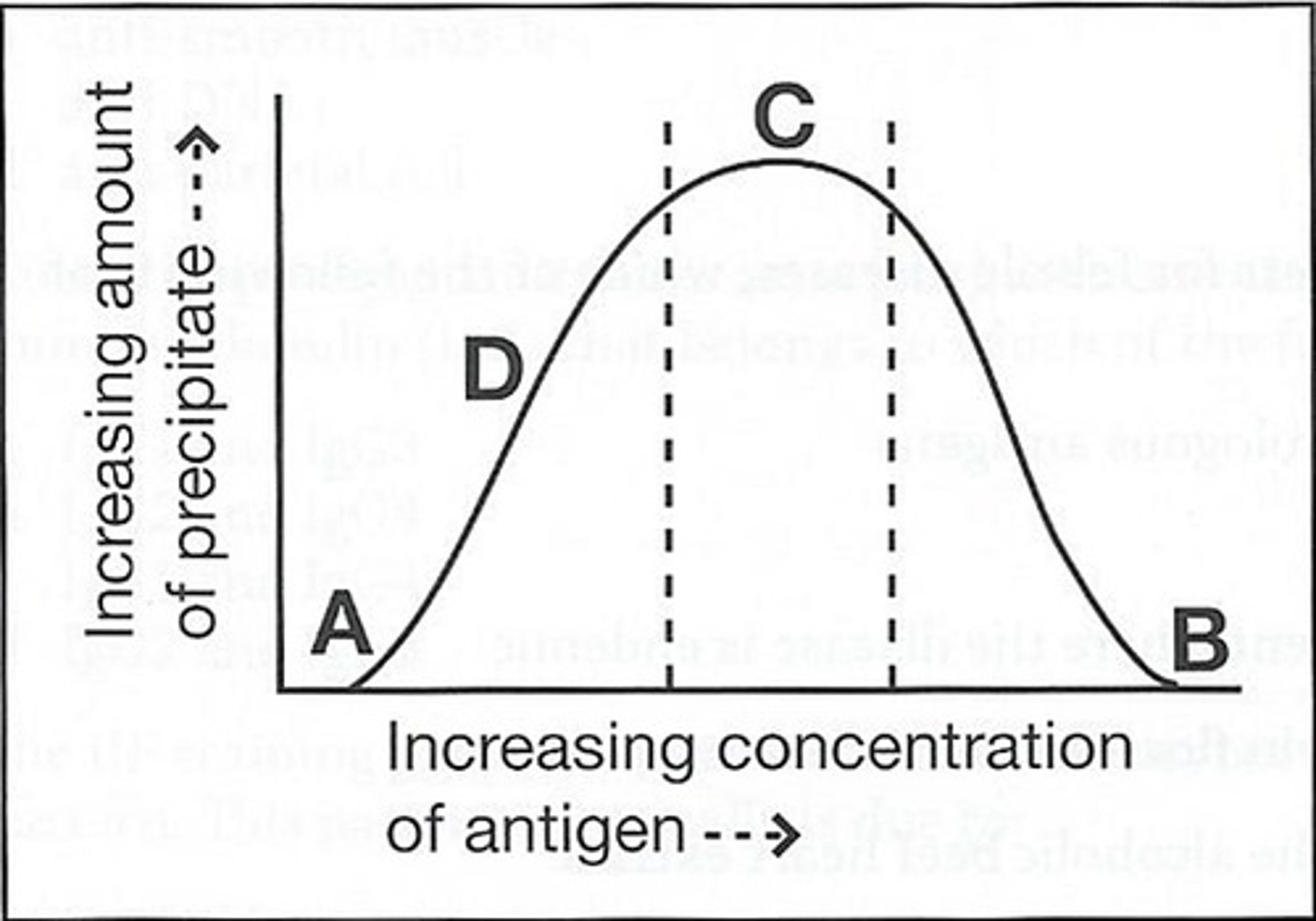
d (D)
57) The curve below obtained by adding increasing amounts of a soluble antigen to fixed volumes of monospecific antisera:
The area on the curve where soluble antigen-antibody complexes have begun to form is:
a. A
b. B
c. C
d. D
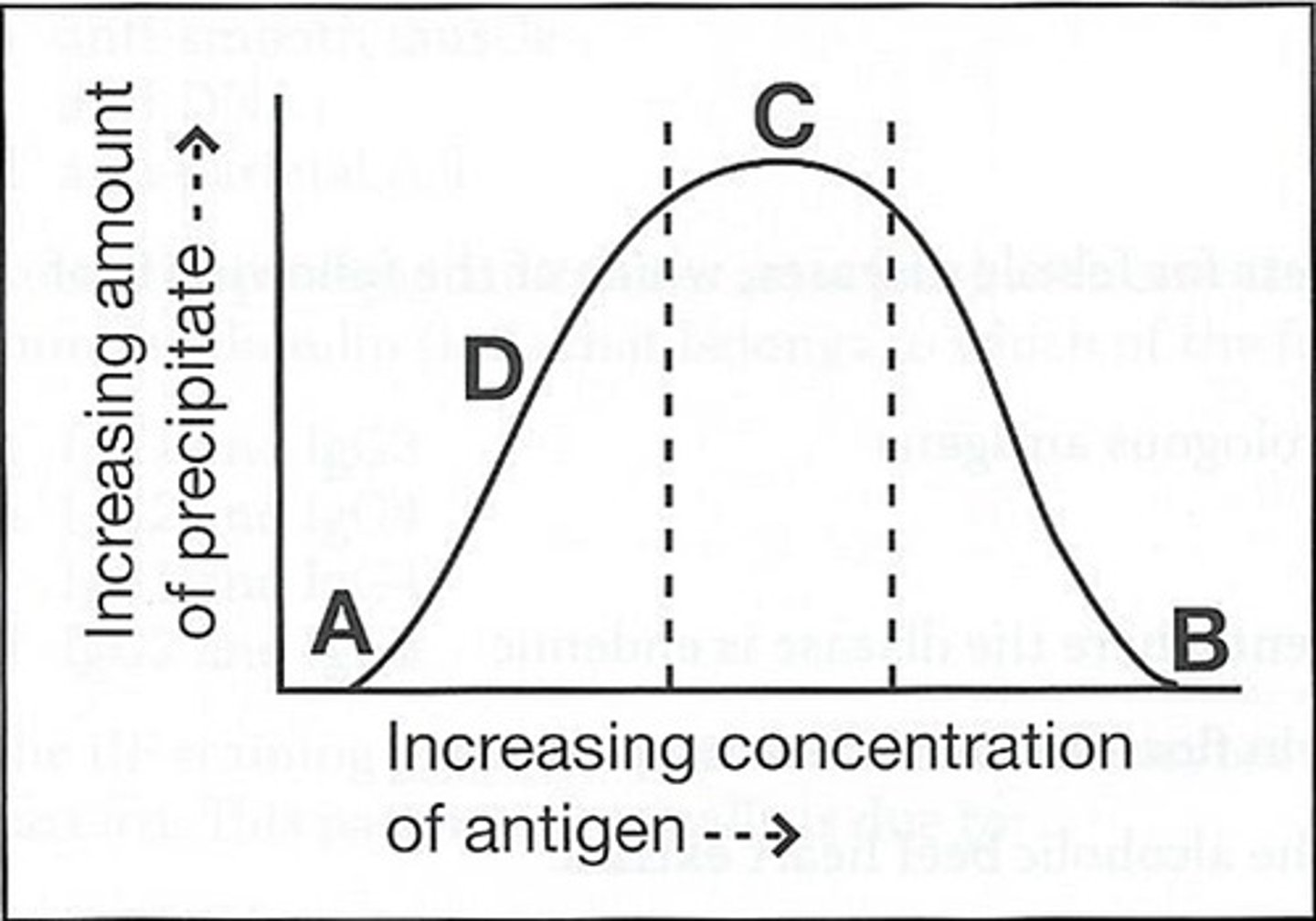
b (B)
58) The curve below obtained by adding increasing amounts of a soluble antigen to fixed volumes of monospecific antisera:
The area in which the addition of more antibody would result in the information of additional precipitate is:
a. A
b. B
c. C
d. D
a (Figure #1)
59) Which of the above figures demonstrates a reaction pattern of identity?
a. Figure #1
b. Figure #2
c. Figure #3
d. Figure #4
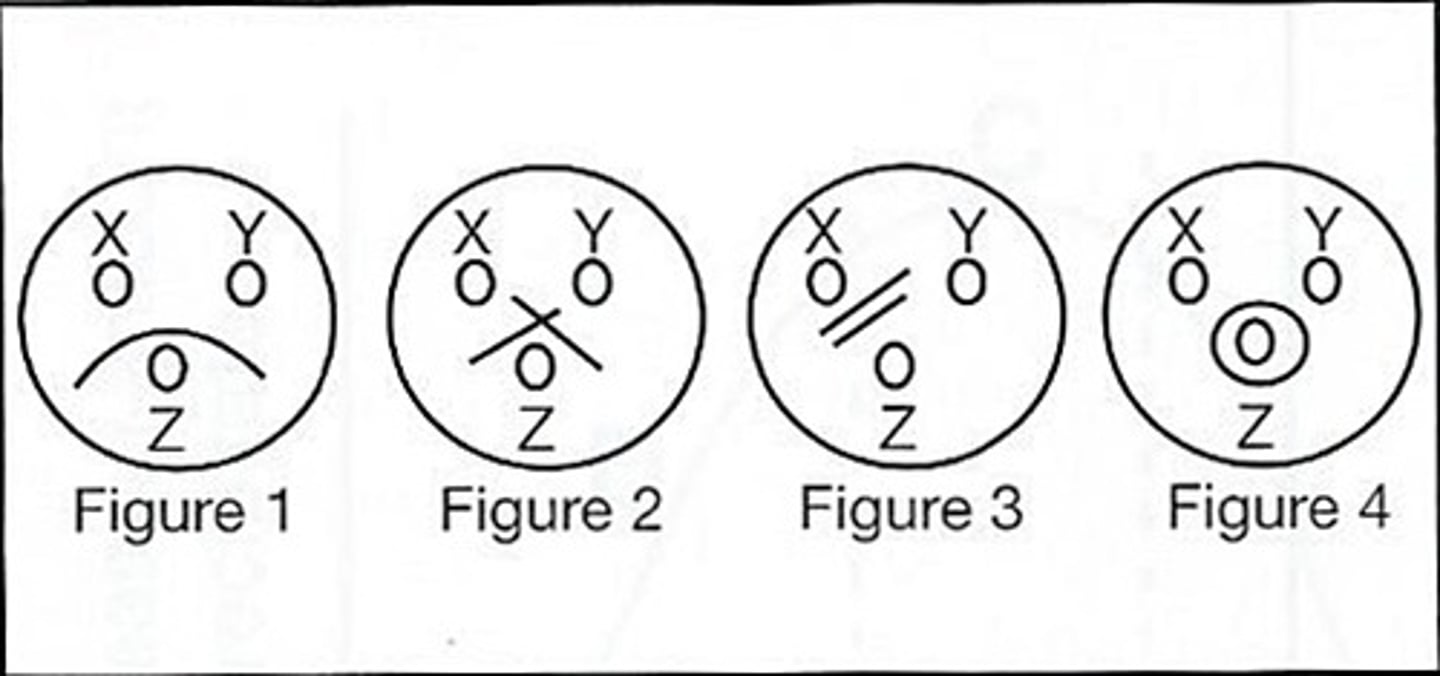
b (Figure #2)
60) Which of the above figures demonstrates a reaction pattern of nonidentity?
a. Figure #1
b. Figure #2
c. Figure #3
d. Figure #4
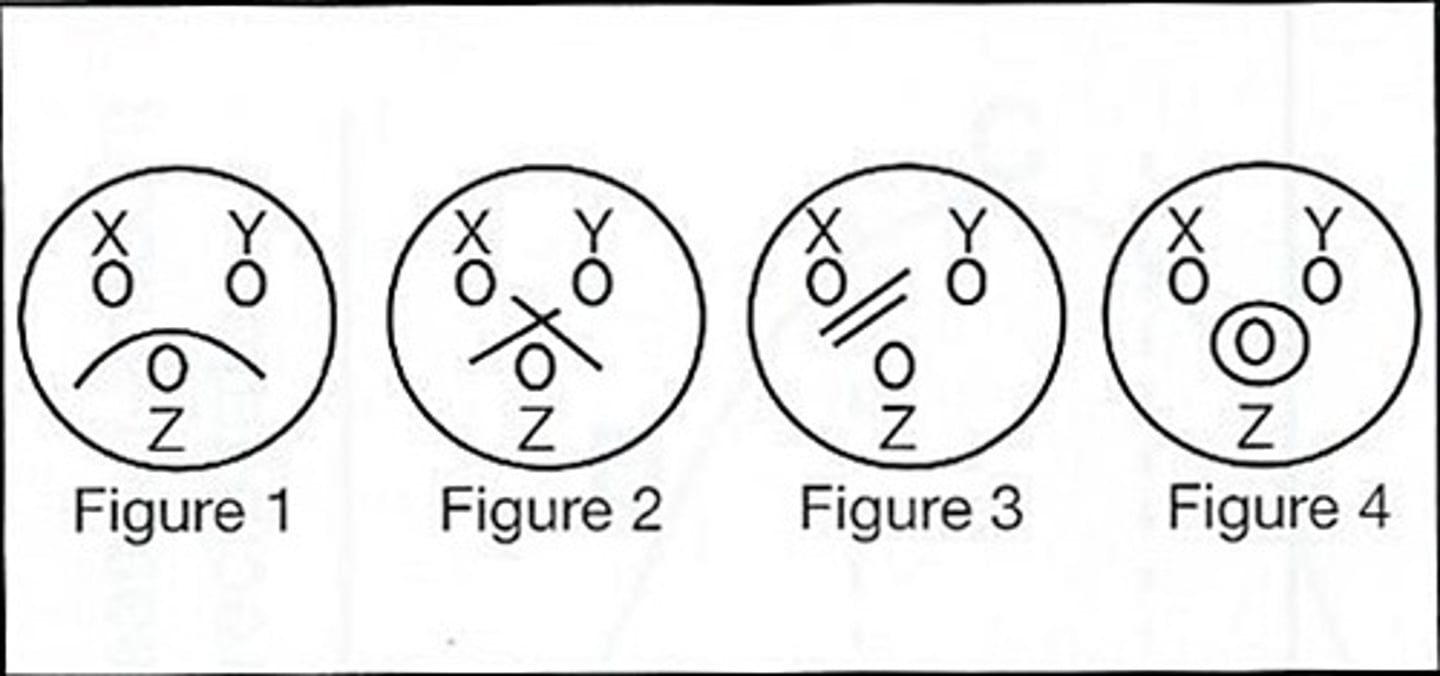
c (Figure #3)
61) Which of the above figures demonstrates a reaction pattern showing 2 different antigenic molecular species?
a. Figure #1
b. Figure #2
c. Figure #3
d. Figure #4
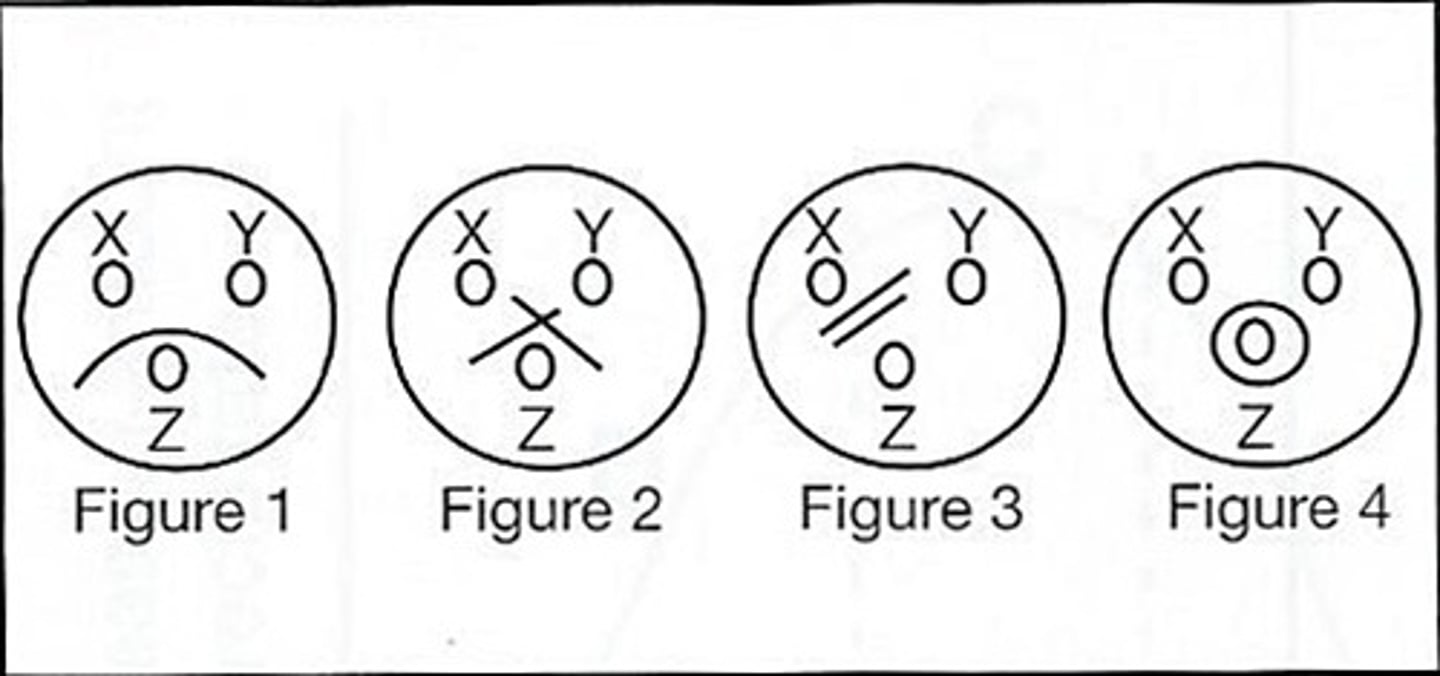
d (Figure #4)
62. Refer to the following illustration:
A nonspecific precipitin reaction is demonstrated is:
a. Figure #1 (1 arc)
b. Figure #2 (crossed, 2 spurs)
c. Figure #3 (2 parallel lines)
d. Figure #4 (circle)
d (1:2.097 x 10^13)
63. A series of 8 tubes are set-up with 0.79 mL of diluent in each. A serial dilution is performed by adding 10µL of serum to the first tube and then transferring 10µL through each remaining tube. What is the serum dilution of tube 7?
a. 1:2.431 × 10^11
b. 1:2.621 × 10^11
c. 1:1.929 × 10^13
d. 1:2.097 × 10^13
c (oxidation of the enzyme)
64. The enzyme control tube in an ASO hemolytic assay exhibits no cell lysis. What is the most likely explanation for this?
a) incorrect ph of buffer
b) low ionic strength buffer
c) oxidation of the enzyme
d) reduction of the enzyme
c (prozoning)
65. The following pattern of aggultination was observed in an antibody titration:
This set of reactions most likely resulted from:
a) faulty pipetting technique
b) postzoning
c) prozoning
d) the presence of a high-titer, low-avidity antibody

d (anti-streptolysin "O" inhibits the reagent streptolysin "O's" resulting in no hemolysis)
66. In a positive anti-streptolysin O enzyme inhibition test, the patient's:
a) streptolysin "O" enzyme in the patient serum neutralizes the anti-streptolysin "O" reagent, resulting in no hemolysis
b) red blood cells are hemolyzed by the streptolysin"O" enzyme in the reagent
c) anti-streptolysin "O" neutralizes the streptomycin "O" reagent, resulting in hemolysis
d) anti-streptolysin "O" inhibits the reagent streptolysin "O's" resulting in no hemolysis
d (second antibody titer is at least 4x the first)
67. Blood is drawn from a patient for serological tests for a viral disease at the time of onset and again 4 weeks later. The results of the test are considered diagnostic if the:
a) first antibody titer is 2x the second
b) first and second antibody titers are equal
c) first antibody is 4x the second
d) second antibody titer is at least 4x the first
b (serological techniques)
68. Which of the following is most useful in establishing a diagnosis in the convalescence phase of a viral infection?
a) slide culture
b) serological techniques
c) shell vial
d) culture on Mccoy media
d (antibody detection by EIA)
69. The best method to detect infections due to rubella, Epstein-Barr, and human immunodefiency viruses is:
a) antigen detection by EIA
b) cell culture
c) antigen detection by Western blot
d) antibody detection by EIA
b (antibody recognition of homologous antigen)
70. Immunoassays are based on the principle of:
a. separation of bound and free analyte
b. antibody recognition of homologous antigen
c. protein binding to isotopes
d. production of antibodies against drugs
a (active humoral-mediated immunity)
71. A DPT vaccination is an example of:
a) active humoral-mediated immunity
b) passive humoral-mediated immunity
c) cell-mediated immunity
d) immediate hypersensitivity
b (neutrophils, eosinophils, and monocytes)
72. Cells known to be actively phagocytic include:
a) neutrophils, monocytes, basophils
b) neutrophils, eosinophils, monocytes
c) monocytes, lymphocytes, neutrophils
d) lymphocytes, eosinophils, monocytes
a (early acute phase HBV hepatitis)
73. The presence of HbsAg, anti-HBc and often HbeAg is characteristic of:
a) early acute phase HBV hepatitis
b) early convalescent phase HBV hepatitis
c) recovery phase of acute HBV hepatitis
d) past HBV infection
b (acute hepatitis B)
74. Refer to the following data:
HBsAg Anti-HBc IgM Anti-HAV Igm
patient #1 - - +
patient #2 + + -
patient #3 - + -
From the test results above, it can be concluded that patient #3 has:
a. recent acute hepatitis A
b. acute hepatitis B
c. acute hepatitis C (non-A/non-B hepatitis)
d. chronic hepatitis B
c (recovery phase of acute HBV hepatitis)
75. The disappearance of HBsAg and HBeAg, the persistence of anti-HBc, the appearance of anti-HBs, and often of anti-AHe indicate:
a. early acute HBV hepatitis
b. early convalescent phase HBV hepatitis
c. recovery phase of acute HBV hepatitis
d. carrier state of acute HBV hepatitis
c (Hashimoto thyroiditis)
76. An example of an organ specific disease with autoimmune antibodies is:
a. Wegener granulomatosus
b. rheumatoid arthritis
c. Hashimoto thyroiditis
d. systemic lupus erythematosus
b (Western blot)
77. When testing a patient for HIV antibody, which of the following is used to confirm a positive screening test?
a) radioimmunoassay
b) Western blot
c) immunofluorescence
d) Elisa
d (measles)
78. An example of a live attenuated vaccine used for human immunization is:
a. rabies
b. tetanus
c. hepatitis B
d. measles
d (test for antibody specificity)
79. A cold agglutinin titer end point is 1:16 after incubating overnight in the refrigerator and remains 1:16 after warming. The best course of action is to:
a. report the titer as negative
b. report the titer as positive, 1:16
c. repeat the titer with a fresh sample
d. test for antibody specificity
a (precipitation)
80. What kind of antigen-antibody reaction would be expected if soluble antigen is added to homologous antibody?
a) precipitation
b) agglutination
c) complement fixation
d) hemagglutination
a (useful in screening for syphilis)
81. The rapid plasma reagin test:
a) is useful in screening for syphilis
b) is useful in diagnosing syphilis
c) does not give false-positives
d) uses heated plasma
a (reagin antibody)
82. Flocculation tests for syphilis detect the presence of:
a) reagin antibody
b) antigen
c) hemolysin
d) Forssman antigen
a (4+ reaction)
83. In the cold agglutination test, the tubes containing the serum and erythrocytes are allowed to stand overnight in the fridge, and results are read next morning. If a disk of the erythrocytes floats up from the bottom of the tube with only the flick of a finger, this is read as a:
a) 4+ reaction
b) 2+ reaction
c) 1+ reaction
d) negative reaction
c (cardiolipin and lecithin)
84. Flocculation tests for syphilis use antigen composed of:
a) Treponema pallidum
b) reagin
c) cardiolipin and lecithin
d) charcoal
a (positive, 1:128)
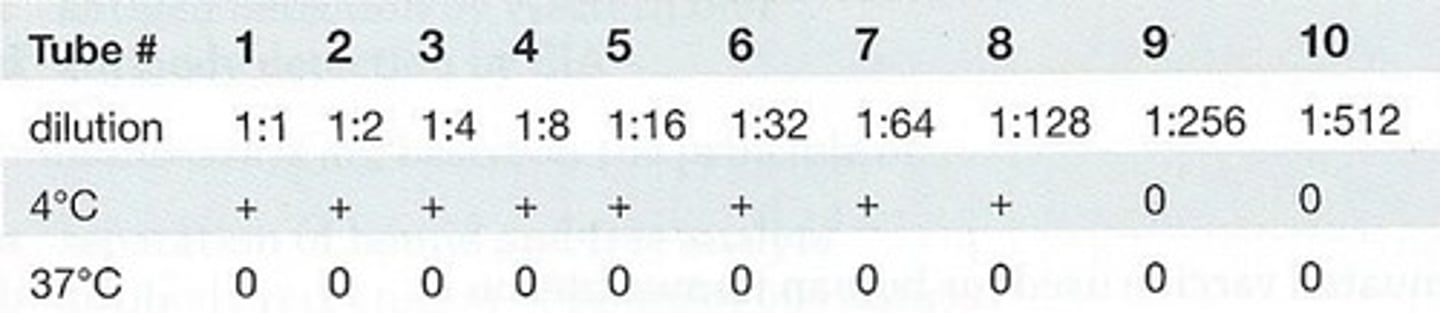
85. The following cold agglutinin titer results are observed:
The best interpretation is:
a. positive, 1:128
b. negative
c. invalid because 37°C reading is negative
d. repeat the 4°C readings
d (reheated to 56°C for 10 minutes)
86. A VDRL serum sample is heat inactivated, then placed in a fridge for overnight storage. Before being tested, the serum must be:
a) kept colder than 10° C
b) allowed to equilibrate to room temperature
c) warmed to 37°C
d) reheated to 56°C for 10 minutes
b (haptens)
87. Substances that are antigenic only when coupled to a protein carrier are:
a) opsonins
b) haptens
c) adjuvants
d) allergens
d (antibody but not T cells)
88. A haptenic determinant will react with:
a. both T cells and antibody
b. T cells but not antibody
c. neither T cells nor antibody
d. antibody but not T cells
b (RPR)
89. A serological test for syphilis that depends upon the detection of cardiolipin-lecithin-cholesterol antigen is:
a) FTA-ABS
b) RPR
c) MHA-TP
d) TPI
c (evaluation of the success of therapy)
90. The most important use of a nontreponemal antibody (NTA) test alone is in:
a. establishing the diagnosis of acute active syphilis
b. establishing the diagnosis of chronic syphilis
c. evaluation of the success of therapy
d. determining the prevalence of disease in the general population
b (CSF-VDRL)
91. The serological test for syphilis recommended for detecting antibody in Cerebrospinal fluid is:
a) nontreponemal antibody
b) CSF-VDRL
c) FTA-ABS
d) MHA-TP
a (Treponema pallidum)
92. In the direct fluorescent antibody test for primary syphilis, spirochetes are detected by addition of labeled antibody to?
a. Treponema pallidum
b. cardiolipin
c. human immunoglobulin
d. nonpathogenic treponemes
d (false-positive reaction)
93. In the FTA-ABS test the presence of a beaded pattern of fluorescence along
a. positive identification of Treponema pallidum
b. presumptive diagnosis of active syphilis
c. presence of nontreponemal antibody (NTA)
d. false-positive reaction
b (likely to remain positive after adequate antibiotic therapy)
94. The FTA-ABS test for the serological diagnosis of syphilis is:
a. less sensitive and specific than the VDRL if properly performed
b. likely to remain positive after adequate antibiotic therapy
c. currently recommended for testing cerebrospinal fluid
d. preferred over darkfield microscopy for diagnosing g primary syphilis
a (thermal range)
95. A 16-year-old boy with infectious mononucleosis has a cold agglutinin titer of 1:2000. An important consideration of this antibody's clinical relevance is the:
a. thermal range
b. titer at 4℃
c. specificity
d. light chain type
b (anti-HBs)
96. What assay would confirm the immune status of hepatitis B virus?
a) HBsAg
b) anti-HBs
c) IgM anti-HBcAg
d) hepatitis C Ag
d (ELISA)
97. The following procedure has been routinely used for detection of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) because of its high level of sensitivity:
a) hemagglutination
b) counterimmunoelectrophoresis
c) radial immunodiffusion
d) ELISA
a (anti-human IgG conjugated to an enzyme)
98. In an indirect ELISA method desiged to detect antibody to the rubella virus in patient serum, the conjugate used should be:
a) anti-human IgG conjugated to an enzyme
b) anti-rubella antibody conjugated to an enzyme
c) rubella antigen conjugated to an enzyme
d) anti-rubella antibody conjugated to a substrate
b (The organism is difficult to isolate, and antibody titers will provide the most help.)
99. A request is received in the laboratory for assistance in selecting the appropriate test(s) for detecting Lyme disease. Which of the following would be suggested?
a. Stool culture should be done to isolate the causative organism.
b. The organism is difficult to isolate, and antibody titers will provide the most help.
c. Borrelia burgdorferi is easily isolated form routine blood cultures.
d. This is an immunologic syndrome, and cultures are not indicated.
c (Staphylococcal protein A)
100. A bacterial protein used to bind human immunoglobulins is:
a. HAV antibody, IgA type
b. Escherichia coli protein C
c. Staphylococcal protein A
d. HAV antibody, IgG type