Anxiety
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What is anxiety
state of nervousness and worry
What are the 4 types of anxiety in sport
Trait = personality => genetic and stable
State = situation dependent
Cognitive = psychological => the irrational thinking or worries about performance => the performer may believe they do not have the ability to perform the task and therefore experience nervousness which can lead to a loss in concentration
Somatic = physiological => it is the response of the body. Symptoms include inc. HR, sweating, muscular tension and sickness
What is competitive trait anxiety
a personality trait when a player feels nervous in most sporting situations --> genetic and stable
what is competitive state anxiety
a response to a particular sporting situation a temporary rush of anxiety caused by a threatening circumstance e.g. taking a penalty
give an example of competitive state anxiety
An individual with a high trait anxiety is more likely to experience high state anxiety when faced with stressful situation, especially if others are watching or evaluating their performance.
what is cognitive anxiety
psychological => it is the irrational thinking or worries about performance. The performer may believe they do not have the ability to perform the task and therefore experience nervousness which can lead to loss in concentration
what is somatic anxiety
physiological = has an identical effect on performance as arousal does in the inverted-U theory.
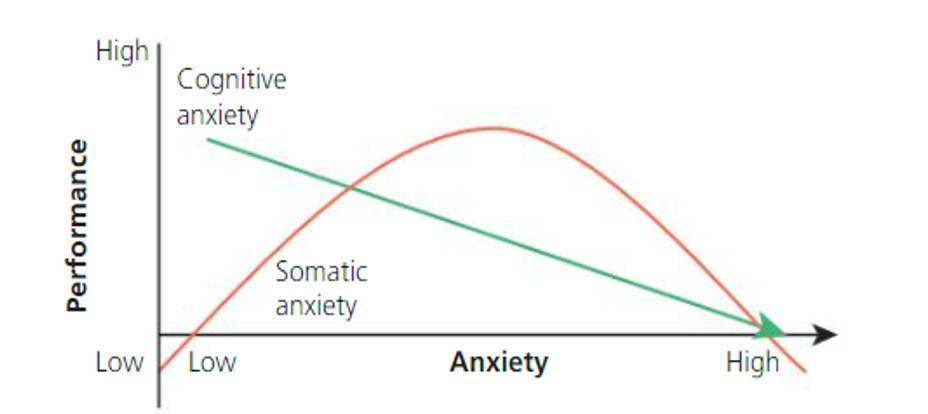
What does this graph show about cognitive and somatic anxiety when it comes to the inverted U theory
Increases in somatic anxiety improves performance up to a point => beyond which performance is impaired => cognitive anxiety has a negative effect on performance as cognitive anxiety increases, performance decreases.
How can you measure anxiety
Self-report questionnaires
Observation
Physiological testing
What are the strengths of questionnaires
Quick
Cheap
Efficient = large numbers that can be assessed quickly
What are the limitations of questionnaires
Players might not answer truthfully
Dependent on mood (answers can be given differently after they win or loose a match)
Time pressure could cause answers to be rushed => leading to incorrect answers
What are strengths of observations
True to life
what are some limitations to observations
Subjective (based on opinions)
Time consuming as prior knowledge of performer required
Performers can change behaviour if they know they are being watched
What are physiological measures
HR, inc. sweating, inc. respiration and hormone levels can be measured to assess anxiety
What are some strengths of physiological measures
Results = factual
Can be measured in both training and competition
Advanced in technology mean that HR can be measured by electronic devices within clothing and relayed immediately back to the coach
What are some limitations of physiological measures
Training is required to use devices
Costs may deter amateur performers
Wearing a device can restrict movement => affecting performance
If a performer is aware they are being measured is can lead to additional stress and false readings