cognitive and behaviourist
1/4
Earn XP
Description and Tags
compare and contrast the cognitve and behaviorist approach in terms of simialrities and differences
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
5 Terms
table
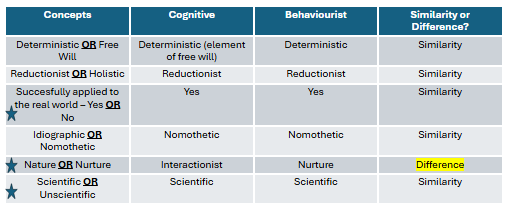
similarity - successful application to the real world
Cognitive Approach
Legal impact:
Loftus & Palmer — showed eyewitness testimony is unreliable, influencing legal reforms.
Innocence Project: 68–75% of wrongful convictions involved mistaken eyewitness ID.
Clinical impact:
Led to CBT, widely used by NHS for treating depression and anxiety.
Theoretical focus:
Explores internal mental processes.
Limitation: Relies on self-report and inference, reducing objectivity.
Behaviourist Approach
Everyday impact:
Gill (1998) — rewards increased chore completion in children.
McAllister et al. (1969) — teacher praise/disapproval shaped classroom behaviour.
Theoretical focus:
Focuses on observable behaviour.
Limitation: Ignores internal processes and meaning, may miss underlying causes.
Judgement
Cognitive: Targets thought processes, effective in clinical/legal contexts.
Behaviourist: Targets learned behaviour, effective in education and everyday settings.
Both: Valuable, but differ in depth vs objectivity.
Want this added to your AO3 mega-deck or turned into flashcards with visual cues?
differnce - nature v nurture
Cognitive Approach
Interactionist: Considers both innate mental processes (nature) and environmental influences (nurture).
Example: Language acquisition (nature) and schemas shaped by experience (nurture).
Strength: Offers a balanced explanation of behaviour.
Limitations:
May underplay genetic influences.
May neglect wider social factors (e.g., culture, education).
Behaviourist Approach
Entirely nurture-based: Behaviour is learned through environmental interaction.
Example: Bandura’s Bobo doll — children imitated aggression when model was rewarded.
Strength: Strong empirical support for learning through reinforcement.
Limitation: Ignores genetic and internal influences, limiting scope for biologically influenced behaviours (e.g., MAOA-L gene and aggression).
Judgement
Cognitive: More comprehensive, integrating nature and nurture.
Behaviourist: Narrower, purely environmental — less effective for explaining biologically rooted behaviours.
similairty - scienfic v unscientific
Cognitive Approach
Investigates internal mental processes using lab experiments.
Loftus & Palmer: Standardised procedures to study eyewitness memory.
Early reliance on introspection (low objectivity), but now uses brain imaging (e.g., MRI).
Led to cognitive neuroscience, boosting scientific credibility.
Limitation: Involves inference, reducing objectivity and reliability.
Behaviourist Approach
Focuses on observable, measurable behaviour.
Skinner: Rat studies showed reinforcement shaping behaviour.
Uses animal studies for high control of extraneous variables.
Avoids inference → greater objectivity and reliability.
Limitation: Lacks explanatory depth for internal processes.
Judgement
Behaviourist: More methodologically rigorous, high control and objectivity.
Cognitive: Increasingly scientific via neuroscience, offers greater explanatory depth.
Both: Empirical, but differ in what they measure and how deeply they explain behaviour.
conclusion
both are valuable for their real world application and scientific mdoels
the cognitive approach provide a more comprehensie understanding by considering internal mental processes and the interaction of nature b nurture
allowing personal change such as CBT
whlst the behaviourist approach is more objective and methdologically rigorous , focussing on obserbale behavioru and predictability but ifnores internal and biologcal infleunces
overal cognitive approach offers greaer explanatory depth
behavioirst excel in control and reliability