Biology - Meiosis and genetic diversity (20/02/25)
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
3.4.3-3.3.5, Topic 4A + 4B
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
What are the 8 taxonomic groups?
Domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species (dkpcofgs)
What is a species?
A group of similar organisms that can successfully breed together to produce fertile offspring. It is the only way to definitively prove two similar animals are not from the same species.
How are species named?
Homo (genus) sapiens (species)
What are courtship behaviors?
Behaviors carried out by organisms to attract a mate of the same species. Examples are making sounds, releasing chemicals or dancing.
Describe DNA structure
To strands of deoxyribose-phosphate backbone running antiparallel to each other from a 5’ to 3’ direction, with 4 bases that connect complimentary to each other.
What is the difference between chromosomes, chromatin and chromatids?
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and proteins found in the nucleus of non-dividing cells, in a loose and uncoiled state. When a cell prepares to divide, chromatin condenses and coils, winding over histone proteins to form visible chromosomes, which carry genetic information. Each chromosome consists of two sister chromatids, which are identical copies of the chromosome, joined together at a region called the centromere. During cell division, the chromatids separate, ensuring that each daughter cell receives an exact copy of the genetic material.
Describe evolution and the survival of the fittest:
Evolution is a change in the inherited characteristics of a population overtime. These changes happen through the process of natural selection. Natural selection is the process where organisms that are best adapted to their environment survive, reproduce and pass on those characteristics.
When does variation take place?
Variation is present in a population due to random mutation, some organisms may have phenotypes that make them adapted to their environment. This gives them a survival advantage due to their advantageous alleles.
What does non-disjunction mean?
Non-disjunction is the failure of the chromosomes to separate, which produces daughter cells with abnormal numbers of chromosomes, leading to diseases such as down syndrome.
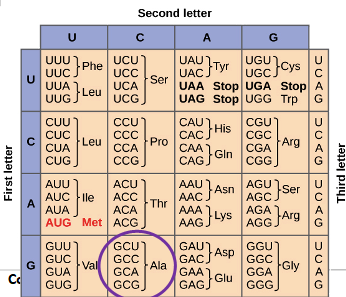
What does degenerate mean?
Although each codon is specific for only one amino acid (or one stop signal), the genetic code is described as degenerate, or redundant, because a single amino acid may be coded for by more than one codon.
What happens when a base is deleted?
Removal of one of the bases in DNA. This can result in a frameshift mutation and a change in all the amino acids downstream of the deletion.
What happens when a base is substituted?
Replacement of a base of DNA. Due to the redundance of the genetic code this may or may not result in a change of amino acid, mutations in introns will have no effect on proteins. Sometimes this small change can affect the tertiary structure of the protein and therefore its functionality