AP Microeconomics Unit 5 Review
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
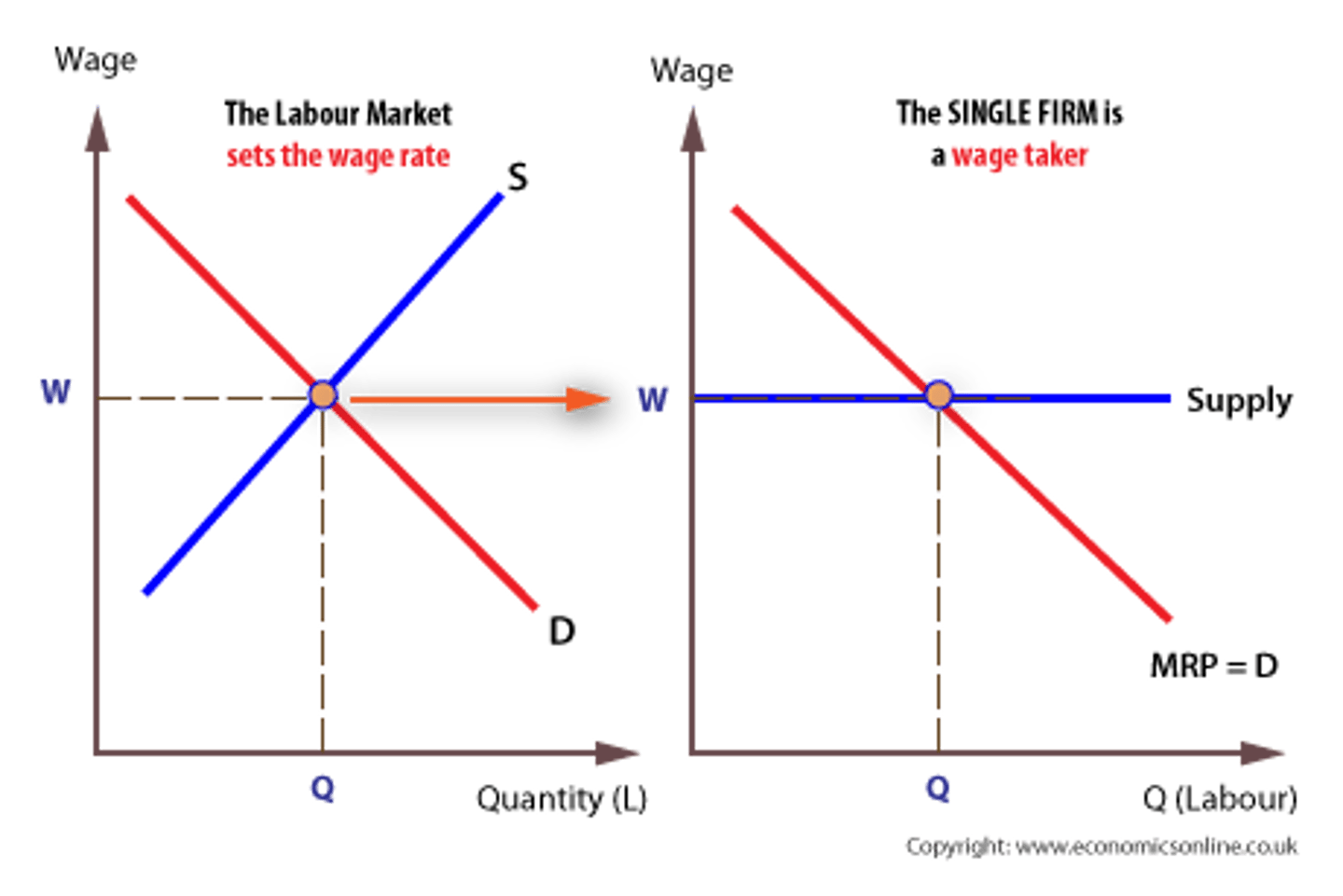
perfectly competitive labor market
many small firms are hiring workers
- no one firm is large enough to manipulate the market
- many workers with identical skills
- wage is constant (at equilbirum)
- workers are wage takers
demand for labor
the different quantities of workers that businesses are willing and able to hire at different wages
law of demand for labor
there is an inverse relationship between wage and quantity of labor demanded
supply for labor
the different quantities of individuals that are willing and able to sell their labor at different wages
law of supply for labor
there is a direct relationship between wage and quantity of labor supplied
derived demand
the demand for resources is determined (derived) by the products they help produce
- demand in product market causes demand for resoruces in labor market to fulfill needs in the product market
changes in demand for the product (shifters of resource demand)
price increase of the product increases the demand for the resource
changes in productivity of the resource (shifters of resource demand)
technological advances in resources make the resource more profitable
changes in price of other resources (shifters of resource deamand)
substitute resources - direct relationship
complementary resources - inverse relationship
number of qualified workers (supply shifters of labor)
changes the number of workers supplied in the labor market
government regulation/licensing (supply shifters of labor)
if different professions had to have qualifications to work in that field, that changes the number of workers (ex. waiters, surgeons)
personal values regarding leisure time/societal roles (supply shifters of labor)
personal values and beliefs concerning who works and if they should work changes the supply of labor
minimum wage
the minimum amount employers are allowed to pay their workers
- wage floor
marginal resource cost (MRC)
the additional cost of an additional resource in a perfectly competitive labor market
- equals the wage set by the market and is constant

marginal revenue product (MRP)
the additional revenue generated by an additional resource in a perfectly competitive labor market
- determines demand for labor
- each worker is worth the amount of money they generate

MRP declining (why does it do this?)
diminishing marginal returns
- fixed resources prohibit growth at a certain point
labor maximization rule
MRP = MRC
- continue to produce until MRP = MRC
- aim to keep MRP > MRC because you want more revenue than costs to make a profit
perfectly competitive labor market and firm graph
unskilled workers vs. skilled workers
- no change in qualities or action when solving problems
- however, the starting point for demand the supply curves are higher on the axises for skilled labor
least cost rule
need marginal product per dollar for each resource at each output quantity
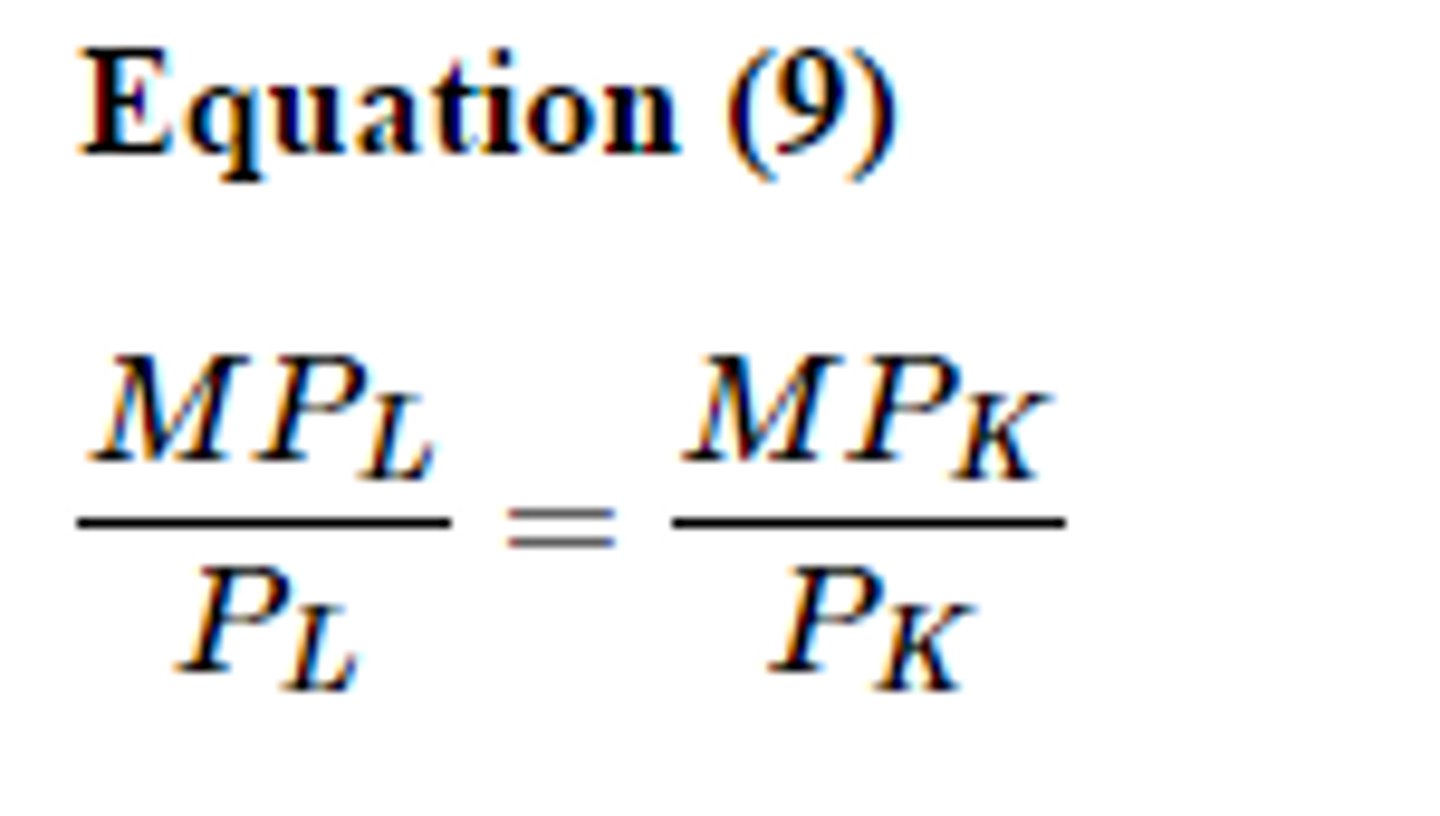
profit maximizing rule for combining resources
the firm is hiring where MRP = MRC for each resources
- MRPx/MRCx = MRPy/MRCy = 1
monopsony
one firm hiring workers
- firm is large enough to manipulate the market
- workers are relatively immobile
- firm is wage maker (to hire additional workers, the firm must increase the wage)
- cannot price discriminate, so must pay workers the same wage
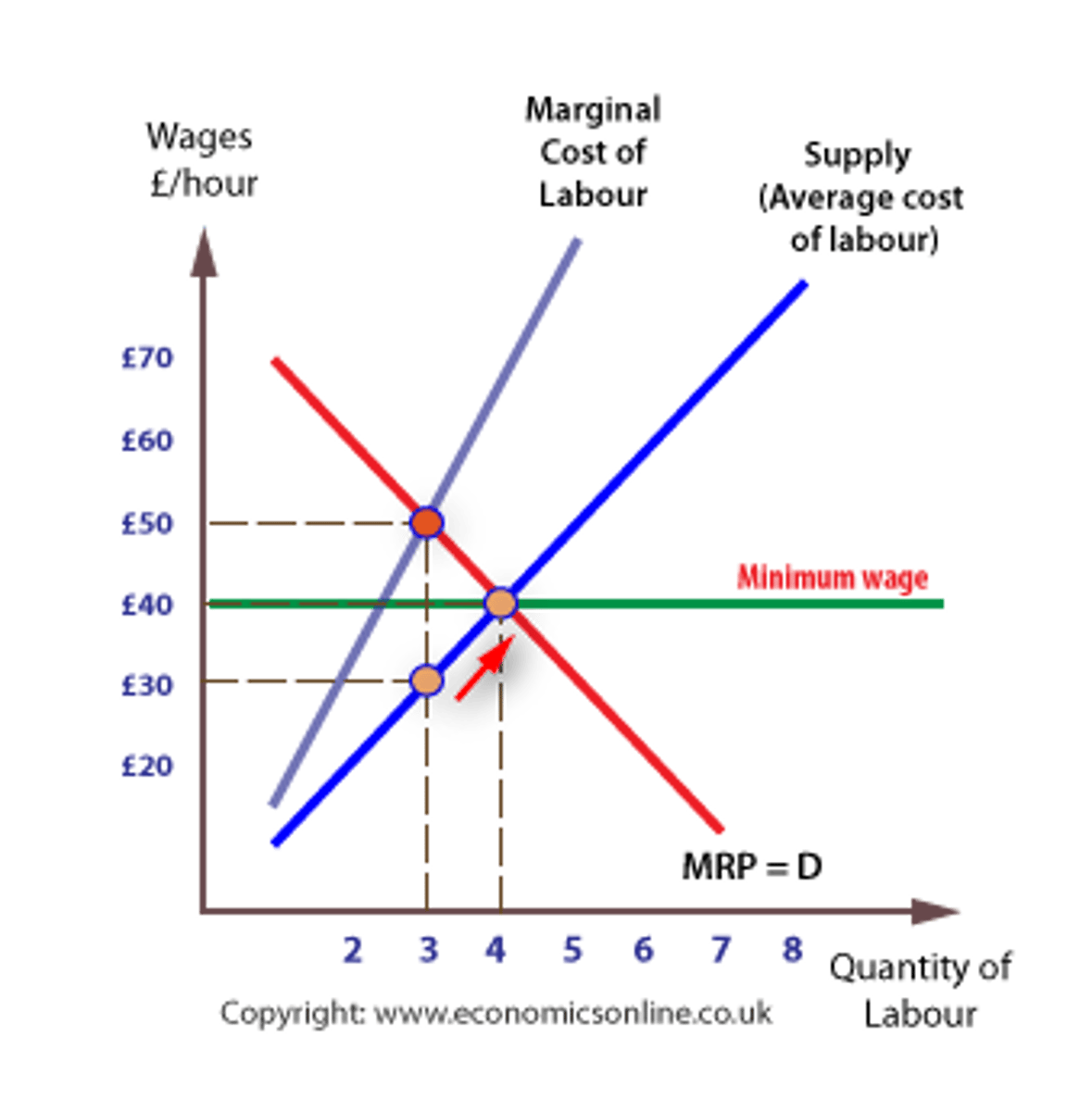
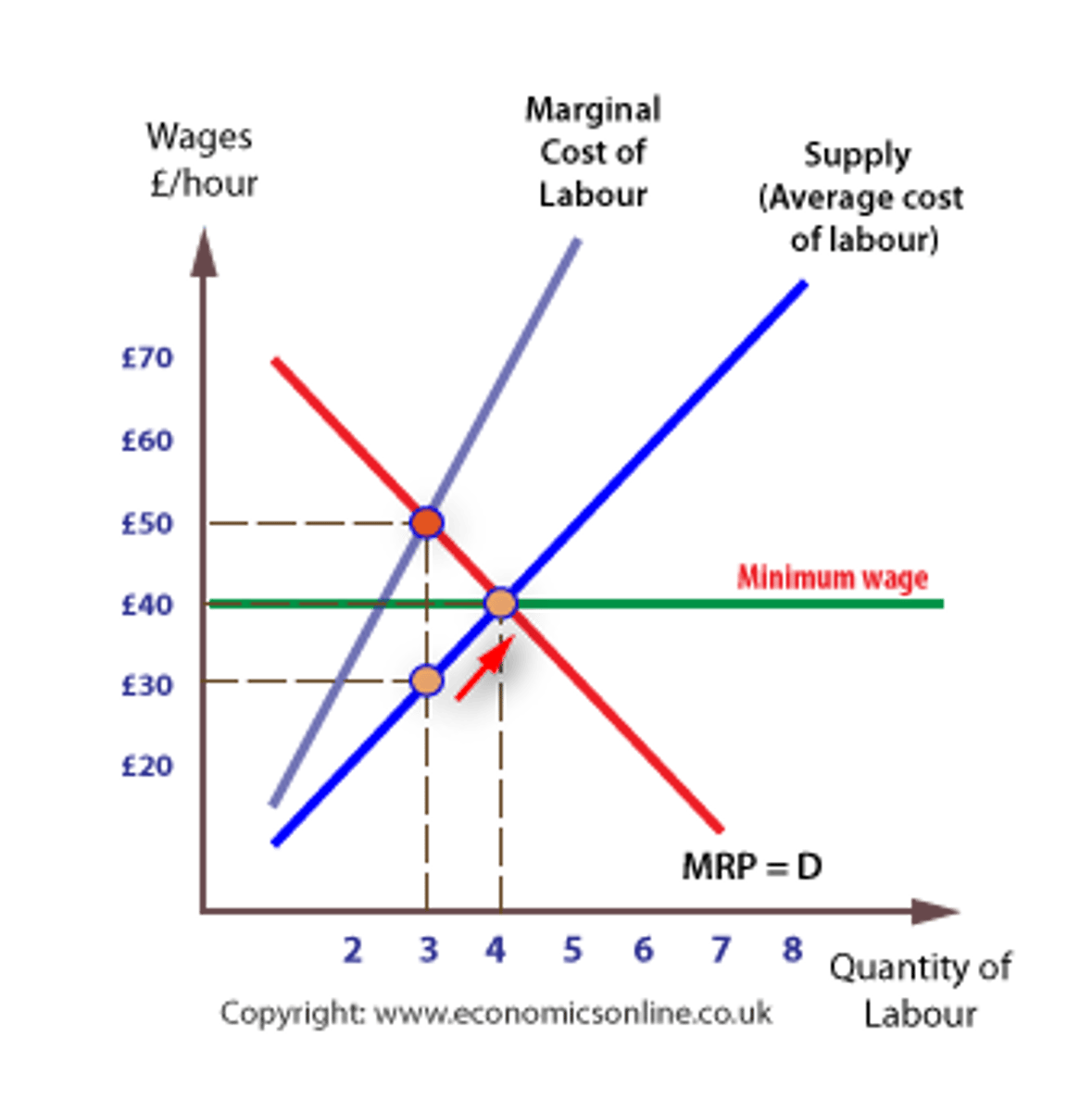
monopsony graph
- hire where MRC = MRP
- pays workers to the extent of the supply curve, not the MRC curve because the monopsony is the wage maker
labor union goals
1. convince consumers to buy only union products
2. lobbying officials to increase deamnd
3. increase the price of substitute resources (non-unionzed workers)
- increase wages