Exam 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/114
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:36 PM on 9/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
1
New cards
PTT
appropriate tube for CBC (complete blood count)
2
New cards
RTT
appropriate tube for serum diagnostic profile
3
New cards
BTT
appropriate tube for coagulation assays
4
New cards
gray top tube
appropriate tube for glucose when serum cannot be separated from the clot
5
New cards
pre-analytical
* Any part of the testing process that occurs BEFORE the actual measurement of the analyte(s)
* Includes pt ID, sample labeling, pt prep, clean venipuncture, proper tubes, proper filling, proper handling of tubes after filling, etc
* Includes pt ID, sample labeling, pt prep, clean venipuncture, proper tubes, proper filling, proper handling of tubes after filling, etc
6
New cards
Errors that occur when EDTA contaminated serum for diagnostic profiles
* Blood in RTT may not clot
* EDTA chelates bivalent cations such as calcium, magnesium, and iron, causing falsely low determinations of these analytes
* EDTA consists of a potassium salt, it adds potassium to the sample
* Severely low calcium, magnesium, and markedly high potassium
* EDTA chelates bivalent cations such as calcium, magnesium, and iron, causing falsely low determinations of these analytes
* EDTA consists of a potassium salt, it adds potassium to the sample
* Severely low calcium, magnesium, and markedly high potassium
7
New cards
errors that result when blood is collected inappropriately from indwelling catheters
the blood may be overly contaminated w the other components. In other words, if the animal is receiving calcium gluconate, the analyzed serum may have calcium that is artifactually high. The same w dextrose or potassium supplementation
8
New cards
errors that occur when blood is not separated soon enough for diagnostic profiles in horses
RBC, which contain a high concentration of potassium (diff from other spp), can leak potassium into the serum and cause artifactually high potassium concentrations in the serum submitted for analysis (HYPERKALEMIA)
9
New cards
inadequately filled PTT
* excess EDTA
* RBCs shrink, decrease in PCV
* RBCs shrink, decrease in PCV
10
New cards
inadequately filled BTT
* excess citrate
* prolonged clotting times in coag testing
* prolonged clotting times in coag testing
11
New cards
heparin
Green top tube additive
12
New cards
sodium citrate
BTT additive
13
New cards
K2- or K3 EDTA
PTT additive
14
New cards
artifactual hypoglycemia and artifactual hyperkalemia
delayed removal of serum from RTT can cause
15
New cards
cellular elements (mostly RBC) consume glucose
causes artifactual hypoglycemia in delayed removal of serum from RTT
16
New cards
cellular elements leak cytoplasmic contents
causes artifactual hyperkalemia in delayed removal of serum from RTT
17
New cards
fibrinogen
RTT provides clotting factor and ____ free serum
18
New cards
10-15x
minimum amount of times to mix blood prior to testing
19
New cards
packed cell volume (PCV)
% of whole blood composed of RBCs
20
New cards
HCT (hematocrit)
ratio of volume of RBCS to volume of blood
21
New cards
HCT on a CBC
derived from a CALCULATED value using mean cell volume (MCV) and RBC count
* (MCV x RBC count)/10
* (MCV x RBC count)/10
22
New cards
buffy coat
layer btwn plasma and RBCs in PCV
* composed of leukocytes, platelets, and nRBCs
* composed of leukocytes, platelets, and nRBCs
23
New cards
bottom of buffy coat
read PCV here
24
New cards
icterus
yellow plasma on PCV
25
New cards
increased \[bilirubin\] in blood
icterus w PCV indicates
26
New cards
plasma icterus in large animals
* not reliable
* high levels of diet-associated carotene pigment give plasma NORMAL yellow color
* high levels of diet-associated carotene pigment give plasma NORMAL yellow color
27
New cards
lipemia
hazy to opaque white plasma on PCV
28
New cards
increased lipids in circulation
lipemia on PCV indicates
29
New cards
Causes of lipemia on PCV
* Post-prandial (after meal) blood collection
* Diseases associated w abnx lipid metabolism
* Diseases associated w abnx lipid metabolism
30
New cards
hemolysis
red colored plasma on PCV
31
New cards
presence of free hemoglobin from ruptures RBCs in plasma
hemolysis in PCV indicates
32
New cards
causes of hemolysis in PCV
* May be **in vitro** artifact
* Collection technique
* Erythrocyte fragility in lipemic samples
* Suspect artifact if PCV nx or high
* May result from **in vivo** (pathologic) hemolysis
* Intravascular hemolysis due to hemolytic anemia or other disorders
* Suspect pathologic hemolysis if PCV low
* Collection technique
* Erythrocyte fragility in lipemic samples
* Suspect artifact if PCV nx or high
* May result from **in vivo** (pathologic) hemolysis
* Intravascular hemolysis due to hemolytic anemia or other disorders
* Suspect pathologic hemolysis if PCV low
33
New cards
Plasma protein estimation by refractometer
* **ESTIMATED** protein concentration based on refractive index
* Assumes other solutes in plasma are present in nx concentrations
34
New cards
clumps, critters, cancer
things found on the feathered edge of a smear
35
New cards
Body of smear
* too dense and WBCs too rounded to ID
* May be useful for detecting microfilaria and platelet clumps
* Evaluate briefly as part of blood film review
* May be useful for detecting microfilaria and platelet clumps
* Evaluate briefly as part of blood film review
36
New cards
Monolayer
* Cell details visible
* Perform nucleated cell differential, RBC morphology assessment, and platelet evaluation here
* Perform nucleated cell differential, RBC morphology assessment, and platelet evaluation here
37
New cards
* Differential cell count - confirm automated analyzer data
* Evaluate morphologic abnormalities - leukocytes, erythrocytes, and platelets
* Examine for blood parasites - never detected by analyzer
* Evaluate morphologic abnormalities - leukocytes, erythrocytes, and platelets
* Examine for blood parasites - never detected by analyzer
Reasons to look at a blood film even if our instrument performs a differential count
38
New cards
Differential nucleated cell count
* Count 100 nucleated cells w/in the monolayer
* Classify nucleated cells as
* Segmented neutrophils ("segs")
* Band neutrophils ("bands")
* Lymphocytes ("lymphs")
* Monocytes ("monos")
* Eosinophils ("eos")
* Basophils ("basos")
* Nucleated RBCs (nRBCs)
* Other
* Classify nucleated cells as
* Segmented neutrophils ("segs")
* Band neutrophils ("bands")
* Lymphocytes ("lymphs")
* Monocytes ("monos")
* Eosinophils ("eos")
* Basophils ("basos")
* Nucleated RBCs (nRBCs)
* Other
39
New cards
Total nucleated cell count (TNCC or NCC)
* Includes nucleated RBCs
* Usually automated for mammals
* WBC and TNCC often used interchangeably
* But not the same if nRBCs present
* By itself is NOT v useful for interpretative purposes
* used primarily to CALCULATE the concentration of specific leukocyte types
* Usually automated for mammals
* WBC and TNCC often used interchangeably
* But not the same if nRBCs present
* By itself is NOT v useful for interpretative purposes
* used primarily to CALCULATE the concentration of specific leukocyte types
40
New cards
components of blood
plasma, RBCs, WBCs, platelets
41
New cards
fxn of RBCs
transport O2 & CO2, buffer plasma pH
42
New cards
20%
how much total blood volume can be lost w/o complication
43
New cards
1%
how much of blood we can take per BW
44
New cards
10%
estimate of blood volume as a % of body wt
45
New cards
hemoglobin (Hb)
* (g/dL)
* Indicates the O2 transport capacity of the blood
* \~1/3 x Hct
* Indicates the O2 transport capacity of the blood
* \~1/3 x Hct
46
New cards
hematocrit (Hct)
* (%)
* % of blood volume composed of RBCs
* (%) = RBCs (millions/uL) x MCV (fL) /10
* Reported by automated cell counters
* % of blood volume composed of RBCs
* (%) = RBCs (millions/uL) x MCV (fL) /10
* Reported by automated cell counters
47
New cards
mean cell hemoglobin (MCH)
* (pg)
* Avg amount of Hb in RBCs
* (pg) = \[Hb(g/dL) x 10\] / RBC count
48
New cards
mean cell hemoglobin concentration (MCHC)
* (g/dL)
* Corrects the Hb measurement for RBC volume
* (g/dL) = \[Hb(g/dL)x 100\]/Hct(%)
* Low = hypochromasia (pale)
* High = increased extracellular Hb
* Decrease
* Reticulocytosis
* Iron deficiency
* Lead toxicity
* Increase
* Hemolysis
* Oxyglobin administration
* Corrects the Hb measurement for RBC volume
* (g/dL) = \[Hb(g/dL)x 100\]/Hct(%)
* Low = hypochromasia (pale)
* High = increased extracellular Hb
* Decrease
* Reticulocytosis
* Iron deficiency
* Lead toxicity
* Increase
* Hemolysis
* Oxyglobin administration
49
New cards
mean cell volume (MCV)
* (fL)
* Automated cell counter measure size directly (doesn't usually get messed up)
* (fL) = \[Hct(%) x 10\] / RBC count
* Decreased = microcytosis
* Causes
* Iron deficiency
* Portosystemic venous shunt
* Heinz body anemia
* Fragmentation anemia
* Hyponatremia
* Asian dog breeds
* Increased = macrocytosis
* Causes
* Reticulocytosis
* FeLV (abnx maturation of RBC bc it affects bone marrow)
* Leukemia
* Nx greyhound RBCs (why they are used as donors=> carry more O2)
* Inherited malabsorption of cobalamin (B12) of giant schnauzers
* Congenital macrocytosis of poodles
* Hereditary stomatocytosis
* Alaskan malamutes, drentse-partrijshonds & mini schnauzers)
* agglutination
* There is spp variation
* Automated cell counter measure size directly (doesn't usually get messed up)
* (fL) = \[Hct(%) x 10\] / RBC count
* Decreased = microcytosis
* Causes
* Iron deficiency
* Portosystemic venous shunt
* Heinz body anemia
* Fragmentation anemia
* Hyponatremia
* Asian dog breeds
* Increased = macrocytosis
* Causes
* Reticulocytosis
* FeLV (abnx maturation of RBC bc it affects bone marrow)
* Leukemia
* Nx greyhound RBCs (why they are used as donors=> carry more O2)
* Inherited malabsorption of cobalamin (B12) of giant schnauzers
* Congenital macrocytosis of poodles
* Hereditary stomatocytosis
* Alaskan malamutes, drentse-partrijshonds & mini schnauzers)
* agglutination
* There is spp variation
50
New cards
red cell distribution width (RDW)
* (%)
* Indicates variation in RBC size, if they are diff sizes, RDW goes up
* RDW = (SDmcv/MCV) x 100
* Increased RDW
* Reticulocytosis
* Microcytosis
* macrocytosis
* Indicates variation in RBC size, if they are diff sizes, RDW goes up
* RDW = (SDmcv/MCV) x 100
* Increased RDW
* Reticulocytosis
* Microcytosis
* macrocytosis
51
New cards
Metarubricyte (nRBC)
* Last erythroid stage w a nucleus
* Hemoglobin concentration continues to increase
* Nucleus continues to condense
* Hemoglobin concentration continues to increase
* Nucleus continues to condense
52
New cards
Reticulocyte (polychromatophilic RBC)
* Hemoglobin content high
* Nucleus has been extruded
* Ribosomes stain basophilic w new methylene blue stain
* Aggregate reticulocytes have larger amounts of mRNA, ribosomes and mitochondria
* Nucleus has been extruded
* Ribosomes stain basophilic w new methylene blue stain
* Aggregate reticulocytes have larger amounts of mRNA, ribosomes and mitochondria
53
New cards
Erythrocyte (mature RBCs)
* Mammalian
* No nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes, de novo protein synthesis
* Anaerobic glycolysis
* Pretty inactive cells, only job is to move around O2
* Fxns: CO2 transport, H+ buffer, O2 transport
* No nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes, de novo protein synthesis
* Anaerobic glycolysis
* Pretty inactive cells, only job is to move around O2
* Fxns: CO2 transport, H+ buffer, O2 transport
54
New cards
factors that decrease O2 affinity of Hb
Increased H+, Decreased pH, Increased CO2, Increased temp, Increased 2,3-diphosphoglycerate (2,3-DPG)
55
New cards
factors that increase O2 affinity of Hb
Decreased H+, increased pH, Decreased CO2, Decreased temp, Decreased 2,3-DPG
56
New cards
Rouleaux
* stacking of RBCs in lines
* Nx in cats & horses
* Disperses in saline
* Nx in cats & horses
* Disperses in saline
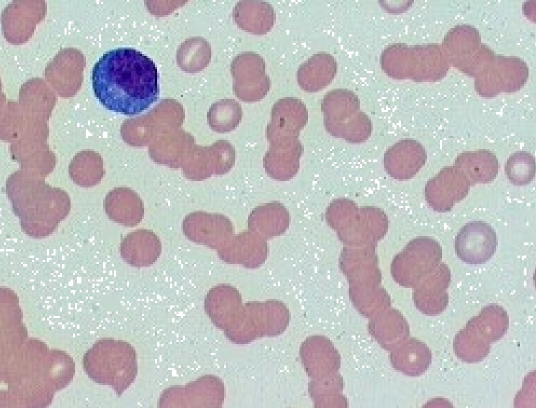
57
New cards
Agglutination
* aggregation of RBCs in clumps/clusters
* Does NOT disperse w saline
* Indicates ongoing immune-mediated diseases
* Does NOT disperse w saline
* Indicates ongoing immune-mediated diseases
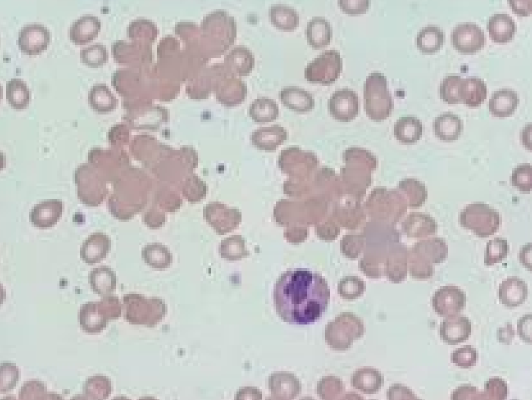
58
New cards
Anisocytosis
all diff sizes
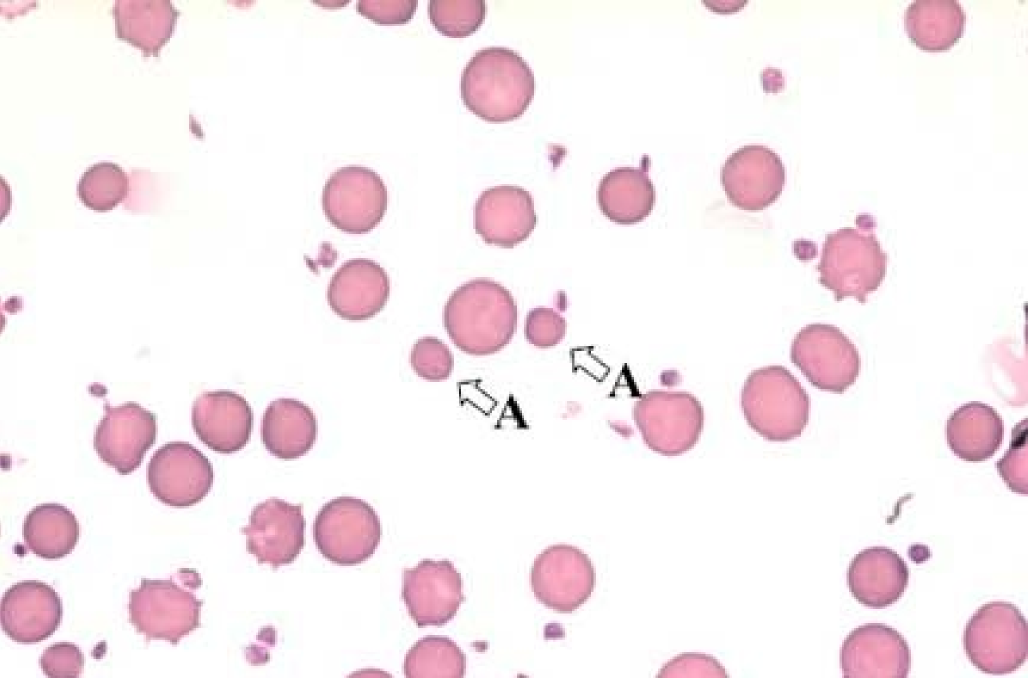
59
New cards
Polychromasia
* staining of retics (blue)
* Usually correlates to regenerative response
* Usually correlates to regenerative response
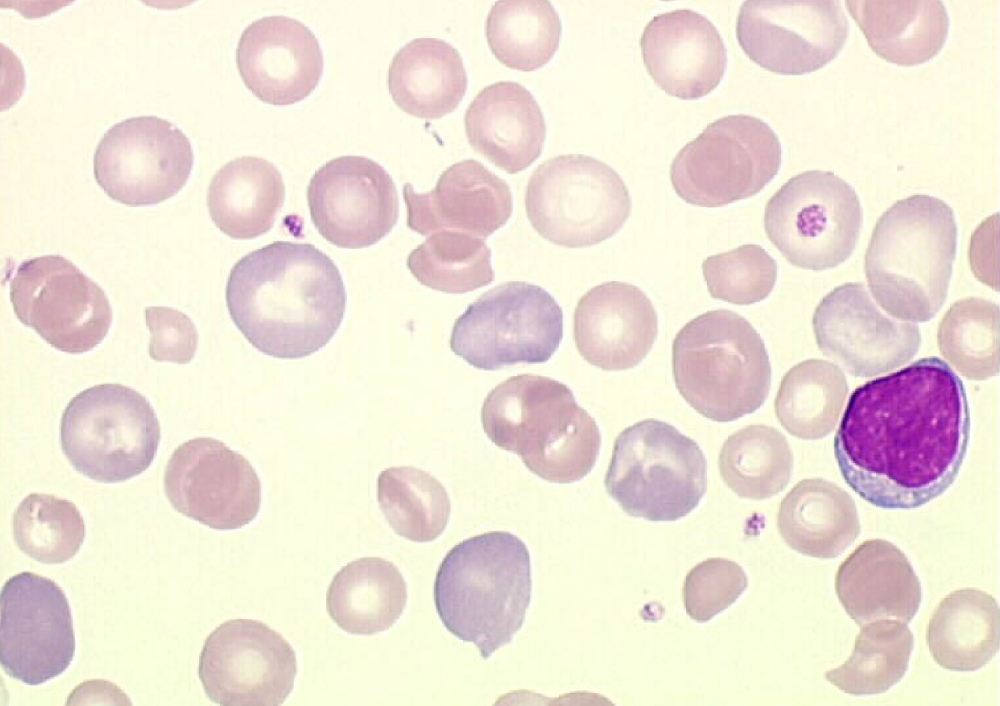
60
New cards
Basophilic Stippling
* Nx in anemic Rums, good sign bc responding to anemia
* Lead toxicity
* Lead toxicity
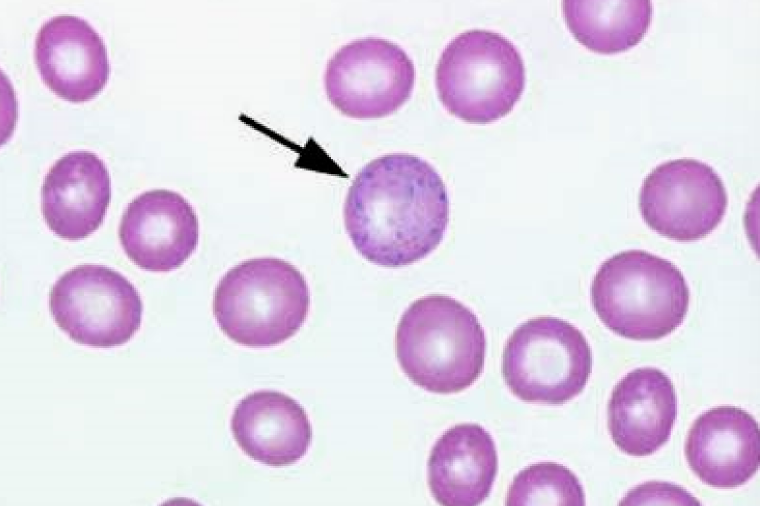
61
New cards
Siderocytes
* contain blue/black aggregates
* Stain blue w Prussian blue stain
* More centralized
* Iron excess
* causes : Lead poisoning, Hemolytic anemia, Dyserythropoiesis, Myeloproliferative dz: effect bone marrow production of RCs, Some drugs (chloramphenicol, hydroxyzine in dogs)
* Stain blue w Prussian blue stain
* More centralized
* Iron excess
* causes : Lead poisoning, Hemolytic anemia, Dyserythropoiesis, Myeloproliferative dz: effect bone marrow production of RCs, Some drugs (chloramphenicol, hydroxyzine in dogs)
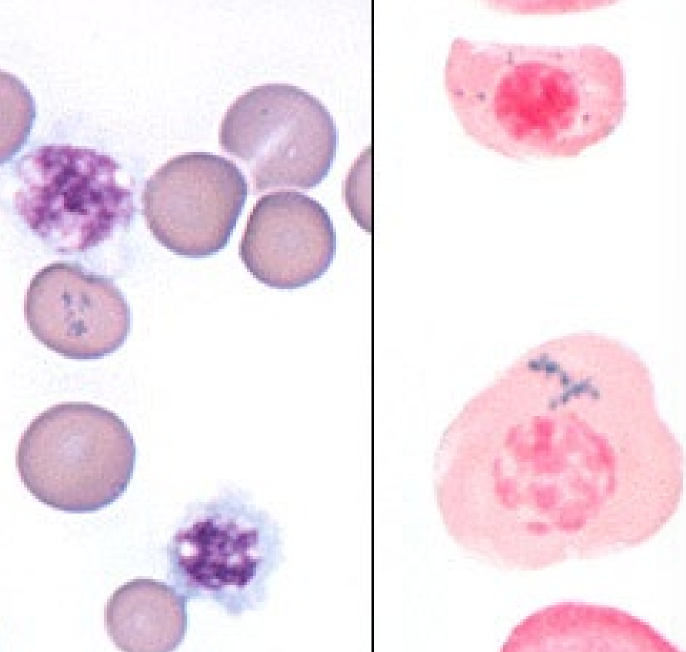
62
New cards
nRBCs
* metarubricytes or earlier erythroid precursors
* Low #s are appropriate during regenerative anemia or hypoxia
* Seen in piglets
* Low #s are appropriate during regenerative anemia or hypoxia
* Seen in piglets
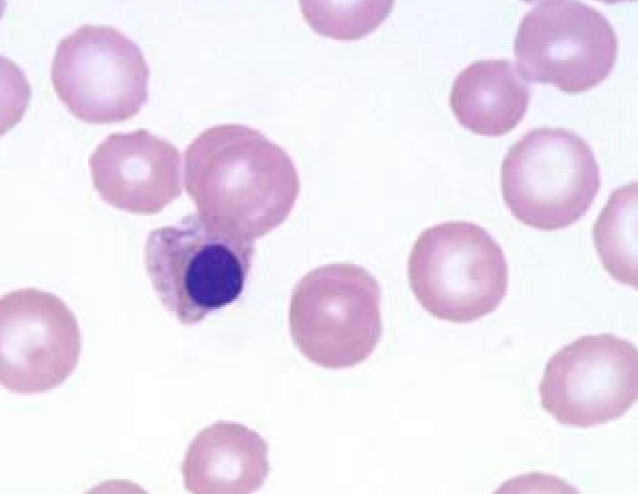
63
New cards
Howell-Jolly Bodies
* basophilic nuclear remnant
* causes: Splenectomy, Chemotherapeutics, Glucocorticoids, Regenerative responses
* causes: Splenectomy, Chemotherapeutics, Glucocorticoids, Regenerative responses
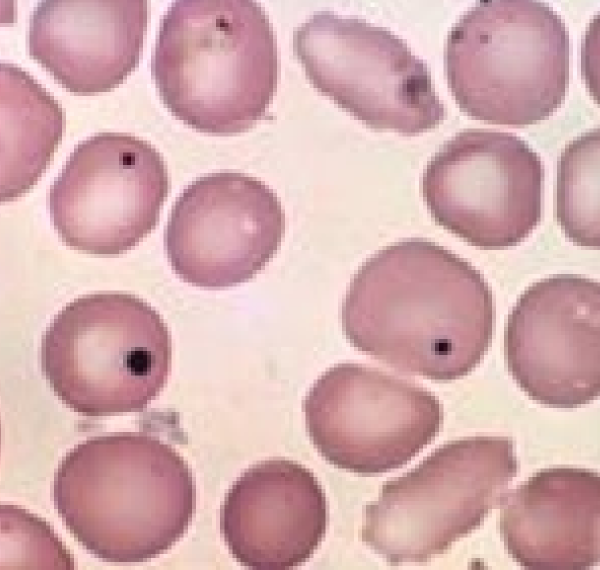
64
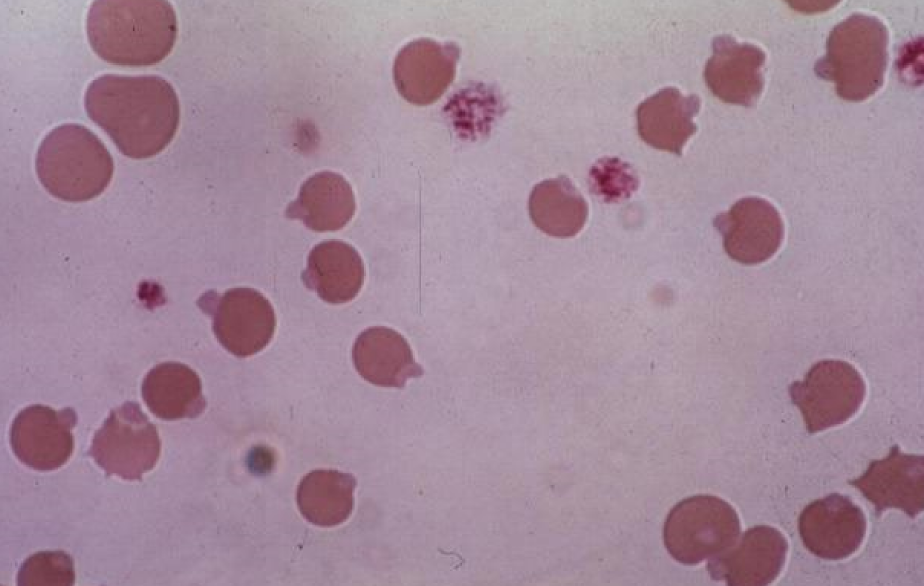
New cards
Heinz Bodies
* denatured & precipitated Hb
* Caused by oxidative damage
* Stain light red w Romanowsky stains
* Stain blue w NMB stain
* Up to 5% of the RBCs in nx cats
* causes: Onion, Kale (RUMs), Winter rye (cattle), Red maple leaves (horses) , Copper toxicity (sheep, goats), Zinc (dogs, eating pennies), Acetaminophen (cats), Methylene blue (cats, dogs), Methionine (cats), Phenazopyridine (cats), Vitamin K3 (dogs), Phenothiazine (horses), Crude oil (marine birds), DM, Lymphoma, Hyperthyroidism (cats)
* Caused by oxidative damage
* Stain light red w Romanowsky stains
* Stain blue w NMB stain
* Up to 5% of the RBCs in nx cats
* causes: Onion, Kale (RUMs), Winter rye (cattle), Red maple leaves (horses) , Copper toxicity (sheep, goats), Zinc (dogs, eating pennies), Acetaminophen (cats), Methylene blue (cats, dogs), Methionine (cats), Phenazopyridine (cats), Vitamin K3 (dogs), Phenothiazine (horses), Crude oil (marine birds), DM, Lymphoma, Hyperthyroidism (cats)
65
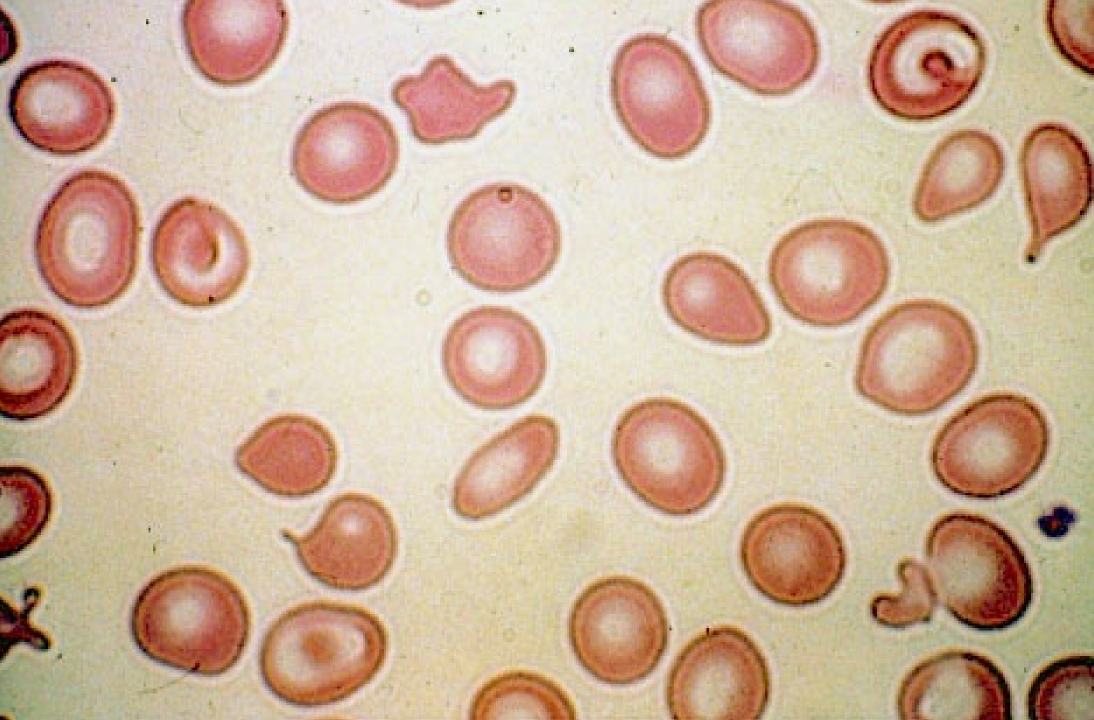
New cards
Poikilocytosis
irregular shapes
66
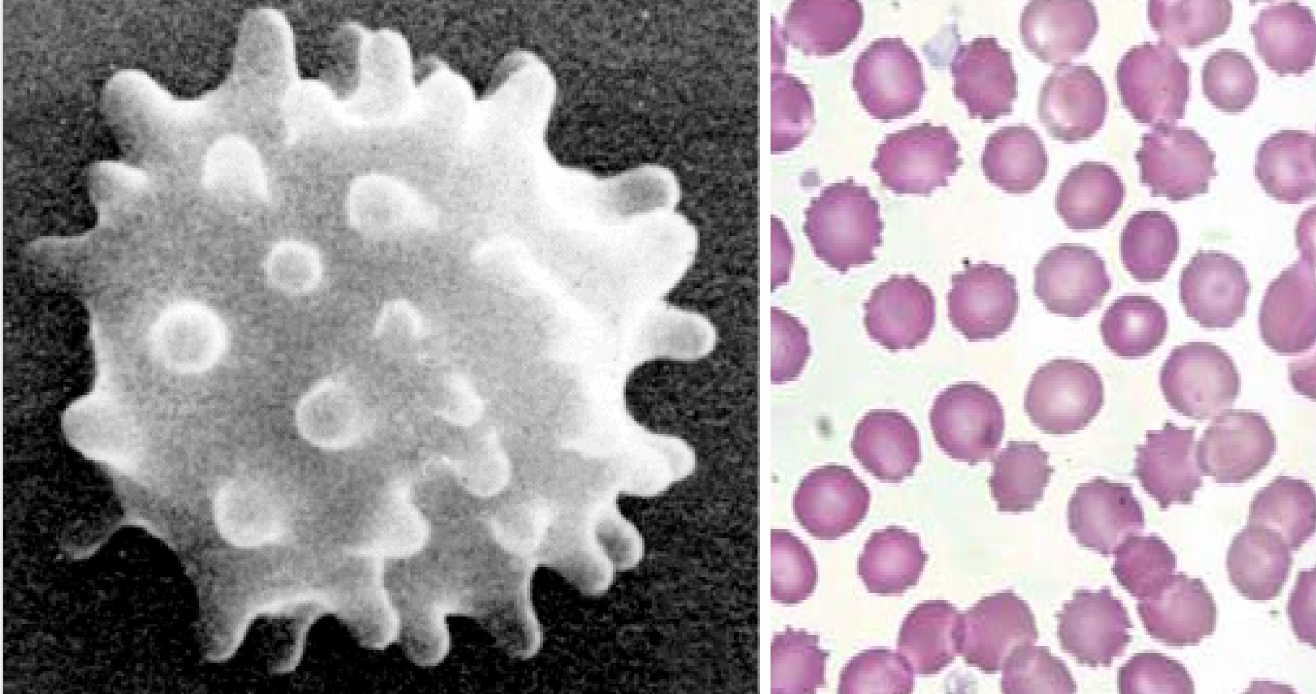
New cards
Echinocyte
* burr cell, crenated cell
* Drying artifact, nx in pigs
* causes: Electrolyte imbalance, Uremia, Glomerulonephritis, Neoplasia, Doxorubicin toxicity, Coral/rattlesnake venom, Transfusion w stored blood
* Drying artifact, nx in pigs
* causes: Electrolyte imbalance, Uremia, Glomerulonephritis, Neoplasia, Doxorubicin toxicity, Coral/rattlesnake venom, Transfusion w stored blood
67
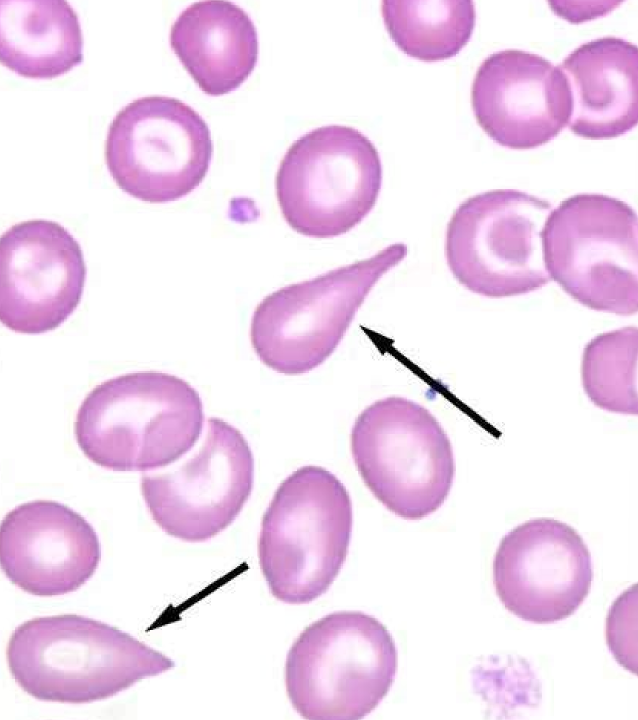
New cards
Dacrocytes
* tear-drop shaped
* Nx in goats
* causes: Iron deficient camelids, Glomerulonephritis, Myeloproliferative disorders
* Nx in goats
* causes: Iron deficient camelids, Glomerulonephritis, Myeloproliferative disorders
68
New cards
Elliptocytes (Ovalocytes)
* Nx in camelids
* causes: 4.1 band deficiency (dog), Iron deficiency, Myelodysplasia, Glomerulonephritis, Portosystemic shunts, Doxyrubicin toxicity, Hepatic lipidosis
* causes: 4.1 band deficiency (dog), Iron deficiency, Myelodysplasia, Glomerulonephritis, Portosystemic shunts, Doxyrubicin toxicity, Hepatic lipidosis
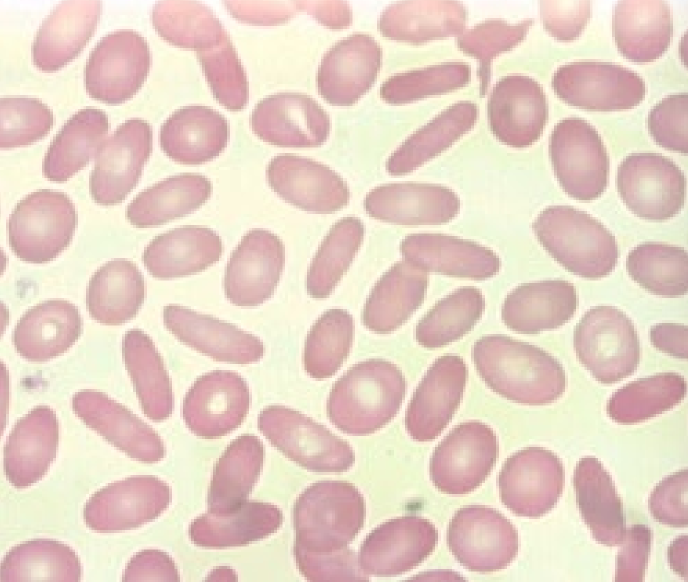
69
New cards
Drepanocyte
Nx in deer
(Sickle Cell)
(Sickle Cell)
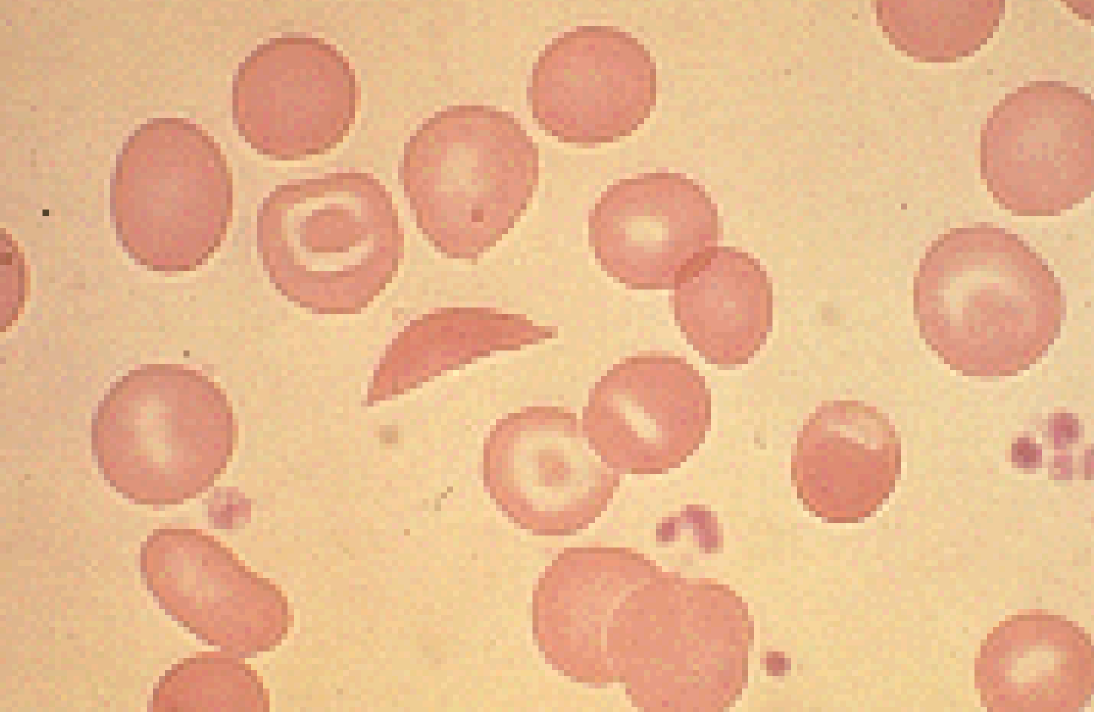
70
New cards
Acanthocytes
* irregular spicules
* Altered lipid:cholesterol
* causes: Hepatopathy, Hemangiosarcoma, Glomerulonephritis, Lymphoma, DIC, Young goats & cattle
* Altered lipid:cholesterol
* causes: Hepatopathy, Hemangiosarcoma, Glomerulonephritis, Lymphoma, DIC, Young goats & cattle
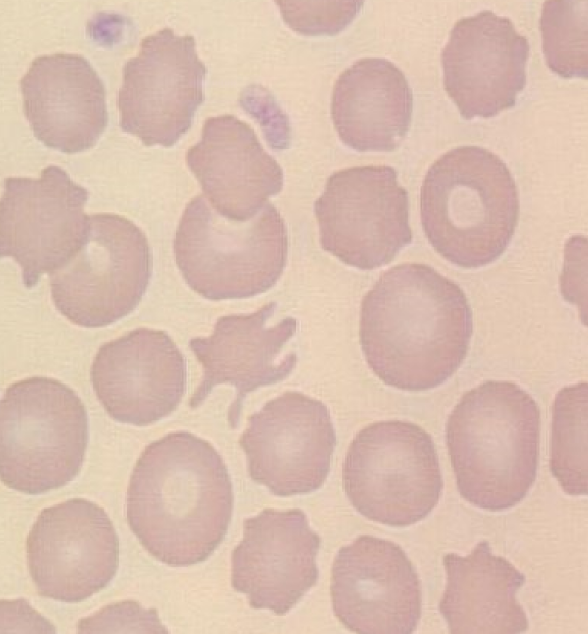
71
New cards
Schistocytes
* Fragments formed by passing through fibrin strands or turbulent blood flow
* causes: DIC, Hemangiosarcoma, Vasculitis, Glomerulonephritis, Congestive heart failure, Myelofibrosis,
Doxorubicin toxicity, Severe hepatopathy, Iron deficiency, Dyserythropoiesis (dogs)
* causes: DIC, Hemangiosarcoma, Vasculitis, Glomerulonephritis, Congestive heart failure, Myelofibrosis,
Doxorubicin toxicity, Severe hepatopathy, Iron deficiency, Dyserythropoiesis (dogs)
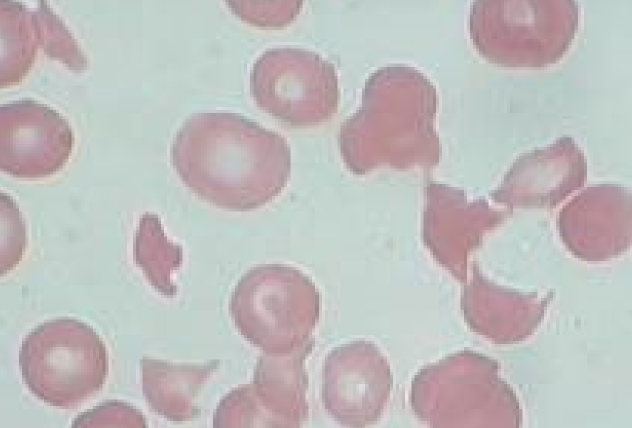
72
New cards
Eccentrocytes
Condensed Hb
Oxidative damage
Oxidative damage
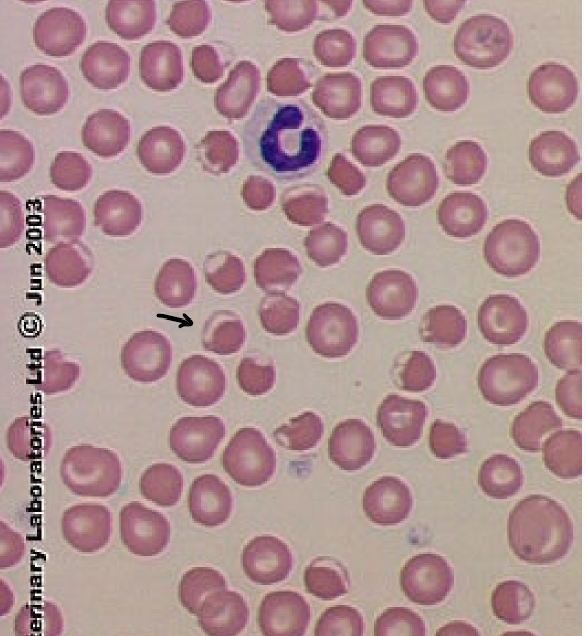
73
New cards
Keratocytes
* Contained a vesicle
* (Helmet cells)
* causes: Oxidative damage, Iron deficiency, Hepatopathy, Doxyrubicin toxicity
* (Helmet cells)
* causes: Oxidative damage, Iron deficiency, Hepatopathy, Doxyrubicin toxicity
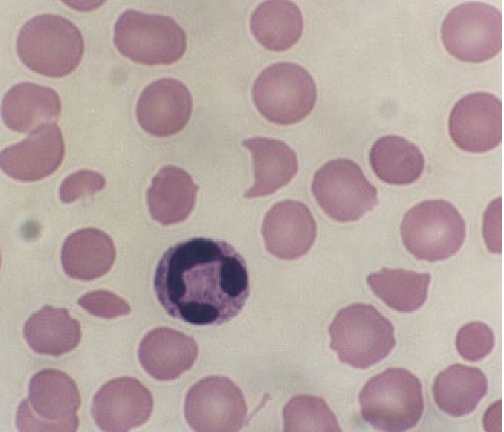
74
New cards
Leptocytes
* Thin, too much central pallor
* causes: Portosystemic shunts, Hepatopathy, Iron deficiency
* causes: Portosystemic shunts, Hepatopathy, Iron deficiency
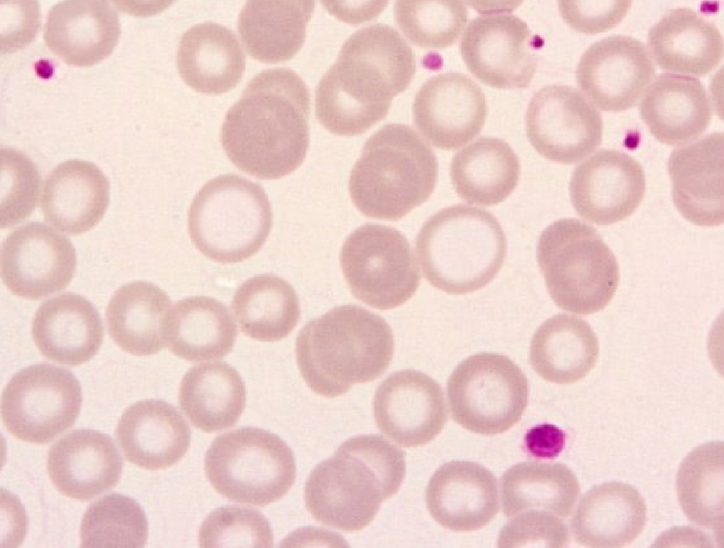
75
New cards
Target Cells
* Hb at the edges & center of the cell
* (Codocytes)
* causes: Hepatopathy, Iron deficiency
* (Codocytes)
* causes: Hepatopathy, Iron deficiency
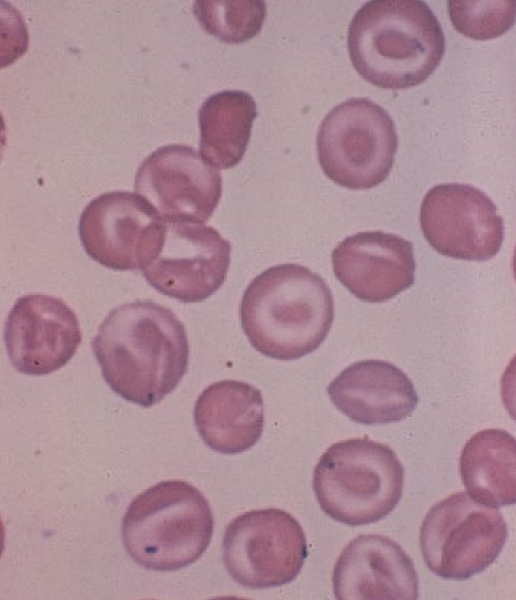
76
New cards
Stomatocytes
* Oval area of central pallor
* causes: Hereditary stomatocytosis, Hepatopathy, Iron deficiency
* causes: Hereditary stomatocytosis, Hepatopathy, Iron deficiency
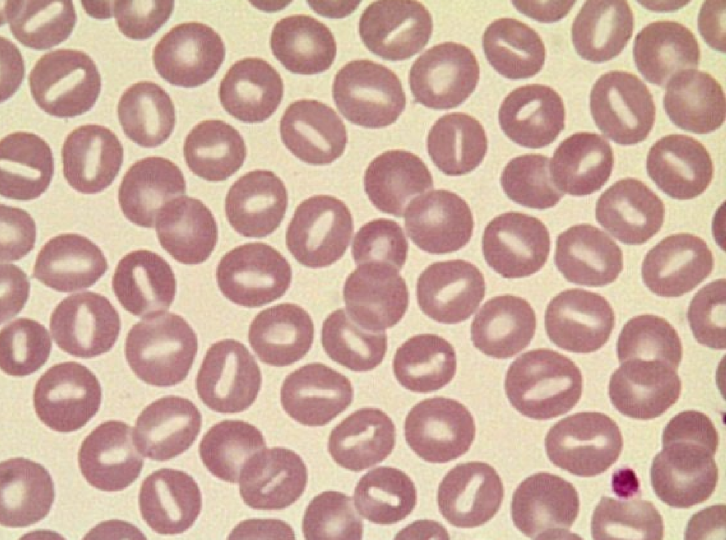
77
New cards
leukogram
numeric and morphologic info about WBCs
78
New cards
Segmented Neutrophil
* Most abundant circulating cell in most spp
* Basophilic cytoplasm
* Chromatin gets condensed
FXN: Inflammation
* Migrate to tissue site, phagocytize microorganisms if present
* Die in the tissues
* Basophilic cytoplasm
* Chromatin gets condensed
FXN: Inflammation
* Migrate to tissue site, phagocytize microorganisms if present
* Die in the tissues
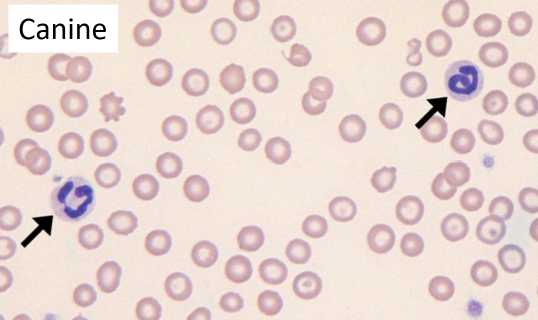
79
New cards
Band Neutrophil
* Lack any nuclear constriction/ segmentation
FXN
* Immature neutrophil released from bone marrow
* Usually seen w marked inflammation
FXN
* Immature neutrophil released from bone marrow
* Usually seen w marked inflammation
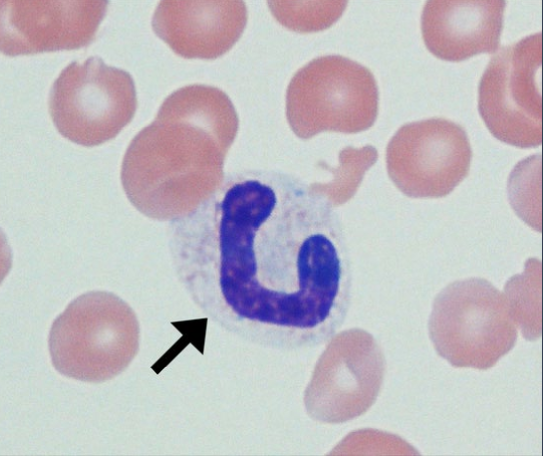
80
New cards
Heterophil
segmented nucleus
Basophilic cytoplasm
Exotic neutrophils
Basophilic cytoplasm
Exotic neutrophils
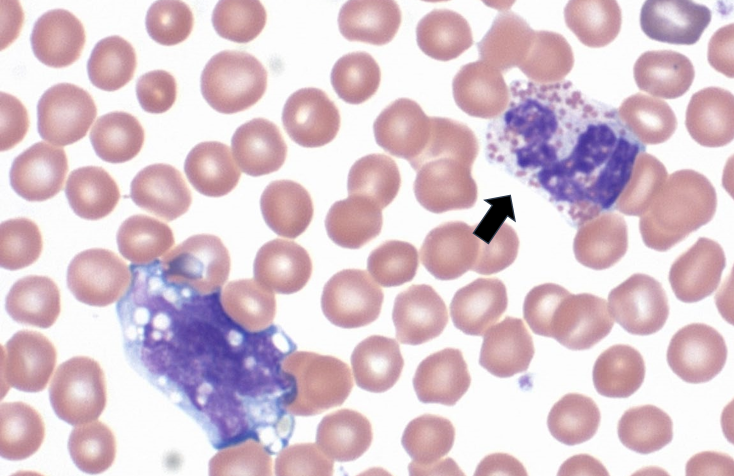
81
New cards
Monocytes
* Typically larger than neuts
* Less nuclear segmentation
* Nuclear chromatin less coarse/dense
* Bc still actively transcribing things
* Blue cytoplasm
* Often contain vacuoles
FXN
* Migrate into tissues to become macrophages
* Phagocytize foreign material, dead/dying cells
* Critical role in initiating, maintaining, and resolving inflammation
* Antigen presentation
* Cytokine production
* Less nuclear segmentation
* Nuclear chromatin less coarse/dense
* Bc still actively transcribing things
* Blue cytoplasm
* Often contain vacuoles
FXN
* Migrate into tissues to become macrophages
* Phagocytize foreign material, dead/dying cells
* Critical role in initiating, maintaining, and resolving inflammation
* Antigen presentation
* Cytokine production
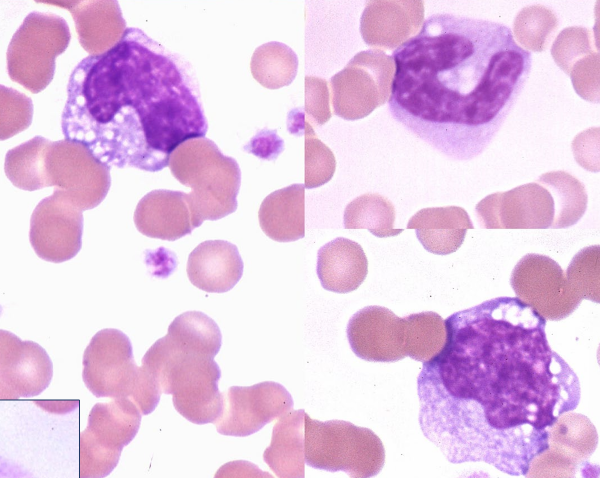
82
New cards
Eosinophils
* Pink orange staining cytoplasmic granules
* Shape, density, staining can very among spp
FXN
Worms, wheezes, weird diseases
* Parasites
* Hypersensitivity, allergy
* Inflammation of skin, gut, respiratory system
* Addison's disease, etc
* Shape, density, staining can very among spp
FXN
Worms, wheezes, weird diseases
* Parasites
* Hypersensitivity, allergy
* Inflammation of skin, gut, respiratory system
* Addison's disease, etc
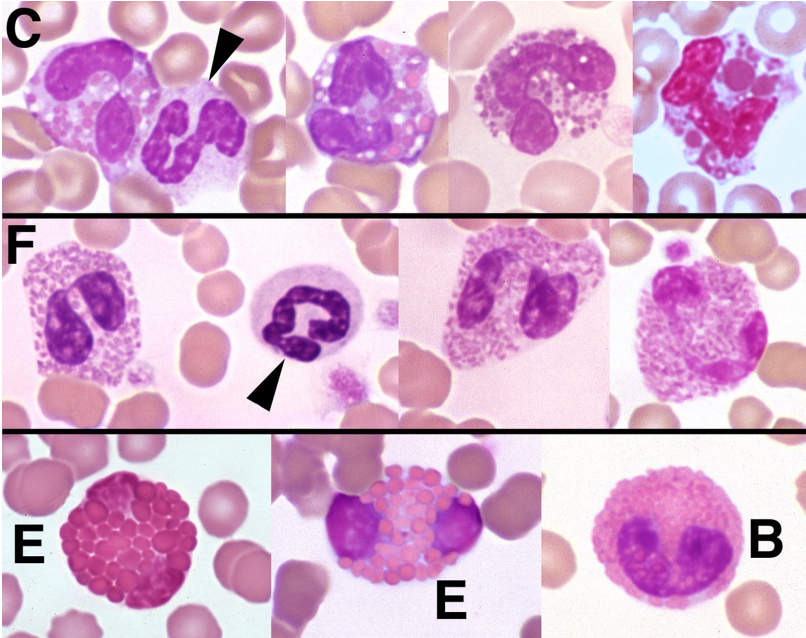
83
New cards
Basophils
* Variable density of purple granules
* Large animals typically contain abundant, dark granules
* Dogs have sparser granules
* Cats have paler granules
Similar response patterns as eosinophils
* Large animals typically contain abundant, dark granules
* Dogs have sparser granules
* Cats have paler granules
Similar response patterns as eosinophils
84
New cards
Lymphocytes
* Small cells w smooth, dense nuclear chromatin and a small rim of pale blue cytoplasm
* Larger forms can be seen in smaller #s normally
* More abundant, pale cytoplasm
* Can have scant, fine cytoplasmic granules
* RUMs tend to be larger w more abundant cytoplasm
Lymphs w azurophilic granules
* Can be seen normally
* Marked increase or majority of lymphs
* Ehrlichia
* Canine CLL (CD8 T cell)
* Vax
* Larger forms can be seen in smaller #s normally
* More abundant, pale cytoplasm
* Can have scant, fine cytoplasmic granules
* RUMs tend to be larger w more abundant cytoplasm
Lymphs w azurophilic granules
* Can be seen normally
* Marked increase or majority of lymphs
* Ehrlichia
* Canine CLL (CD8 T cell)
* Vax
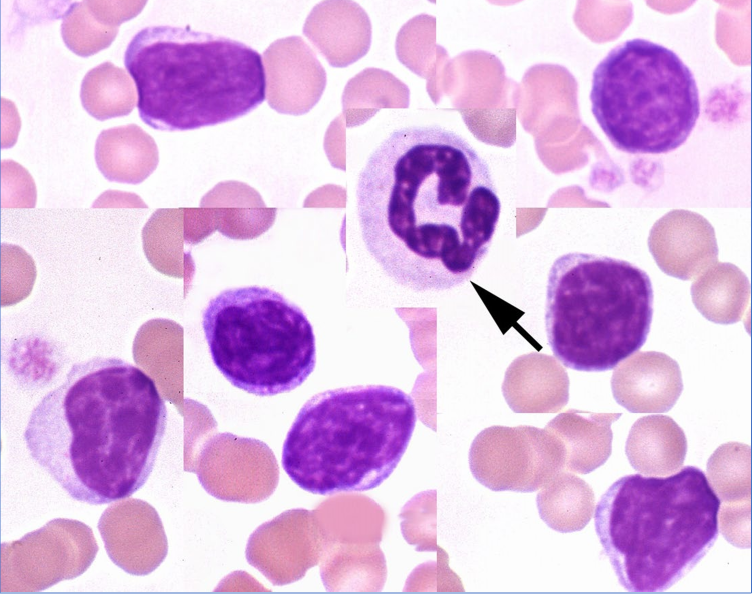
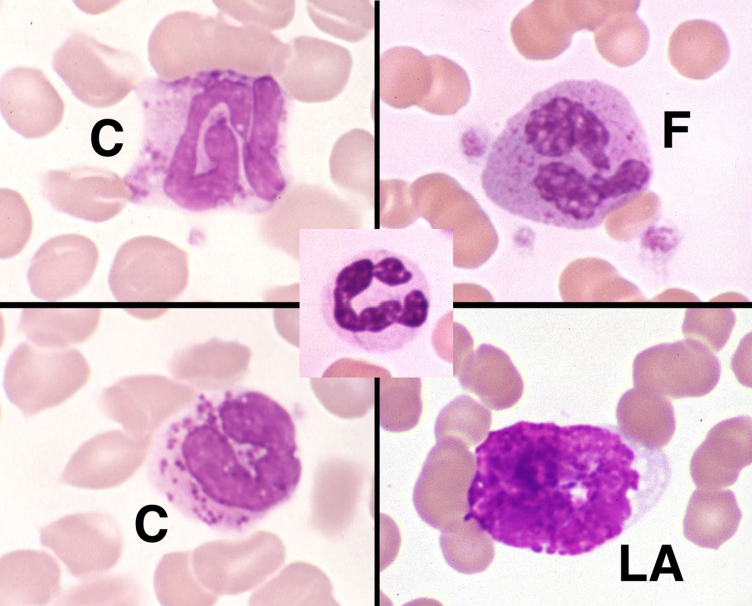
85
New cards
Toxic Change in neutrophils
* Seen in CYTOPLASM:
* Increased basophilia - (persistence of cytoplasmic RNA)
* Dohle bodies- irregular margin (aggregates of rough ER)
* Vacuolization/foamy-(dispersing of organelles)
* Can start to resemble monocytes
* Mono chromatin is patchy, looks more condensed
* Neuts have more segmentation
* In bone marrow, accelerated production, can still do their job
* Indicates accelerated production/increased demand
* Inflammation
* Secondary to accelerated production/release from BM
* Persistence of organelles
* Indicate increased peripheral demand or inflammation
* Increased basophilia - (persistence of cytoplasmic RNA)
* Dohle bodies- irregular margin (aggregates of rough ER)
* Vacuolization/foamy-(dispersing of organelles)
* Can start to resemble monocytes
* Mono chromatin is patchy, looks more condensed
* Neuts have more segmentation
* In bone marrow, accelerated production, can still do their job
* Indicates accelerated production/increased demand
* Inflammation
* Secondary to accelerated production/release from BM
* Persistence of organelles
* Indicate increased peripheral demand or inflammation
86
New cards
Degeneration of neutrophils
* Outside of circulation
* Seen in NUCLEUS
* Nuclear swelling
* Loss of segmentation
* Loss of coarse nuclear chromatin pattern
* In peripheral tissues, starting to fall apart, doing their job
* Found as neutrophils break down/die
* Can become prominent w bacterial infections
* Seen in NUCLEUS
* Nuclear swelling
* Loss of segmentation
* Loss of coarse nuclear chromatin pattern
* In peripheral tissues, starting to fall apart, doing their job
* Found as neutrophils break down/die
* Can become prominent w bacterial infections
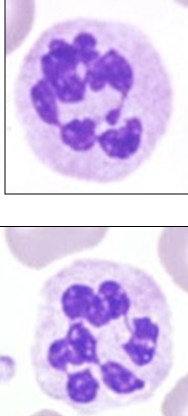
87
New cards
Hypersegmentation (neutrophil)
* More nuclear segmentation
* Not v significant clinically
* Aging
* Old blood sample
* A result of increased circulation time
* Coritcosteroids
* others
* Not v significant clinically
* Aging
* Old blood sample
* A result of increased circulation time
* Coritcosteroids
* others
88
New cards
Pelger-Huet anomaly (neutrophil)
* Inherited (nuclear)
* Lack segmentation (eosinophils too)
* Virtually q neutrophil will look like band or earlier
* No toxic changes
* Impacts eos too
* Nucleus matures normally, but doesn’t shape normally
* Nx mature chromatin
* Nx fxn
* Seen in Australian shepherds
* Less commonly reported in foxhounds, Samoyeds
* Rarely reported in Arabian horses
* Lack segmentation (eosinophils too)
* Virtually q neutrophil will look like band or earlier
* No toxic changes
* Impacts eos too
* Nucleus matures normally, but doesn’t shape normally
* Nx mature chromatin
* Nx fxn
* Seen in Australian shepherds
* Less commonly reported in foxhounds, Samoyeds
* Rarely reported in Arabian horses
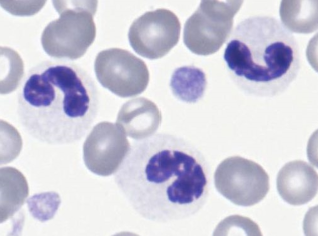
89
New cards
Lysosomal Storage disorder (neutrophil)
* inherited(cytoplasmic)
* Cytoplasmic granulation helps ID issue
* Rare lysosomal trafficking or storage disorders
* Generally systemic dysfunction, physical abnormalities
* Can affect lymphocytes too
* Lysosomal defects; mucopolysaccharidoses (MPS)
* Clinical manifestations are generally readily apparent
* Cytoplasmic granulation helps ID issue
* Rare lysosomal trafficking or storage disorders
* Generally systemic dysfunction, physical abnormalities
* Can affect lymphocytes too
* Lysosomal defects; mucopolysaccharidoses (MPS)
* Clinical manifestations are generally readily apparent
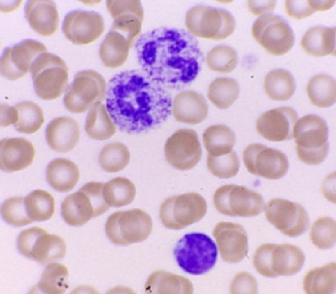
90
New cards
Cytoplasmic vacuoles (lymphocyte)
* Most commonly an aging artifact
* Avoid by sending PTT and blood smear
* Some of the lysosomal storage disorders (inherited)
* Ingestion of plants containing swainsonine (acquired)
* Locoweed toxicity
* Avoid by sending PTT and blood smear
* Some of the lysosomal storage disorders (inherited)
* Ingestion of plants containing swainsonine (acquired)
* Locoweed toxicity
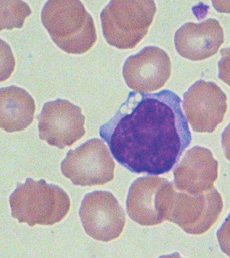
91
New cards
Reactive lymphocytes
A subset of cell contain **increased amounts** of **deeply basophilic** cytoplasm
Associated w an immune response/inflammation
Associated w an immune response/inflammation
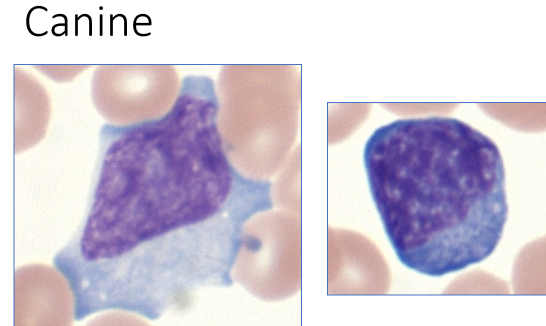
92
New cards
penia
Decreased concentration of cells in whole blood (cells/uL
93
New cards
Pancytopenia
decrease in all 3 cell lines
94
New cards
"philia" or "cytosis"
Increased concentration of cells in whole blood (cells/mL >RI)
95
New cards
Left Shift
* Increase in circulating immature neutrophils
* Typically involves band forms
* Can extend back to metamyelocytes when severe
* Typically involves band forms
* Can extend back to metamyelocytes when severe
96
New cards
regenerative left shift
When mature forms outnumber immature forms
97
New cards
degenerative left shift
When immature forms outnumber mature forms
* Total WBC may be nx or deceased
* Generally indicates severe demand, inadequate response
* Can occur early in less severe inflammation in cattle (bc they dont have as much stores)
* Total WBC may be nx or deceased
* Generally indicates severe demand, inadequate response
* Can occur early in less severe inflammation in cattle (bc they dont have as much stores)
98
New cards
Leukemia (WBC cancer)
* Presence of neoplastic hematopoietic cells in the blood or bone marrow
* Any of the cell lines can become neoplastic
* Myeloid, lymphoid, erythroid, megakaryocytic
* Lymphoproliferative disorders
* Neoplasms of lymphocytes and plasma cells
* Myeloproliferative disorders
* Neoplasms arising from bone marrow stem cells
* Can involve neutrophils, monocytes, erythrocytes,
* rarely eosinophils, basophils, megakaryocytes
* Any of the cell lines can become neoplastic
* Myeloid, lymphoid, erythroid, megakaryocytic
* Lymphoproliferative disorders
* Neoplasms of lymphocytes and plasma cells
* Myeloproliferative disorders
* Neoplasms arising from bone marrow stem cells
* Can involve neutrophils, monocytes, erythrocytes,
* rarely eosinophils, basophils, megakaryocytes
99
New cards
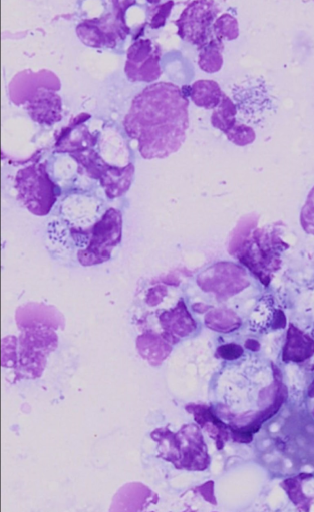
Acute Leukemia
* (NOT commenting on how long it's been going on but rather what stage the cells are at)
* Immature cells; often blast forms w prominent nucleoli
* Aggressive disease
* Often result in other cytopenias
* Animals typically clinically ill
* Can be lymphoid or myeloid
* Immature cells; often blast forms w prominent nucleoli
* Aggressive disease
* Often result in other cytopenias
* Animals typically clinically ill
* Can be lymphoid or myeloid
100
New cards
chronic leukemia
* Well differentiated cells
* Less aggressive
* May be incidental finding (pre-op/dental bloodwork, annual exam etc)
* Myeloid forms are v rare
* Lymphoid forms seen more commonly in dogs and cats
* Less aggressive
* May be incidental finding (pre-op/dental bloodwork, annual exam etc)
* Myeloid forms are v rare
* Lymphoid forms seen more commonly in dogs and cats