GR 9 SCIENCE FLASHCARDS
1/88
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
1ST QUARTER FLASHCARDS
1ST QUARTER FLASHCARDS
This body system allows gas exchange; it brings oxygen into the body and expels carbon dioxide.
The Respiratory System
Part of the human brain that regulates the breathing rate of a person through the respiratory center located
Medulla Oblongata
Name the vital parts of the upper respiratory tract
Nostrils, nasal cavities, pharynx, and larynx
Name the vital parts of the lower respiratory tract
Trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli
The hair inside the nose that filters air by trapping dust particles in them
Cilia / Coarse hairs
The common passageway for food and air
Pharynx (Throat)
The flappy tissue that closes the entrance to the rest of the respiratory system when you swallow
Epiglottis
The main passageway of air to the lungs; one of the passageways of the pharynx
Trachea (Windpipe)
Located atop the trachea; contains two elastic ligaments called vocal cords that produce vibrations
Larynx (Voicebox)
The several curved pieces of cartilage supporting the larynx
Thyroid Cartilage (Adam’s apple)
The sponge-like organs located in the chest cavity; the main organs of the respiratory system
The Lungs
The dome shaped muscle that aids in respiration; contracts when breathing
Diaphragm
The sections that divide the lungs
Lobes
Two layers of membrane that surround the lungs; closed sacs filled with fluid
Pleura
Two connecting tubes from the trachea leading to the two individual lungs
Bronchi
The smaller, divided versions of Bronchi found inside the lungs
Bronchioles
Small air sacs that inflate or deflate depending on inhaling or exhaling; found at the end of each bronchiole
Alveoli (Air sacs)
A network of tiny blood vessels that surround the alveoli
Capillaries
Gas exchange; the physical action of taking air in and out of the body (inspiration and expiration/inhalation and exhalation)
Breathing / Ventilation
Gas exchange; the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the air and the blood in the lungs
External Respiration
Gas exchange; the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the blood and the body cells
Internal Respiration
Gas exchange; the process of using oxygen to break down sugar (glucose) in food and producing energy (ATP)
Cellular Respiration
An infection caused by a viral infection called the rhinovirus; does not have a cure, but can be relieved by resting and drinking lots of water
Common Cold
An infection caused by several viruses called myxovirus; treatment includes vaccination and antiviral drugs
Influenza
Refers to any infection of the lungs caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or protozoa; treatment includes taking all doctor-prescribed medications
Pneumonia
Caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium Tuberculosis, requiring prolonged exposure to become infected; treatment includes taking prescribed antibiotics
Tuberculosis
A chronic allergic condition that makes the breathing airways narrower and swollen; can be relieved by eliminating a triggering agent
Asthma
The inflammation/swelling, and clogging of breathing passages due to mucus; acute condition can be treated and eased with proper rest and drinking fluids
Bronchitis
A long-term disease of the lungs caused by prolonged exposure to respiratory irritants that damages the alveoli and breathing passageways
Emphysema
Associated with emphysema, asthma, & chronic bronchitis; curing is impossible once emphysema sets in
COPD: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Triggered by long-term exposure to carcinogens; these chemicals can cause the growth of tumors; treatments include surgical removal of the damaged part, chemotherapy, and radiation
Lung Cancer
This body system is responsible for transporting nutrients, oxygen, and waste products within the body
Circulatory System
The muscular organ located in the center of your chest; pumps blood through the blood vessels
The Heart
A protective sac that encloses the heart
Pericardium
The two upper chambers of the heart
Right and left Atria
The two lower chambers of the heart
Right and left Ventricles
The wall of tissue that divides the heart in half
Septum
Name the four main valves that regulate blood flow in the heart
Tricuspid valve
Pulmonary valve
Mitral valve
Aortic valve
Name the full process of blood flow in the heart
Vena Cava → Right Atrium → Right Ventricle → Pulmonary Artery → Lungs → Pulmonary Veins → Left Atrium → Left Ventricle → Aorta → The body
A fluid tissue also known as the river of life; consists of a fluid where cells and platelets are suspended
Blood
A pale yellowish liquid that is about 92% water
Plasma
Also called erythrocytes; hemoglobin makes them red and carry oxygen throughout the body
Red Blood Cells
Also called leukocytes; protects the body from diseases
White Blood Cells
Type of WBC that combats bacterial and fungal infections
Neutrophil
Type of WBC that defends against parasitic infections
Eosinophil
Type of WBC that functions during allergic and antigen reactions.
Basophil
Also called thrombocytes; fragments of cytoplasm with a nucleus from large bone marrow cells; play a part in the clotting of blood
Platelets
Blood vessels that move away from the heart; carries oxyenated blood
Arteries
Blood vessels that move blood with wastes toward the heart; carries deoxygenated blood
Veins
Small blood vessels that connect arteries and veins; allow oxygen and nutrients to diffuse through cell walls and into body cells
Capillaries
What is the difference between Genetics and Heredity?
Genetics is a branch of biology that studies hereditary information, while heredity is the transmission of characteristics from parents to their offspring
Division of Genetics; reviews the basic laws of inheritance described by Gregor Mendel
Mendelian Genetics
Division of Genetics; deals with the chemical nature of genes, the mechanism of transmission, and their varied applications
Molecular Genetics
Division of Genetics; focuses on the behavior of a particular gene in a group of organisms
Population Genetics
The differences among individuals belonging to the same species
Variations
The father of genetics, who described the basic laws of inheritance; he first presented his work on pea plants
Gregor Mendel
Contrasting expressions or alternate forms of a trait
Allele
Traits that are observed in every generation
Dominant Traits
Traits that have skipped a few generations yet will possibly appear in future generations
Recessive Traits
The form of the gene that is responsible for the observed trait
Genotype
The observable expressions of the trait
Phenotype
A condition in which two similar alleles are present
Homozygosity
A condition in which two different alleles are present
Heterozygosity
When dominant traits are expressed at the same time, producing a third phenotype
Codominance
A pattern of inheritance where an intermediate phenotype other than the two parental phenotypes is observed
Incomplete Dominance
A trait that is manifesting only in one sex for physiological or anatomical reasons
Sex-limited Traits
Manifest only in one trait for physiological or anatomical reasons
Sex-linked Traits
Traits influenced by the presence of male and female sex hormones
Sex-influenced Traits
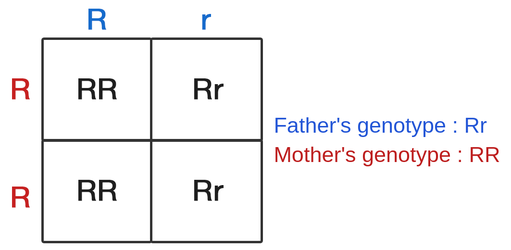
A diagram made of grids used to predict the outcome traits of two parents; each square is represented as 25% of an outcome
Punnett Square
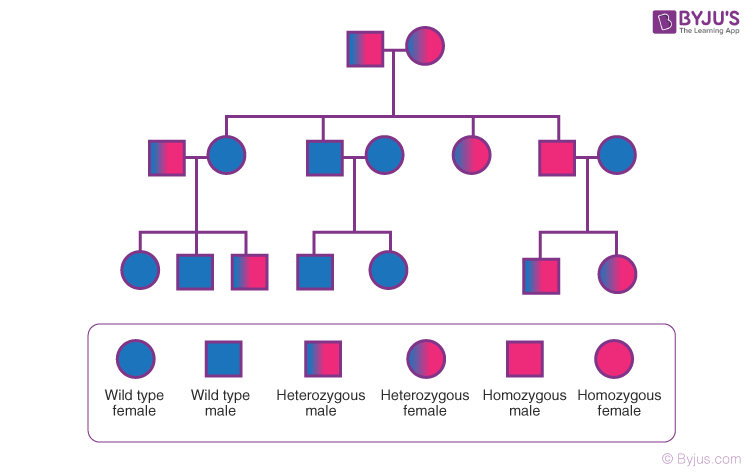
A family tree visual representation of a family's genetic history, showing how traits or genetic conditions are passed down through generations
Pedigree Chart
3RD QUARTER FLASHCARDS
3RD QUARTER FLASHCARDS
An elevated landform with an opening at the top called a crater through which lava and other rock fragments, steam, gases, ash, heat, and other volcanic materials are ejected
Volcano
part of a volcano; underground compartment where magma is stored
Magma Chamber
part of a volcano; passageway through which magma travels to reach the Earth’s surface
Conduit
part of a volcano; opening through which volcanic materials are released
Vent
part of a volcano; bowl-shaped depression at the top of the volcano where the vent is located
Crater
part of a volcano; elongated fracture or crack on Earth’s crust from which lava erupts
Fissure
the side of a volcano
Flank
type of volcano; formed by highly viscous or thick, slow-moving lava; composite cone volcano; steep upper slopes and relaxed lower slopes with a large reservoir of magma; the most dangerous volcanoes
Stratovolcano
Give atleast 3 examples of stratovolcanoes
Mayon Volcano, Mt. Pinatubo, Mt. Kilimanjaro, Mt. Vesuvius, Mt. Fujiyama, etc.
type of volcano; formed by loose and fluid lava over layers of solidified lava from previous eruptions; low and broad; lava does not shoot high in the air, it instead flows and runs down the flank and spreads, increasing the size of the volcano
Shield volcano
Give atleast 3 examples of shield volcanoes
Kilauea, Mauna Kea, Mauna Loa, etc.
type of volcano; formed when pressure builds up in the magma chamber, ejecting fluid lava into the air; scoria cone; as the lava falls down, it cools and forms small solid fragments which fall around the volcano’s vent, forming a cinder cone
Cinder cones
Give atleast 3 examples of cinder cones
Paricutin, Mojave volcano, Cerro Negro, Mt. Fox, etc.
least violent type of eruption; consists of highly fluid or runny lava flowing out of a volcano’s vents; Hawaiian eruptions lead to the formation of shield volcanoes
Hawaiian eruption
violent and marked by a continuous ejection of magma and gas; results in the formation of volcanic bombs and cinder cones
Strombolian eruption
viscous magma flows out of a volcano’s vent, accompanied by a dense cloud of ash and gases that rises high into the atmosphere
Vulcanian eruption
most violent and explosive type of eruption; caused by the buildup of viscous magma and dissolved gas; large ash columns and fast-flowing pyroclastic flows, and lahars
Plinian eruption