1.3 Scalars & Vectors, 1.4 Errors & Uncertainties
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Scalar
phys quantity w/ only magnitude
Vector
phys quantity w/ magnitude & direction
Scalar examples:
t__, d__, v__, de__, te__
time, distance, volume, density, temp
Vector examples:
v__, a__, d__, f__
velocity, acceleration, displacement, force
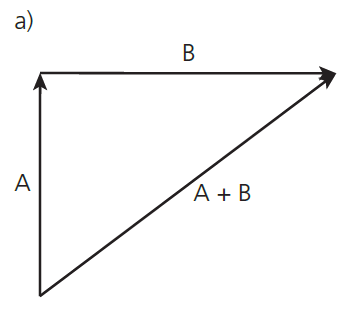
Vectors at right angles: find resultant using __
pythagoras
Vectors NOT at right angles
> Create dotted line that is p__ to bottom vector
> Use pythagoras
perpendicular
Random errors
> u__ error w/ measurement being a__/below true v__
> reduced via m__ measurements, then a__
uncontrollable, above, value, multiple, avg
Systematic errors
> from i__, reduced via s__ error
instrument, subtracting
Uncertainty (Δ)
2 types:
> A__
> P__
absolute, percentage
Uncertainty is usually either:
1. ± h__ of s__ division on instr. (usually when no possible e__)
2. ± 1 of smallest d__ - when possible error
half, smallest, error, division
If uncertainty can have random error (i.e. if given a range of values)
> Δ = ±(h__ of r__ of values)
half, range
Calculating uncertainties
+ or -: ADD __ uncertainties i.e. ΔP = ΔA + ΔB
absolute
Calculating uncertainties
x or /: ADD __ uncertainties i.e. Δ%P = Δ%A + Δ%B
percentage
Calculating uncertainties
Powers: x the __ uncertainty by p__, then by value to get Δ
e.g. if P = An, ΔP = n(ΔA/A) x P
percentage, power
Uncertainty
+ or - uses a__ uncertainty thus constants d__ (do/don’t) matter
absolute, do
Uncertainty
x, /, power uses __ uncertainty thus constants d__ (do/don’t) matter
percentage, dont
Precision: s__/r__ of values of data
spread, range
Accuracy: how c__ the m__ values are to t__ values
close, measured, true