PART 2 - Meteorology: Cloud Formation, Weather Fronts, and Precipitation Types
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
Convection
Vertical movement of warm, less dense air that rises, cools, condenses, and forms clouds and precipitation, often producing showers and storms.
Convergence
Air flowing toward a central point (low pressure), forcing it upward where it cools, condenses, and forms clouds.
Orographic Effect
Air forced up a mountain slope, cooling, condensing, and forming clouds/precipitation on windward side with dry conditions on leeward side (rain shadow).
Frontal Lifting
Warm air forced aloft when meeting cold dense air, causing cloud formation and precipitation.
Cirro-
Prefix describing high, thin ice-crystal clouds above ~20,000 feet.
Alto-
Prefix describing mid-level clouds between ~6,500-20,000 feet.
Strato-
Prefix describing low, layered, blanket-like clouds.
Cumulo-
Prefix describing puffy, vertically growing clouds associated with strong updrafts.
Nimbus
Suffix indicating precipitation-producing clouds.
Cumulonimbus
Towering thunderstorm cloud, producing heavy rain, lightning, hail, tornadoes.
Nimbostratus
Thick, layered gray cloud producing steady, long-duration rain.
Cirrus
Thin, wispy ice-crystal clouds that often indicate approaching warm fronts.
Cumulus
Puffy cotton-like clouds forming from convection; can grow into storms.
Stratus
Low blanket-like clouds covering large areas with drizzle and gloomy skies.
Fog
Ground-level cloud formed when air reaches saturation through cooling or moisture addition, reducing visibility below 1 km.
Radiation Fog
Fog formed overnight on clear, calm nights when the ground cools air to dew point.
Advection Fog
Fog formed when warm moist air moves over a cooler surface, cooling to saturation.
Upslope Fog
Fog formed when moist air is lifted up a slope and cools adiabatically to dew point.
Evaporation Fog
Fog formed when cold air moves over warm water, causing rapid condensation.
Steam Fog
Type of evaporation fog appearing like steam over lakes or rivers.
Valley Fog
Cold dense air drains into valleys, trapping moisture and forming fog.
Precipitation Fog
Fog formed when rain evaporates into cooler air near the ground, saturating it.
Warm Cloud Process (Collision-Coalescence)
Raindrops grow when droplets collide and merge inside warm clouds until heavy enough to fall.
Cold Cloud Process (Bergeron)
Ice crystals attract vapor and grow in subfreezing clouds, falling as snow or melting into rain.
Virga
Precipitation that evaporates before reaching the ground, common in dry air.
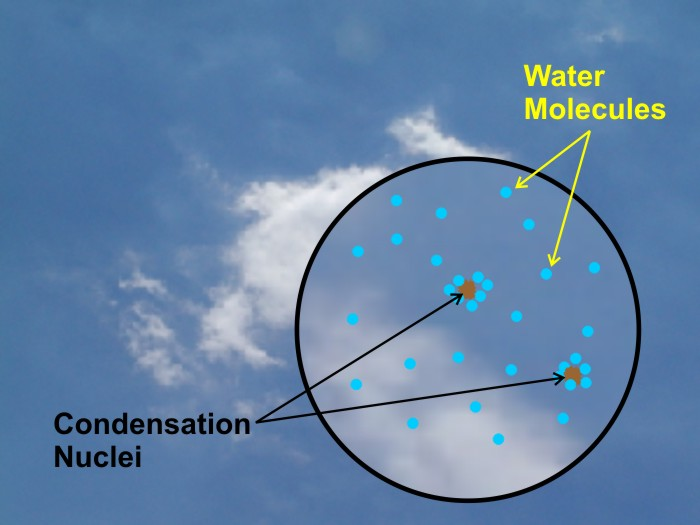
Condensation Nuclei
Tiny particles (dust, smoke, salt) that water vapor condenses onto to form droplets.
Snow
Frozen ice crystals that reach the ground without melting.
Freezing Rain
Raindrops freeze on contact with subfreezing surfaces, forming glaze ice.
Sleet
Raindrops that melt then refreeze mid-air into ice pellets before reaching the ground.
Wintry Mix
Combination of snow, sleet, and freezing rain caused by layered freezing/melting conditions.
Return Period/Interval
Statistical estimate of how often an extreme event occurs based on historical records.
PDI (Palmer Drought Index)
System measuring drought severity based on precipitation deficits and temperature.
Air Mass
Large body of air with uniform temperature and humidity characteristics.
Source Region
Geographic area where air masses form, typically with flat, calm, uniform surfaces.
cP (Continental Polar)
Cold, dry air mass from northern Canada; brings winter cold outbreaks.
mP (Maritime Polar)
Cool, moist air mass from northern oceans; causes cloudy, raw weather.
cT (Continental Tropical)
Hot, very dry desert air mass; causes heat waves and drought.
mT (Maritime Tropical)
Warm, humid air mass from Gulf/subtropics; fuels thunderstorms.
Air Mass Modification
Process by which an air mass changes characteristics as it moves over new surfaces.
Dryline
Boundary separating moist and dry air; common trigger for severe thunderstorms in the Plains.
Lake Effect Snow
Heavy snow formed when cold air passes over warm lakes and picks up moisture and heat.
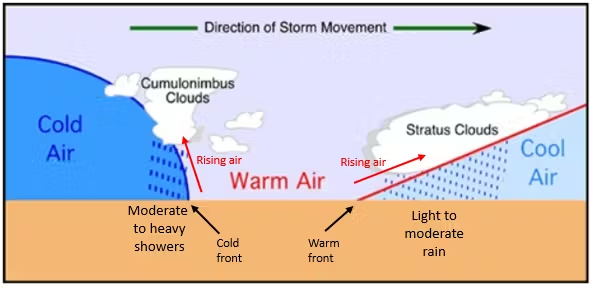
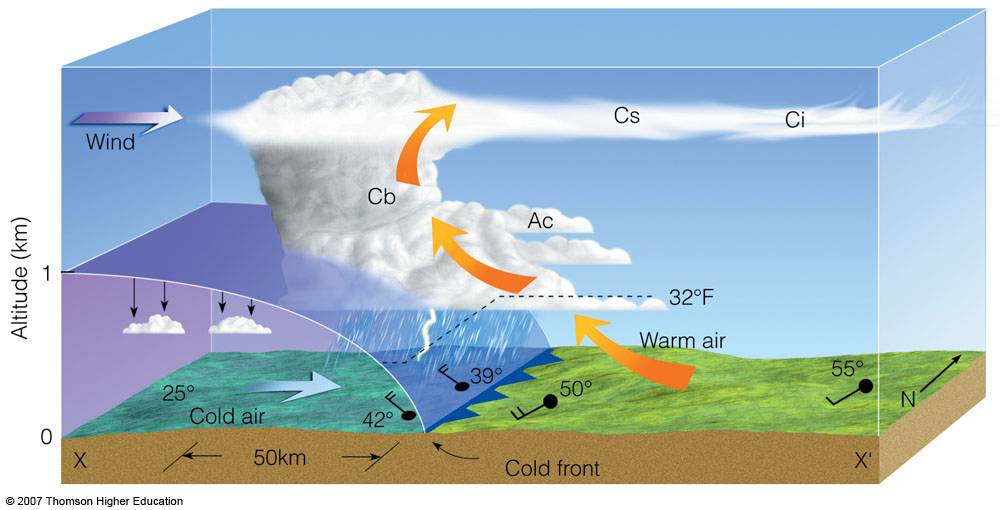
Cold Front
Cold dense air rapidly displaces warm air upward, producing thunderstorms, heavy rain, wind shifts, and sharp cooling.
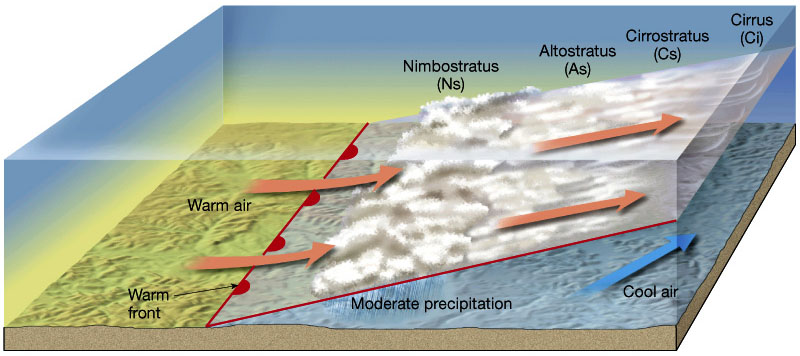
Warm Front
Warm air gradually rides over cool air, producing layered clouds and steady precipitation.
Stationary Front
Boundary where neither air mass moves; produces days of clouds and rain.
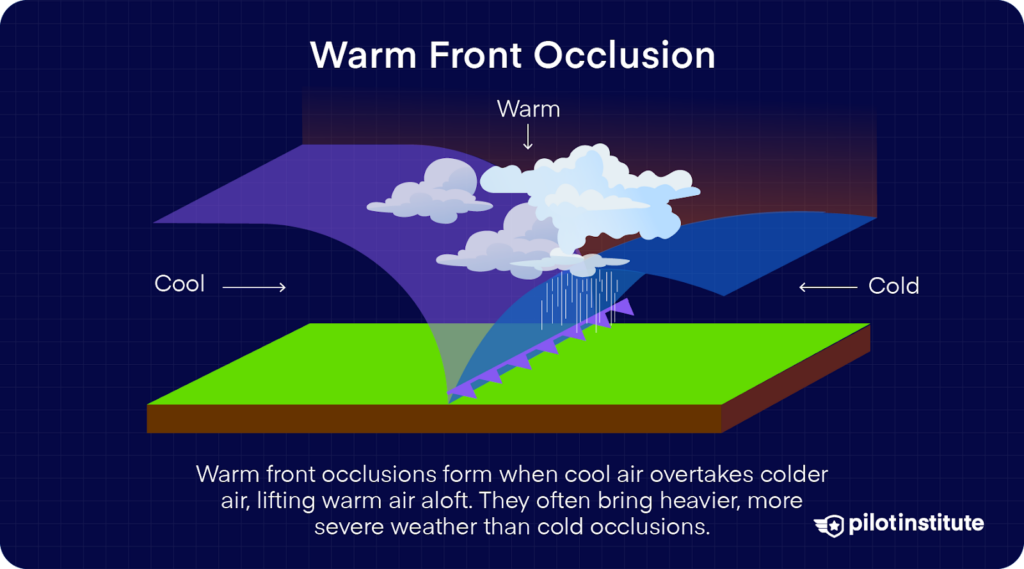
Occluded Front
Cold front overtakes warm front, lifting warm air off the ground and signaling cyclone maturity/weakened system.
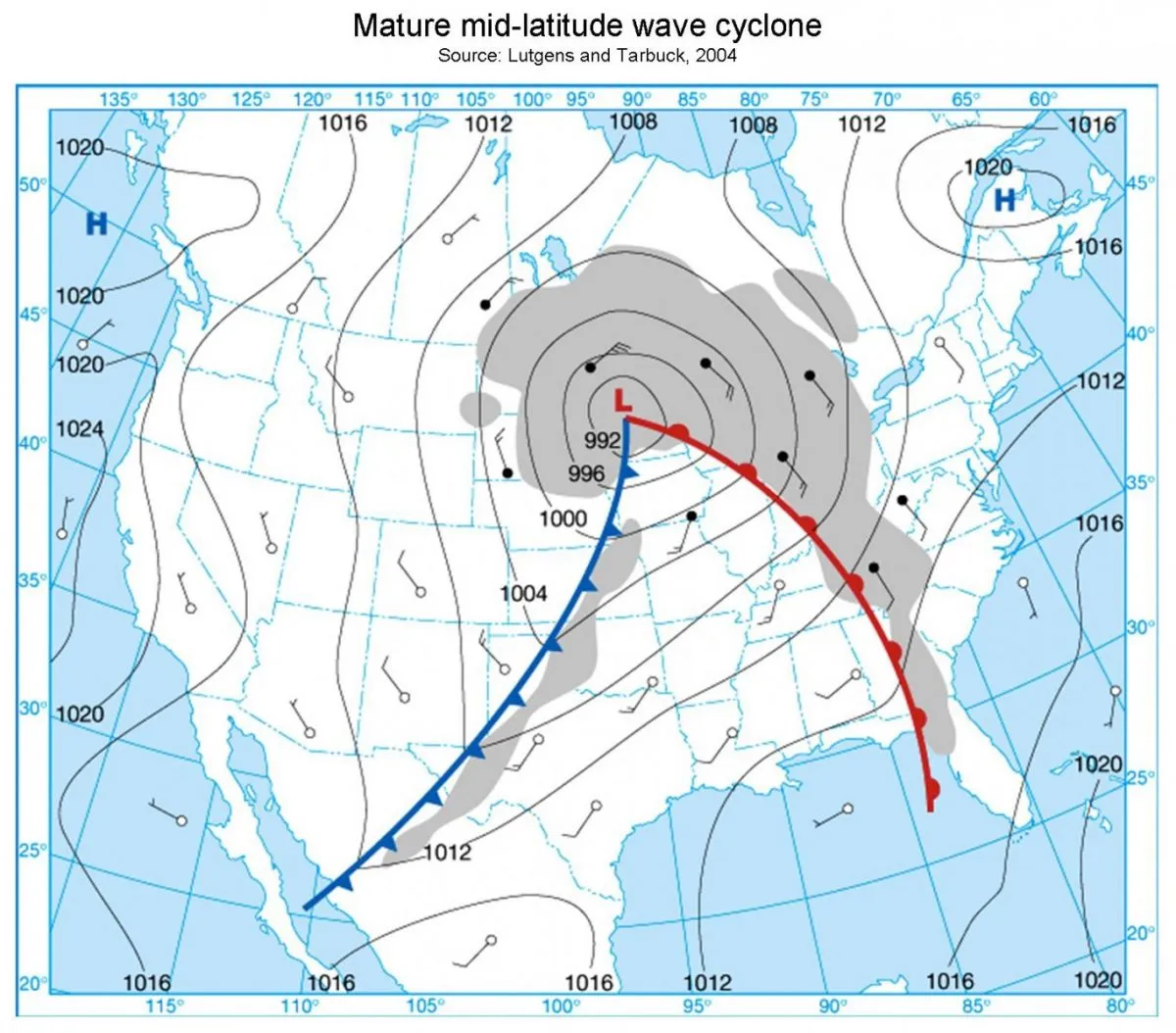
Mid-Latitude Cyclone
Rotating low-pressure weather system with warm and cold fronts, producing widespread precipitation in mid-latitudes.
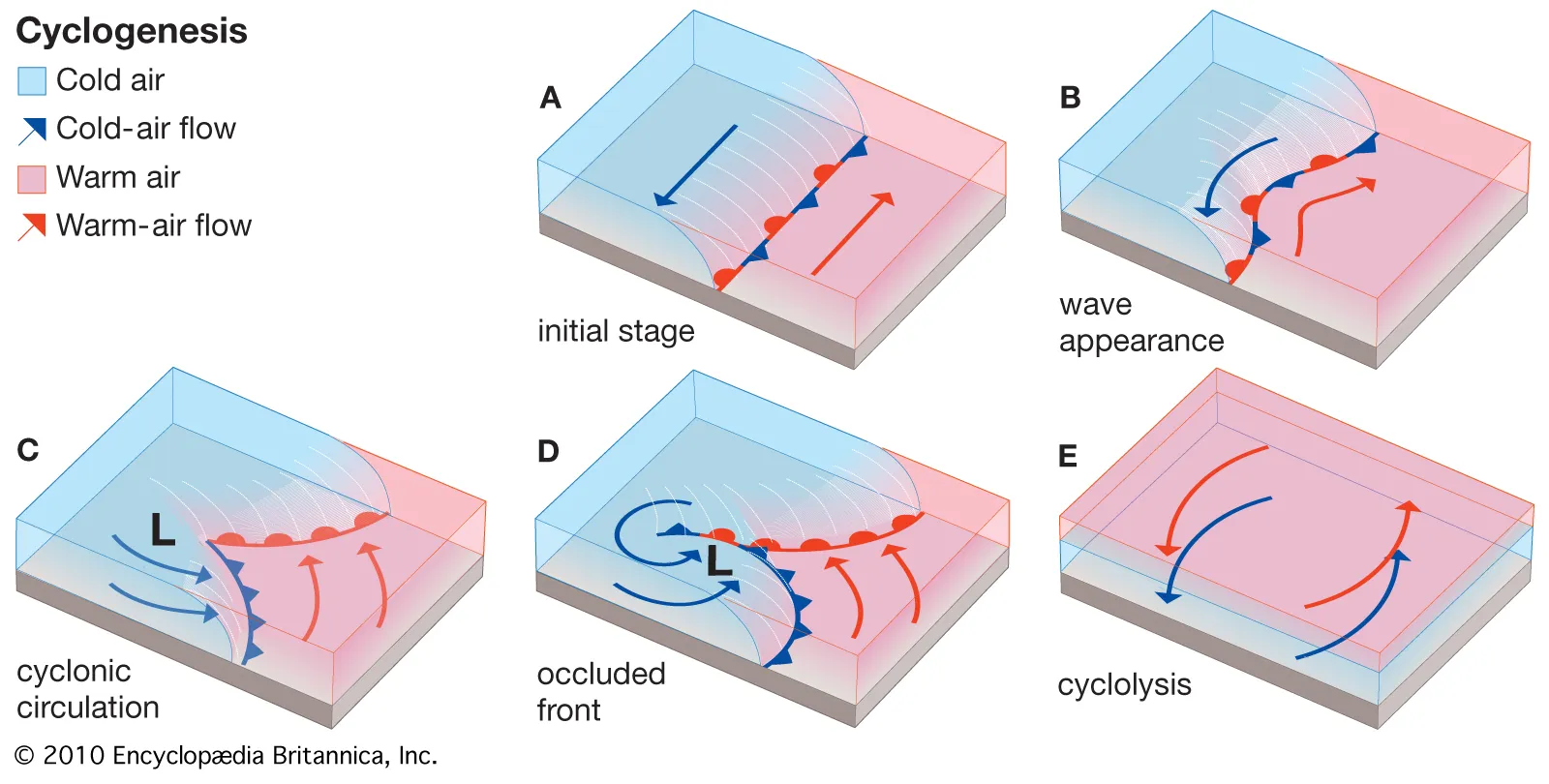
Cyclogenesis
Formation and strengthening of a mid-latitude cyclone along strong temperature gradients and jet stream support.
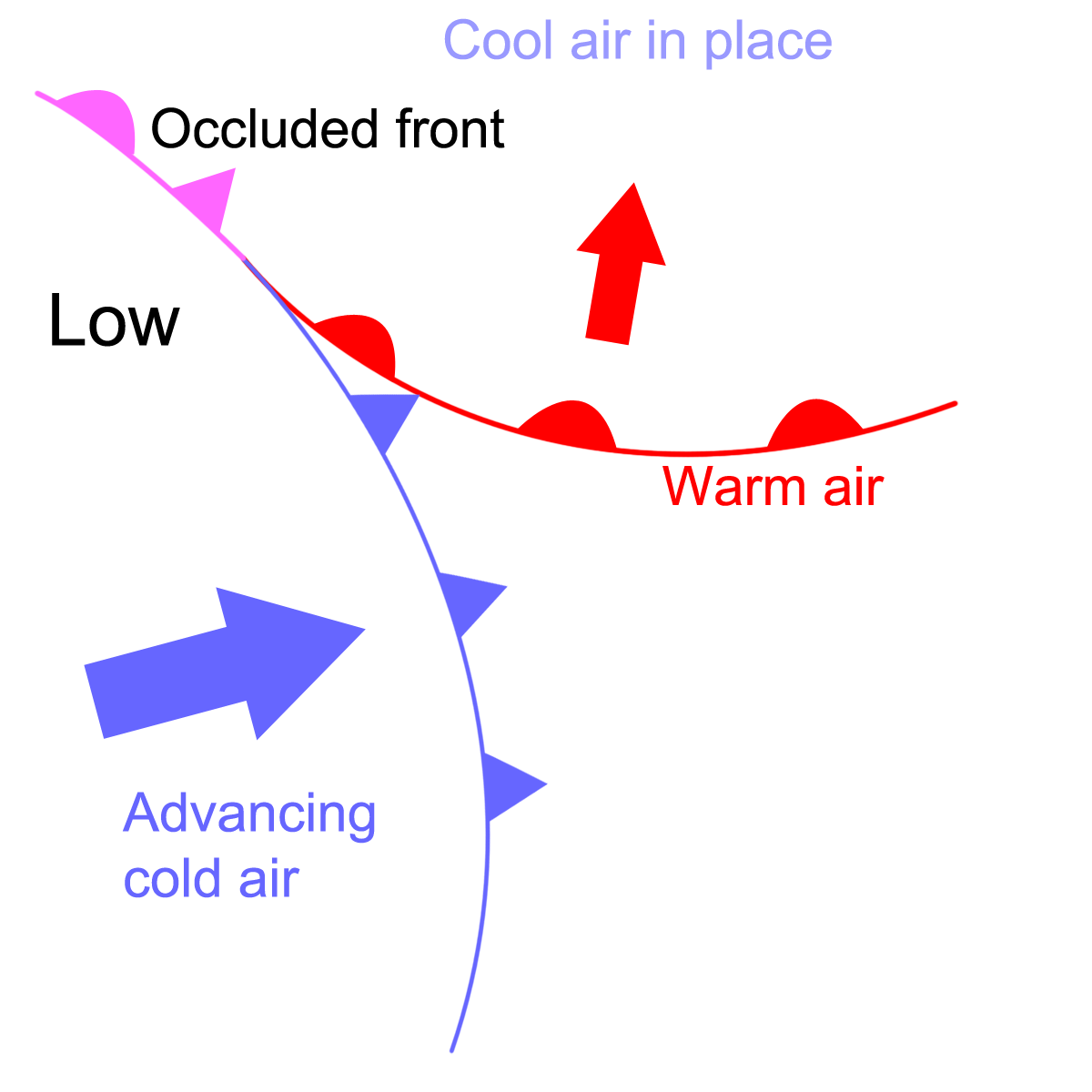
Cold Sector
Region behind a cold front, featuring cold, dry, windy conditions and clearing skies.
Warm Sector
Warm moist air between cold and warm fronts, often unstable with thunderstorms.
Cool Sector
Cooler region ahead of a warm front with widespread cloudiness and steady rain.
Comma Cloud Signature
Satellite image pattern indicating a mature mid-latitude cyclone.
Occlusion
Stage where cold front catches warm front, cutting off energy supply and weakening the cyclone.
Colorado Low
Mid-latitude cyclone forming east of Rockies, often producing severe winter storms.
Gulf Low
Moist cyclones forming over Gulf of Mexico that can produce flooding rains.
Hatteras Low
Cyclone forming off North Carolina coast, often leading to nor'easters.
Alberta Clipper
Fast, dry, cold cyclones moving southeast from Canada, producing light snow and strong winds.
Nor'easter
Coastal low-pressure storm bringing heavy snow, coastal flooding, high winds to Northeast U.S.
Single-Cell Thunderstorm
Short-lived storm with distinct updraft, mature, and dissipating phases.
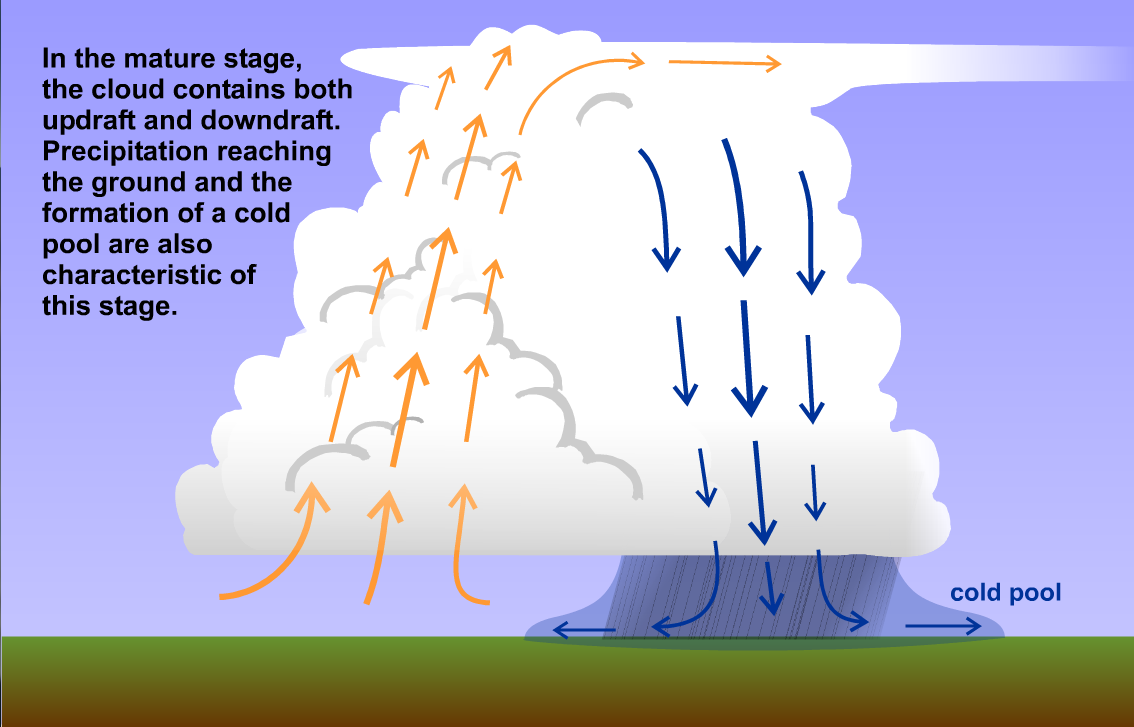
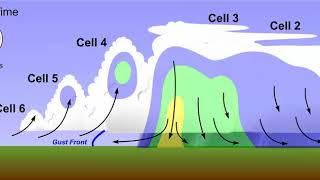
Multi-Cell Thunderstorm
Cluster of storms formed by outflow boundaries, sustaining longer-lived severe weather.
Supercell Thunderstorm
Rotating thunderstorm with strong persistent updraft (mesocyclone), capable of producing major tornadoes.
Mesocyclone
Rotating updraft within a supercell, precursor to tornado formation.
Outflow Boundary
Leading edge of cooler air from downdraft that can trigger new storms.
Anvil Cloud
Flattened cloud top of a thunderstorm spread by upper-level winds.
Squall Line
Organized line of intense thunderstorms ahead of a cold front.
Severe Thunderstorm
Storm producing hail ≥1", winds ≥58 mph, and/or tornadoes.
Watch
Conditions are favorable for severe weather; stay alert.
Warning
Severe weather is occurring or imminent; take shelter immediately.
Hail
Ice that forms in strong updrafts, gaining layers as it cycles within the storm.
Wet Growth
Clear hail layers formed by water freezing slowly in abundant moisture.
Dry Growth
Opaque hail layers formed by rapid freezing of droplets.
Lightning
Electrical discharge balancing differences in charge within clouds or between cloud and ground.
Thunder
Sound wave caused by rapid expansion of superheated air from lightning.
Stepped Leader
Initial invisible channel of negative charge descending from a cloud before lightning strike.
Return Stroke
Visible upward current creating the bright flash of lightning.
Dart Leader
Subsequent lightning channel that recharges the pathway and produces multiple flashes.
Anvil Crawler
Lightning traveling horizontally across the top of thunderstorm anvils.
Waterspout
Tornado occurring over water, usually weaker than land tornadoes.
Derecho
Long-lived windstorm caused by fast-moving bow-shaped thunderstorms, producing widespread damage.
Microburst
Powerful localized downdraft producing damaging straight-line winds over small areas.
Haboob
Large dust storm produced by thunderstorm outflow winds in arid regions.
Dust Devil
Small rotating column of air formed on hot, dry surfaces; non-thunderstorm phenomenon.
Weather Balloon
Instrument package launched twice daily to measure temperature, humidity, wind, and pressure in upper atmosphere.
Radar
Uses radio waves to detect precipitation location, movement, intensity, and rotation.
Satellite
Observes cloud cover, storm development, and temperature from space, especially over oceans.
UTC/Zulu Time
Coordinated universal time used on weather maps; Knoxville = 4-5 hours behind depending on daylight saving.
Model Output Statistics (MOS)
Computer-based forecast data offering temperature, precipitation, and cloud predictions for local areas.
Tornado
Narrow, violently rotating column of air extending from thunderstorms to the ground.
Wall Cloud
Lowered, rotating cloud base beneath a mesocyclone; often where tornadoes form.
Rear Flank Downdraft (RFD)
Dry descending air wrapping around a mesocyclone, helping tighten rotation.
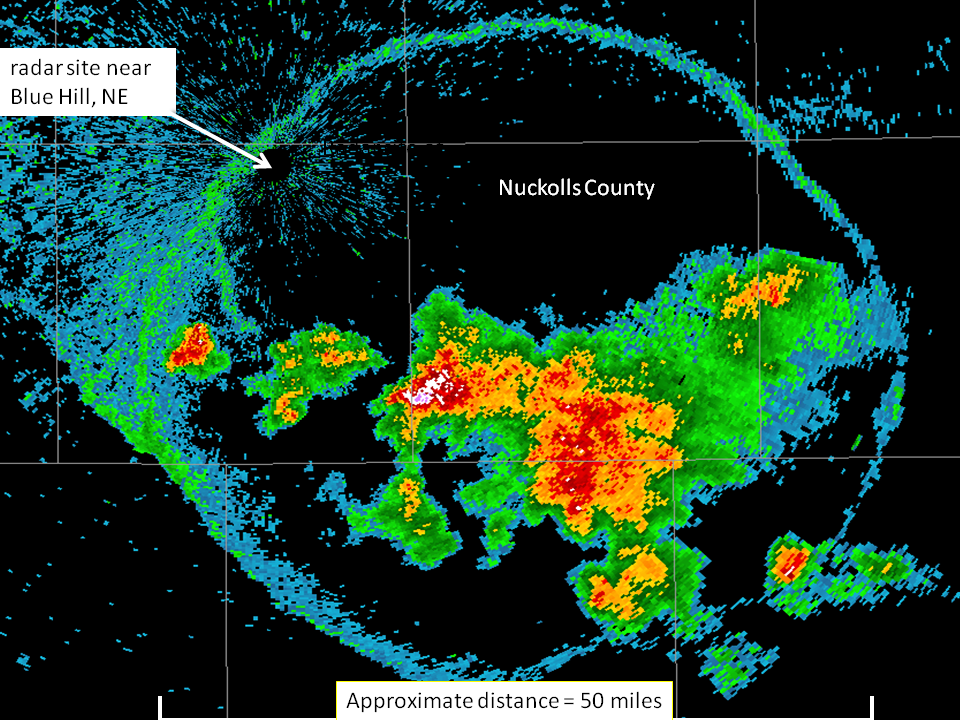
Hook Echo
Radar signature showing rotation and potential tornado development.
Enhanced Fujita Scale (EF Scale)
Damage-based tornado rating scale from EF0 to EF5 estimating wind speed.
Tornado Climatology
Study showing most tornadoes occur in central U.S. due to unique geography and air mass collisions.
Tropical Cyclone
Warm-core rotating storm system fueled by ocean heat, with no attached fronts.
Eye
Calm, clear center of a tropical cyclone with sinking air.
Eyewall
Ring of strongest winds, heaviest rain surrounding the eye.
Storm Surge
Coastal flooding caused by hurricane winds pushing ocean water onshore.
Hurricane Ingredients
Warm water ≥80°F, low wind shear, moist environment, instability, Coriolis force.
Hurricane Strengthening
Occurs over warm water with low shear and high moisture.
Hurricane Weakening
Occurs when storms encounter land, cold water, dry air, or high wind shear.
Cabo Verde Hurricane
Long-track hurricanes originating near West Africa that can impact Caribbean and U.S.