kang - UTI
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
anatomy
the urinary tract filers and excretes waste and extra fluid from the bloodstream
kidneys work to filer 120-150 quarts of blood to produce 1-2 quarts of urine
ureters carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder
bladder stores urine and will empty through the urethra
urinary tract infection (UTI)
defined as the presence of microorganisms in the urinary tract that canNOT be accounted for by contamination
classified as either uncomplicated or complicated
uncomplicated UTI
infection confined to the bladder in afebrile women or men
complicated UTI
infection beyond the bladder in women or men
pyelonephritis
febrile or bacteremic UTI
catheter-associated (CAUTI)
prostatitis (*not covered by these guidelines)
epidemiology
7 million cases of acute cystitis in the US per year
health care costs = ≥ $1 billion annually
25-40% of women will experience at least one UTI during their lifetime
UTIs in men occur much less frequently until the age of 65 years which incidence rates in men and women are similar
ascending UTI pathophysiology
most common:
bacteria enter into urethra and travel up to bladder
in the bladder, bacteria may replicate, colonize, and ascend through the ureter to the kidneys
may be caused through sexual intercourse, inappropriate bathroom hygiene
descending UTI pathophysiology
hematogenous spread (infection from blood gets into urine)
S. aureus, Candida spp., Salmonella spp., Mycobacterium tuberculosis
why are UTIs more common in females then males?
urethra:
men have longer urethra to the bladder —> heard to reach
prostate:
men have prostates that can get larger and block the urethrea
host defense mechanisms
urination:
low pH (~6)
high urea concentration
extremes in osmolality
urinary mucus:
coats bladder epithelial cells (interferes w/ bacterial adherence)
females:
vaginal flora (Lactobacillus)
males:
prostate secretes zinc (inhibit bacterial growth)
risk factors
age:
females: post-menopause results in ↓ estrogen & lactobacili —> ↑ vaginal pH
males: BPH —> urinary retnetion
female:
shorter urethra, proximity to perirectal area
diabetes:
glucose in urine promotes bacterial growth and impairs leukocyte function; predisposition to neuropathy
pregnancy:
↑ progesterone leads to ureter dilation, slowing the flow of urine
neurological dysfunction:
urethral sphincter muscle functions abnormally —> problems w/ continence or voiding
urinary obstruction:
results in incomplete bladder emptying
inhibits normal flow of urine
urinary catheterization:
inhibits normal flow of urine
foreign body that creates opening into bladder
sexual intercourse:
facilitate transport of bacteria
use of spermicides:
disrupts vaginal normal flora
UTI etiology
UPEC: Uropathogenic E. Coli
subjective — symptoms
pyelonephritis (kidney) — upper UTIs
flank pain
costovertebral angle (CVA) tenderness
fever
N/V
+ all all sx of cystitis
cystitis (bladder) — lower UTIs
dysuria
urinary frequency/urgency
suprapubic pain
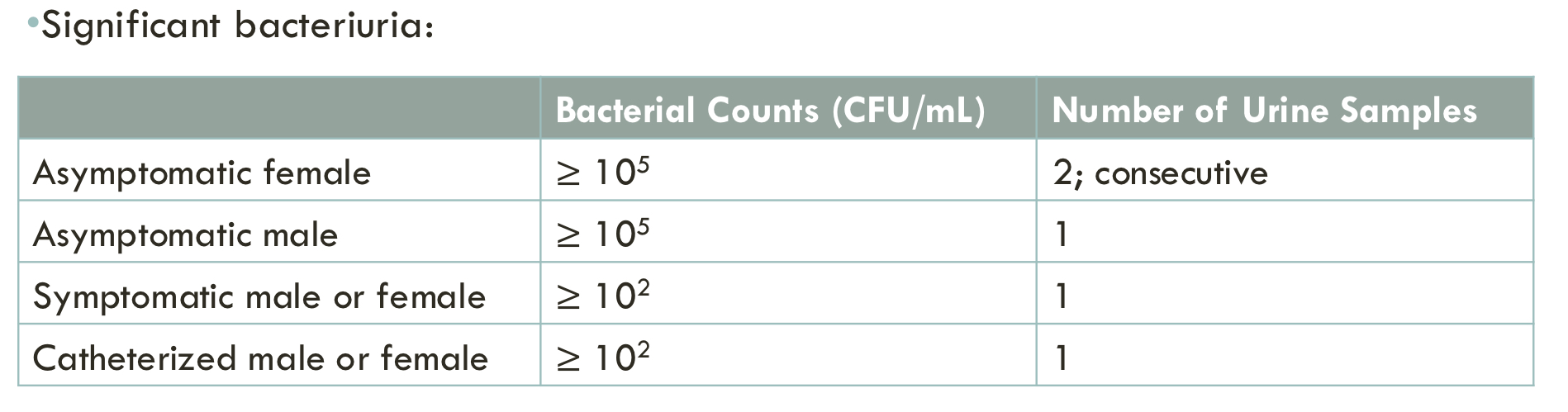
urine culture sampling
proper interpretation depends on appropriate urine collection techniques
mid-stream clean catch (most practical/preferred method)
minimizes probability of catching skin contaminants
catheterization
change out catheter if possible before sampling
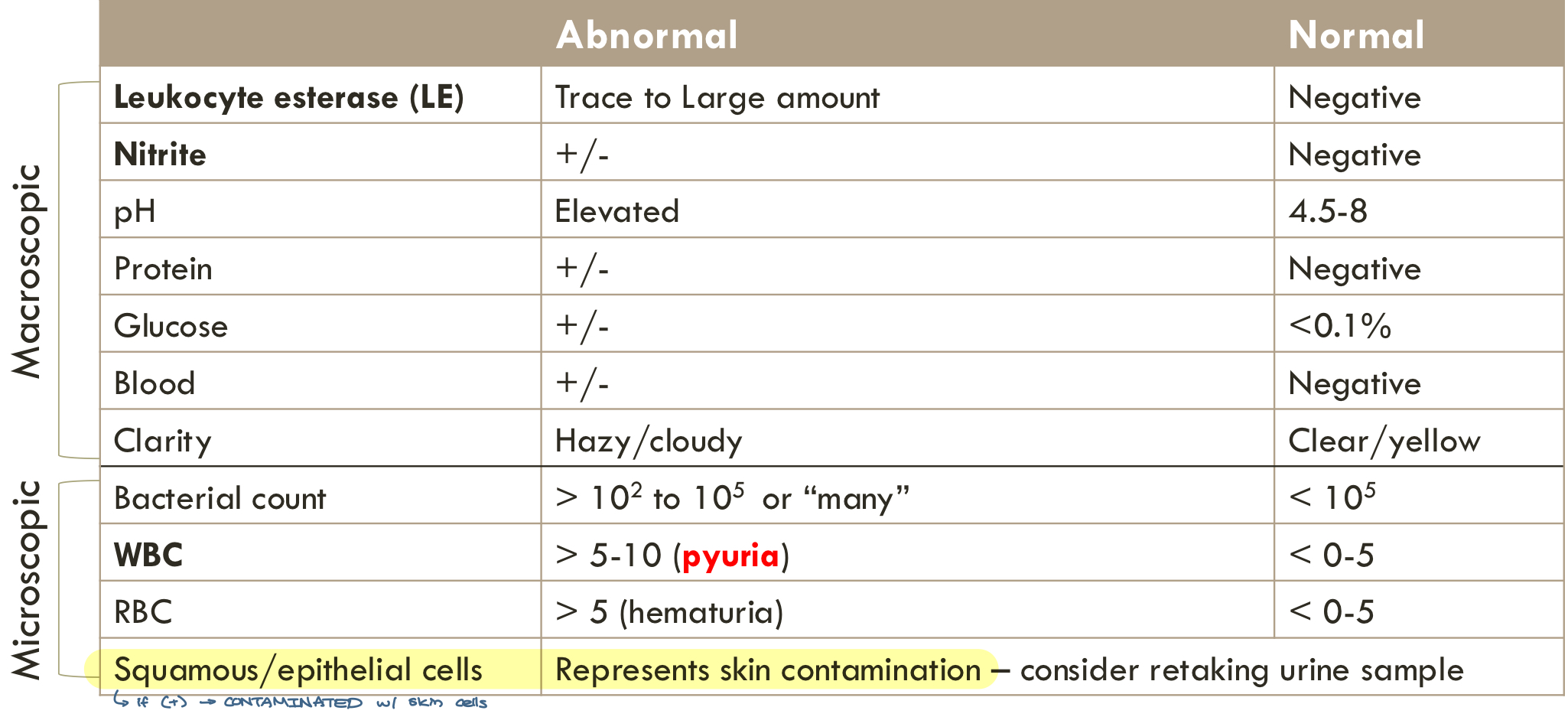
objective urinary analysis (UA) — macroscopic/dipstick
*always preformed + urine culture
leukocyte esterase
nitrate
specific gravity
pH
protein, glucose, ketones
bilirubin
blood
objective urinary analysis (UA) — microscopic
*NOT always preformed
bacterial count
WBC
RBC
squamous epithelial cells
casts
abnormal urinary analysis
objective — urinary culture (UC)
reports organisms grown from culture obtained, results take 24-48 hrs
always interpret results in conjunction with urinalysis and patient presentation
urosepsis
commonly used to describe the sepsis syndrome caused by UTI
includes clinical evidence of UTI plus 2 or more of the follwoing:
temp > 38°C or < 36°C
HR > 90 bpm
RR > 20/min or PaCo2 < 32 mmHg
WBC > 12k/mm3, < 4k/mm3, or > 10% band forms
factors affecting antibiotic selection
host factors:
allergy
age
comorbidities/immune status
clinical status
history of resistant infections
recent hospitalization/previous antibiotics
site of infection
drug factors:
SOA
PK/PD
route of administration
ADEs
DDIs
cost-effectiveness
other factors:
local resistance patterns (look at antibiogram)
stewardship
ease of administration
first line for uncomplicated cystitis
nitrofurantoin (Macrobid) 100 mg pO BID w/ food for 5 days
trimethoprim (TMP)-sulfamethoxazole (SMX) (Bactrim) 160-800mg 1 tab PO BID for 3 days
fosfomycin (Monurol) 3gm PO x 1 dose (mix in 120 mL water) for 1 day
*less effective than Bactrim & FQ
nitrofurantoin (Macrobid)
covers: E. coli (includes ESBL), E. faecalis (includes VRE), S. saprophyticus
a combination of nitrofurantoin monohydrate and nitrofurantoin macrocrystals (Macrobid) BID vs Nitrofurantoin macrocrystals (Furadantin, Macrodantin) QID
AVOID if suspecting any of the following infections: pyelonephritis or prostatitis
does NOT achieve therapeutic drug concentrations
does NOT penetrate prostatic secretions
eliminated by glomerular filtration, use if CrCl ≥ 30 mL/min (Beer’s criteria)
pregnancy: avoid during late 3rd trimester, weeks 38-42 (hemolytic anemia)
Bactrim
Spectrum of coverage includes: E. coli, S. saprophyticus
may be used in pyelonephritis and prostatitis
AVOID if local E. coli resistance >20% or if used for UTI in previous 3 months
ADR: rash, hyperkalemia, bone marrow suppression (high dose: 15 mg/kg/day TMP)
pregnancy: AVOID during 1st (congenital malformations) and 3rd (kernicterus)
fosfomycin (Monurol)
spectrum coverage includes: E. coli (including ESBL), E. faecalis (including VRE)
AVOID if suspecting pyelonephritis for Fosfomycin PO
oral powder: limited systemic absorption achieve therapeutic blood concentrations
ADR: diarrhea, nausea, dyspepsia
pregnancy: animal data shows no teratogenic effects, limited studies report efficacy and safety in all stages
2nd line treatment for uncomplicated cystitis
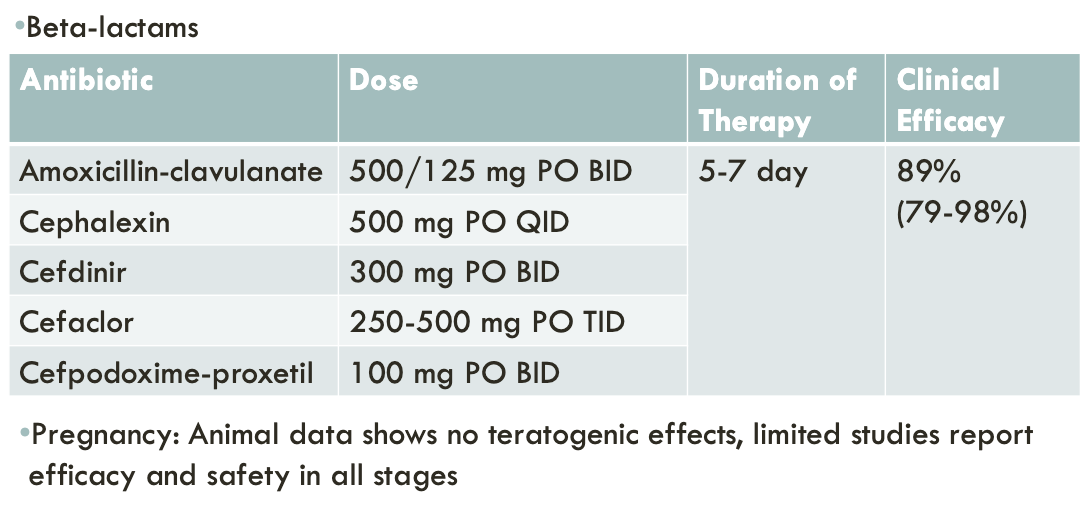
last line treatment for uncomplicated cystitis
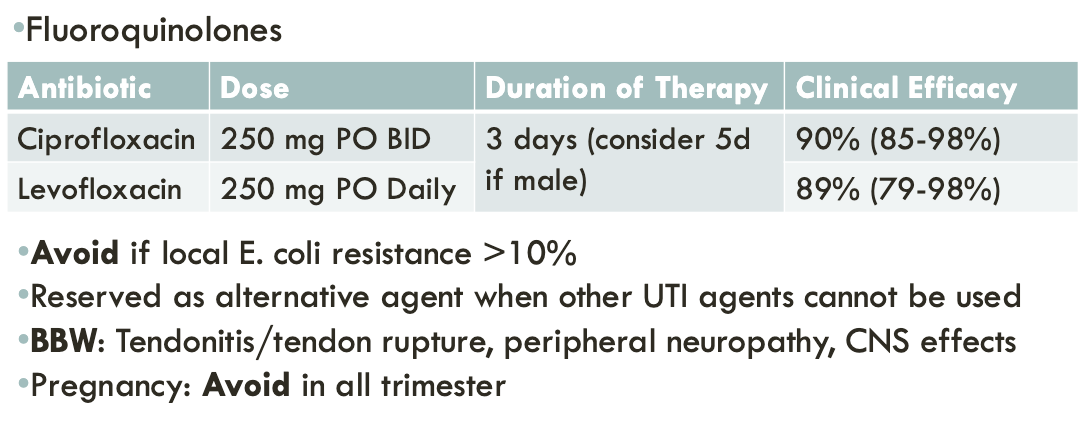
complicated UTI (cUTI)
therapy depends on:
severity of illness
risk factors for resistance
patient-specific considerations
if septic, consider the antibiogram
empiric antibiotic options for complicated UTI
sepsis with or without shock
preferred:
3rd or 4th generation generation cephalosporins
carbapenems
pip/tazo
fluroquinolones
alternatives:
novel beta-lactam-beta lactamase inhibitors
cefiderocol
plazomicin
older aminoglycosides
empiric antibiotic options for complicated UTI:
without sepsis, IV route of therapy
preferred:
3rd or 4th generation cephalosporin
pip/tazo
fluoroquinolones
alternatives:
carbapenems
novel beta-lactam-beta lactamase inhibitors
cefiderocol
plazomicin
older aminoglycosides
empiric antibiotic options for complicated UTI:
without sepsis, oral route of therapy
preferred:
fluoroquinolones
oral cephalosporins
alternatives:
Bactrim
Augmentin
empiric therapy for complicated UTI:
cefotaxime, ceftriaxone
coverage for enterobacterales
empiric therapy for complicated UTI:
cefepime, ceftazidime, pip/tazo
enterobacterales plus PSA
empiric therapy for complicated UTI:
carbapenems (meropenem, imipenem, ertapenem)
ESBL-producing enterobacterales
plus PSA (more meropenem and imipenem)
stepwise assessment of IV to PO switch
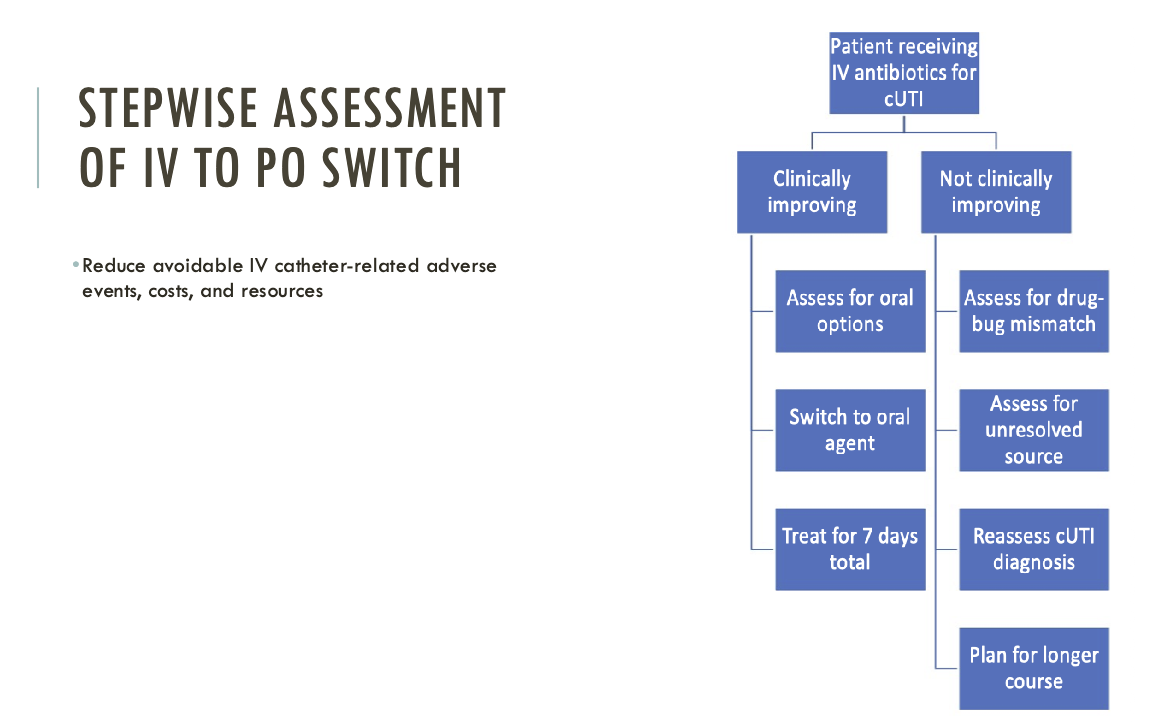
complicated UTI — catheter-associated
IDSA guidelines available to help guide therapy for catheter-associated UTI
makes 70-80% of complicated UTIs
complicated UTI treatment should be guided by patient history and presentation
does pt have a prior history of infeciton?
what are the likely pathogens causing infections?
is there evidence of urinary obstruction?
7 days is the recommended duration of therapy
if delayed response, treatment duration can be extended to 10-14 days
catheter-associated UTI (CA-UTI) treatment
after 30 days of catheterization, 75-95% of patients will have bacteriuria
asymptomatic pts —> do NOT treat
pyuria alone is not diagnostic
symptomatic pts —> catheter removal/change and treat for 7 days
if delayed response (> 72 hrs), may treat for 10-14 days
many present with nonspecific symptoms: fever, pelvic discomfort, altered mental status
complicated UTI — pregnancy
always treat both asymptomatic and symptomatic infections to prevent any complications
treat for 5-7 days
DOC:
cephalexin
amoxicillin-clavulante
AVOID:
all terms: fluoroquinolones
1st trimester: TMP-SMX
3rd trimester: TMP-SMX, nitrofurantoin (late, week 38-42)
asymptomatic bacteruria
presence of bacteriuria in pts without symptoms of lower or upper UTI
do NOT screen/treat UNLESS:
pregnant
undergoing urological surgical procedure
kidney transplant within 1 month
asymptomatic bacteriuria screening
in older pts with functional and/or cognitive impairment with bacteriuria and delirium (acute mental status change, confusion) and without local genitourinary symptoms or other systemic signs of infection (eg, fever or hemodynamic instability) we recommend assessment for other causes and careful observation rather than antimicrobial treatment
in renal transplant recipients who have had renal transplant surgery > 1 month prior, we recommend against screening for or treating ASB
candiduria asymptomatic
recurrent UTI
either:
≥ 2 UTIs occurring within 6 months OR
≥ 3 UTIs within one year
reinfections are caused by a different organism and account for the majority of recurrent UTIs
relapse represents the development of repeated infections caused by the same initial organism
recurrent UTI — lifestyle modifcations
behavioral modifications for prevention:
change contraceptive method if using spermicides
postcoital voiding
do NOT routinely delay voiding; after voiding wipe front to back
maintain adequate hydration
OTC options for prevention:
cranberry juice: help prevent bacterial attachment to uroepithelium (weak evidence)
lactobacillus: probiotics can help lower vaginal pH
may consider antimicrobial prophylaxis if ALL nonantimicrobial strategies attempted
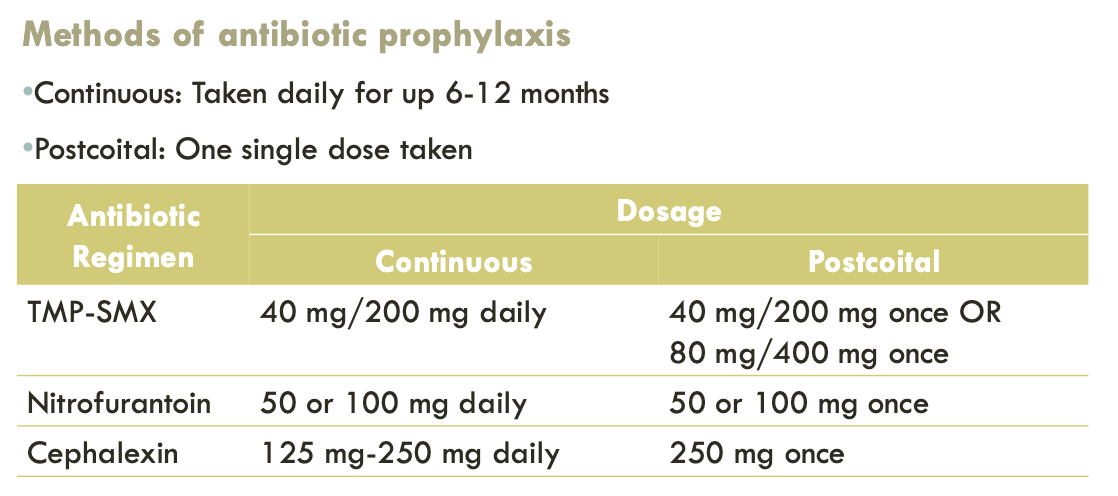
recurrent UTI — antibiotic prophylaxis
urinary tract analgesics

prostatitis — anatomy
the prostate functions to make fluid that goes into semen (sperm cells + fluid)
prostatitis is a painful or inflammatory condition affecting the prostate gland with or without bacterial eitology
the lifetime probability of a man receiving a diagnosis of prostatitis is >25%
if bacterial, will be classified as either acute or chronic bacterial postatitis
acute bacterial prostatitis — clinical presentation
urinary frequency, urgency, dysuria, nocturia
pain in the genital area, groin, lower abdomen, or lower back
urinary retentioin
urinary blockage
fever, chills, nausea, and vomiting
body aches
chronic bacterial prostatitis — clinical presentation
urinary frequency, urgency, dysuria, nocturia
pain in the genital area, groin, lower abdomen, or lower back
urinary retention
urinary blockage
painful ejaculation
acute bacterial prostatitis — treatment
ciprofloxacin 400 mg IV or 500 mg PO BID
levofloxacin 500-750 mg IV or PO daily
bactrim DS PO BID
treat 2-4 weeks
chronic bacterial prostatits — treatment
ciprofloxacin 400 mg IV or 500 mg PO BID
levofloxacin 500-750 mg IV or PO daily
bactrim DS PO BID
treat 4-6 weeks