2. diffusion and facilitated diffusion
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
TRANSPORT METHODS
PROPERTIES of cell membrane and molecules determine how they’re transported in and out of cells
SIZE of molecule and whether it’s SOLUBLE in lipids or water
small molecules that dissolve in lipids (hydrophobic) can pass through bilayer by diffusion (e.g. O2 and CO2)
larger lipid soluble molecules (e.g. steroid hormones) won’t pass through
many charged particles (hydrophilic) need specific carriers and channel proteins to make it through as they are water soluble
DIFFUSION AND CELLS
whether a substance can pass in or out of a cell by simple diffusion or not depends on its properties
to pass through a membrane by simple diffusion a substance needs to:
have a conc gradient going down
be small
be non-polar (lipid soluble)
FACILITATED DIFFUSION
substances with strong pos or neg charges (polar/water soluble) and large molecules can’t cross the membrane by simple diffusion
they still move passively from high to low conc using proteins
each type of protein will only allow one particular type of molecule through depending on its shape or charge
2 types of intrinsic proteins involved:
channel proteins (pores)
carrier proteins
FACILITATED DIFFUSION- VIA CHANNEL PROTEINS
channel proteins are water filled pores
water soluble ions (e.g. Na+) and polar molecules (glucose and AAs) can diffuse through these to the opposite side of the membrane
movement through channel protein faster than carrier
some have a gate that controls their permeability- can opened and closed
FACILITATED DIFFUSION- VIA CARRIER PROTEINS
carrier proteins have specific binding sites (receptors)
water soluble molecules bind to it causing protein to change shape
causes protein to rotate so molecule can cross membrane
FACILITATED DIFFUSION- INCREASE ROFR
increase no. of proteins
increase concentration gradient
increase temp
increase pressure
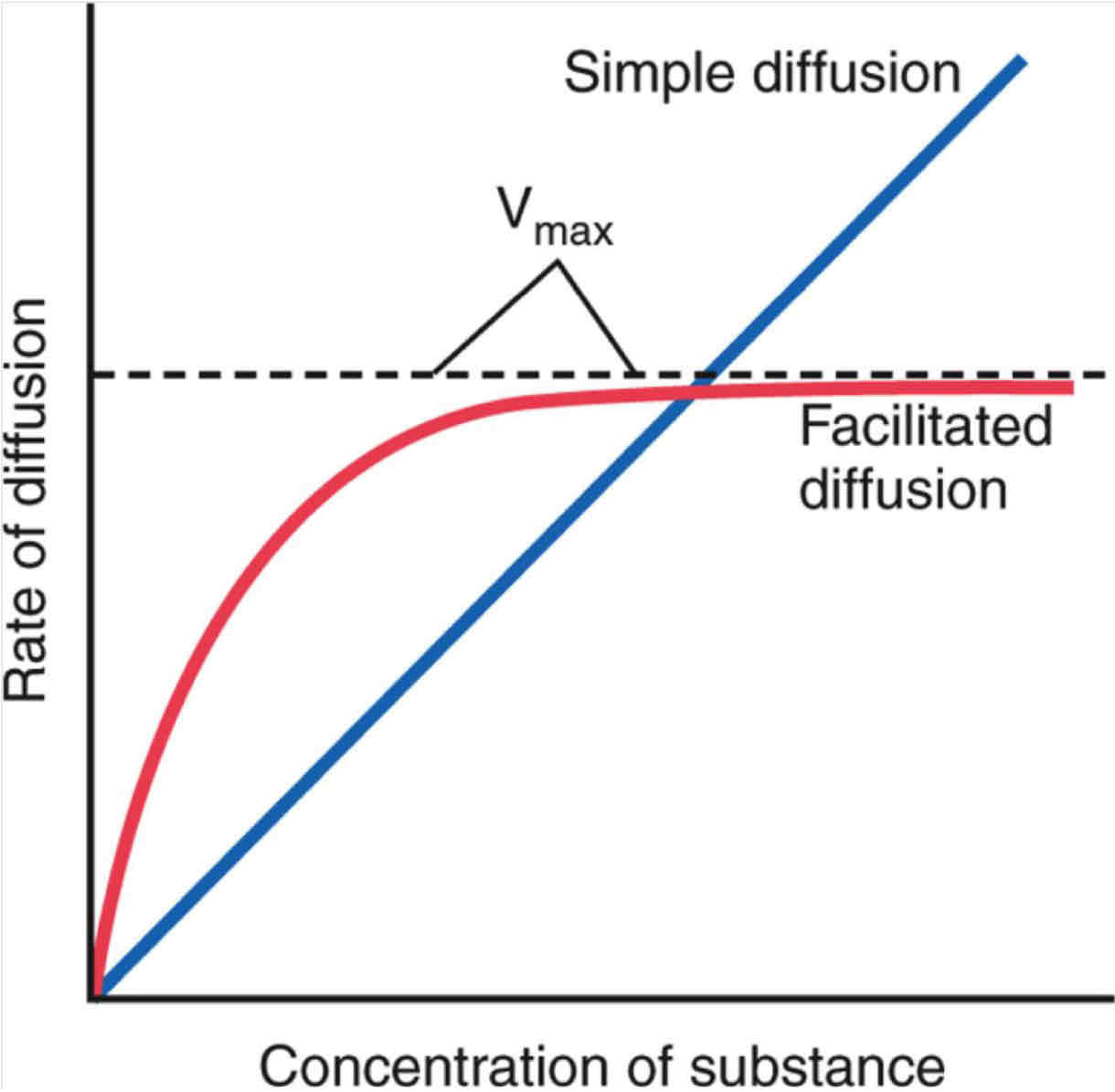
SIMPLE/FACILITATED DIFFUSION-GRAPHS
at low concs, facilitated diffusion is faster than simple
bc proteins in membrane allow substances to get through membrane easily
as conc increases the no. of available proteins becomes a limiting factor- eventually they will be at their max rate and at this point the rate of diffusion stops increasing (Vmax- max velocity)