Genomics and DNA Sequencing Techniques: Sanger and PCR Methods
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What is the purpose of DNA sequencing?
To identify gene and regulatory sequences from cloned DNA fragments.
What is dideoxy sequencing based on?
It is based on DNA polymerase extending a short oligo (primer) using cloned DNA as a template.
What happens to dsDNA during the dideoxy sequencing procedure?
It is heat-denatured to single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) before a primer anneals to one strand.
What components are included in the reaction mix for dideoxy sequencing?
ssDNA template, radioactive oligo primer, DNA polymerase, and four deoxynucleotide precursors.
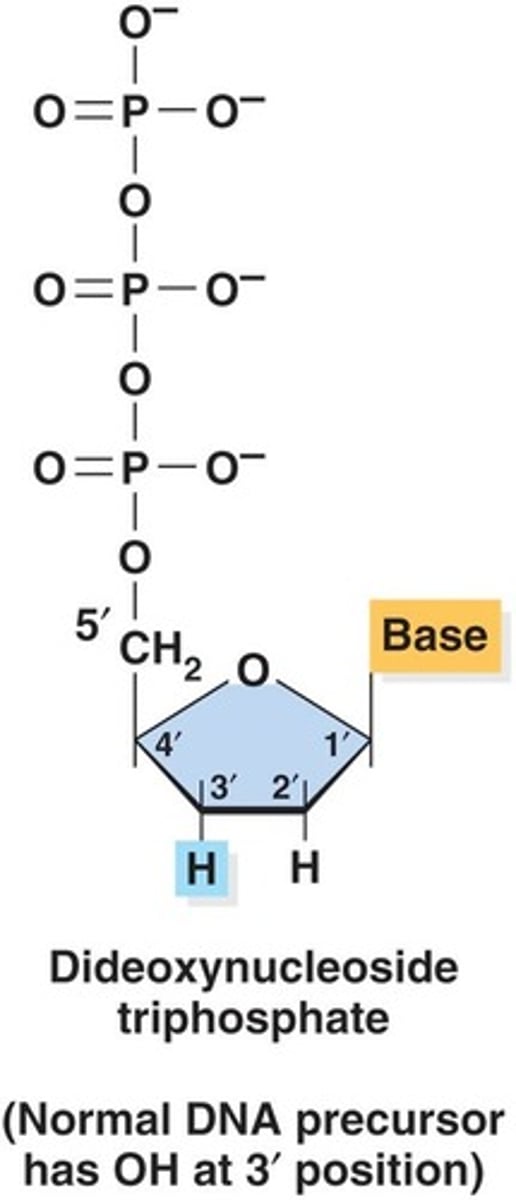
What is the role of dideoxynucleotides (ddNTP) in sequencing?
They lack 3'-OH and prevent the formation of phosphodiester linkages, terminating the DNA chain.
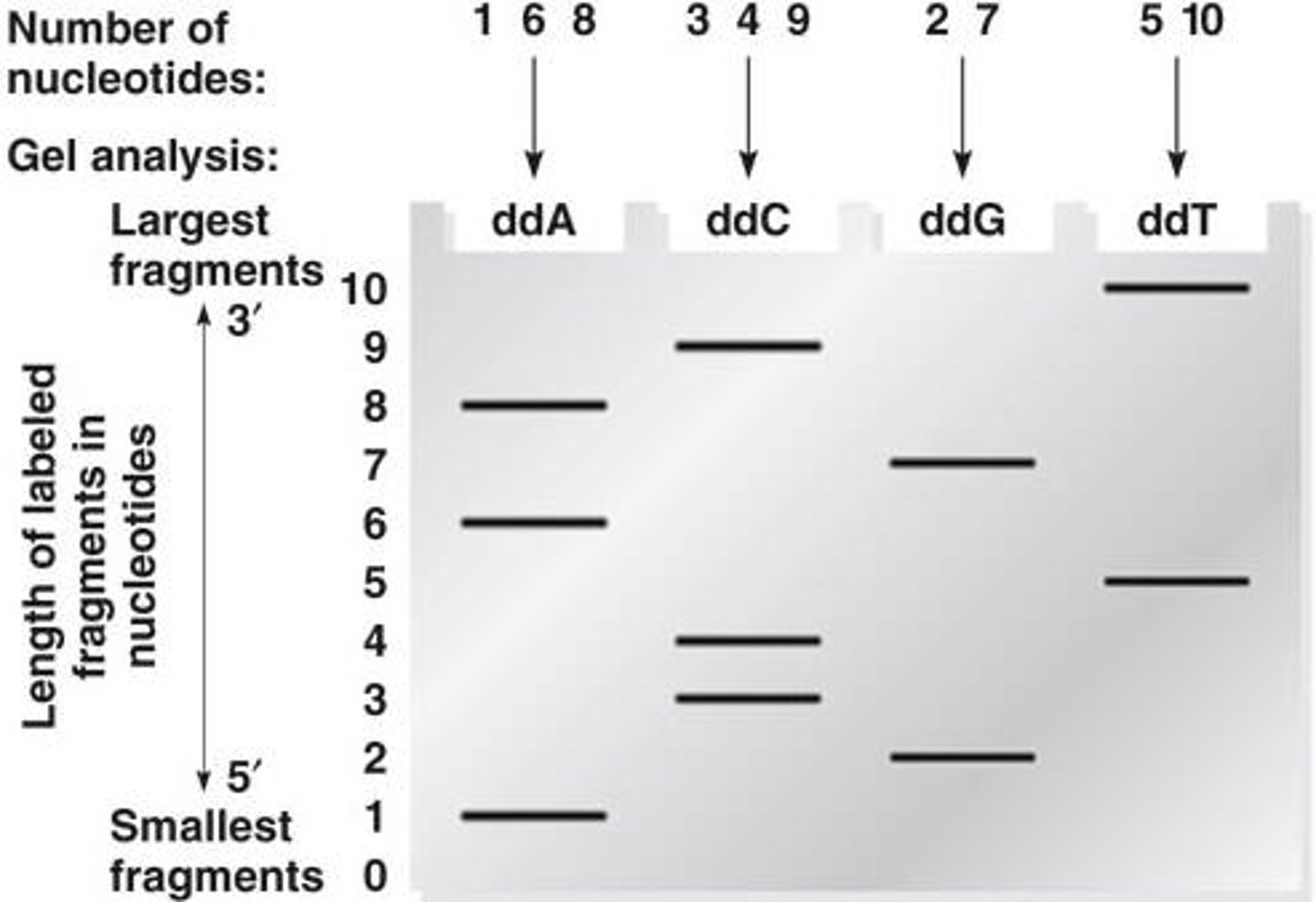
How is the sequence read in dideoxy sequencing?
The sequence is read from bottom to top (5' to 3') on a polyacrylamide gel.
What innovation does automated DNA sequencing introduce?
It uses a single reaction mix with all four ddNTPs, each tagged with a different fluorescent color.
What is the function of the laser scanner in automated DNA sequencing?
It scans the gel to determine the fluorescent label in each nucleotide band and sends the data to a computer.
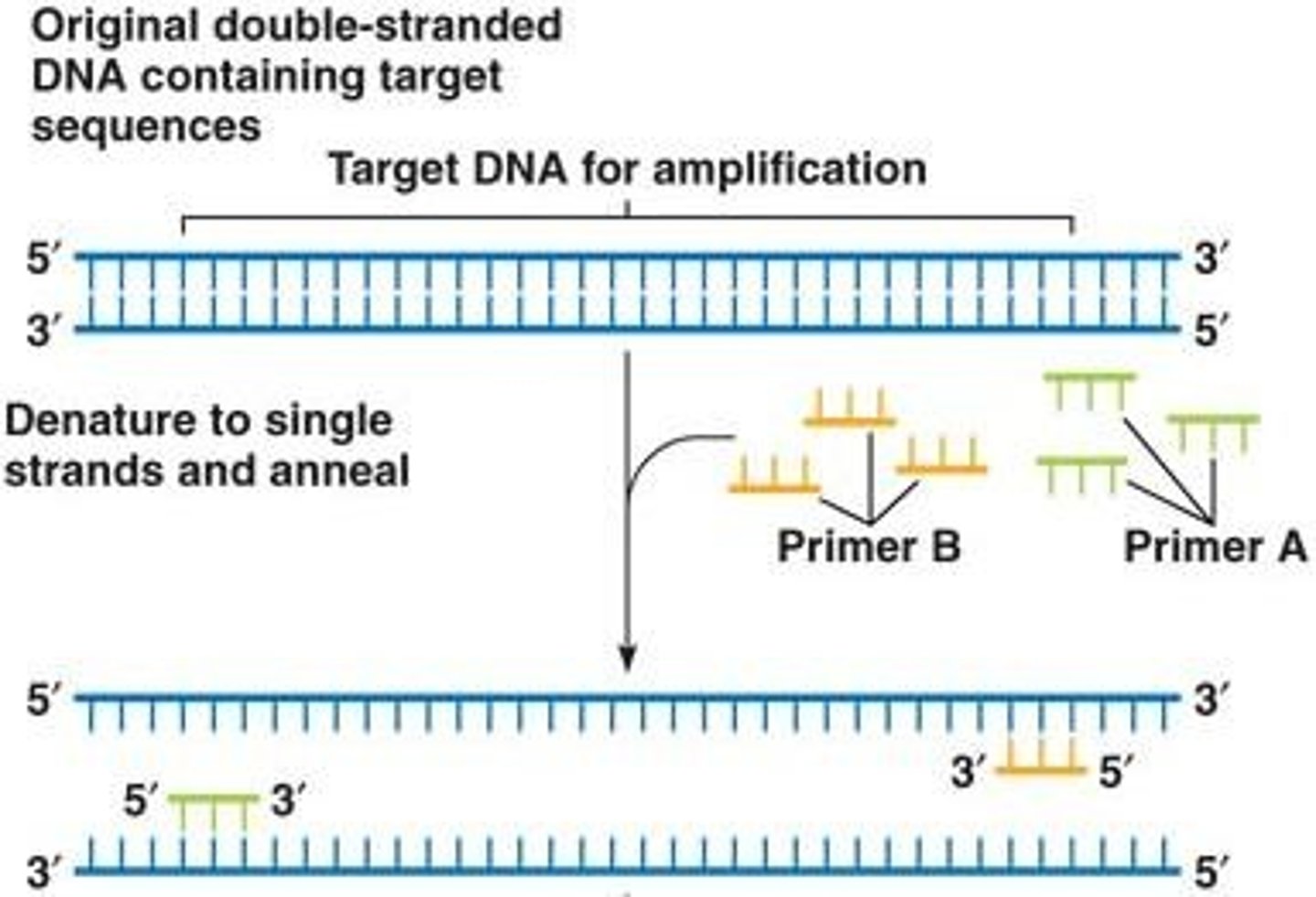
What is the purpose of the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)?
To produce many copies of a specific DNA sequence from a DNA mixture without cloning.
What type of DNA polymerase is used in PCR?
A heat-resistant DNA polymerase, such as Taq polymerase from Thermus aquaticus.
What are the main steps in the PCR process?
Denaturation, annealing of primers, and extension of primers with DNA polymerase.
How many cycles are typically repeated in PCR to achieve amplification?
Typically, 30 cycles are repeated to achieve millionfold amplification of the target DNA.
What are some applications of PCR?
Amplifying DNA for cloning, sequencing, disease diagnosis, and forensic analysis.
What is a limitation of PCR?
Specific primers require that sequence information be known, and PCR can only amplify up to ~40 Kb.
Who won the Nobel Prize for the dideoxy sequencing method?
Fred Sanger won his second Chemistry Nobel Prize in 1980.
What is the significance of Kary Mullis in relation to PCR?
He invented PCR and won the Chemistry Nobel Prize in 1993.