Laboratory Equipments | Flashcards
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
For memory and remembering of the different laboratory equipments and its usage.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
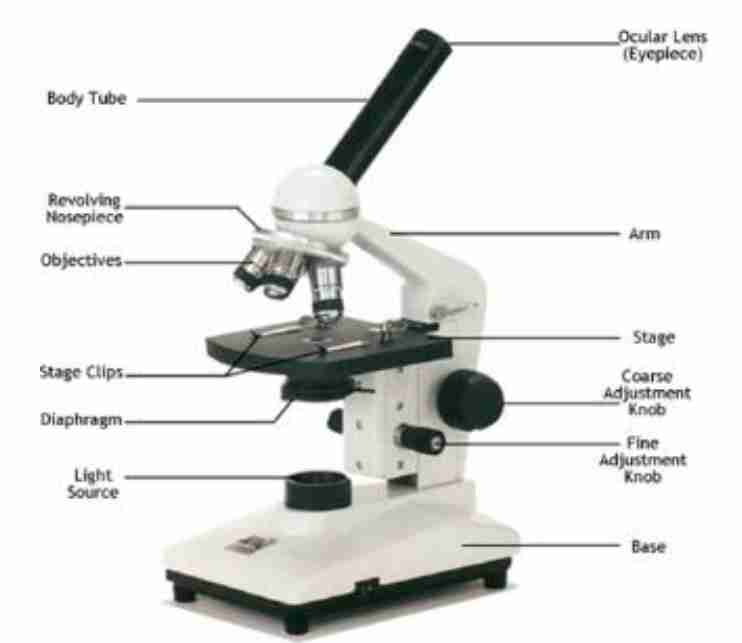

Microscope
Is an instrument used for magnifying and observing small objects.


Test tube
Are widely used by chemists to hold, mix, or heat small quantities of solid or liquid chemicals, especially for qualitative experiments and assays. Their round bottom and straight sides minimize mass loss when pouring, make them easier to clean, and allow convenient monitoring of the contents.


Beaker
Is a cylindrical glass or plastic vessel used for holding liquids. It is a multi- purpose piece of equipment used for containing a chemical reaction, measuring liquids, heating them over a Bunsen burner's flame or collecting them in a titration experiment.


Magnifying glass
The lens is used to magnify small objects such as insects or individual leaves on plants so that the viewer can better see them and the details on them. The amount of magnification depends on the power of the lens used, as well as the distance between the lens and the object


Volumetric Flask (measuring flask or graduated flask)
Is a piece of laboratory apparatus, a type of laboratory flask, calibrated to contain a precise volume at a certain temperature. It is used for precise dilutions and preparation of standard solutions.
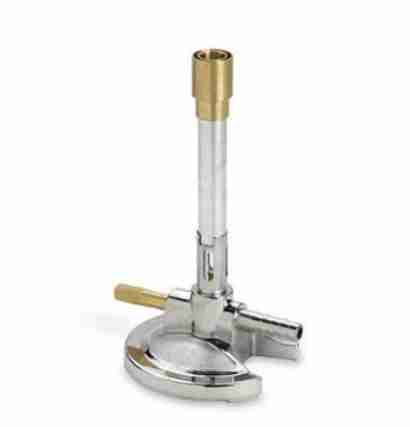


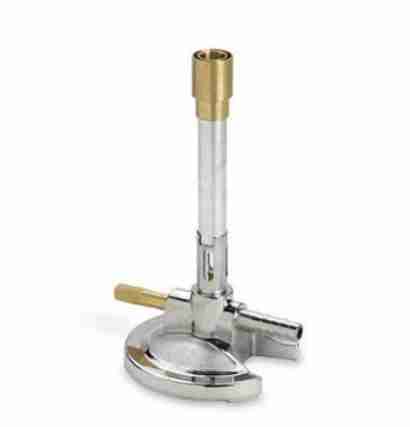
Bunsen Burner
Is a type of gas burner that is used in many chemistry procedures in a laboratory setting. It is used to heat substances, to combust substances, and to sterilize objects on high heat.
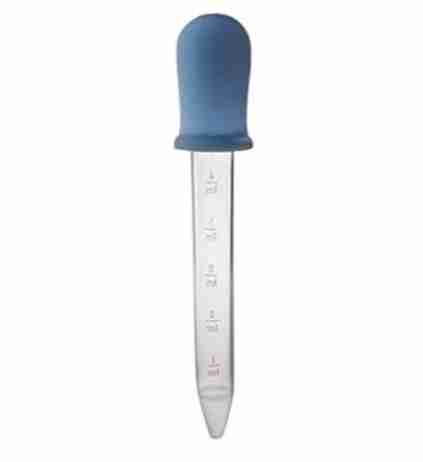


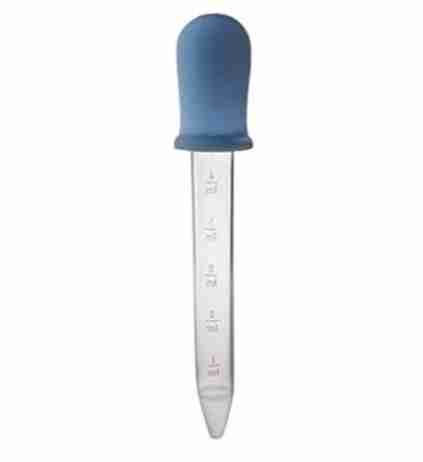
Dropper, also called Pasteur pipette or simply dropper
Is a device used to transfer small quantities of liquids. They are used in the laboratory and also to dispense small amounts of liquid medicines.
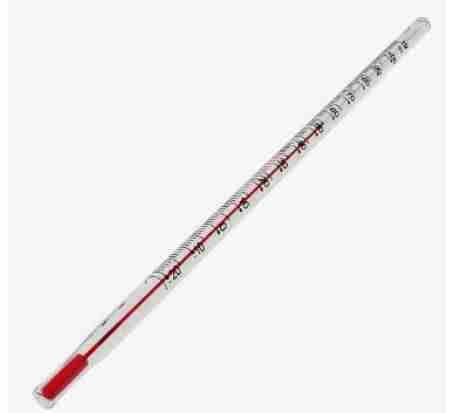


Thermometer
Are used to measure temperatures or temperature changes with a high degree of precision. They are made of metal or glass and strengthened through thermal tempering or annealing.


Tongs
Are tools used for grasping and handling hot materials.


Brushes
Is a brush with metal bristles used for cleaning equipment.


Weighing machines
Is an instrument used to measure the weight of materials.


Wash Bottles
Are laboratory consumables used for cleansing and sterilization purposes. These bottles are made up of plastic, which serves as a squeezy container with a long nozzle. They mostly contain distilled water, ethanol or deionized water.


Spatula
These are very much similar to the kitchen like utensil found in our home but they are just very smaller in size in comparison. They are usually resistant to heat and acids, hence making them suitable for large range use in the laboratory experiments.


Spring Balance
Also referred to as Newton meters, it is an another instrument helpful in measuring the weight of an object. This apparatus consists of a spring and a hook and it works on the principle of Hooke’s law, according to which, the force applied to an object is directly proportional to the extension, provided that the elastic limit is not reached.


Burette
Its mostly used in the titration reactions, and is handful in delivering a known volume of any substance to other equipment. This apparatus is a long-graduated tube, with a stopcock present at the lower end. It usually comes in the sizes of 10ml, 25ml or 50ml.


Watch Glass
This apparatus is more commonly found in chemistry laboratories and is made up of a concave piece of glass. It is normally used to hold solids, evaporate liquids, and heat small quantities of different substances as per the need of the experiment.


Funnel
Are necessary equipment to pour substances and solutions in narrow-mouthed test tubes and conical flasks. There is variety of its available, most common ones are filter, thistle, and dropping funnels.


Crucible
Are made up of porcelain and are used to store and heat substances when required to be heated at high temperatures since glassware are not always suitable for such high heat involving experiments.

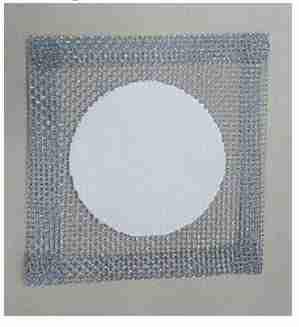
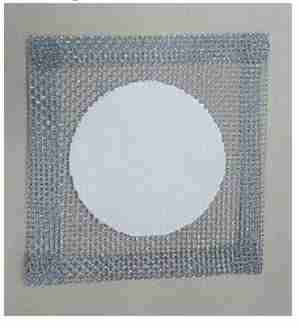
Wire gauze
Is a mesh screen used to support flasks and beakers during heating.

Petri Dish
Is a shallow, circular dish with a lid, used to culture microorganisms.


Centrifuge
Is a machine used to separate materials of different densities using centrifugal force.


Tripod
Is a three-legged stand used to support equipment such as beakers and flasks.


Graduated Cylinder
Is a cylindrical container used for measuring the volume of liquids.


Test Tube Holder
Is a tool used for holding and transporting test tubes.


Rubber Tubing
Is a flexible tube used to transfer liquids and gases.


Evaporating Dish
Is a shallow dish used for evaporating liquids.


Filter Paper
Is a thin, porous paper used for filtration.


Mortar and Pestle
Are tools used for grinding and mixing small amounts of materials.


Stirring Rod
Is a long, thin rod used for stirring solutions and suspensions.


pH meter
Is an instrument used to measure the acidity or basicity of a solution.


Test Tube Rack
Is a rack used to hold test tubes during experiments.


Clamps
Are used to hold equipment in place during experiments.


Rubber Stopper
Is a stopper made of rubber used to seal test tubes and flasks.


Retort Stand
Is a metal stand used to hold equipment such as clamps and wire gauze.

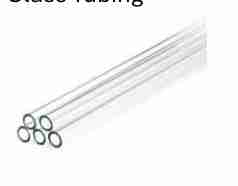
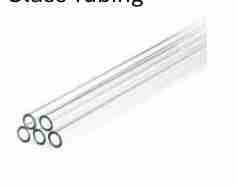
Glass Tubing
Is a thin, cylindrical glass tube used in chemical reactions and experiments.
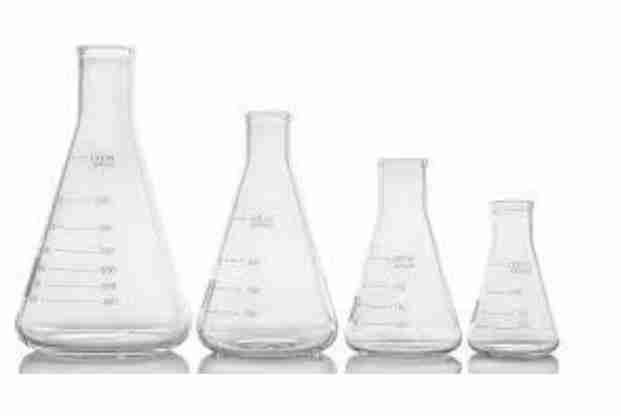

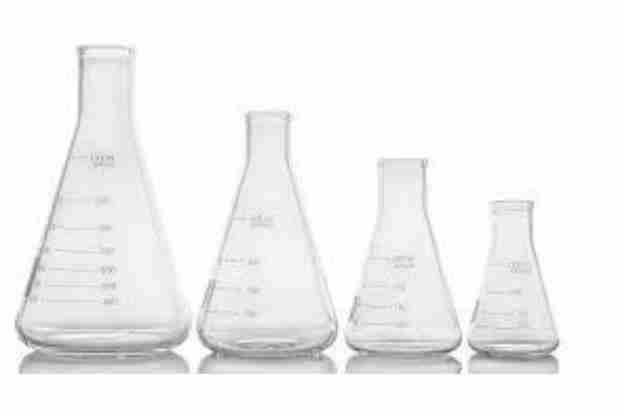
Erlenmeyer Flask
Are used to contain liquids and for mixing, heating, cooling, incubation, filtration, storage, and other liquidhandling processes
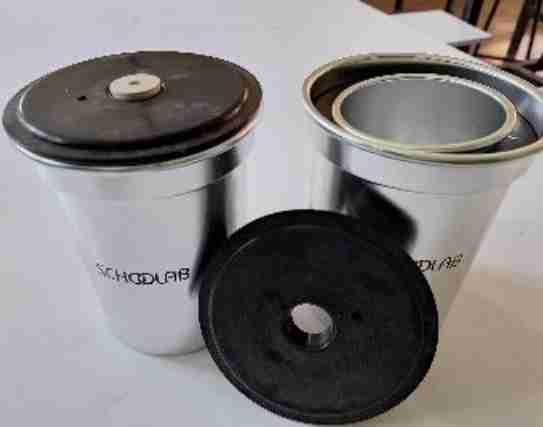


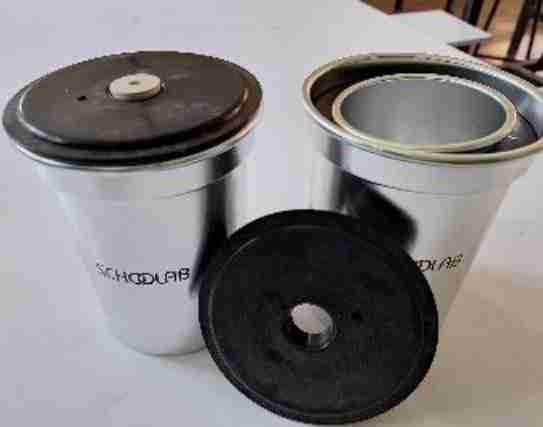
Calorimeter
Is a device used to measure the amount of heat involved in a chemical or physical process.


Alcohol Lamp or Spirit Lamp
Is a piece of laboratory equipment used to produce an open flame. It can be made from brass, glass, stainless steel or aluminium.


Reagent Bottle
Also known as media bottles or graduated bottles, are containers made of glass, plastic, borosilicate or related substances, and topped by special caps or stoppers. They are intended to contain chemicals in liquid or powder form for laboratories and stored in cabinets or on shelves.
