Lecture 18: Synapses & Sensory Receptors
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
2 types of synaptic transmissions
Chemincal, Electrial
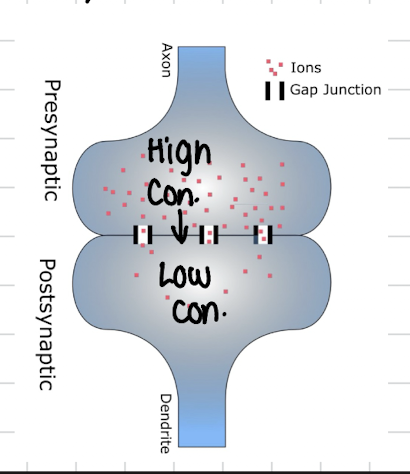
Electrical transmission
fast
connected to pre/post-synapses via junctions
transmits a signal directly
less common
allow ion flow
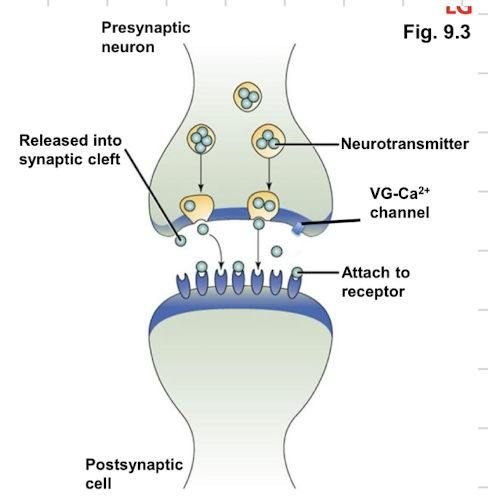
Chemical transmission
slower compared to electrical
signals transmitted via the synaptic vesicle (pre)
makes neurotransmitter (pre)
VG Ca2+ channels (pre)
NT binds to specific receptors in PM (post membrane)
Ligand-gated channels (post)
What are NT reduced by
Reuptake from the presynaptic neuron
Enzymatic decay
Diffusions
Types of changes in post-synaptic potential
Inhibitory ISPS (hyperpolaraztion)
Excitatory EPSP (depolarization)
depolarization
increases chance of AP
EPSP makes more +
Hyperpolarization
lowers changes of AP
IPSP, makes more -
Long Term Potenetion (LTP)
Long-lasting
greater synaptic strength
activity-dependent
Short term memory (STM)
7+/ 2
thrown away if not used
15-30secs
prefrontal cortex+ hippocampus
LTM
sleep consolidation
“Last forever”
LTP
Cerebal cortex+ hippocampus
What does LTP cause
more NT
More Ampa receptors
Synapse
junction btw synaptic terminal and another neuron
Synaptic cleft
The small gap between the presynaptic and postsynaptic neuron.
What triggers neurotransmitter release?
Calcium (Ca²⁺) entering the presynaptic terminal
Main excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain
Glutamate
AMPA receptor
A glutamate receptor that allows sodium to enter and causes fast excitation, triggered by Ca2+
Front: NMDA receptor
: A glutamate receptor involved in learning that allows calcium to enter.
What blocks NMDA receptors at rest?
Mg
What is required for NMDA receptors to open?
Glutamate binding and strong depolarization (CA2+ influx).
Why is calcium entry important?
It triggers long-term changes at the synapse.
What causes LTP?
Repeated stimulation and calcium entry through NMDA receptors.
One synaptic change during LTP
More AMPA receptors are added to the postsynaptic membrane
Sensory receptor
A cell that detects stimuli and converts them into electrical signals.
Sensory transduction
The conversion of a physical stimulus into a neural signal.
Sensory adaptation
A decrease in receptor response over time to a constant stimulus.
Mechanoreceptors
Receptors that respond to touch, pressure, or stretch.
Chemoreceptors
Receptors that respond to chemical stimuli.
Photoreceptors
Receptors that respond to light.
Thermoreceptors
Receptors that respond to temperature.
Key difference between AMPA and NMDA
AMPA is fast and lets in sodium; NMDA controls learning and lets in calcium.
Big picture of sensory pathway
stimulus → CNS → Response
Sensory reception
where stm is deteced detected
Transmission
sensory info travels via sensory neuron
Pathway of sensory
stim → sensory reception → Transduction → transmission → perception → response
What triggers an AP in the SN
receptor potential
2 types of photoreceptors
rods (strongly photosensitive, no color)
cones (less photosensitive, color)
Sensory reception of eyes
Corena → Aqueous humor → Lens → iris → pupil → viterous huomor → retina → Fovea → optic never
Retinal processing
rods and conn → bipolar cells → ganglion cells → optic nerve
Corena
Transparent
Aqueous humor
clear fluid
Lens
foucs light on retina and fovea Focus
Iris
Regulation the entry of the eye
pupil
opening
Vitreous humor
clear gel
Retina
lines back wall
Fovea
sharp ccentral vision
optic nerve
cranial nerve. Visual infro from retina to brain