Contraception
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
what are 3 reasons contraceptive are used for?
Prevent pregnancy
Space pregnancies
Avoid high risk pregnancy
A health-care provider can be reasonably certain that a woman is not pregnant if she _________ and meets _____ of the following criteria:
is ≤7 days after the start of normal menses
has not had sexual intercourse since the start of last normal menses
has been correctly and consistently using a reliable method of contraception
is ≤7 days after spontaneous or induced abortion
is within 4 weeks postpartum
is fully or nearly fully breastfeeding (exclusively breastfeeding or the vast majority [≥85%] of feeds are breastfeeds),* amenorrheic, and <6 months postpartum
has no symptoms or signs of pregnancy; one
what are 3 natural contraception methods? briefly explain each
coitus interruptus- pulling out
fertility awareness- avoiding intercourse while fertile
lactational amenorrhea-amenorrhea secondary to breastfeeding
what are the 3 categories on non-hormonal contraception methods?
barrier methods, vaginal preparations, copper IUD
what are the 2 barrier methods?
condoms and diaphragm/cervical cap
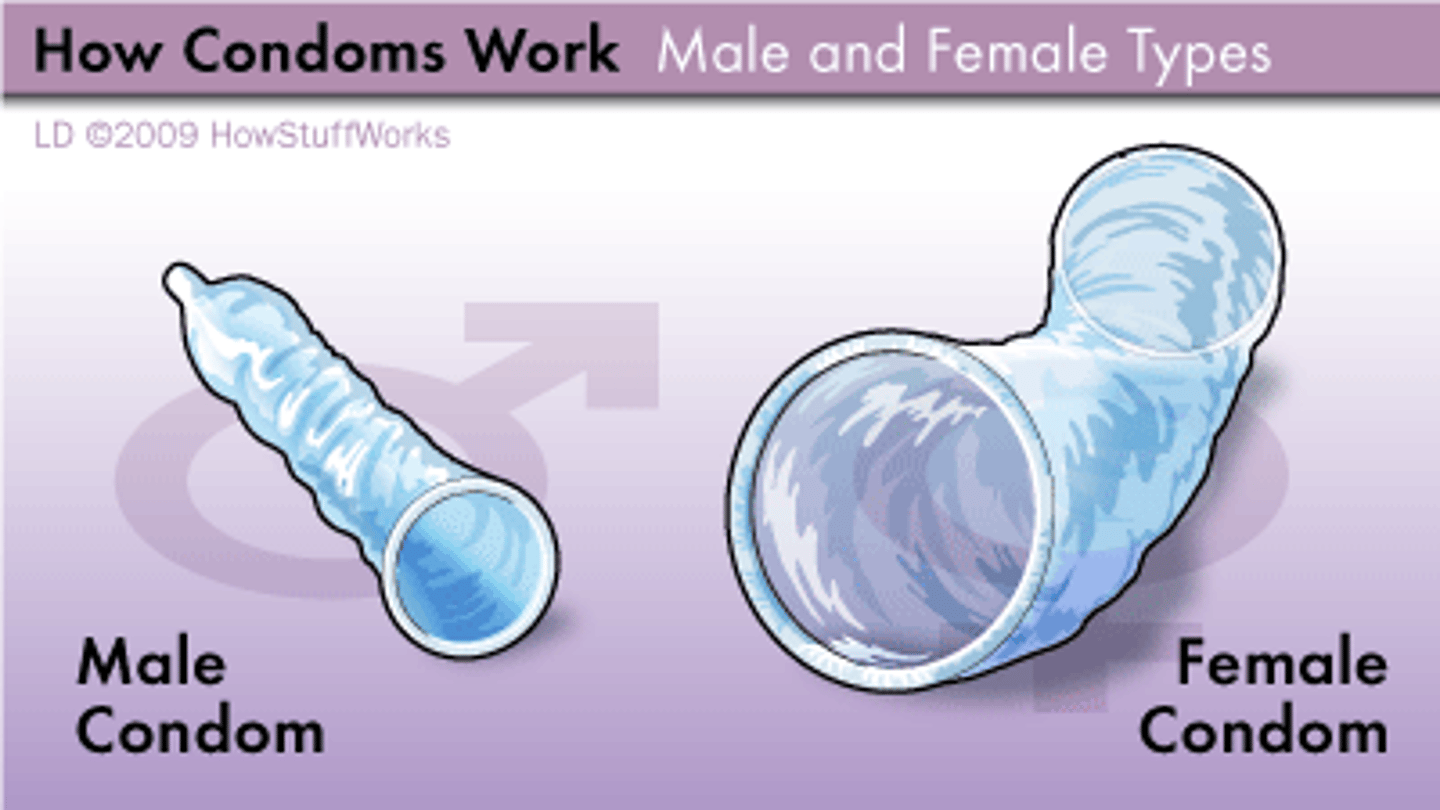
condoms
male and female Impermeable to sperm and STDs Can be used in combination with jelly or foam
what are some things to note about diaphragms/cervical caps?
Spermicide must be applied
Can be inserted up to 6 hours before sex, should stay in for 6 hours after sex but not longer than or 24 hours total
Must be fitted and prescribed by a provider (small, medium large)
Side effects include vaginal wall or cervical irritation from device or spermicide, TSS is rare but possible
diaphragm
Flexible rings with a membrane that covers the cervix
Decreased effectiveness with prolapse syndromes, retroflexed or anteflexed uterus, or shortened vagina
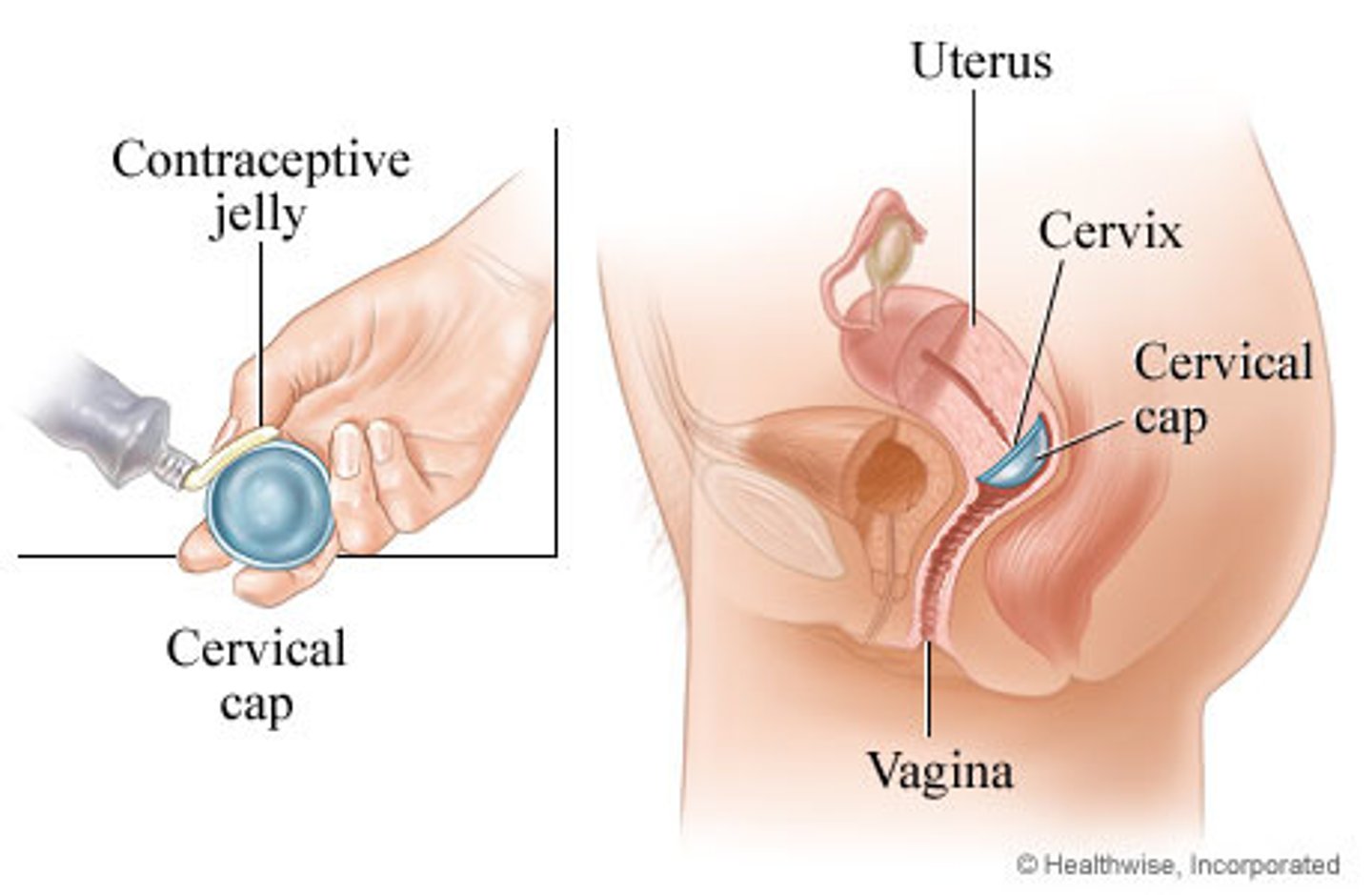
cervical cap
Fits with suction over the cervix
More difficult to insert and remove than the diaphragm
what are the 2 kinds of vaginal preparations? describe them
Prescription contraceptive gel (Phexxi®): Lowers vaginal pH (to 3.5-4.5), which incapacitates sperm
Spermicides: Contains nonoxynol-9, which results in sperm immobilization and death
what are some things to note about vaginal preparations?
Must be inserted shortly before intercourse, effective for up to one hour
Not considered effective in preventing STDs, some studies show that spermicides may increase STD risk
Side effects include vaginal and vulvar irritation
what are the 3 types of combination hormonal birth control methods?
pills, rings, transdermal patches
what are combination oral contraceptive pills initiated? what are the possible ratios/patterns of pills/placebo pill dosing?
Initiated on day 1 of menses, or any time if the provider is reasonably certain that there is no pregnancy
21/7, 24/4, 84/7, 365/0, continuous active pills
which progesterone only OCP is approved for mild-moderate acne and PMDD?
Drospirenone
what are the 2 brands of vaginal rings? differentiate them
Nuvaring®
transparent, ethinyl estradiol/etonogestrel continuous release, lifespan of 1 cycle, refrigeration required
Annovera®
thicker, white, softer, ethinyl estradiol/segesterone acetate continuous release, life span of 13 cycles, no refrigeration
what are the 2 brands of transdermal patches? what is the day system?
Xulane® and Twirla®
28 day system - one patch is applied weekly for three weeks and on the fourth week no patch is worn
what is the MOA for cOCPs?
Inhibition of ovulation by negative feedback on the synthesis and release of GnRH from the hypothalamus, limiting pituitary gonadotropin effect which suppress ovulation
cOCPs suppress ovulation but what other secondary mechanisms do they have to prevent pregnancy
thickening of cervical mucous, decreased ciliary action in the fallopian tubes, and thinning of the endometrium
what are contradictions based upon CDC and WHO date for cOCPs?
Known or suspected pregnancy
Age ≥35 years and smoking ≥15 cigarettes per day (vaping)
Known ischemic heart disease or two or more risk factors for IHD
Hypertension with ≥ 160, diastolic ≥ 100, and/or with vascular disease
Current venous thromboembolism, or history of not receiving anticoagulation
Thrombogenic mutations
History of stroke
Complicated valvular heart disease
Current breast cancer
Cirrhosis
Migraine with aura
Hepatocellular adenoma or malignant hepatoma
which combination hormonal method has the advantage of possibly improving sexual function?
ring
2 multiple choice options
which combination hormonal method has the risk of toxic shock syndrome?
ring
2 multiple choice options
which combination hormonal method has the risk of increased thyroxine binding globulin and cortisol binding globulin?
patch
2 multiple choice options
which combination hormonal method has the possible side effect of amenorrhea?
cOCPs
2 multiple choice options
which combination hormonal method has the possible side effect of dysmenorrhea?
patch
2 multiple choice options
which combination hormonal method has the possible side effect of vaginitis?
ring
2 multiple choice options
which combination hormonal method shows lower rates of insulin resistance?
ring
2 multiple choice options
what are 3 systemic progesterone only contraception methods?
progesterone only contraceptive pills
depo-medroxyprogesterone acetate injection
subdermal implant
what are the 3 generic progesterone only contraceptive pills (POPs)? which have 28 active pills? which has 24 active pills? which can be purchased over the counter?
Norethindrone 28)
Drospirenone (24)
Norgestrel (over the counter, 28)
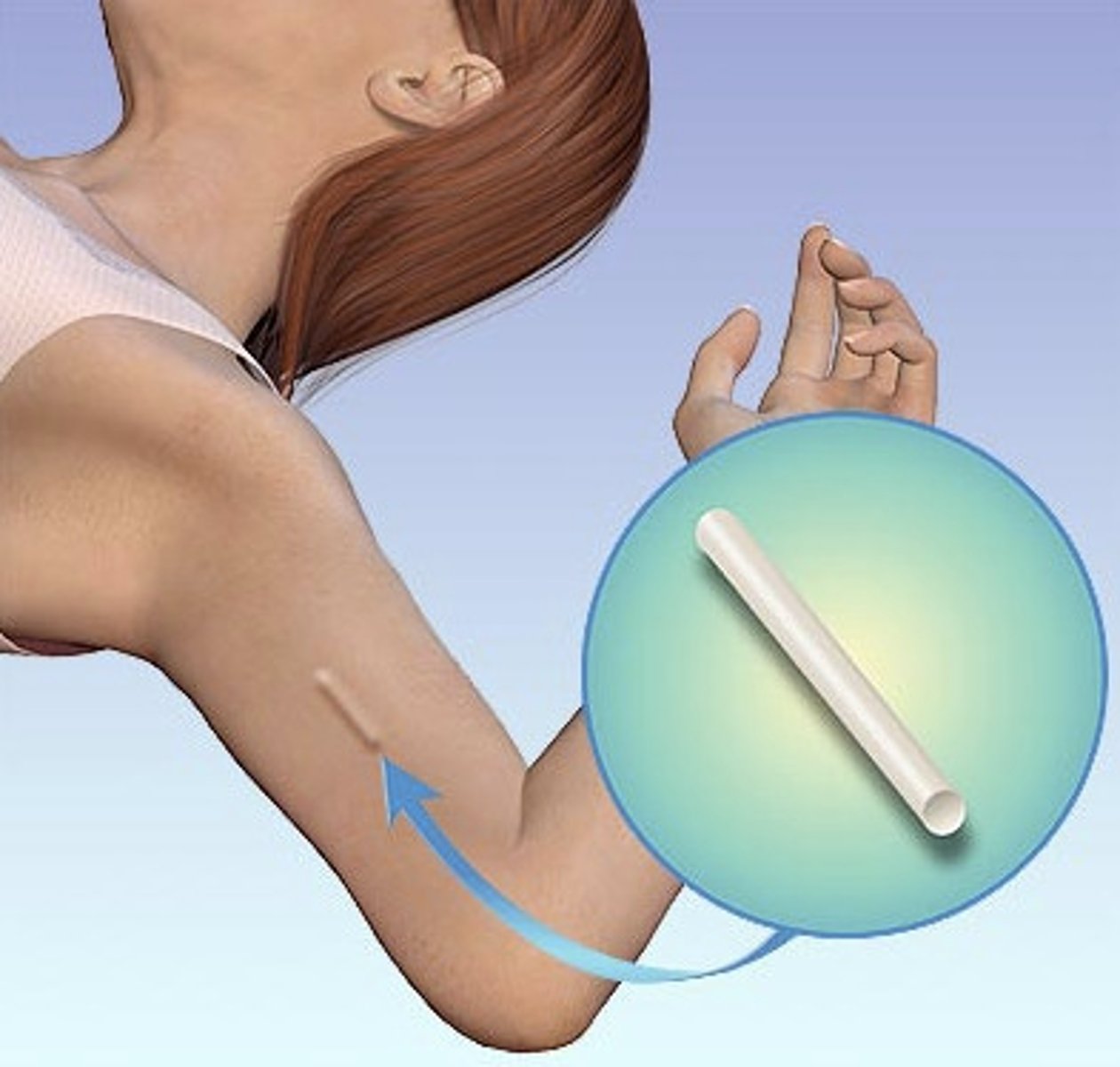
what is the difference between depo (DMPA injection) and nexplanon (subdermal implant)?
depo is injected like a shot in the office every 12-14 weeks; nexplanon is inserted into the upper arm and is effective for 3 years
what is the MOA of systemic progesterone only methods?
Inhibition of ovulation by negative feedback on the synthesis and release of GnRH from the hypothalamus
Cervical mucous changes making it impermeable and hostile to sperm
Decreased ciliary action in the fallopian tubes affecting sperm and egg transport
Endometrial thinning that discourages implantation
what are the contraindications based upon CBC and WHO data for systemic progesterone only methods?
Known or suspected pregnancy
Hepatic tumor or active liver disease
Undiagnosed abnormal genital bleeding
Known or suspected breast cancer, history of breast cancer, or other progestin-sensitive cancer
Some forms of lupus
what are the contraindications for POPs?
History of bariatric surgery
Use of certain anticonvulsants
what are the contraindications for DMPA?
Pregnancy planned in the nest year
Long-term use of corticosteroid therapy with risk of non traumatic fracture
Diabetes with end organ damage
Significant HTN
History of stroke
IHD or significant vascular risk
what are the contraindications for nexplanon?
Allergy to any component of the device
which systemic progesterone only contraceptive has the advantage of regulating menstrual bleeding?
POPs
2 multiple choice options
which systemic progesterone only contraceptive is a LARC (long term reversible contraception)?
Nexplanon
2 multiple choice options
which systemic progesterone only contraceptive has the risk of decreasing bone mineral density?
DMPA
2 multiple choice options
which systemic progesterone only contraceptive has the possible side effect of nausea?
POPs
2 multiple choice options
which systemic progesterone only contraceptive has the possible side effect of extended return of infertility?
DMPA
2 multiple choice options
which POP is the only progesterone only method that offers menstrual regulation?
Slynd® (drospirenone)
what are the 2 types of intrauterine methods?
progesterone (levonorgestrel) IUD
copper IUD
compare and contrast copper and levnogestrel IUDs
copper (Paragard) is T shaped, hormonal free, effective up to 10 years
levnogestrel is T or Y shaped, contains progesterone, effective 3-8 years depending on brand
both are LARCs and are inserted/removed in outpatient settings
which levonogestrel releasing IUD is effective for up to 8 years?
Mirena
3 multiple choice options
which levonogestrel releasing IUD is effective for up to 3 years and is priced under market value?
Liletta
3 multiple choice options
which levonogestrel releasing IUD is effective for up to 5 years and FDA approved for nulliparous patients?
Kyleena
3 multiple choice options
which levonogestrel releasing IUD is effective for up to 3 years and FDA approved for nulliparous patients?
Skyla
3 multiple choice options
the exact MOA for copper IUDs are unknown but what are some theories?
Interference with egg development
Interference with fertilization of the egg
Promotion of phagocytosis of sperm in the endometrial cavity
Creating an unfavorable uterine environment for implantation
what is the MOA for a levonogestrel IUD?
Cervical mucous changes making it impermeable and hostile to sperm
Decreased ciliary action in the fallopian tubes affecting sperm and egg transport (prevents sperm from meeting egg)
Endometrial thinning that discourages implantation
what are contraindications based upon CDC and WHO data for IUDs?
Known or suspected pregnancy
Distorted uterine cavity
Current cervical cancer
Endometrial cancer
Undiagnosed abnormal genital bleeding
PID/septic abortion/postpartum sepsis
Pelvic tuberculosis
Current cervicitis due to active gonorrhea or chlamydia
Gestational trophoblastic disease with persistently elevated ß-hCG
Complicated organ transplant
Lupus with severe thrombocytopenia
what are contraindications for copper IUDs?
Wilson's disease or a copper allergy
what are contraindications for levonogestral IUDs?
Current breast cancer
Hematic tumor or active liver disease
which IUD has significantly less menstrual bleeding and a decrease in dysmenorrhea?
levonorgestrel
1 multiple choice option
which IUD has maintenance of monthly cycle?
copper
1 multiple choice option
which IUD has a possible elevated breast cancer risk?
levonorgestrel
1 multiple choice option
which IUD has a possible side effects of heavier menstrual cycles?
copper
1 multiple choice option
which IUD has possible side effects of headache, acne, and breast tenderness?
levonorgestrel
1 multiple choice option
what are 3 options for emergency contraception?
hormone formulations, paragard, selective progesterone receptor modulator
what are the 2 types of hormone formulations for emergency contraception? how are they taken/when should they be taken?
combination and progesterone only (Plan B) forumula; One tablet taken once, or two tablets taken 12 hours apart
Must be started within 72 hours of intercourse
when must paragard be inserted to work as emergency contraception?
within 7 days if intercourse
when must selective progesterone receptor modulator (Ella) be taken to work as an emergency contraception?
120 hours of unprotected intercourse
what is permanent sterilization for females and males respectively?
females: tubal sterilization via cautery, salpingectomy, or clips/bands
males: vasectomy via excision of a section of the vas deferens
what are birth control options for a postpartum patient that can be initiated immediately?
Progesterone-only methods
Barrier methods
All IUDs
Permanent sterilization
Breastfeeding
Age alone is not a contraindication for any form of contraception t/f
true
1 multiple choice option