Gallbladder and Biliary System
1/145
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
146 Terms
what does the biliary system consist of?
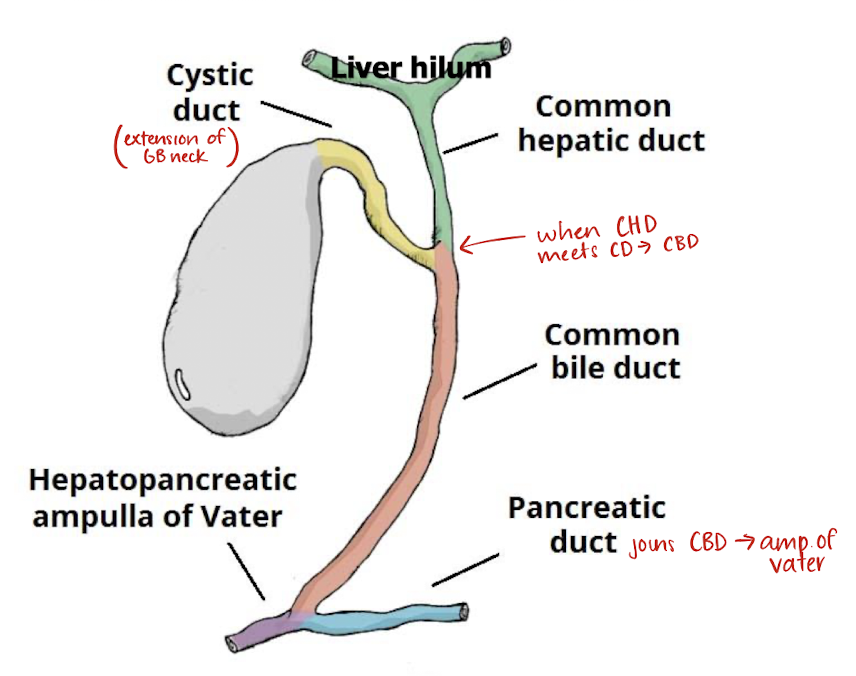
consists of GB and associated (intrahepatic/extrahepatic) ducts
right and left hepatic ducts
common hepatic duct (CHD)
cystic duct
common bile duct (CBD)
CHD is the _____ portion of the biliary tree
proximal
CBD is the _____ portion of the biliary tree
distal
where is the GB “housed” or positioned?
GB fossa (indentation) on posteroinferior portion of RLL
what is the fossa closely related to?
main lobar fissure
anatomy of biliary tree
what organ stores bile?
gallbladder
bile
GB bile is more concentrated than hepatic bile due to rugae (inward folds) which helps to absorb water and secrete mucus
composed of mostly water and bile acids and other things like cholesterol, bilirubin, proteins, electrolytes, and mucus
what are the major components of bile secreted by the liver?
cholesterol and bilirubin
bilious emesis
throw up that has bile (green); may indicate biliary obstruction
what does the GB aid in?
digestion
GB digestive process
liver produce bile
bile travels through biliary ducts (through right and left hepatic ducts which forms CHD)
GB stores bile
fatty meal triggers release of CCK from duodenum
bile is released
sphincter of Oddi opens —> bile drains freely into duodenum
CCK
short for cholecystokinin
hormone secreted into blood from small intestine
stimulates contraction of GB and pancreatic secretion of enzymes
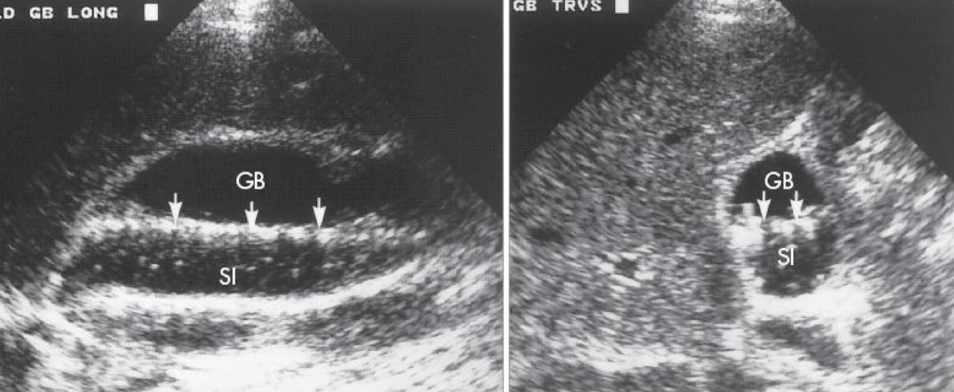
SONO: gallbladder
anechoic, pear-shaped structure
bright echogenic walls
GB wall <3 mm
measured from outer-to-outer
** if patient has cholecystitis or ascites, GB wall mey thick
SONO: ducts
anechoic
2 echogenic walls
SONO: CHD
around 4 mm at RHV and RPV
SONO: CBD
dilated +1 mm per decade at MPV
** if patient has cholecystectomy, CBD my be enlarged
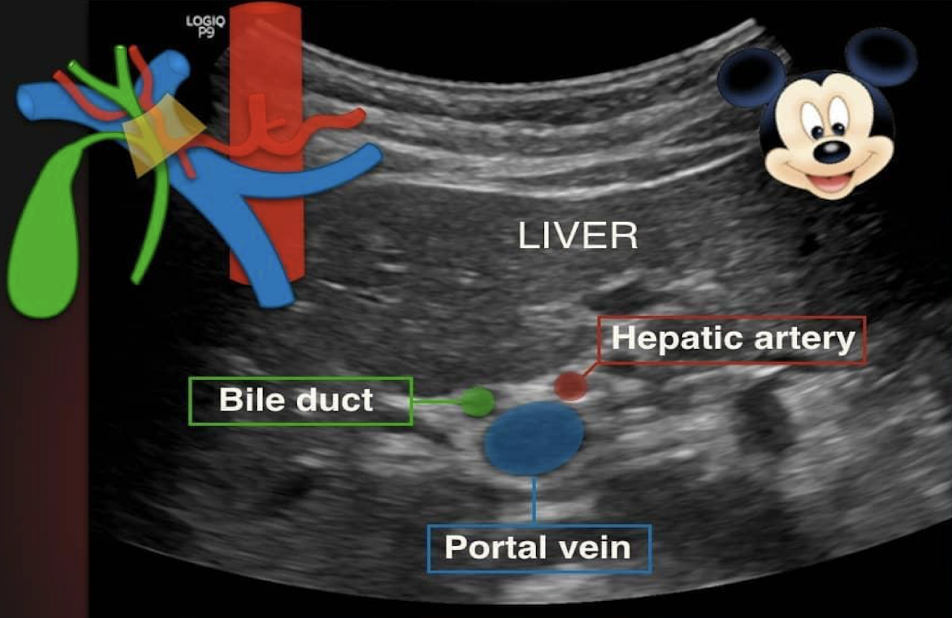
portal triad consists of what?
portal vein (head)
duct (right ear)
hepatic artery (left ear)
Heister’s valve
aka spiral valve of Heister
tiny valves found within cystic duct
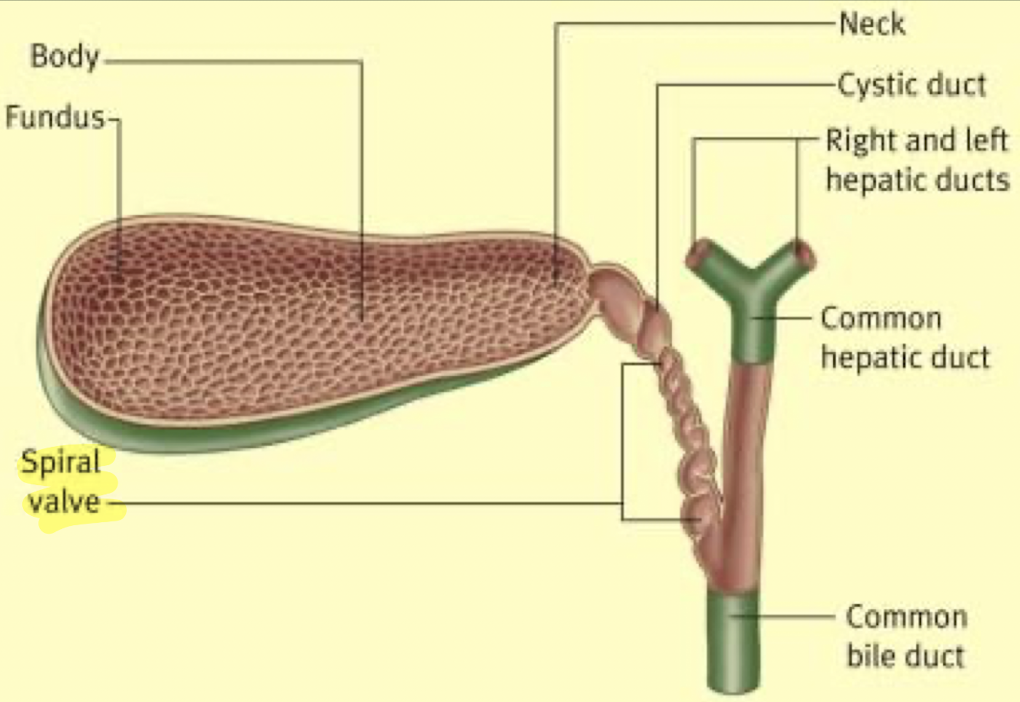
GB parts and info
parts: neck (superior portion), body, and fundus (inferior portion; close to bowel)
around 9 cm from neck to fundus
GB >12 cm is considered hydrops
holds up to 40 mL of bile
supplied by cystic artery
what supplies the GB?
cystic artery
Courvoisier sign
indicates an extrahepatic mass compressing CBD —> GB hydrops
left hepatic artery (LHA)
supplies LLL and caudate lobe
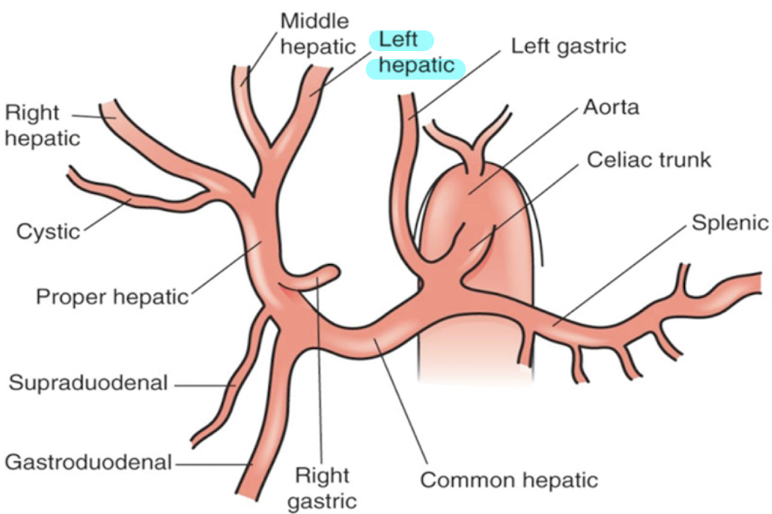
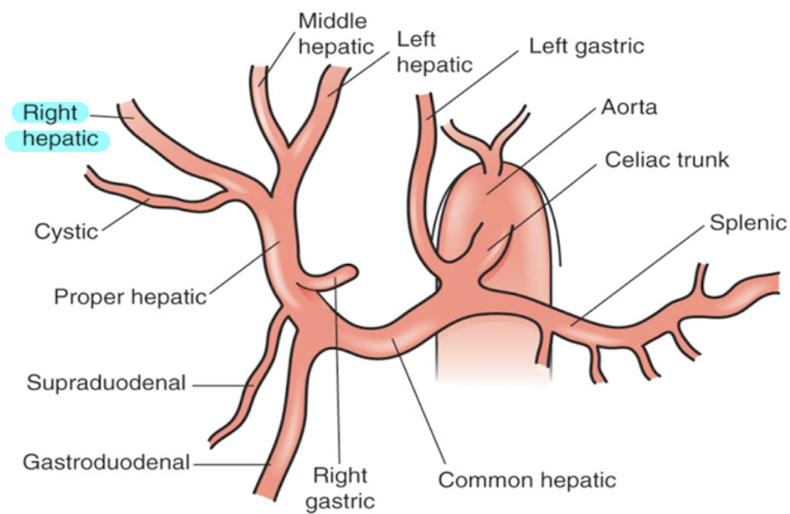
right hepatic artery (RHA)
supplies RLL and branches into cystic artery
indications for imaging the GB
RUQ pain
positive Murphy sign on physical exam
pain radiating to right shoulder
jaundice or abnormal LFTs
loss of appetite
n/v
intolerance to fatty foods or dairy products
scanning techniques and protocol for imaging GB
curvilinear probe
patient NPO for 6-8 hours
breathing technique!! (full inspiration)
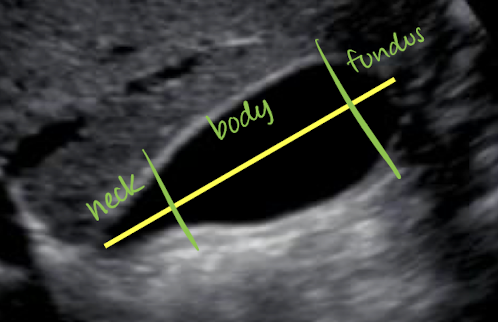
image in SAG and TRANS (to show neck, body, and fundus)
is there a + Murphy’s sign?
place transducer over GB and press
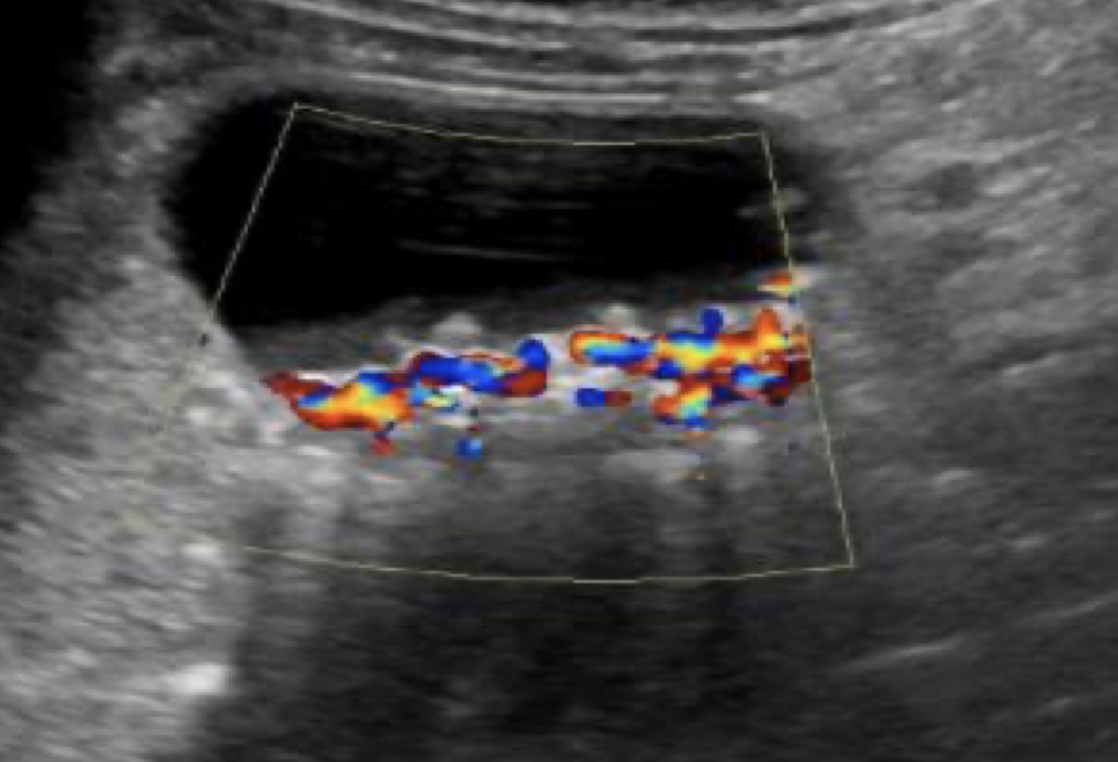
image CBD with and without color to include MPV
LLD/LLO to confirm mobility of abnormalities
normal variants
Hartmann's pouch
Phrygian cap
junctional fold
septations
agenesis
Hartmann’s pouch
aka infundibulum
outpouching near GB neck
small part of GB that lies near cystic duct where stones may collect
what is another name for Hartmann’s pouch?
infundibulum
phrygian cap
folding of GB fundus
junctional fold
fold at neck and body of GB
septations
internal division(s) of GB—hyperechoic line
goes all the way across
if not then it is likely a fold
associated with cholelithiasis
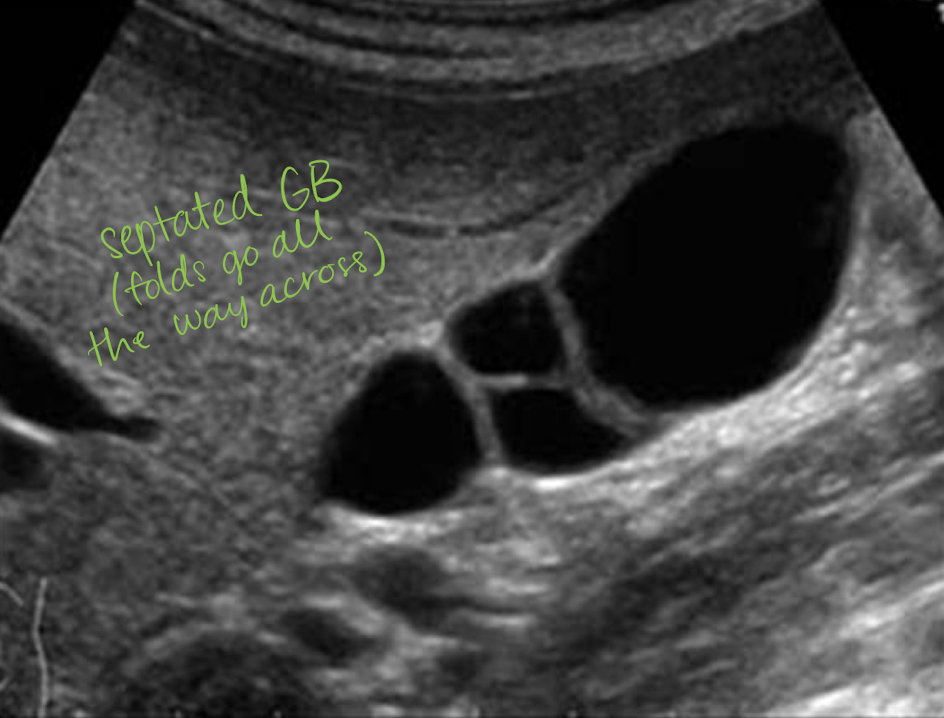
agenesis
congenital abnormality
failure of GB to develop
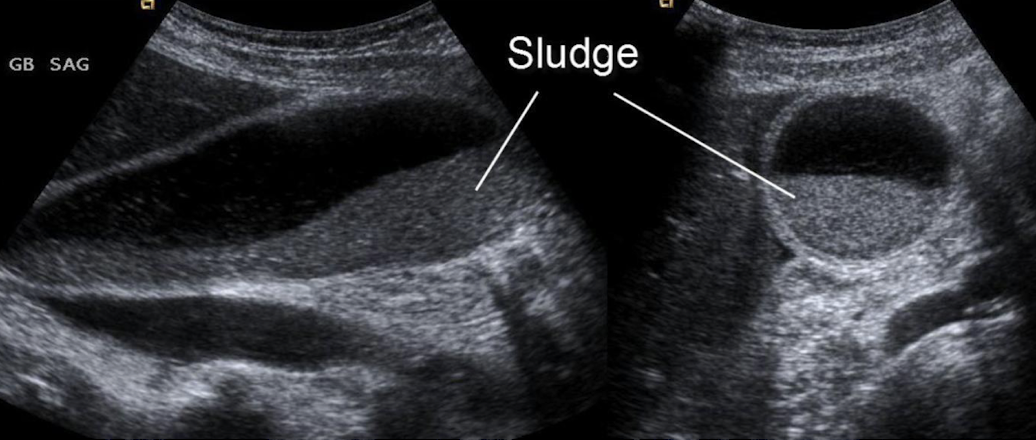
GB sludge
aka thickened bile
results from bile stasis
gravity dependent; slowly resettled upon LLD/LLO repositioning
can cause stone formation, biliary colic (abdominal pain), acalculous cholecystitis, and pancreatitis
SONO: non-shadowing, low-level internal echoes (echogenic)
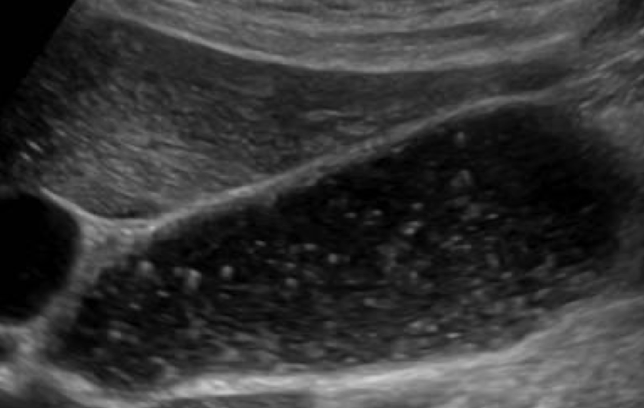
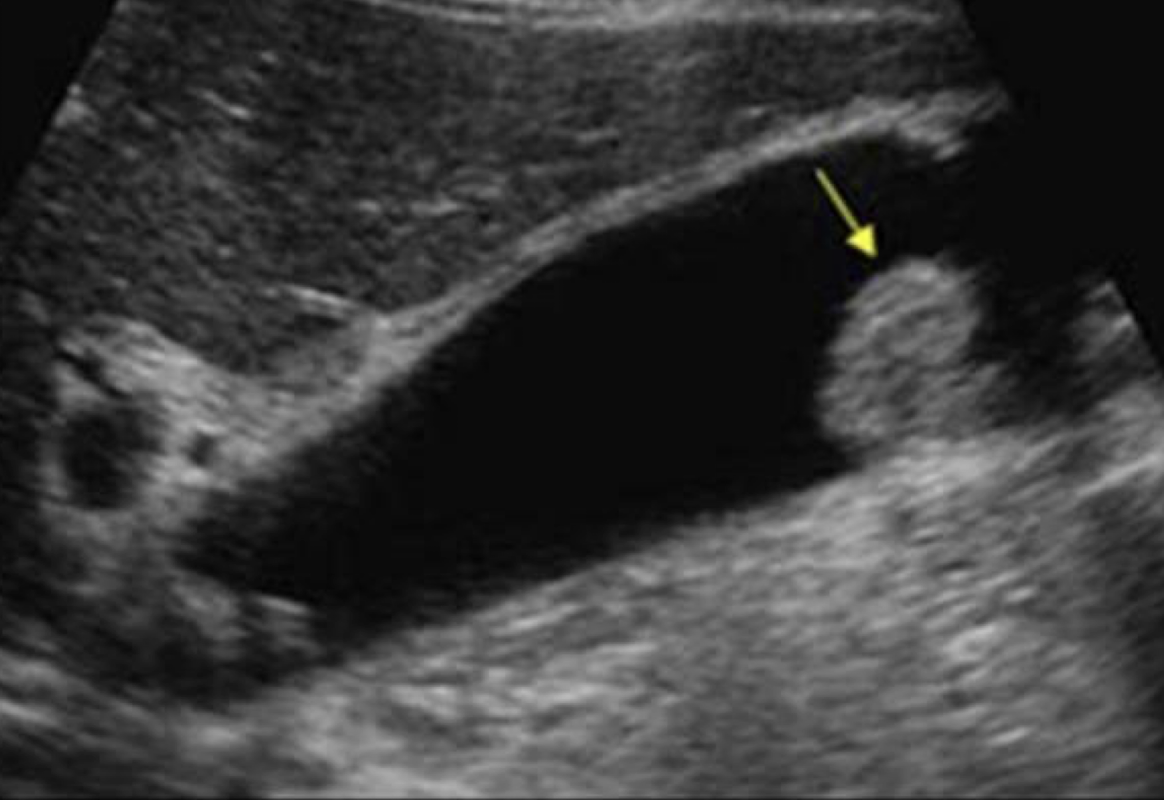
sludge ball
aka tumefactive sludge
clumping of sludge
??
floating sludge
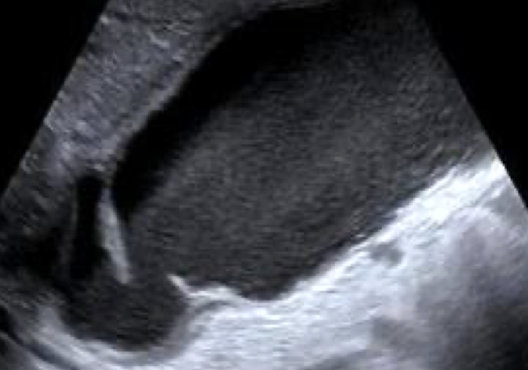
layering sludge
??
sludge ball
larger than gallstone
mobile; no shadowing
what should a normal GB wall thickness be?
less than 3 mm
causes of thickened GB wall
biliary
cholecystitis
GB carcinoma
adenomyomatosis
sclerosing cholangitis
hyperplastic cholecystosis
non-biliary
hepatitis
cirrhosis
ascites
cholecystitis
inflammation of GB
several forms:
acute
chronic
acalculous
emphysematous
gangrenous
acute cholecystitis
MC cause is from gallstones in cystic duct or neck of GB
MC in females over age of 50
s/s: + Murphy’s sign, fever
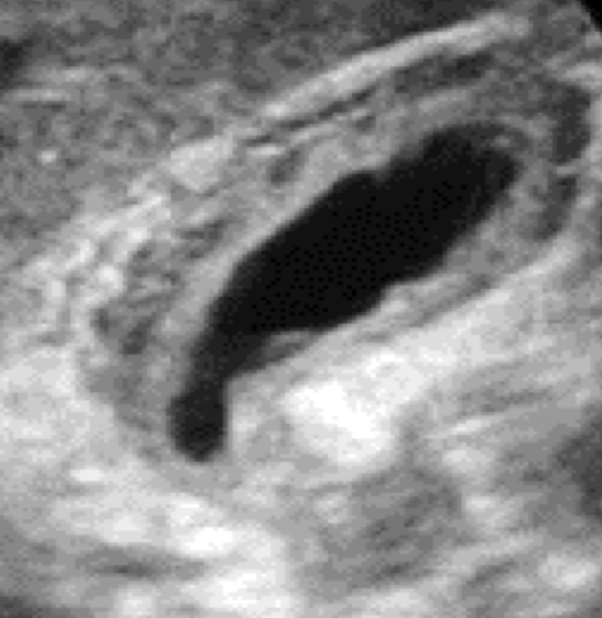
SONO: acute cholecystitis
+ Murphy’s sign
irregular wall > 3 mm
gallstones usually present
wall edema
hyperemia due to inflammation
pericholecystic fluid may be present
??
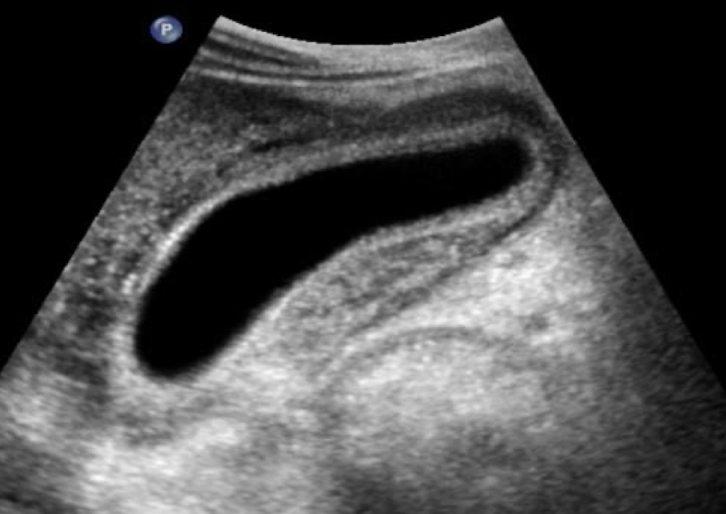
acute cholecystitis
irregular, thickened wall
??
acute cholecystitis
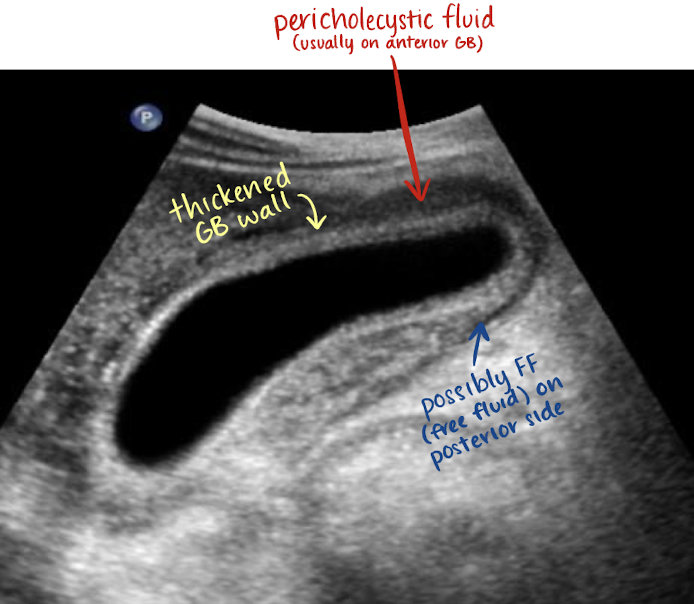
thickened GB wall
pericholecystic fluid in anterior GB
?FF in posterior GB
chronic cholecystitis
recurrent attacks of acute cholecystitis with fibrosis of GB wall
s/s: neg. Murphy’s; RUQ pain but no tenderness
SONO:
neg. Murphy’s sign
contraction of GB
stones
WES sign
acalculous cholecystitis
uncommon
due to decreased cystic artery flow
inflammation of GB wall in absence of stone
SONO:
+ Murphy’s sign
wall > 4-5 mm
sludge within
emphysematous cholecystitis
rare complication of acute cholecystitis
MC in older men and diabetic patients
gas forming bacteria in the GB wall with extension into ducts
Surgical emergency—susceptible to perforation
SONO: emphysematous cholecystitis
bright echoes along anterior GB wall with “ring down” or “comet tail” artifact
gallstones may not be present
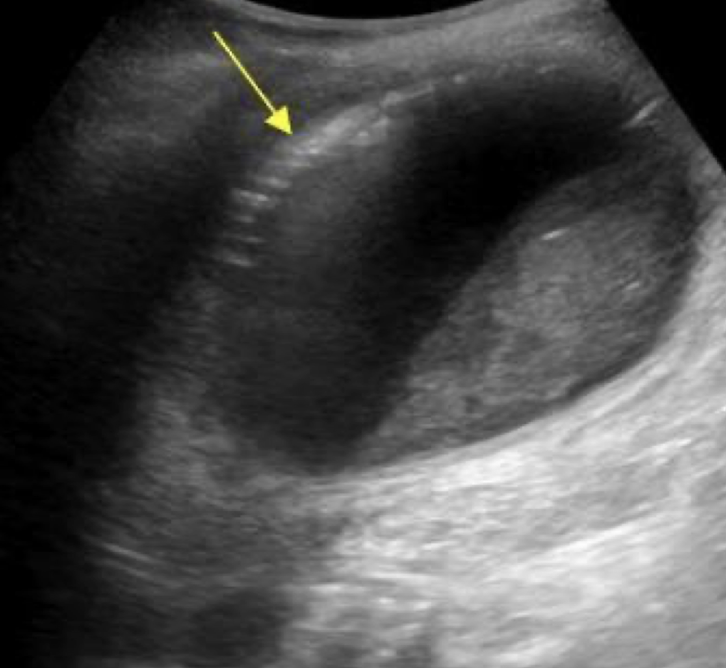
??
emphysematous cholecystitis
“ring down” artifact
gangrenous cholecystitis
necrotic GB due to prolonged infection
s/s: painful
SONO: thickened irregular edematous wall; pericholecystic abscess; perforations; echogenic densities that fill the lumen of the GB that has:
no shadow
not gravity dependent
no layering effect due to increased viscosity of the bile
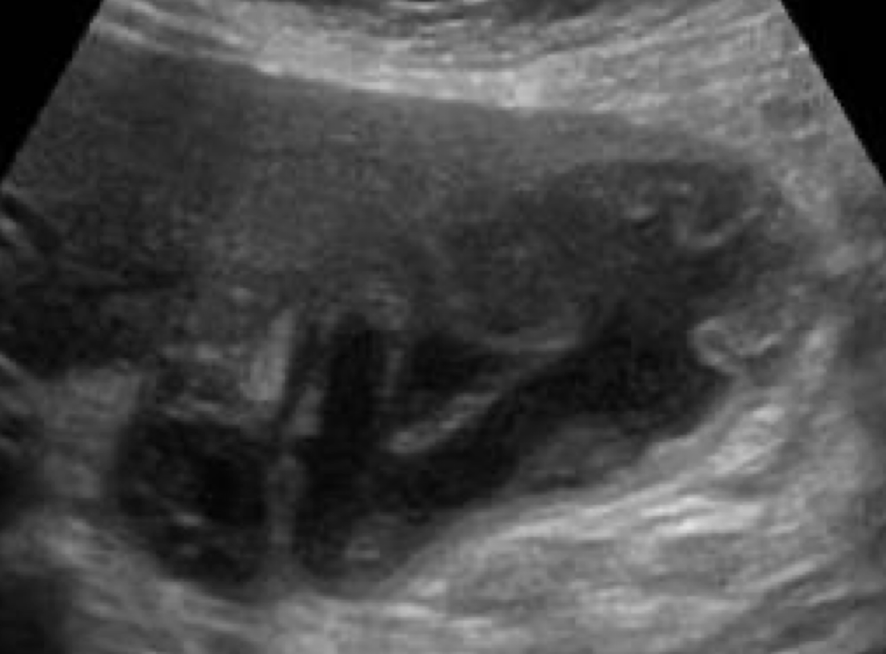
??
gangrenous cholecystitis
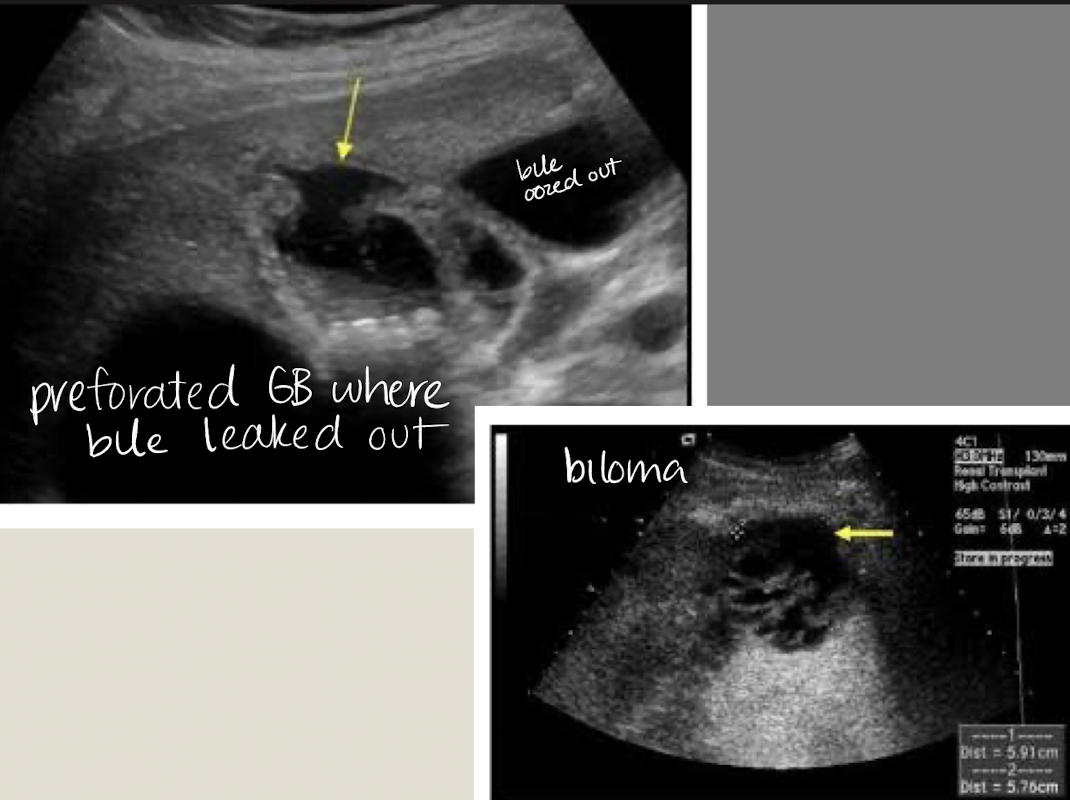
cholecystectomy
removal of GB —>
sphincter of Oddi loses tonus
bile flows freely into duodenum (biloma)
extrahepatic bile ducts dilate, up to 1 cm
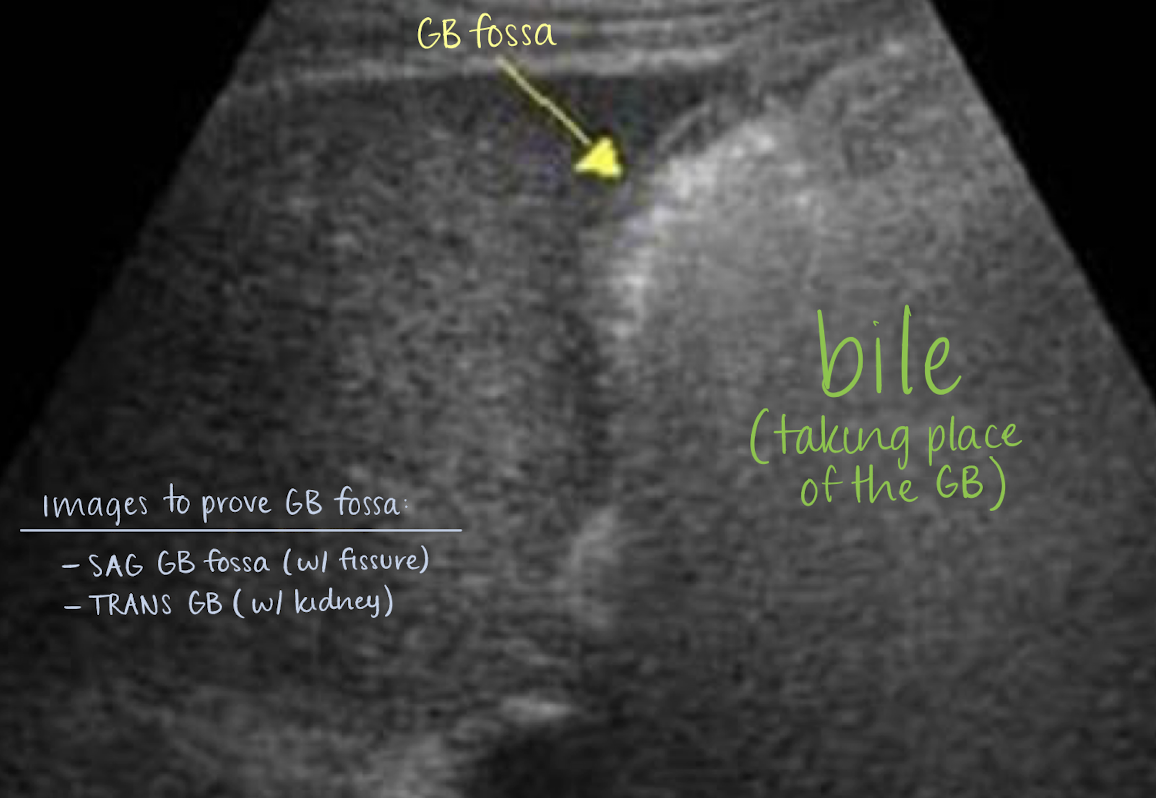
what are some post complications of cholecystectomy?
biloma
stones
abscess
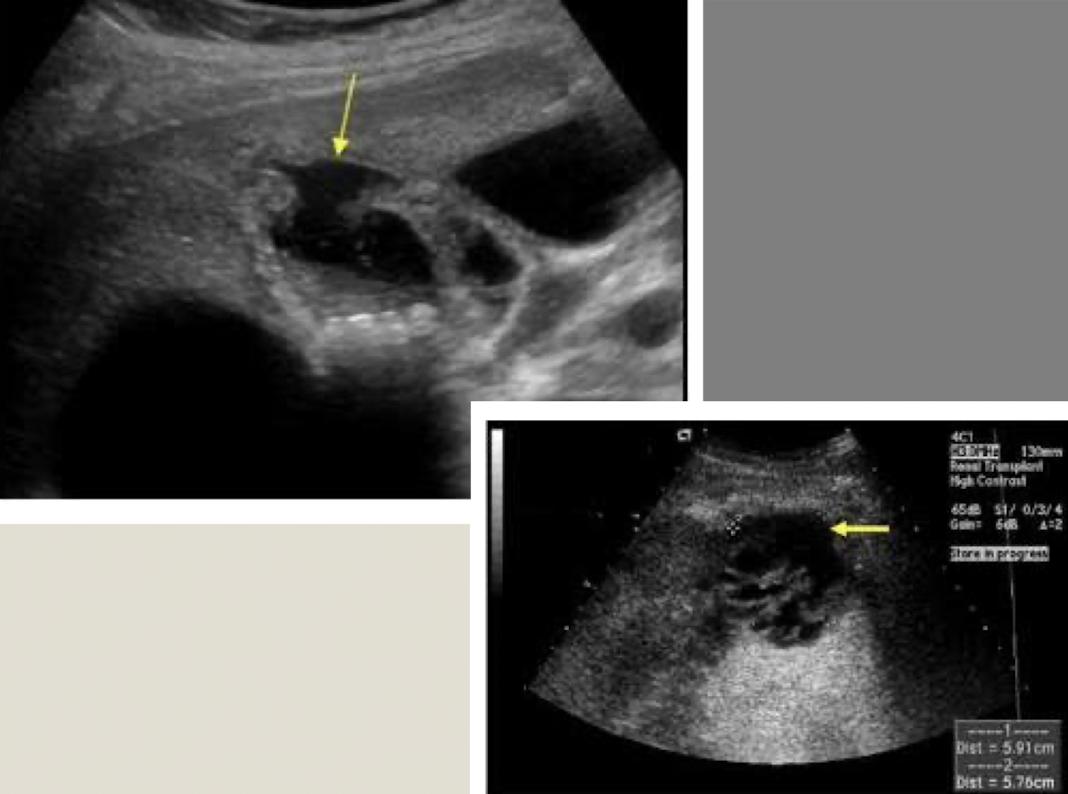
??
biloma
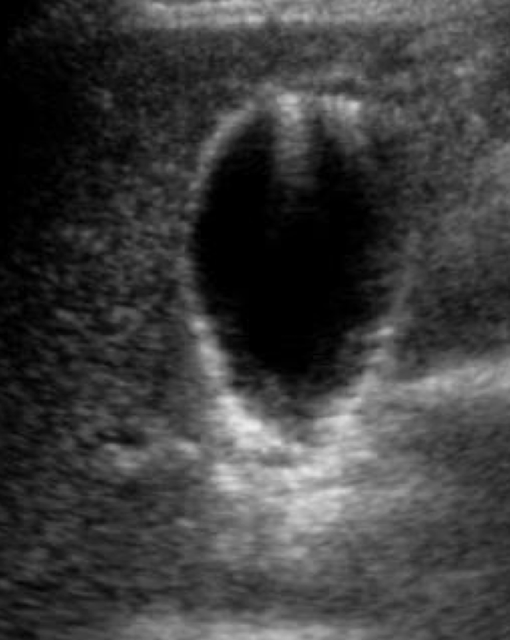
comet-tail artifact
hyperechoic shadow with tapering “tail”
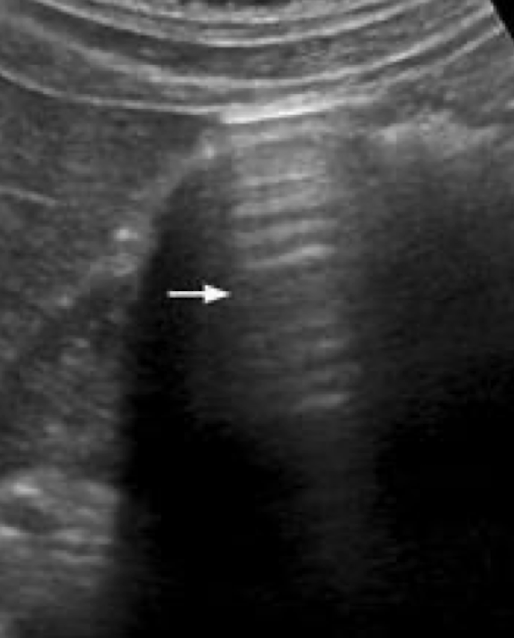
reverberation artifact
hyperechoic ladder-like lines
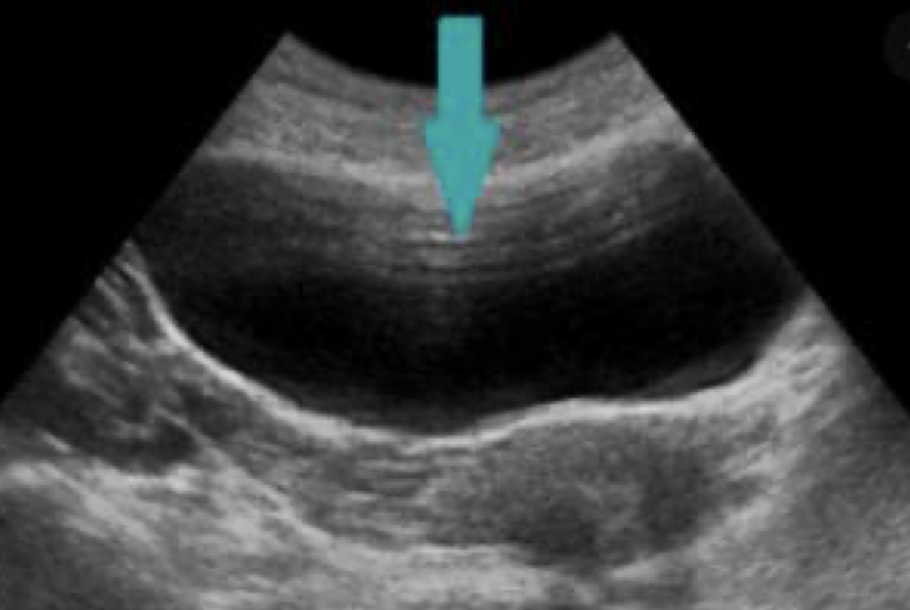
??
reverberation artifact
shown in anterior GB
cholelithiasis
aka gallstones
MC disease of GB
any size and quantity; tiny stones are most dangerous (can get stuck in infundibulum)
reposition patient to note mobility
what are the risk factors for cholelithiasis?
five F’s (risk factors)
fat
female
forty +
fertile
fair
SONO: cholelithiasis
twinkle artifact
posterior shadow (due to refraction, impedance, intensity of the sound beam, and stone(s) size)
WES (wall echo shadow)
indicative of a stone-filled GB (GB is a packed)
3 arched-shaped line
shadow posterior to 3rd line
??
cholelithiasis
calcified stones with posterior shadowing
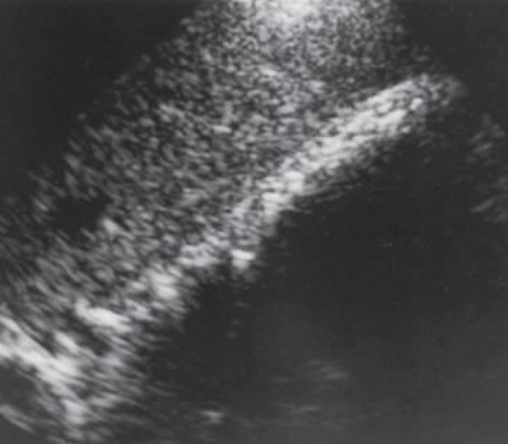
??
cholelithiasis
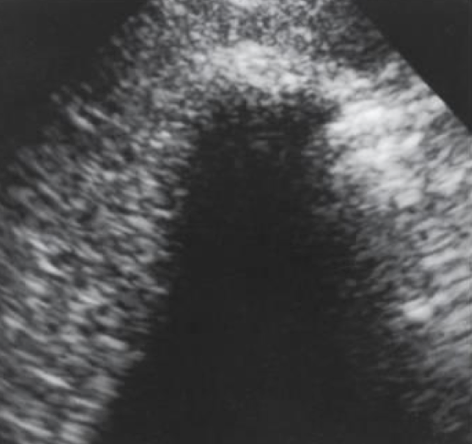
WES sign
??
cholelithiasis
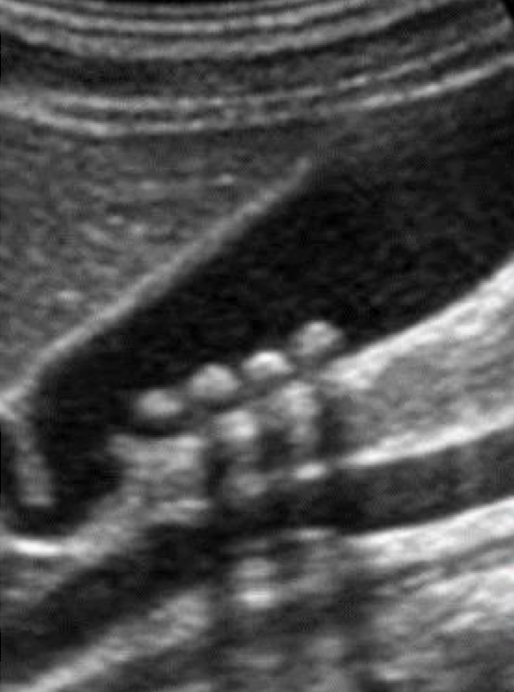
WES sign
??
twinkle artifact from stones
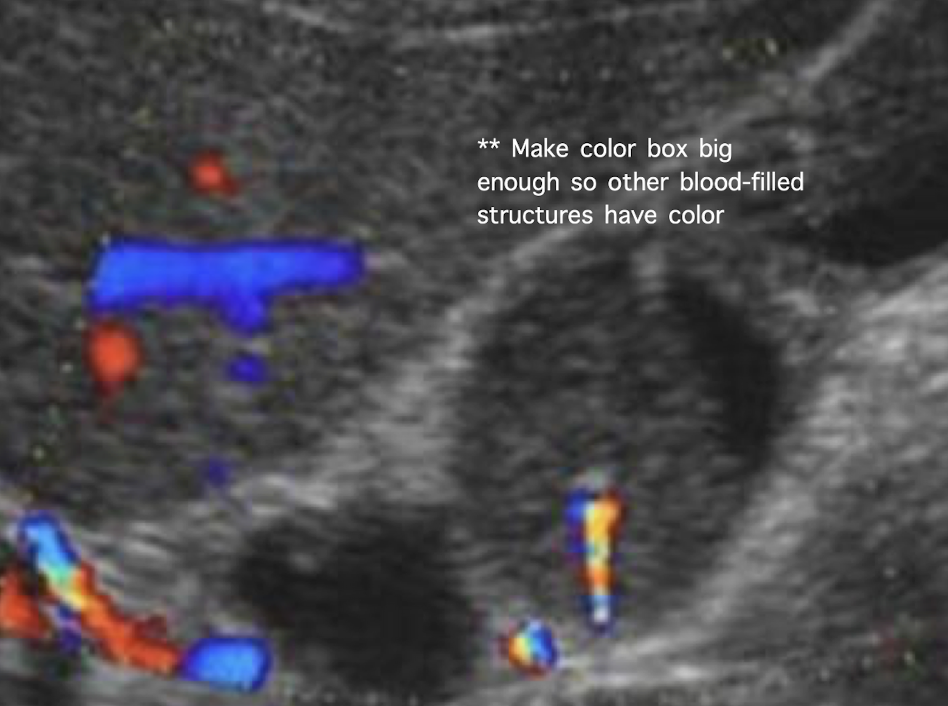
??
twinkle artifact from stone
??
floating stones along sludge layer
??
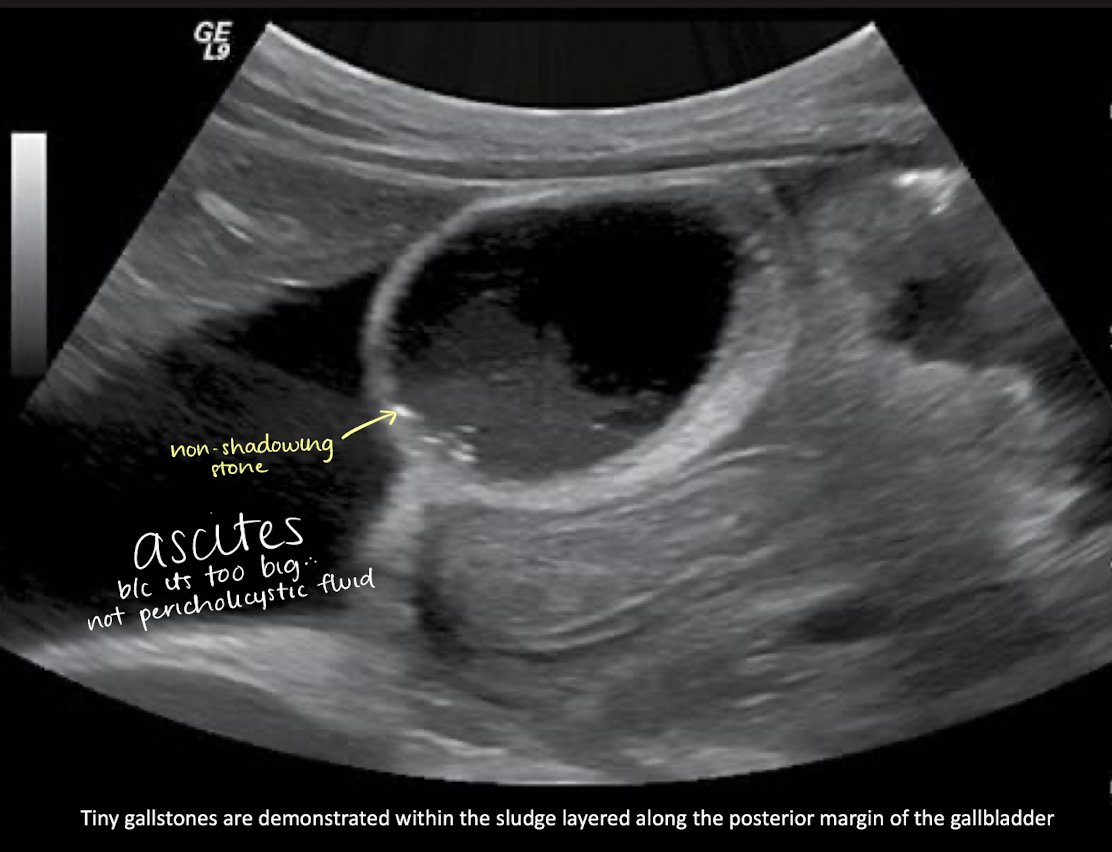
cholelithiasis
tiny stones along sludge layer + ascites
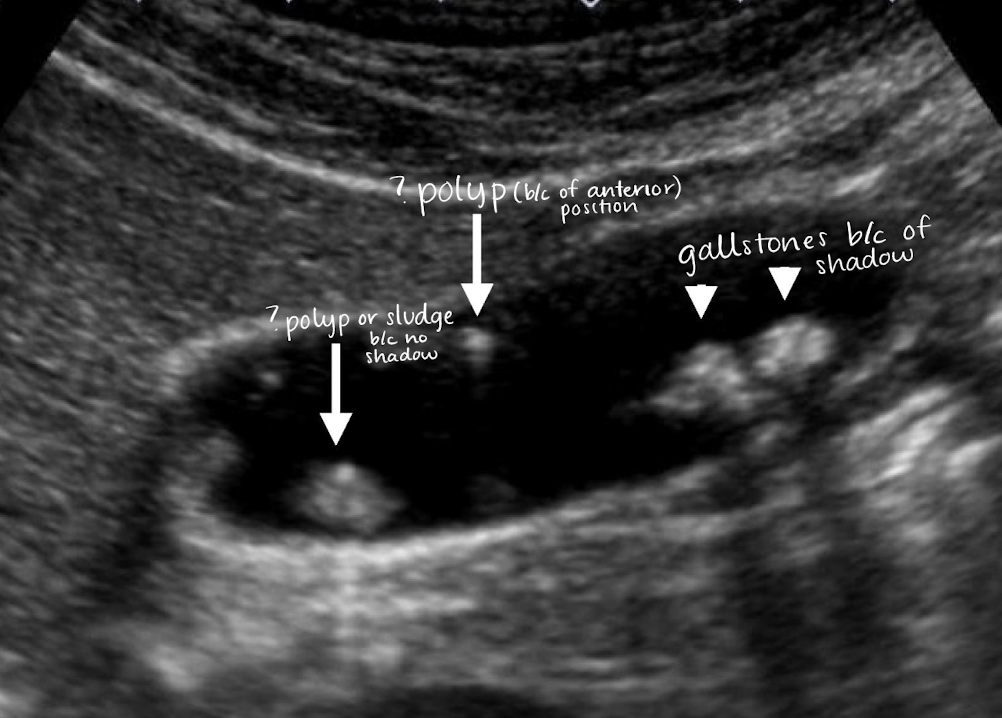
polyp
small, well-defined soft tissue projection adhering to GB wall
SONO:
non-shadowing
non-mobile
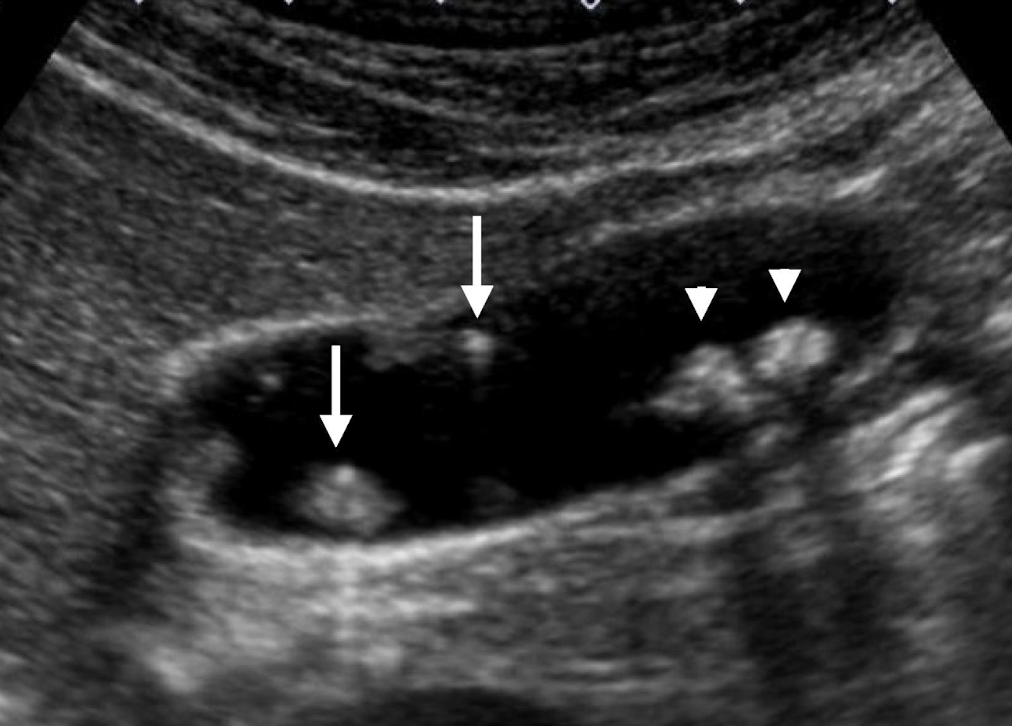
??
porcelain gallbladder
calcium incrustation of GB wall
rare occurrence
associated with gallstones
MC in elderly female
increased risk of GB carcinoma
differential dx: WES sign
SONO: porcelain gallbladder
bright echogenic echo in region of GB with posterior shadowing
GB wall thickly calcified with shadowing
Calcification may not include entire GB wall
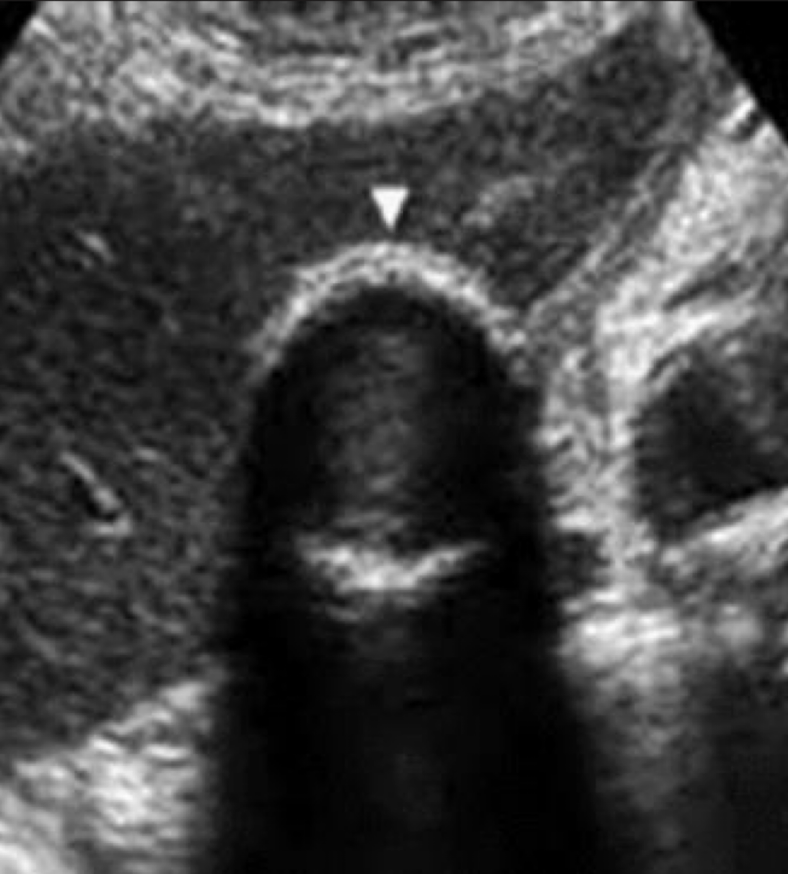
??
porcelain gallbladder
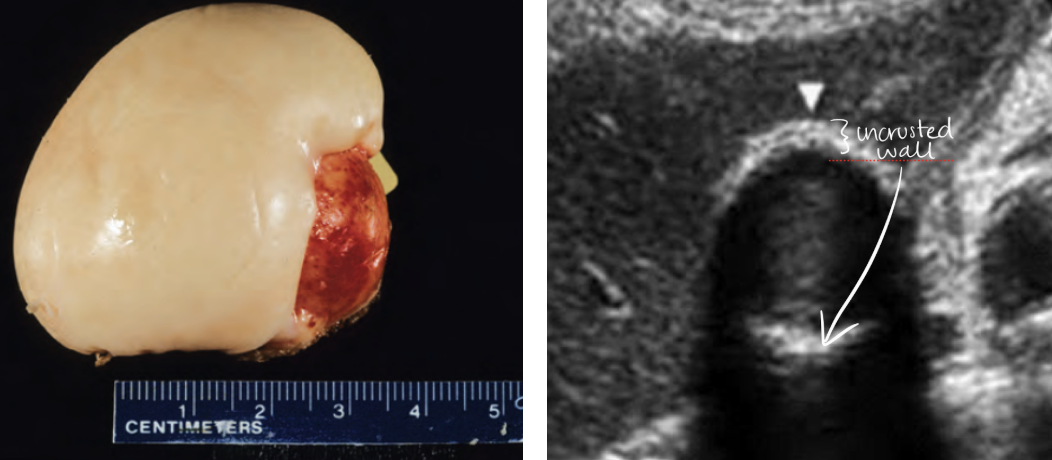
hyperplastic cholecystosis
overgrowth of GB wall —> degenerative and proliferative changes of GB
2 types: cholesterolosis and adenomyomatosis
cholesterolosis
aka strawberry gallbladder
mucosa resembles surface of a strawberry due to deposit of cholesterol in the lamina propria of the GB
some patients may have cholesterol polyps
SONO:
small, ovoid, well-defined soft tissue projections
no shadowing
fixed to wall
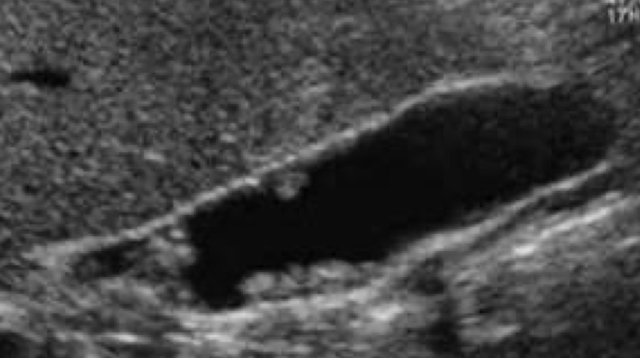
??
cholesterolosis
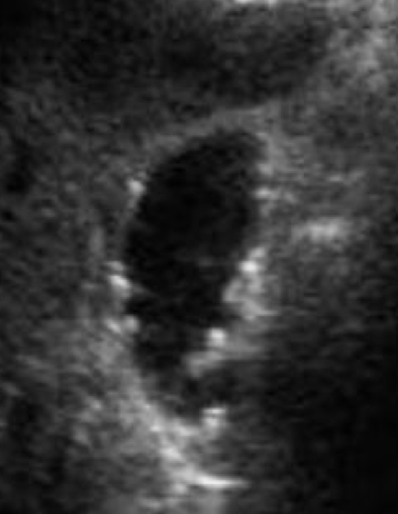
??
cholesterolosis
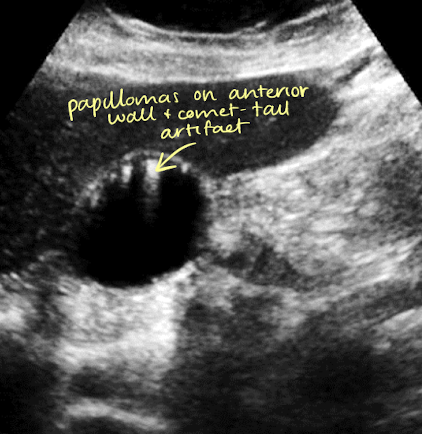
adenomyomatosis
cholesterol crystals that settle within the Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses of GB wall
mucosal hyperplasia (thickening of muscular layer of GB wall); papillomas occur
SONO: thickening of wall with internal cystic spaces
echogenic foci on wall with “comet tail” artifact
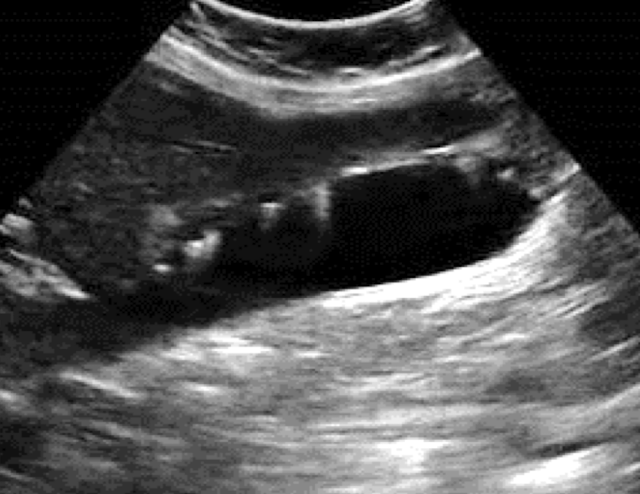
??
adenomyomatosis
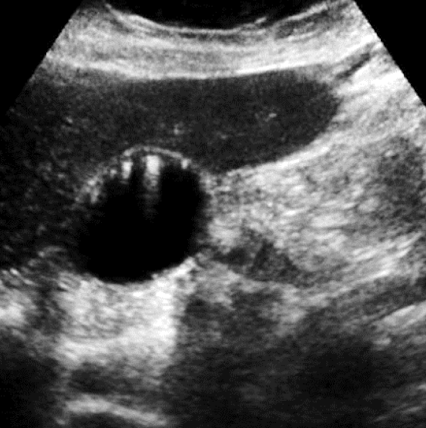
??
adenomyomatosis
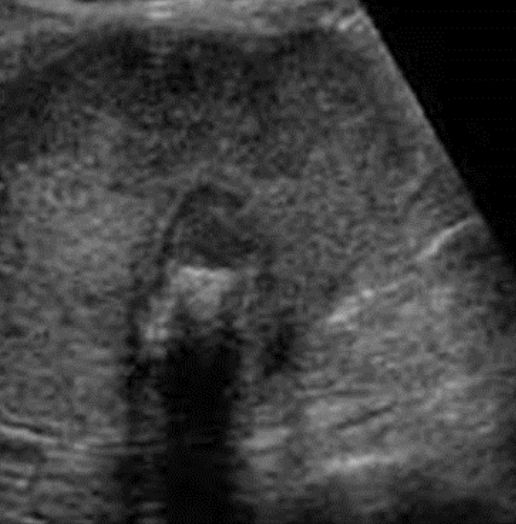
adenoma
benign neoplasms of GB
SONO:
solitary
homogeneously hyperechoic
thickening of wall adjacent to adenoma indicative of malignancy
gallbladder carcinoma
primary carcinoma is rare but have a mortality rate of 100%
high association with cholelithiasis (in 80%-90% of cases)
MC in women older than 60 y/o
tumor arises in GB body
GB tumor is usually columnar cell adenocarcinoma
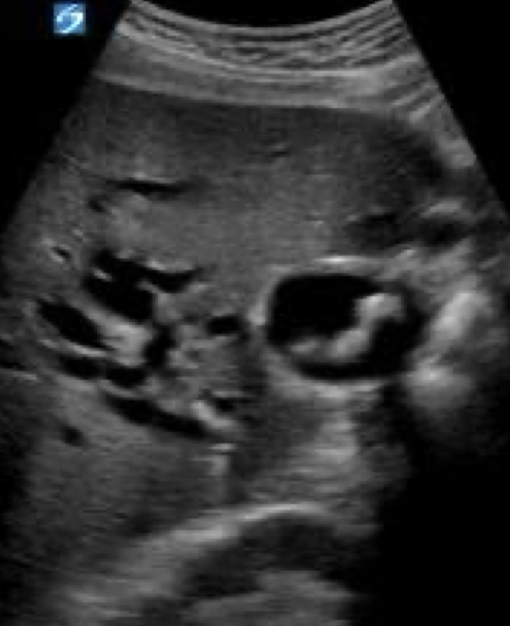
SONO: gallbladder carcinoma
heterogeneous or semi-solid soft tissue mass centered in the GB
thickened and irregular wall
adjacent liver heterogeneous due to invasion
dilated biliary ducts (“bil-dil”)
??
gallbladder carcinoma
heterogeneous mass in GB
adjacent heterogeneous liver
??
gallbladder carcinoma
GB mass —> “bil-dil”
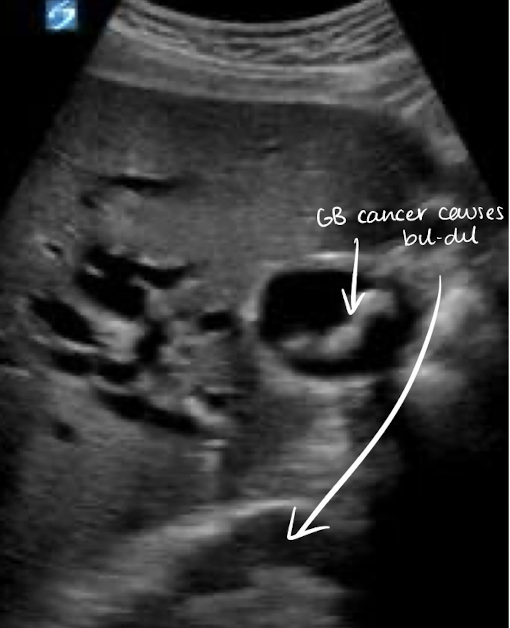
choledochal cysts
rare
congenital, focal, or diffuse dilation of biliary tree
MC in females with increased incidence in infants
Todani and colleagues classify into 5 types (depending on location)
Type 1 is MC
associated with gallstones, pancreatitis, or cirrhosis
s/s of choledochal cysts
abdominal mass
pain
fever
s/s: jaundice, abdominal mass, pain, fever, jaundice
SONO: choledochal cysts
cystic dilation of biliary tree
appear as true cysts in the RUQ
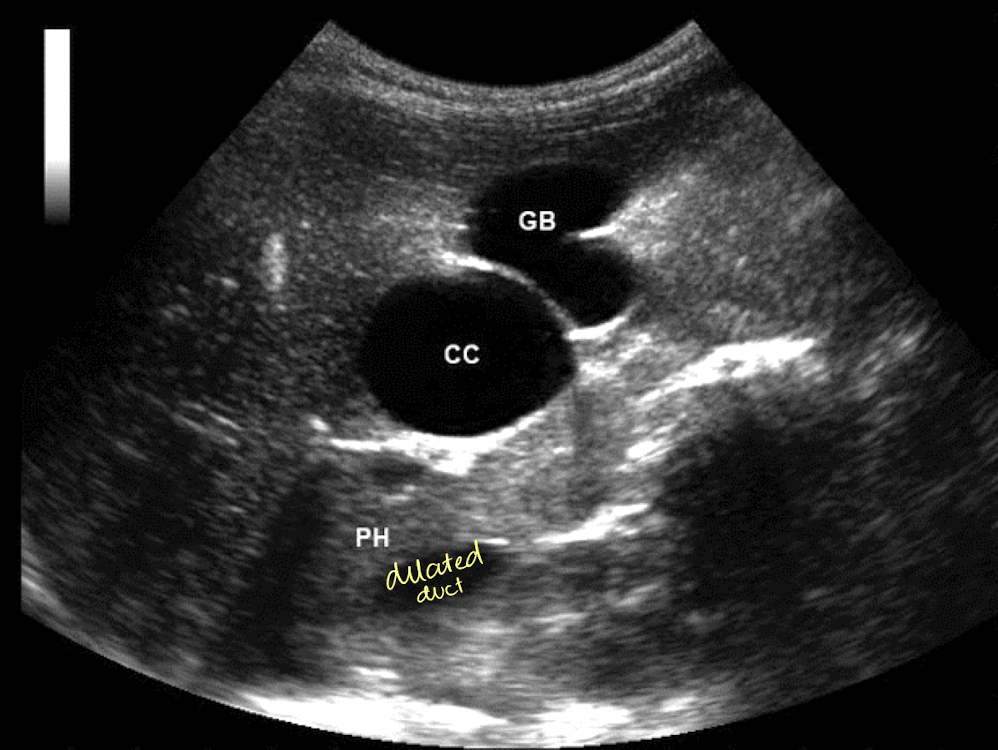
what is another name for Type 5 choledochal cyst?
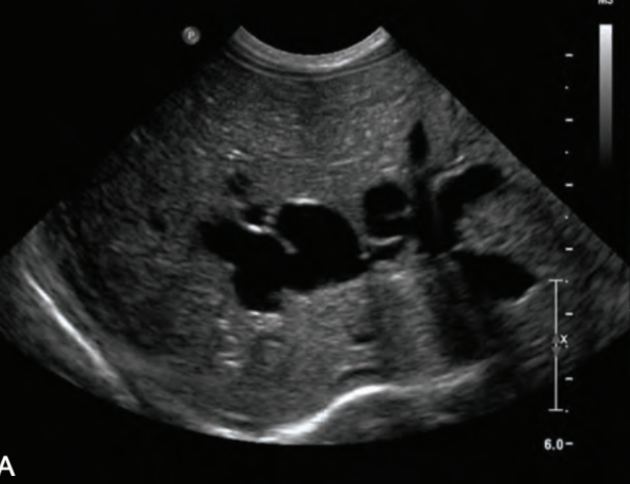
Caroli’s disease
Type 5 choledochal cysts
aka Caroli’s disease
congenital and rare, seen as intrahepatic duct dilation
s/s: Caroli’s disease
pain
cholangitis
medullary sponge kidney
hepatic fibrosis
renal failure
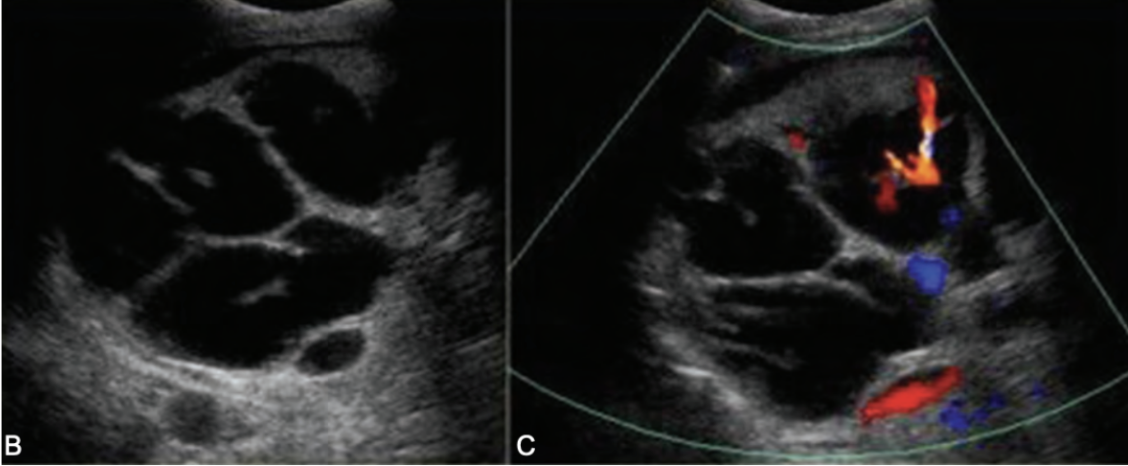
SONO: Caroli’s disease
multiple cystic structures in the track of ducts (in the area of the ductal system) that converge at portal hepatitis
“Central dot” sign = dilated duct surrounding the adjacent HA and PV
one Mickey ear is bigger than the other
??
Type 5 choledochal cysts (Caroli’s disease)
??
Type 5 choledochal cysts (Caroli’s disease)
biliary ductal dilatation
“bil-dil” is ductal dilation due to obstruction
SONO: “bil-dil”
“shot gun” barrel appearance
parallel to the PVs
intrahepatic ducts >2mm
extrahepatic dilation occurs before intra
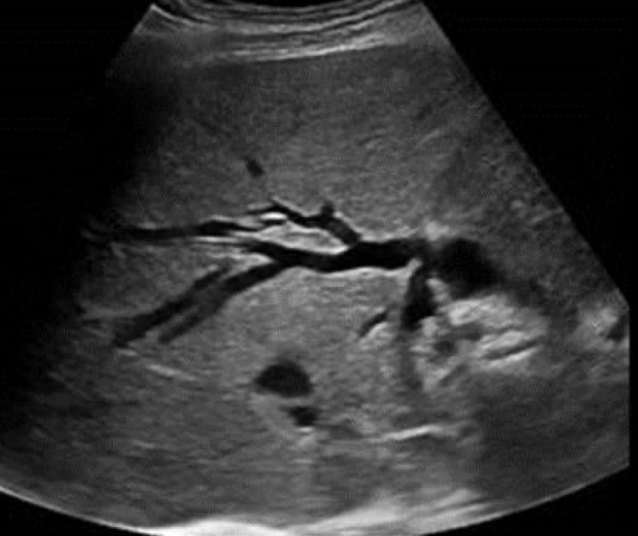
??
biliary ductal dilatation (“bil-dil”)
choledocholithiasis
stones in the duct
primary choledocholithiasis
Starts from thBiliary Obstructione formation of calcium stones in the bile duct
Secondary choledocholithiasis
Indicates that the majority of stone in the duct have migrated (to duct) from GB
biliary obstruction
MC cause is the presence of tumor or thrombus in the ductal system
locations of obstruction:*
intrapancreatic obstruction
suprapancreatic obstruction
porta hepatic obstruction
intrapancreatic obstruction
extrahepatic duct completely dilated
three primary causes:
pancreatic carcinoma
choledocholithiasis
chronic pancreatitis with stricture formation