L4 Immunoglobulins and Biology of T cells
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
VOCAB NOG TOEVOEGEN
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
Humoral immunity
The process of adaptive immunity manifested by the production of antibodies by B lymphocytes
Antibody mediated immunity
immunoglobulin
surface bound + secreted
a large group of glycoproteins that constitute the antibodies formed in response to antigenic stimuli
antibody
antigen specific secreted molecule
immunoglobulin multichain glycoproteins synthesized by B cells and plasma cells in response to the introduction of foreign substances
immunogen
induce immune responsea
antigen
can react with immune components
epitope
antigenic determinants
B cells produce … types of immunoglobulin
surface immunoglobulin
secreted immunoglobulin
Antibody structure
key and lock model
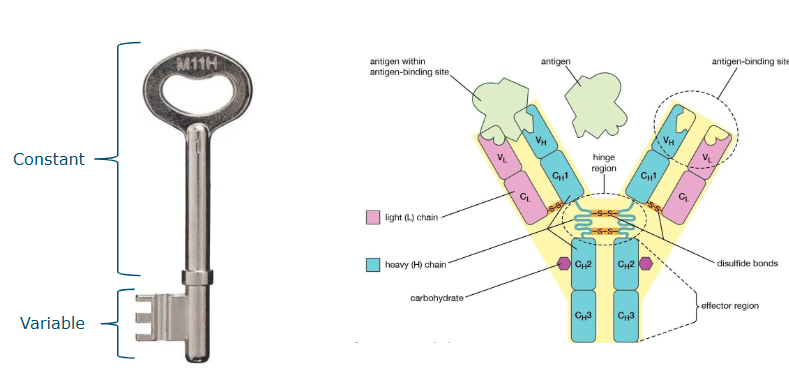
Immunoglobulin structure
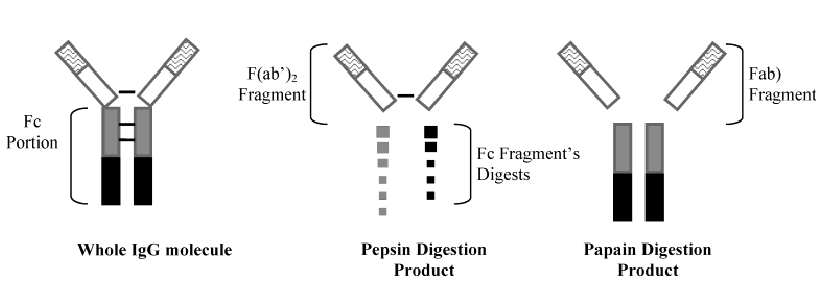
Fab fragment, (variable part?)
Fc fragment
Heavy chain 2x
Light chains 2x
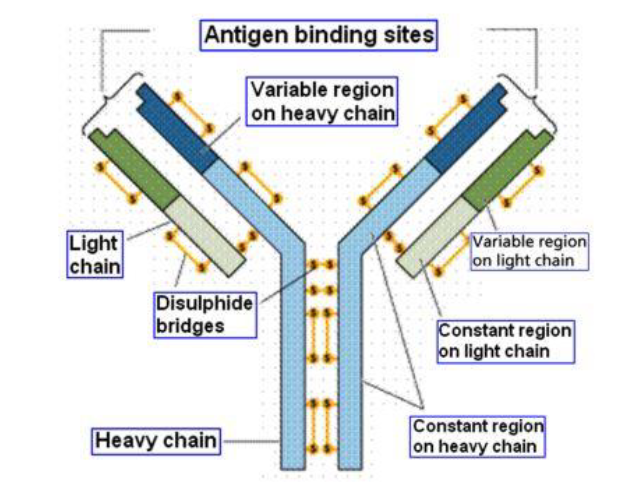
Antigen binding site
Hinge region
4 peptide chains, 2 heavy and 2 light chains
kept together by disulphide bridges
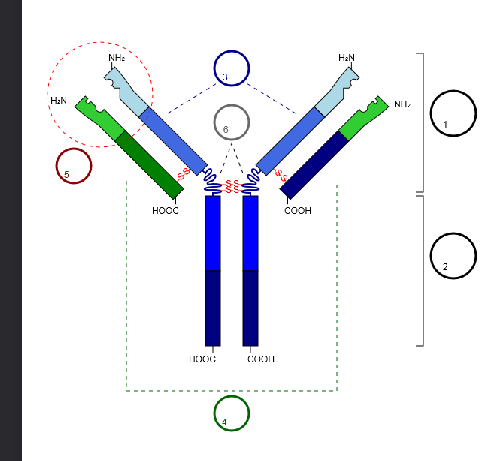
Immunoglobulin structure - drawn out
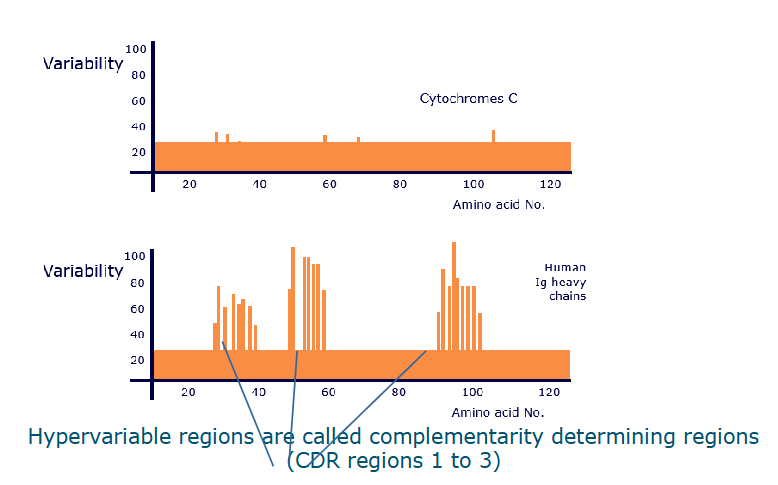
The hypervariable antigen binding site
Hypervariable CDRs are located on loops at the end of the Fv regions
CDR1, 2, 3
Most hypervariable regions coincided with antigen contact points - the complementarity determining regions CDRs
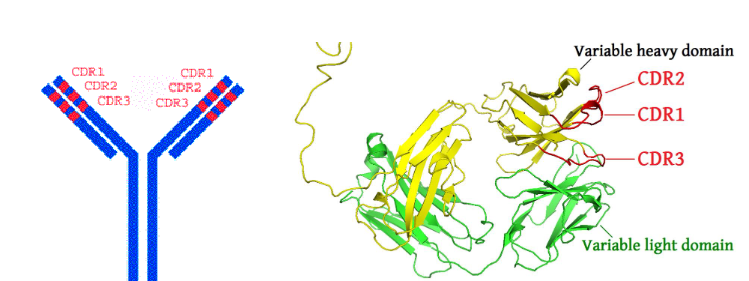
Variability of amino acids in related proteins
antibody molecules - there you see the CDR1, CDR2, CDR3
Digestion with the proteolytic enzyme’s pepsin and papain
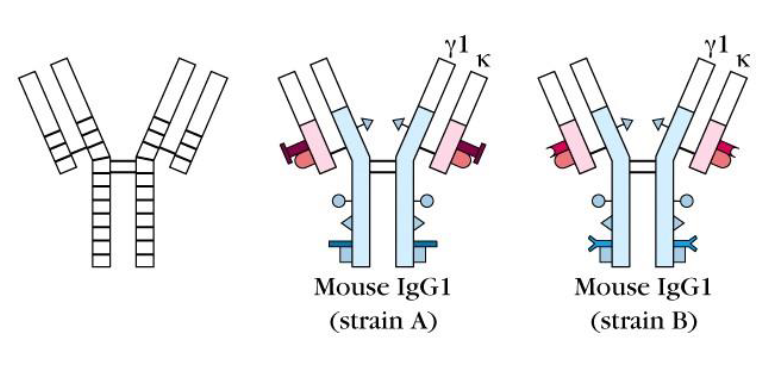
isotypes
have different heavy chains
Found in all animals of the same species
All individuals have IgA, IgM, IgG, etc
allotypes
identical constant regions with minor immunologic differences
found in some but not all members of the species. Thus individuals may possess a given determinant. Antibodies can be obtained by injection of the same species which does not have the determinant. Relaed to certain diseases
Individuals have minor differences in conserved regions based on genetic differences
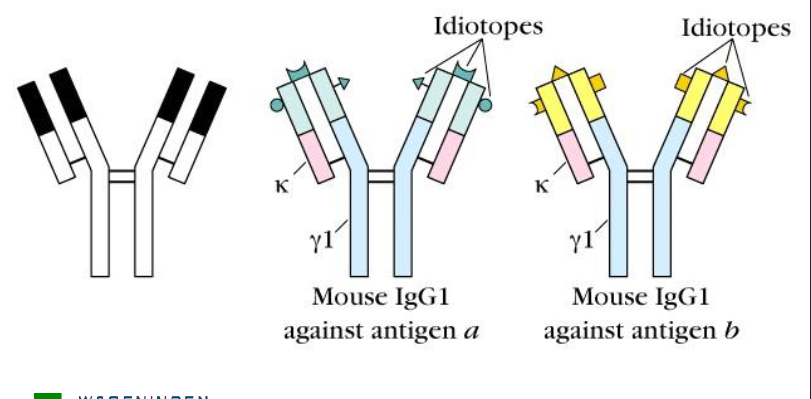
idiotypes
recognize different epitopes (CDR regions differ)
Antigen determinants exists of a result of unique structues generated by the hypervariable subregions (CDRs) on the L and H chains.
Determine binding repertoire
Isotypes of immunoglobulin classes

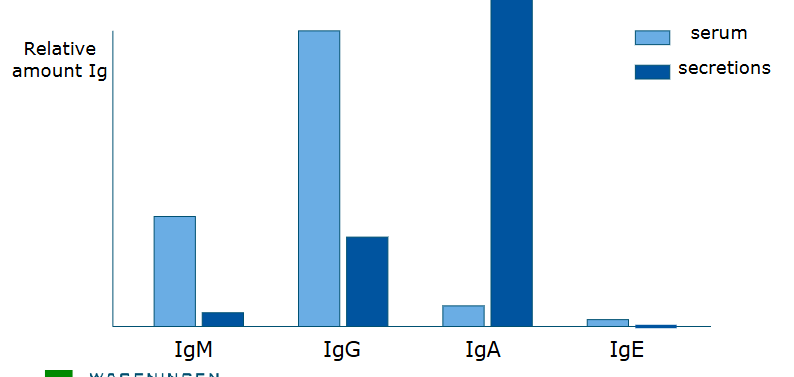
Distribution of IgM, IgG, IgA, IgE in serum and secretionsS
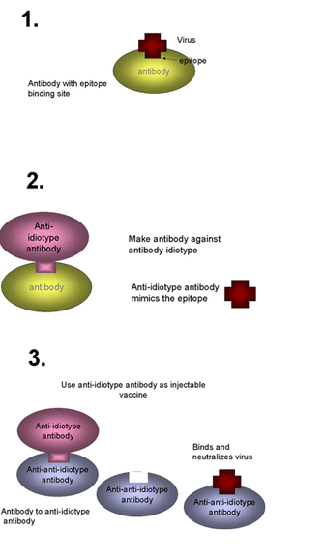
Anti-idotype vaccines
Antigen
Idiotype → anit-idiotype (mimic of epitope) → anit-anit-idiotype (recognizes epitope)
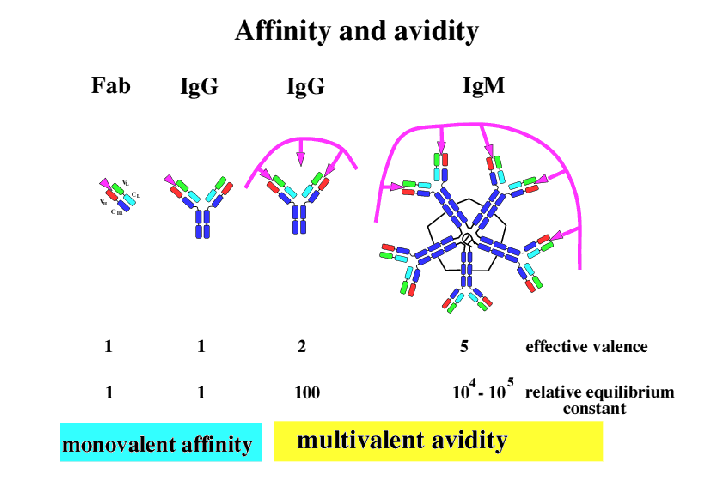
Affinity of an antibody
Affinity is the binding strenght of the interaction beteen epitope and an antibody’s antigen binding site
Binding strenght of a single interaction (1 single Fab fragment + 1 epitope)
[ Ag] + [Ab] ← → [Ag-Ab]
Affinity constant:
Ka = [Ag-Ab]/[Ag][Ab]
Antibody-antigen binding is reversible
Affinity is determined by
Hydrophobic bonds
Hydrogen bonds
Electrostatic bonds
Van der Waals bonds
Avidity
The accumulated strength of multiple affinities of individual non-covalent binding interactions (also called functional affinity)
avidity > sum of individual affinities
Affinity and avidity
Fab/IgG monovalent affinity
IgG/IgM multivalent avidity
Antibody production
Helper T cell → B cell → plasma cell → secreted antibodies
BCR
B cell receptor
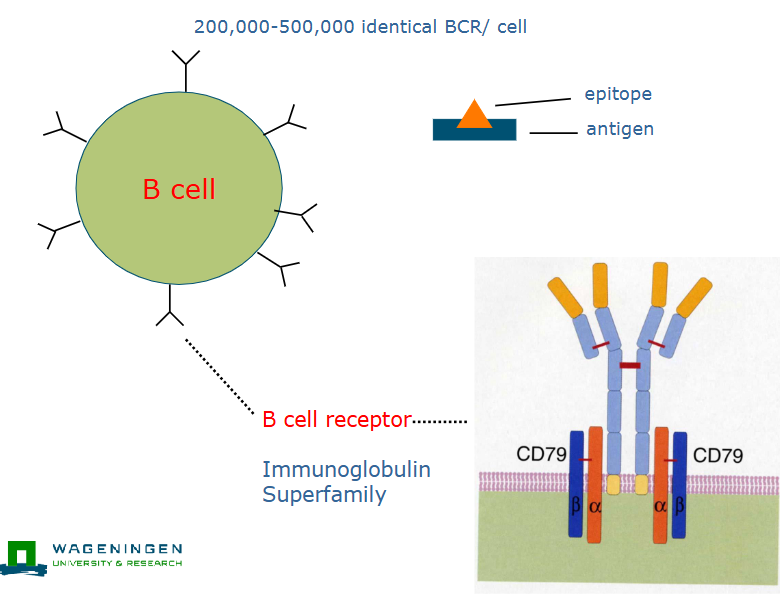
All BCRs are Igs but not all Igs are BCRS

Results of antigen binding to BCR
Ag internalization
Entry into cell cycle
Enhanced survical (anti-apoptotic)
Increased MHC II nad costimulator expression
Increased cytokine receptor expression
B cell is efficient APC especially in priemd individuals
T-dependent antigens
T helper cell helps B cell to become fully activated
Steps to antibody production
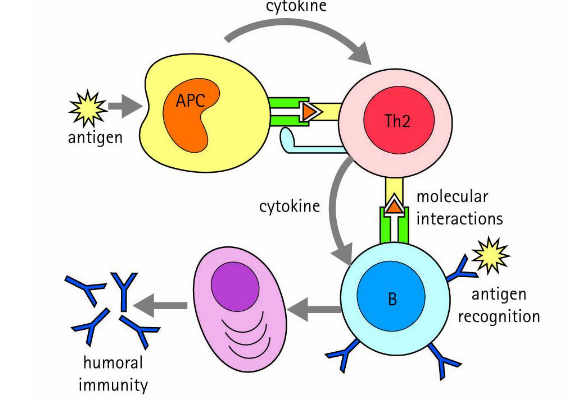
T cell dependent activation of B cells
3 signals required for B cell activation
Antigen binding by B cell receptor = cell bound immunoglobuli
Costimulation by T helper cells
Cytokines (IL-4)
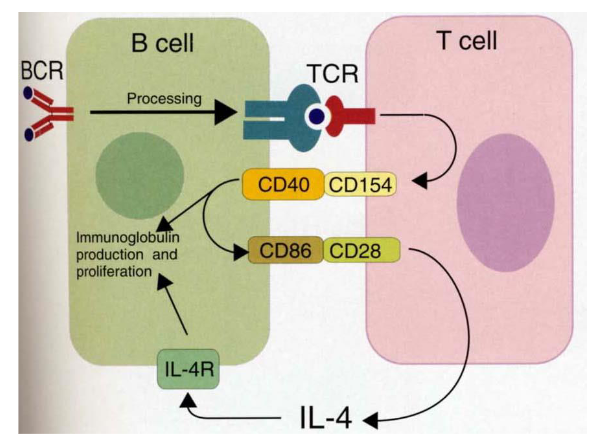
Secondary response
B cell act aslo as antigen presenting cell
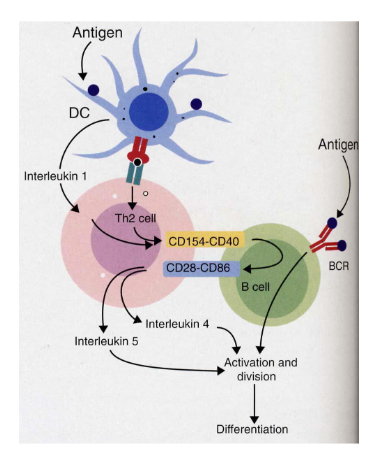
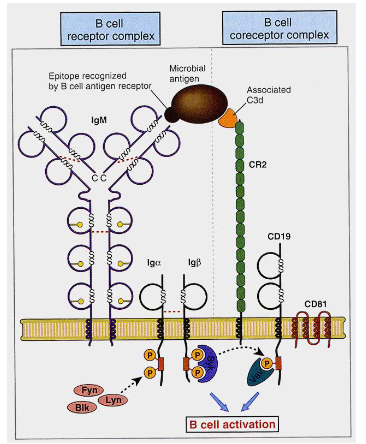
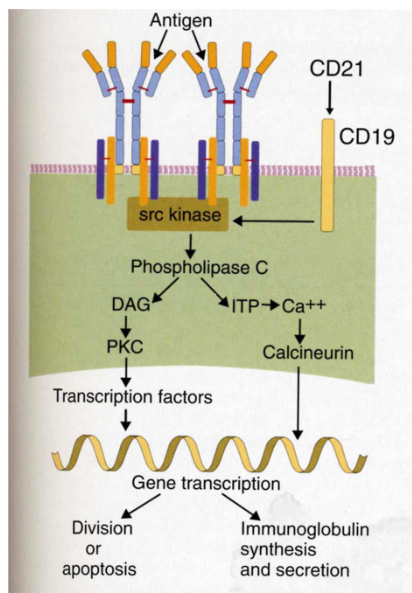
B cell activation by Ag
Synergestic signals of BCR + CD19/CD21 complex (receptor for complement facto 3d) results in 100-fold B cell activation
Factor 3d is derived from complement factor C3b
M
Mechniams isotype (class) swithcing
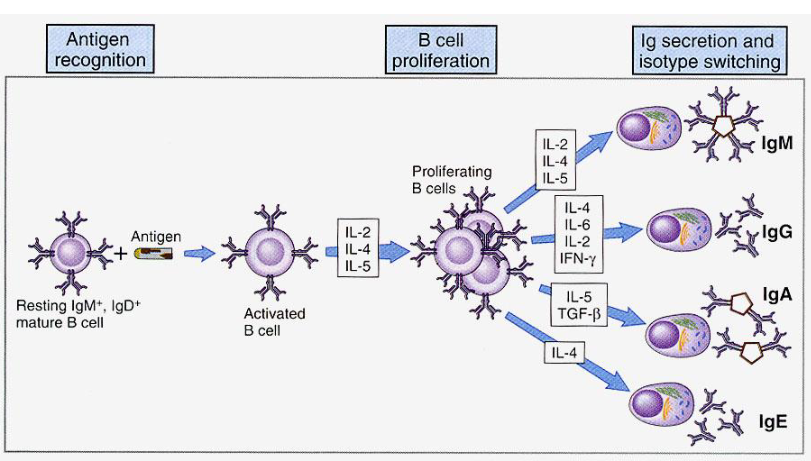
Class swithcing from IgM to IgG
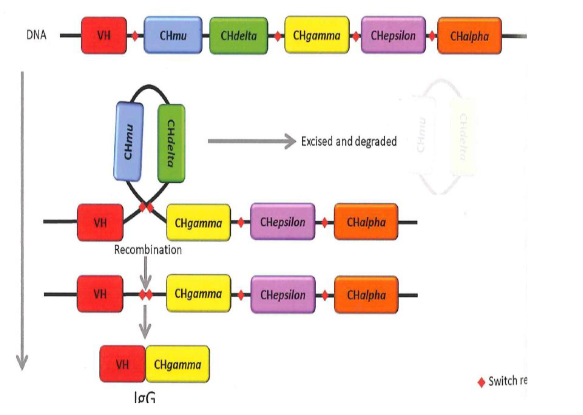
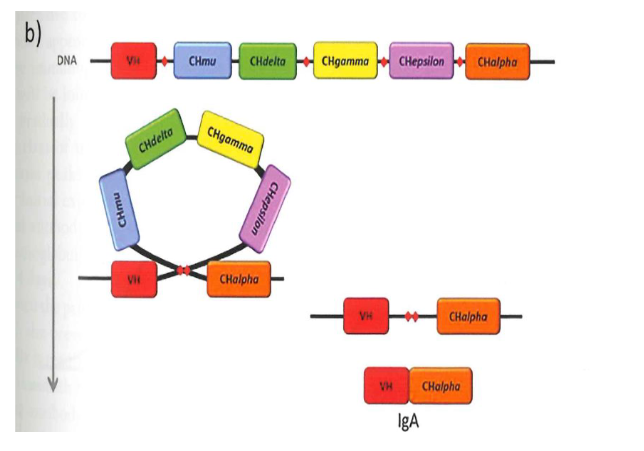
Class switching to IgA
Cytokines induce class switching/isotype switch
IgG - interferon-gamma (IFN-Y)
IgA - tumor growth factor-beta (TGF-B)
IGE - IL4, IL5, IL13
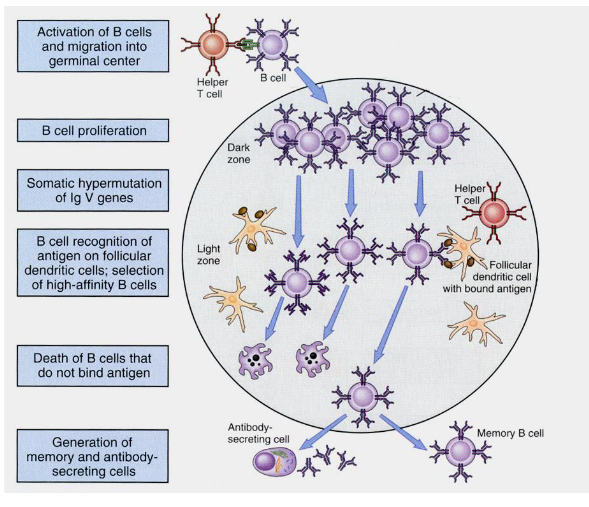
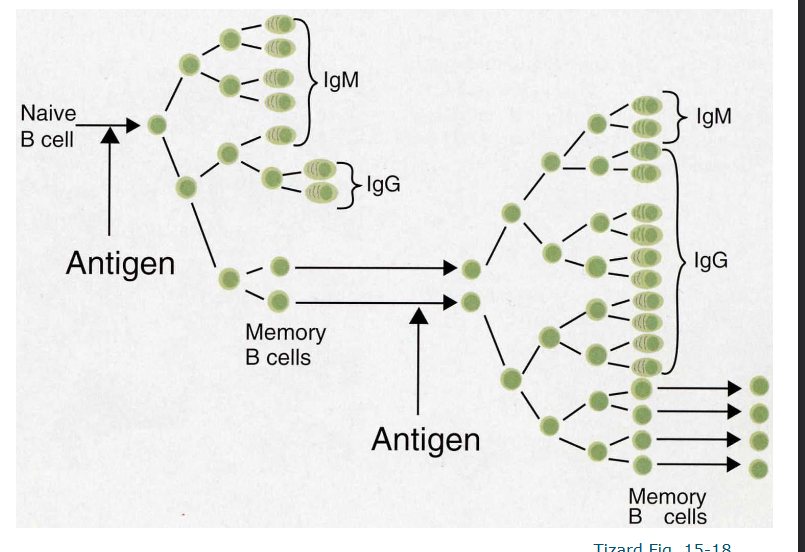
Clonal selection theory
States that a clonal expansion of the original lymphocyte occurs when the orignal lymphocyte is activated by binding to the antigen
Each lymphocyte (B or T cell) bears a single unique receptor with a specific antigen-binding site
When an antigen enters teh body, it selects (binds) only those lymphocytes wtih receptors that specifically recognize it
The selected lymphocyte proliferates (clonal expansion), producing a large populattion (clone) of identical cells, all specific for that same antigen
Some of these cells becoem effector cells (e.g. plasma cells that secrete antibodies) and other become memory cells for faster responses upon re-exposure
T cell dependent and independent antigens
T cell independent: antigen has repeating structures, often carbohydrates, eg. LPS
T cell dependnet: antigen is often protein and B cell needs T cell help
Activation of B cell by thymus independent antigen
T cell dependent and independent antigens - graph of concentration [Ab]
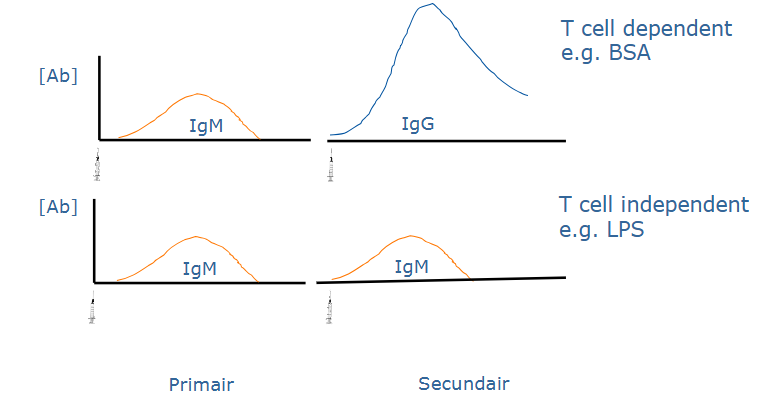
Features of the 2nd response
shorter latent period
prolonged Ab production
higher (IgG) Ab concentration
different isotypes
increased Ab iffinity
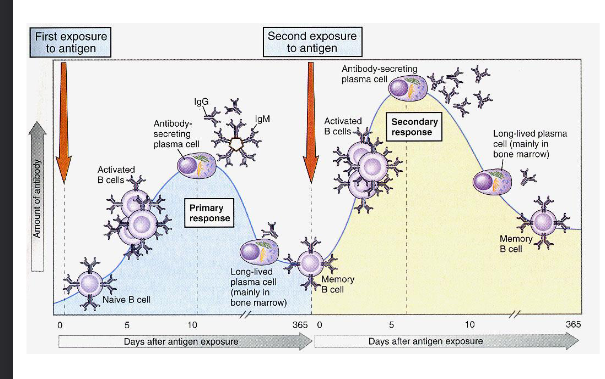
kinetics of the immune response
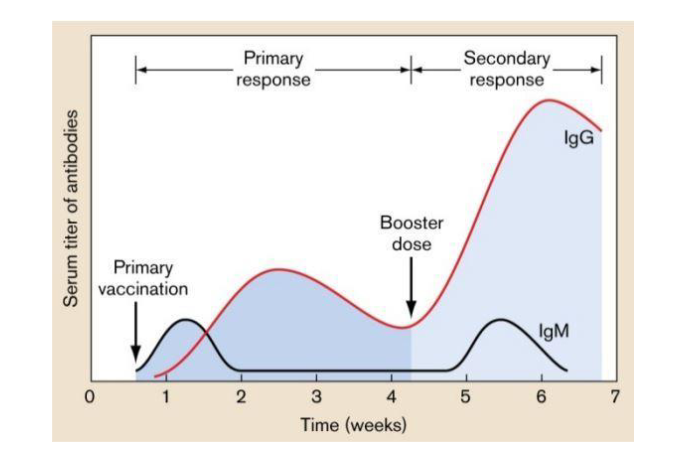
what is the role of the booster dose
How to get from a Naive B cell to a memory B cell
Differences primary and secondary response
Primary
slow (4-7 days)
small amounts of Ab
IgM first
[IgM] >- [IgG]
Low affinity
secondary (booster)
fast 2-4 days
large amounts of Ab
[IgG] > [IgM]
high affinity
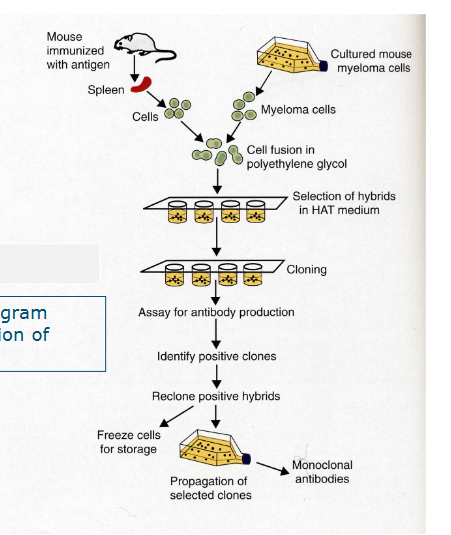
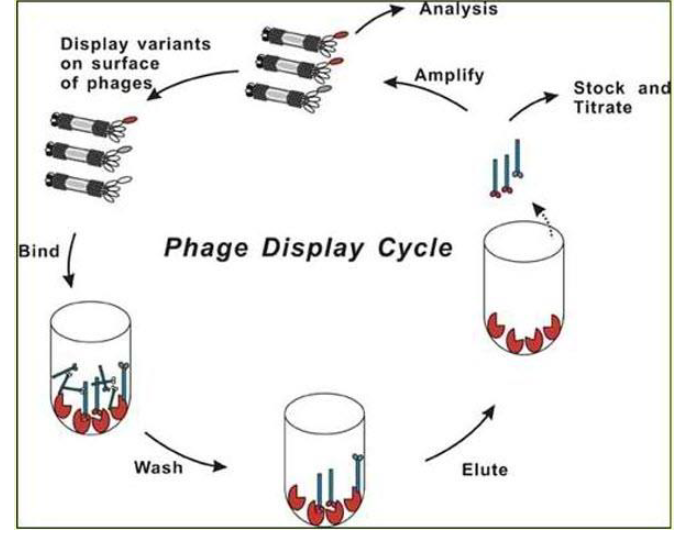
monoclonal antibodies - tests
classical method - hybridoma technique
phage display techniques - recombinant DNA
How to produce monoclonal antibodies
Phage display cycle
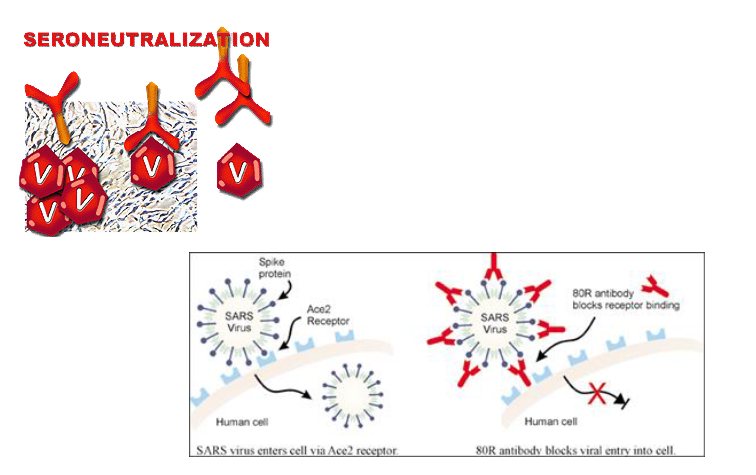
Functions of antibodies
opsonization
neutralization of toxins
complement activation
agglutination
blocking receptor binding
Humoral immunity
the immunity mediated by antibodiesd
ifferent Ig isotypes (classes) provide for … functions
different
different Ig isotypes have .. distributions
different, blood, secretions, mucus, saliva, tears, milk, cross the placenta
seroneutralizatoin
Circulating antibodies
Concentrations of Ab in serum (depending on species)
IgG, IgM, IgA
IgG, 0.3-29 mg/ml
IgM, 0.3-5 mg/ml
IgA, 0.1-5 mg/ml
Adaptive or innate immunity?
Circulating antibodies - forms
Specific antibodies (SpAbs)
Natural antibodies (NAbs)
Maternal antibodies (MAbs)
Natural antibodies (NAbs)
Immunoglobulins that circulate in the body without prior exposure to a specific antigen
CD5 positive B1 cells
Peritoneum
Mainly IgM, (IgG, IgA)
Low affinity
Low specificty (broad range)
No stimulaton
Antigenic triggering required?
Function of NAbs
Regulation Immune responses
networks
binding to cytokines, chemokines
blocking receptors
neutralization pathogens (first line of defence)
link innate and adaptive immunity (opsonization)
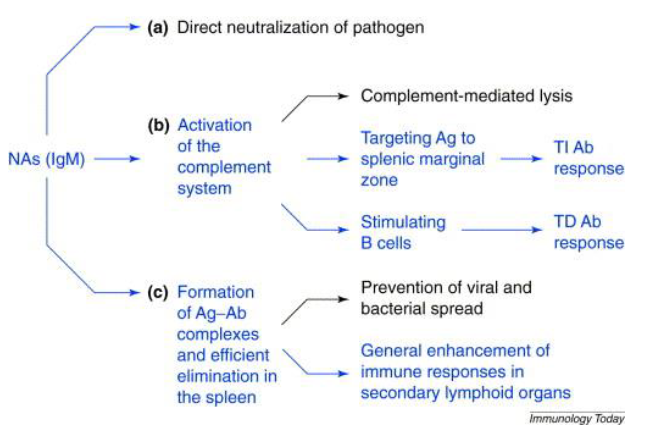
Function fo maternal antibodies
Protection of young animals
Maturation immune system
idiotypic networks
block oral tolerance induction
stimulate endogenous responses to gut microbiota
Adaptive immunity
The response of anitgen-specific lymphocytes to antigen, incluign the development of immunological memory
antibody
an antigen-binding immunoglobulin, produced by B-cells, that functions as the effector of an immune response
antigen
a foreign molecule that does not belong to the host organism and that elicits an immune response
B-cell
a type of lymphocyte that develops in the bone marrow and later produces antibodies, which mediate humoral immunity
complement
an immune response whereby a cascade of proteins attack extracellular forms of pathogens
Fab (fragment, antigen bindingn) region
the regions of the antibody that binds the antigen
Fc (fragment, crystallizable region):
the region of the anitbody that binds to cell receptors
heavy chain
heavy chains come in a variety of heavy chain classes or isotypes, each which confers a distinct function to the antibody
humoral immunity
the type of immunity that fights bacteria and viruses in the body fluids with antibodies that circulate in blood plasma and lymph
immune system
the name used to describe the totality of the host defence mechanism
immunoglobulin
all antibody molecules belong to this family of plasma proteins
isotype
anitbody class determined by the heavy chain
light chains
smaller of the two compents making up an antibody
memory B-cell
a clone of long-lived lymphocytes, formed during the primary immune response, that remains in a lymp node until activated by exposure to the same antigen that triggered it;s formation. activated memroy cells mount hte secondary immune response
naive B-cell
a B cell that has never bound antigen before
neutralization
when antibodies inhibit the infectivity of a virus or the toxicity of a toxin
opsonisation
the atleration of the sruface of a pathogen or other paticles so that it can be ingested by phagocytes
plasma cell
a derivative of B-cells that secretes antibodies, i.e. antibody factory
variable region
regions that contains the antigen binding site