(18): climate classification and biogeography
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
what is expectation?
animals are expected to adapt to their environments
what is buffon’s law?
even though some environments are similar, the plants and animals in those places are different.
what is an example of buffon’s law?
even though Antarctica in the SH is environmentally similar to the polar deserts in the NH, penguins live in the SH and polar bears live in the NH.
what is biogeography?
the study of life
what is historical biogeography?
understanding the past to understand today’s patterns
what is ecological biogeography?
a modern approach of the world today
what are biotic factors?
how plants and animals interact with one another (life interacting with life)
examples of biotic factors:
competition: lions and hyenas both hunting zebras
predation: a lion hunting and eating a zebra
mutualism: a small fish eating parasites off sharks
disturbance: forest fires
what are abiotic factors?
non-living parts of an environment that affect living things
examples of abiotic factors:
climate: makes weather conditions
topography/elevation: shape/height of land
soil: provides nutrients, water, and helps plants grow
who is wladimir koppen?
scientist who connected the distribution of plants to climate characteristics.
also created a classification system that is still used today
what are some important climactic variables?
maximum temp, minimum temp, and precipitation
what is a biome?
an ecosystem of plants and animals that share common traits for their environment
what are climate zones defined by?
temperature and precipitation
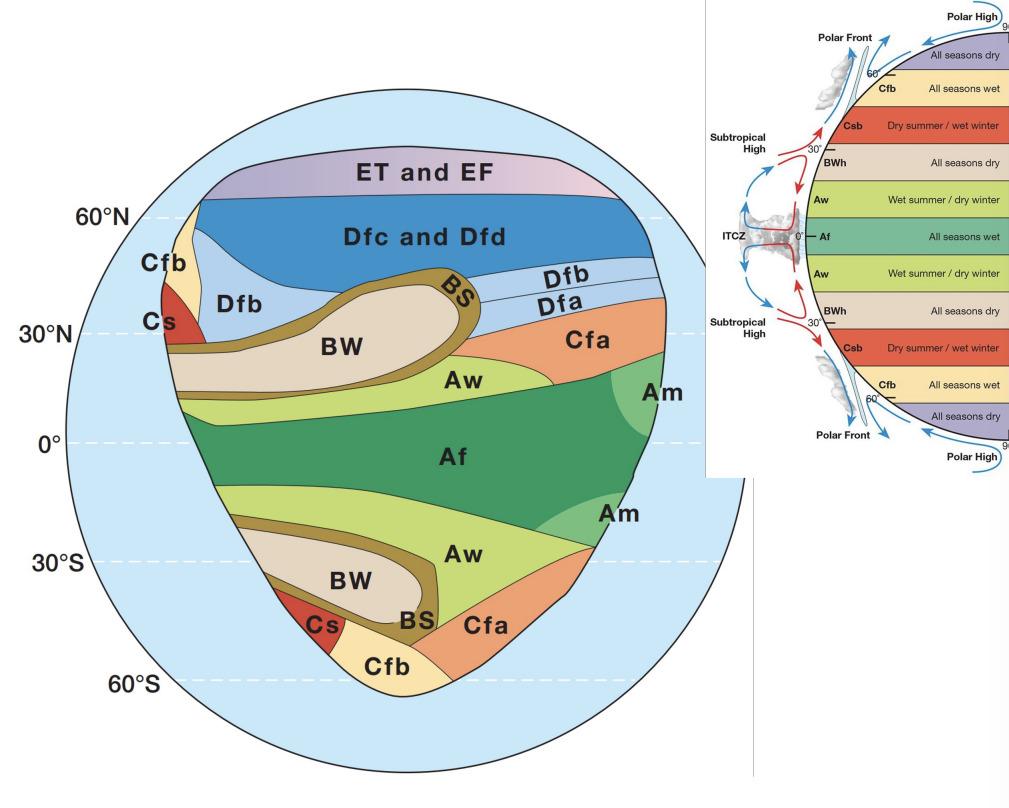
example of some climate regions:
tropics near equator
deserts near subtropics
specific land heats in midlatitude
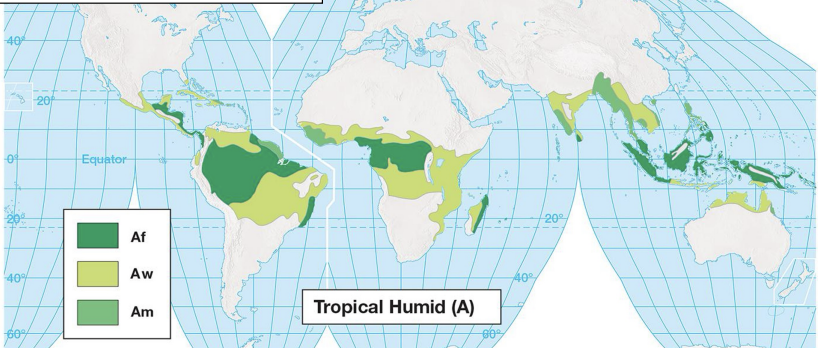
tropical climate characteristics: A
high temperatures and high precipitation
located in a narrow latitudinal band (ITZC)
zone of convergence
tropical climates: A
Af = tropical wet
Am = tropical monsoon
Aw = tropical savanna
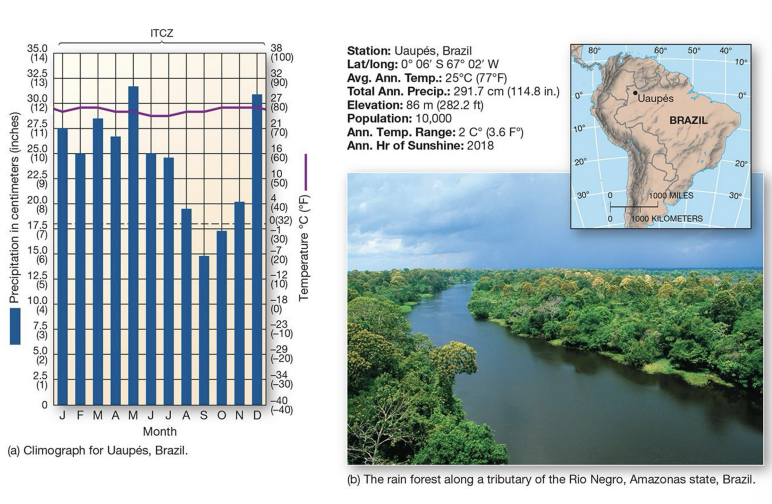
what is an example of an Af climate?
Uaupes, Brazil (South America) - tropical rain forest biome
Af components:
year-round moisture from ICTZ
water surplus throughout the year P > PET
small temp range
dense rainforest with broadleaf evergreen trees
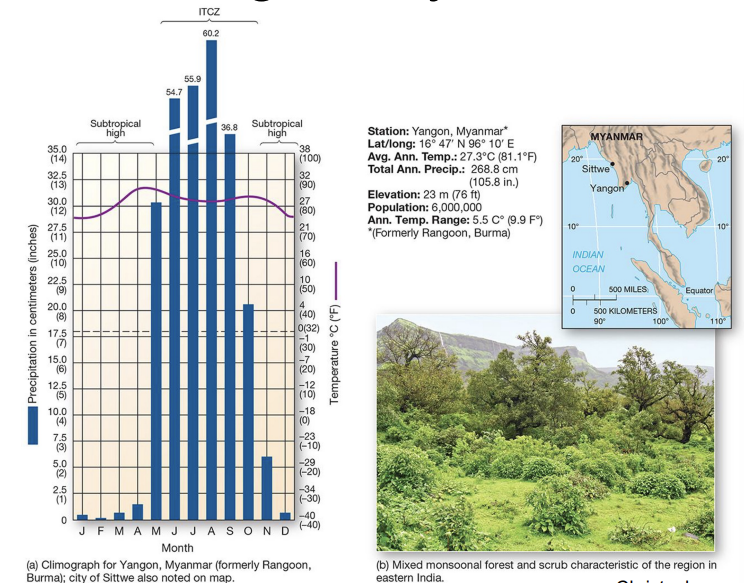
what is an example of an Am climate?
Yangon, Myanmar (SE Asia) - tropical seasonal forest biome
Am components:
monsoonal climate with dry season
ITCZ moves away seasonally
moisture surplus throughout year P > PET
less dense broadleaf evergreen trees with shrubs
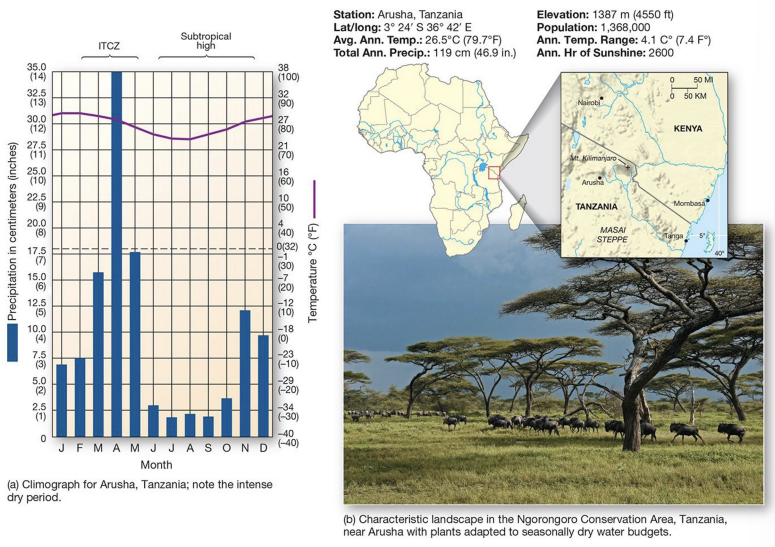
what is an example of an Aw climate?
Arusha, Tanzania (Africa) - tropical savanna biome
Aw components:
tropical climate with a pronounced dry season
scattered broadleaf evergreen trees with shrubs
grass covers most of the landscape
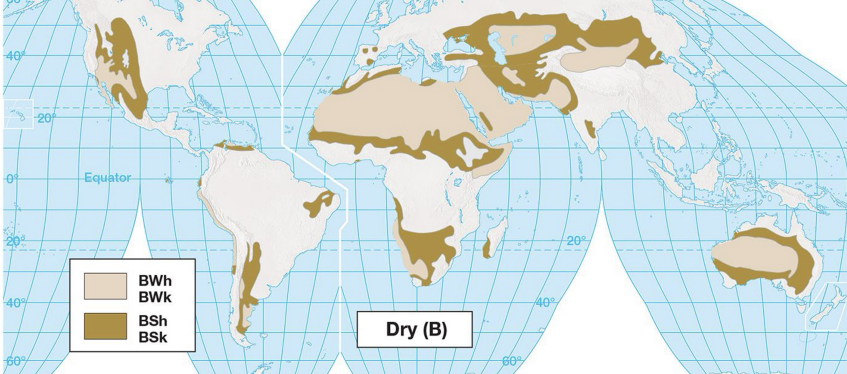
desert climate characteristics: B
covers more land than any other climate
subtropical high is the controlling climate mechanism
moisture deficit throughout the year
desert climates: B
Bw = hot, dry desert
Bs = dry climate with temp and precipitation varying by latitude
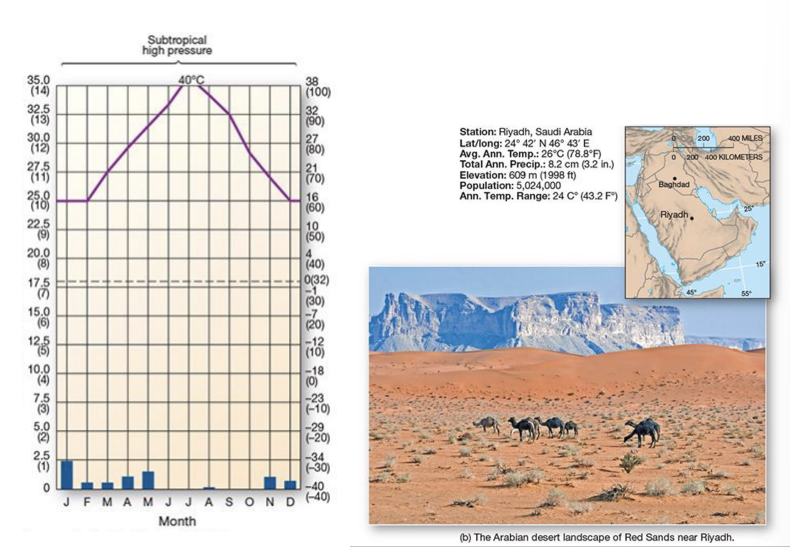
what is an example of a Bw climate?
Riyadh, Saudi Arabia - warm desert and semidesert biome
Bw components:
PET > precipitation
precipitation comes through convective storms
little vegetation, hardy shrubs
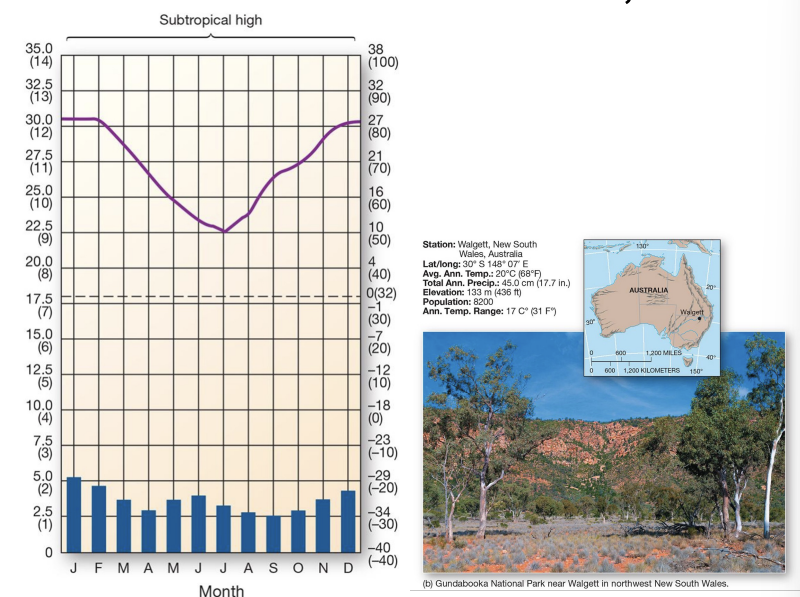
what is an example of a Bs climate?
New South Wales, Australia - warm desert and semidesert biome
Bs components:
short grass, prairie vegetation
transition between desert and subhumid climates
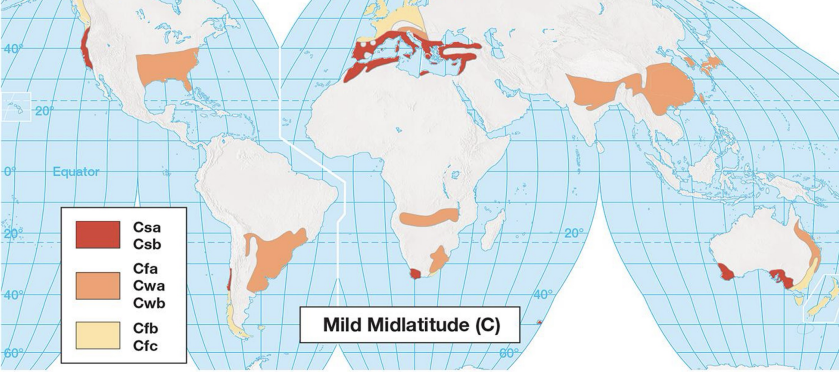
mild midlatitude climates characteristics:
mild temperatures (0-18°C)
precipitation varies by location and latitude
midlatitude cyclones important for rainfall
mild midlatitude climates: C
Cf = mild climate with precipitation throughout the year
Cs = mild, moist winters and hot dry summers
Cw = mild climate with summer monsoon rainfall
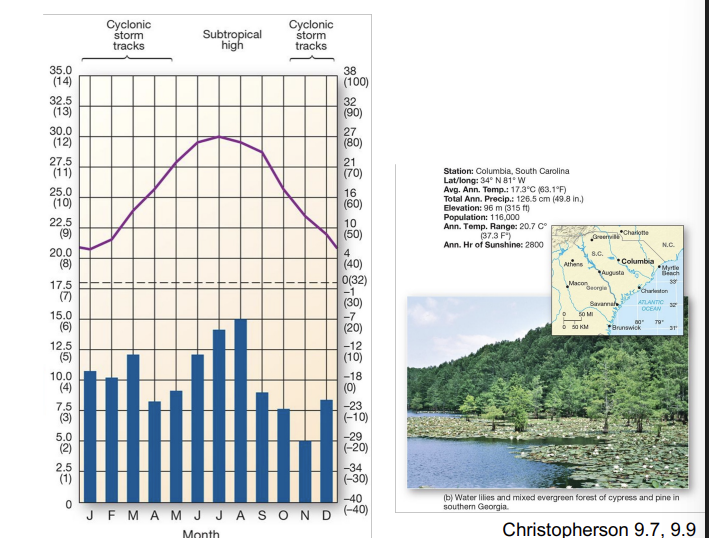
what is an example of a Cf climate?
Columbia, South Carolina - midlatitude broadleaf and mixed forest biome
Cf components:
timing of precipitation divides the climate
deciduous (trees shed annually) vegetation
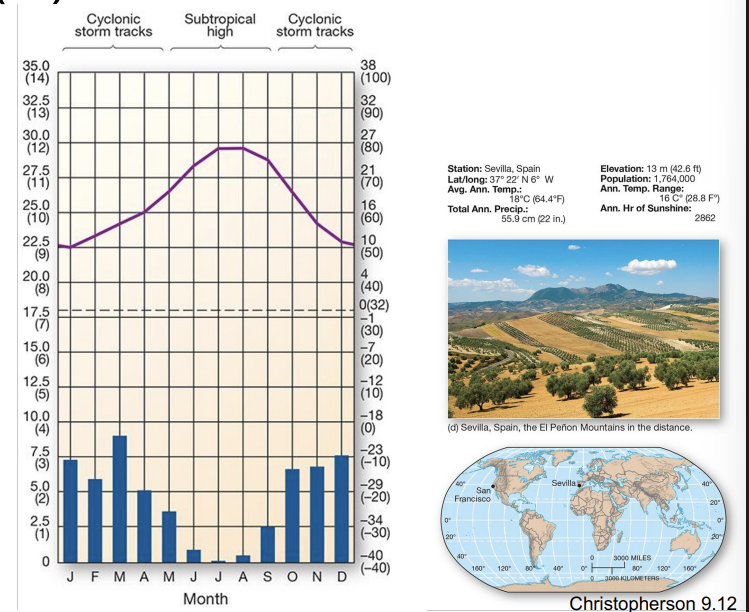
what is an example of a Cs climate?
Sevilla, Spain - Mediterranean shrubland climate biome
Cs components:
precipitation deficit during the summer PET > P
rainfall in winter due to cyclones
savanna / shrubland vegetation
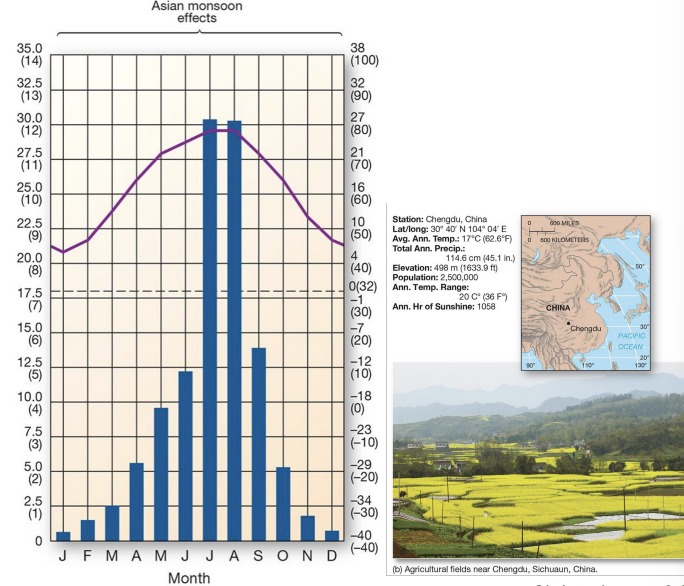
what is an example of a Cw climate?
Chengdu, China - midlatitude broadleaf and mixed forest biome
Cw components:
subtropical monsoon climate
intense summer rainfall can cause natural disasters
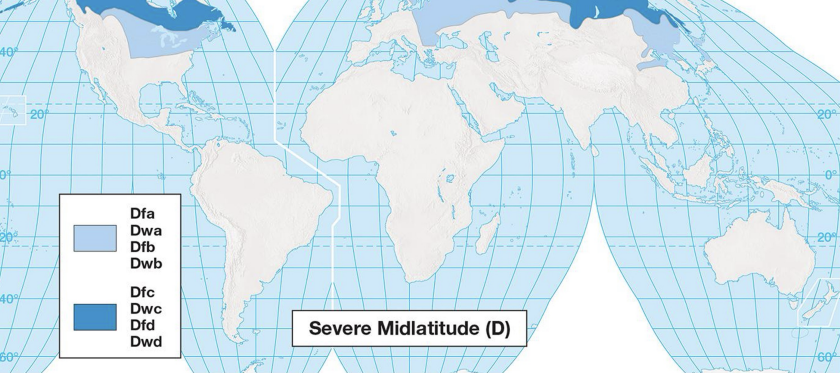
high latitude climate characteristics: D
large summer-winter temp range
permafrost
only exists in NH
high latitude climates: D
Df = large temp range with year round precipitation
Dw = large temp range with convective storms and monsoonal rain
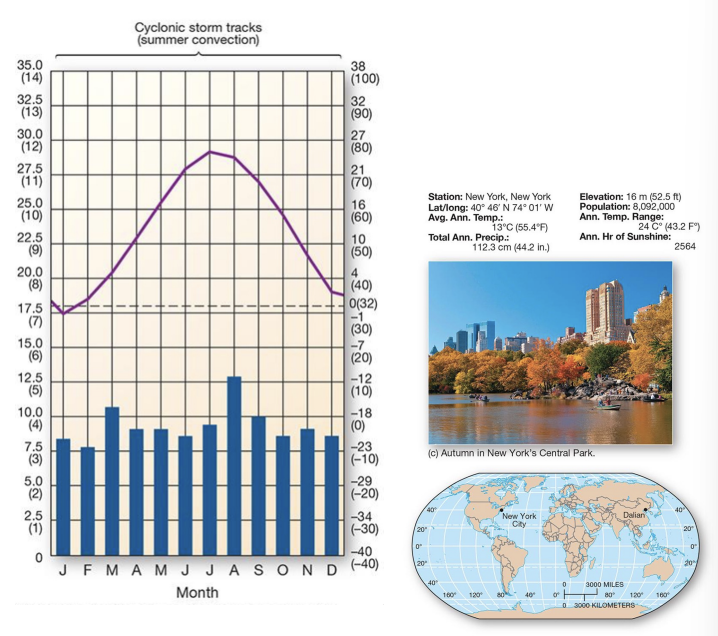
what is an example of a Df climate?
New York City - midlatitude broadleaf and mixed forest climate
Df components:
broadleaf deciduous and needleleaf evergreen trees
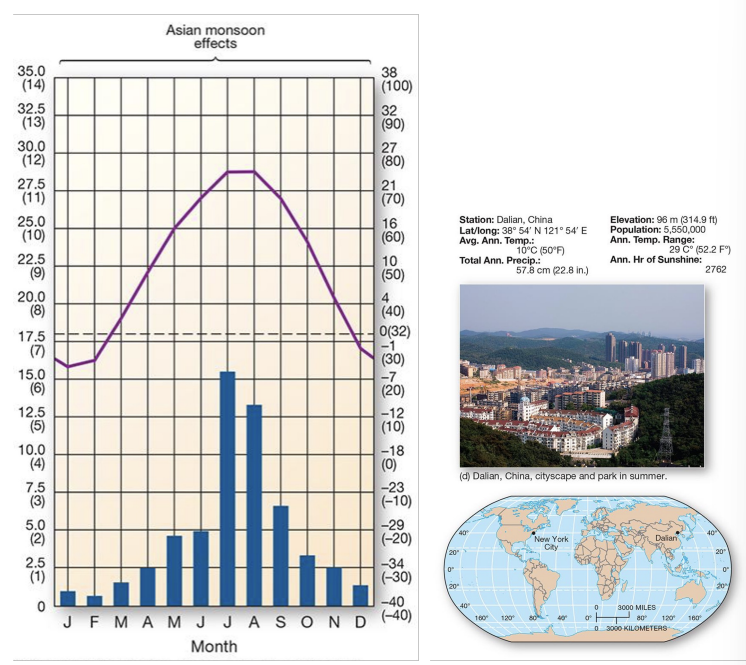
what is an example of a Dw climate?
Dalian, China - midlatitude broadleaf and mixed forest biome
Dw components:
broadleaf deciduous and needleleaf evergreen trees
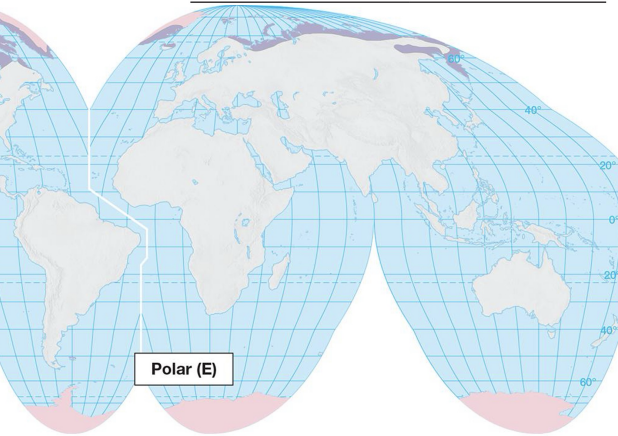
polar climates: E
Verkhoyansk, Russia - polar desert biome
only occur as polar latitudes
no trees
few grasses, dwarf shrubs, lichen
polar night - pitch black in the winter, plants need light to photosynthesize so they adapt to their conditions
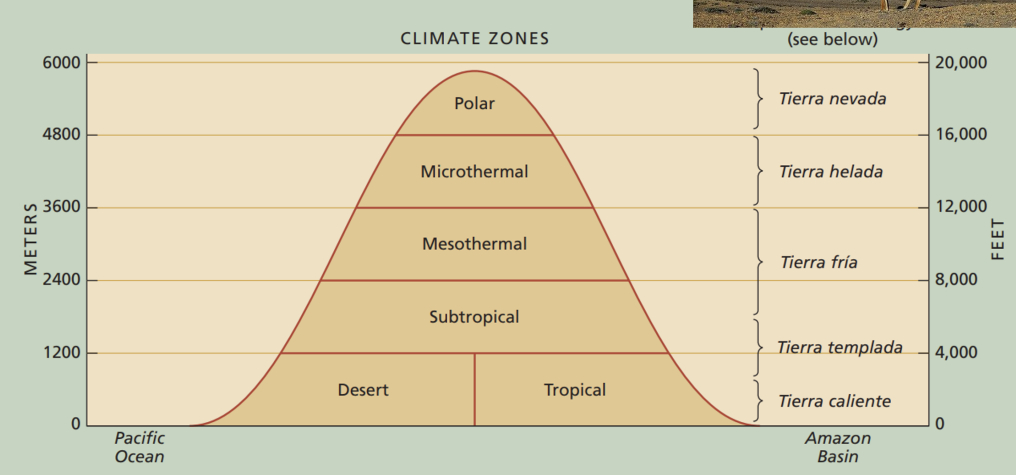
highland climates: H
only exist in mountain ranges
as you go up, you experience different climates and different biomes