Cardiovascular system A/P
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
what is the cardiovascular system made up of
heart, blood and blood vessels
what is Blood
Liquid connective tissue that transports oxygen and nutrients around the body
what are the Main functions of blood
Transport, regulation, protection
what are the key things that blood transports
O₂, CO₂, nutrients, hormones, and waste
what is the Regulation role of blood
Maintains pH, temperature, fluid and electrolyte balance
what is the Protection role of blood
Prevents blood loss (clotting) and infection (WBCs)
Buffy coat percentage
what are the three components of blood
plasma, buffy coat and red blood cells
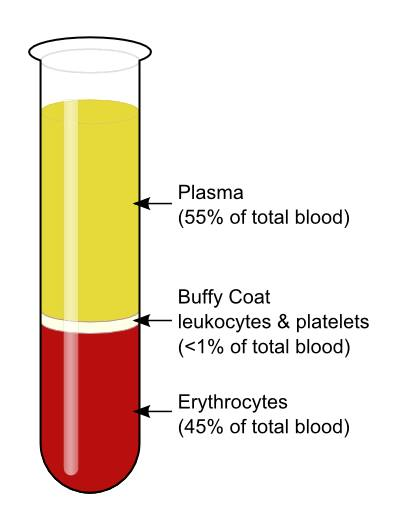
what are the Formed elements in blood
RBCs, WBCs, platelets
where is the Site of blood cell production
Bone marrow
what is Plasma
Non-living liquid matrix of blood
what are the Main plasma solutes
Proteins, electrolytes, nutrients, wastes, hormones
what are some Electrolytes in plasma
sodium, potassium, chloride, magnesium, phosphate
what are the Waste products in plasma
Urea, uric acid
what are the three proteins in plasma
albumins, fibrinogen and globulins
what does Albumin do in plasma
Maintain osmotic pressure and blood viscosity; bind drugs
what does Fibrinogen do in plasma
Essential for blood clotting
what do Globulins do in plasma
Transport substances and support immunity
what are Gamma globulins
Antibodies (immunoglobulins)
what is an Antibody
Y-shaped proteins that bind specific antigens
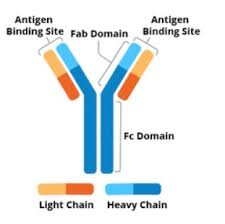
what is an Antigen
Substance that triggers an immune response
what is the difference between an antigen and antibody
antigen= foreign substance such as bacteria or virus, antibody= proteins that bind to antigen and get rid of them
what is the function of an antibody
Bind and agglutinate antigens for immune destruction
what are red blood cells also known as
erythrocyte
what is the primary function of a RBC
Transport oxygen and carbon dioxide
what is the shape of a RBC and why
Biconcave disc increased surface area
does a RBC have a nucleus and why
no, to have maximum space to carry as much oxygen as possible
what is the structure of a haemoglobin
2 alpha subunits and 2 beta subunits
what is a Haem group
Iron-containing site that binds O₂ or CO₂
what is the importance of Iron in haemoglobin
Required for oxygen binding
what is Oxyhaemoglobin
Haemoglobin bound to oxygen
what is Deoxyhaemoglobin
Haemoglobin not bound to oxygen
what is the cause of Cyanosis
Low oxyhaemoglobin, blue colouring on skin
what is the structure of Foetal haemoglobin
2 alpha + 2 gamma subunits
why is foetal haemoglobin have higher oxygen affinity
contain gamma subunits which hold oxygen more tightly than beta chains
Purpose of foetal haemoglobin
Pull oxygen from maternal blood in placenta
what is Erythropoiesis
Production of new red blood cells
what is Erythropoietin
Hormone stimulating RBC production
what triggers the release of Erythropoietin
Low oxygen levels
where is the source of Erythropoietin
Kidneys (and liver)
how are Old RBC removed
Phagocytosis by macrophages in liver and spleen
how is iron recycled in the body
Returned to bone marrow for erythropoiesis
how is Bilirubin formed in the body and how is it removed
Breakdown product of haem → excreted in faeces
what is the function of white blood cells
Immune defence against pathogens
where are WBC located in blood
Buffy coat
when does WBC count change
during increased infection/inflammation and decreased immunosuppression
what is a platelet also known as
thrombocyte
what is the function of a Platelet
Blood clotting
what is blood clotting also known as
haemostasis
what is the structure of a Platelet
Cell fragments without nucleus
where are Platelets recycled
Liver and spleen
what is Haemostasis
Process that prevents blood loss after injury
what is haemostasis also known as
blood clotting
what are the three key steps in haemostasis
vasoconstriction, platelet plug formation and coagulation cascade
Step 1 haemostasis
Vasoconstriction
Vasoconstriction trigger
Vessel injury and pain receptors
Step 2 haemostasis
Platelet plug formation
what is Platelet activation
Platelets stick to exposed collagen
Step 3 haemostasis
Coagulation cascade
what two things form a stable clot mesh
Fibrinogen → fibrin
what does Positive feedback in clotting achieve
Recruits more platelets
what does Negative feedback in haemostasis achieve
Prevents excessive clotting
what are the three steps of clot breakdown in the body
syneresis, fibrinolysis and plasmin
what is Syneresis
Clot retraction pulling wound edges together
what is Fibrinolysis
Breakdown of fibrin clot
what is Plasmin
Enzyme that dissolves fibrin
what are the four blood types
A, B, AB, O
what are Blood group based on
Antigens on RBC surface
what does Type A blood contain
A antigens; anti-B antibodies
what does Type B blood contain
B antigens; anti-A antibodies
what does Type AB blood contain
A and B antigens; no antibodies
what does Type O blood contain
No antigens; anti-A and anti-B antibodies
what does Rh positive contain
D antigen present
what does Rh negative contain
No D antigen; anti-Rh antibodies
what is the Rh transfusion rule
Rh- patients receive only Rh- blood
what blood type can O blood type receive
Can only receive O blood
what can type A blood type receive
Can receive A or O
what can B blood type receive
Can receive B or O
what is AB blood type
Universal recipient
what is O- blood
Universal donor
what can a Transfusion reaction cause
Antibody-antigen agglutination
what is the Risk of wrong blood type being given
Acute haemolytic transfusion reaction (life-threatening)
what is the Vascular system function
Transport blood throughout body
what is the Blood vessel sequence
Arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules , veins
where does Oxygenated blood exit the heart
Via aorta
where does Deoxygenated blood return
Via vena cava
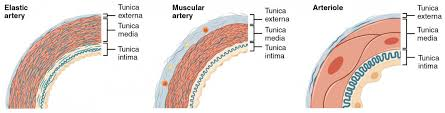
what is the Tunica intima
Inner endothelial layer of blood vessel
what is the Tunica media
middle layer of blood vessel containing Smooth muscle for vasodilation/constriction
what is the Tunica externa
Outer connective tissue layer on the blood vessel
what is structure of Capillaries
Only one endothelial layer (one cell thick)
what is the role of Arteries
Carry blood away from heart under high pressure
what and where are Elastic arteries
Stretchy; near heart (e.g. aorta)
what are Muscular arteries
Thick smooth muscle; regulate flow
what are Arterioles
Small resistance vessels controlling BP
what are Metarterioles
Connect arterioles to capillary beds
what are the three types of arteries
elastic artery, muscular artery and arterioles
what is the function of Capillaries
Exchange gases, nutrients, waste
what is the Capillary wall made up of
Single endothelial cell layer
what is Fenestrae and its purpose
Tiny pores allowing exchange
what do Venules do
Drain capillaries; low pressure