Human evolution
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
The grasping hands and feet of primates are adaptations for
hanging on to tree branches
all modern primates, except what, have a big toe that is widely separated from the other toes
Homo
The thumb is relatively mobile and separate from the fingers in all primates, but a what is found only in anthropoid primates
opposable thumb
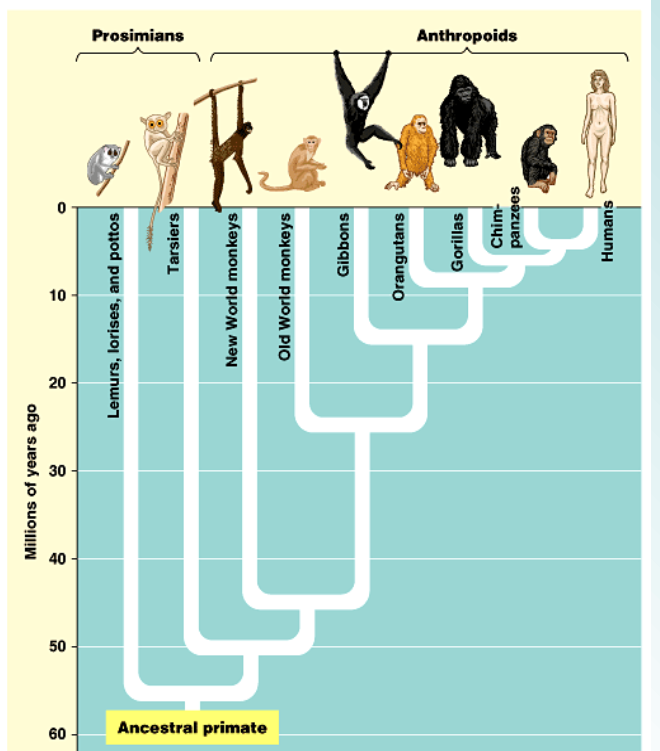
two subgroups of primates
prosimii and anthropoidea
prosimii vs anthropoidea
probably resemble early arboreal primates and include the lemurs of Madagascar and the lorises, pottos, and tarsiers of tropical Africa and southern Asia vs. moneys, apes, and humans
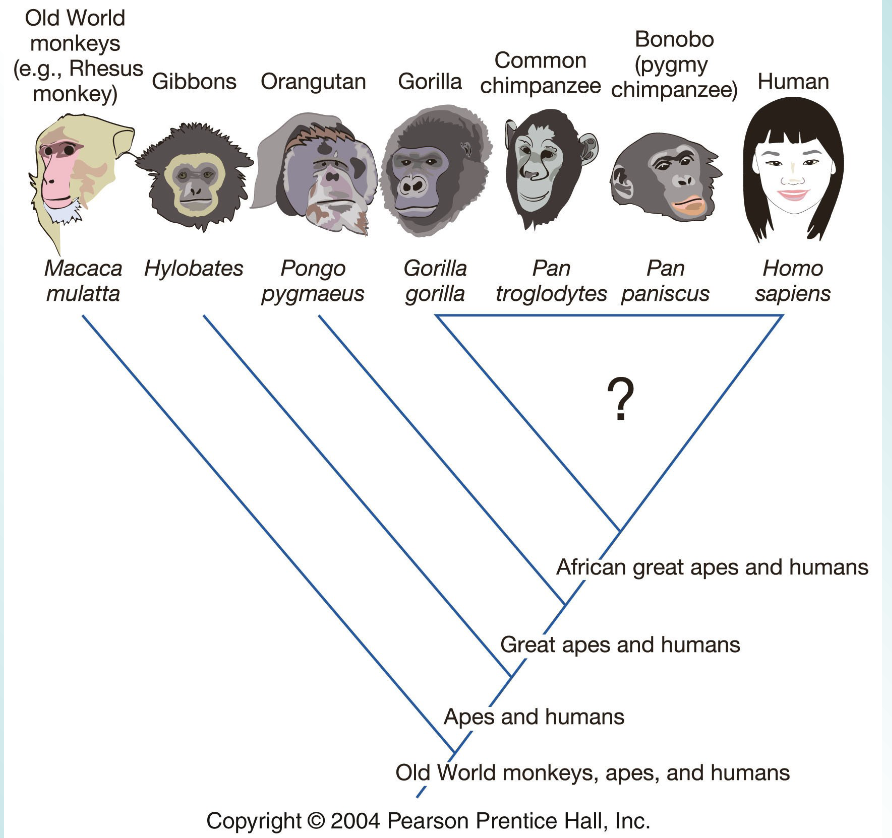
Humans belong to the same clade as
the African Great Apes
first hominids came about
5 mya

our ancestors were not chimpanzees or any other modern apes but
Chimpanzees and humans represent two divergent branches of the hominoid tree that evolved from a common ancestor that was neither a chimpanzee nor a human
human evolution did not occur as a ladder with a series of steps leading directly from an ancestral hominoid to Homo sapiens but
Human phylogeny is more like a multibranched bush with our species as the tip of the only surviving twig
the various human characteristics, such as upright posture and an enlarged brain, did not evolved in
unison
mosaic evolution
Different features evolved at different rates
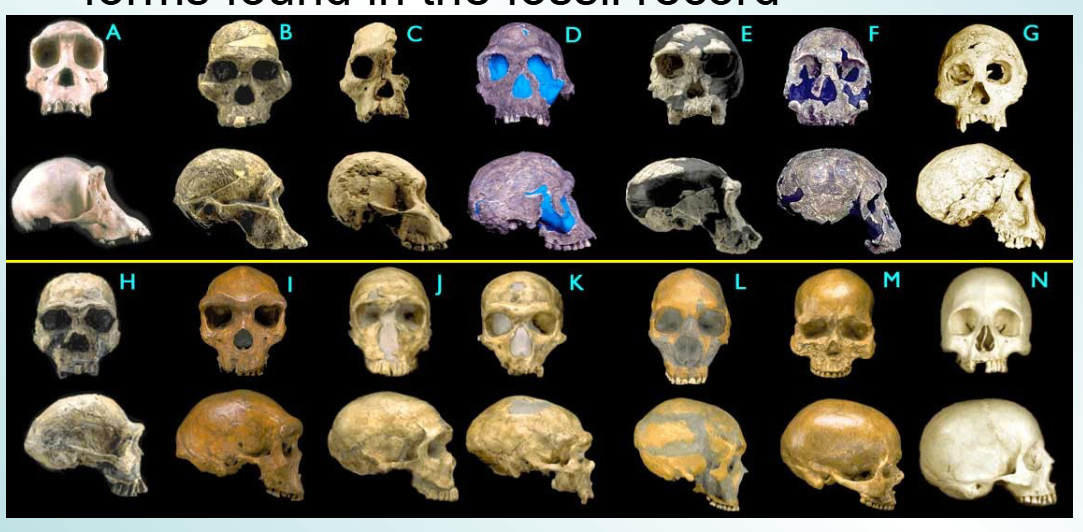
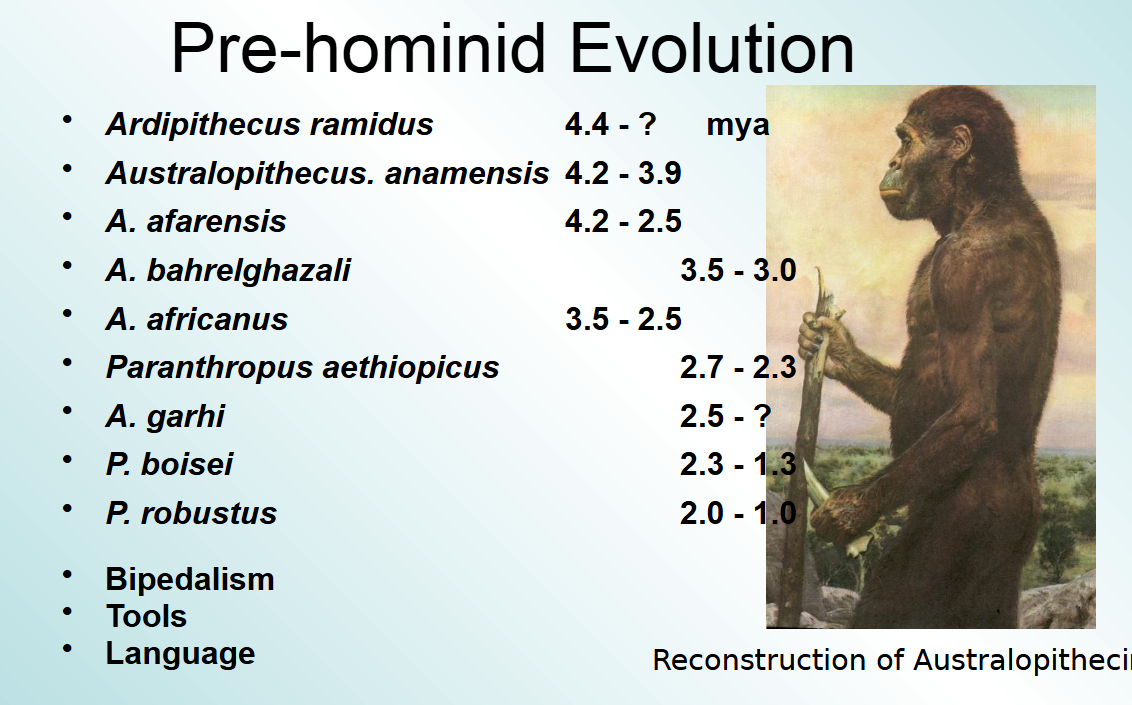
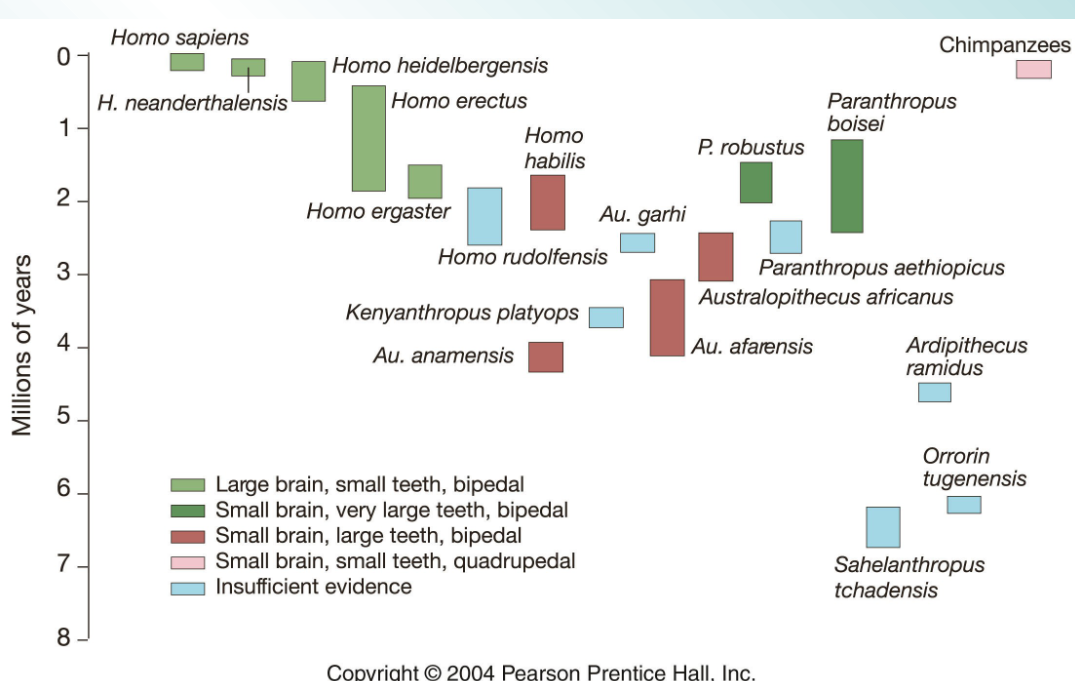
There are at least how many different hominid forms found in the fossil record
20
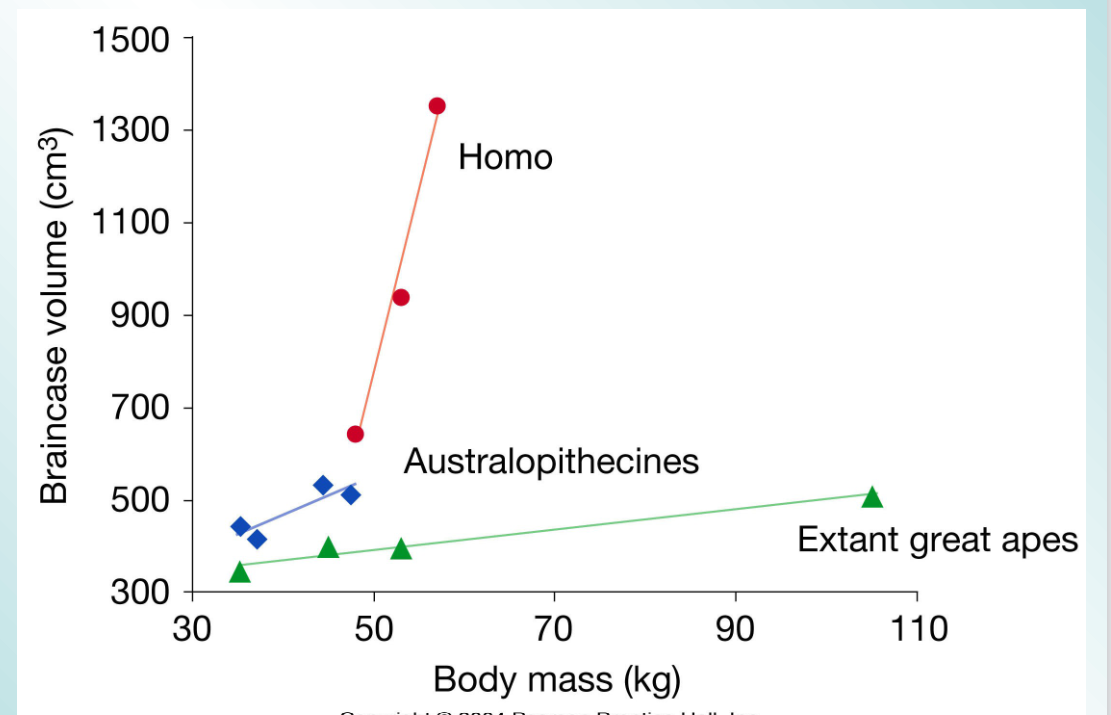
by how much have the brain size of hominids grown over 6 mil yrs
Based on skull measurements, researchers have estimated that brain size in hominoids tripled over the past 6 million years
jaw size of hominoids vs humans
Our hominoid ancestors had longer jaws - prognathic jaws - than those of modern humans
what resulted in flatter face with more pronounced chin for humans
the prognathic jaws/longer jaws
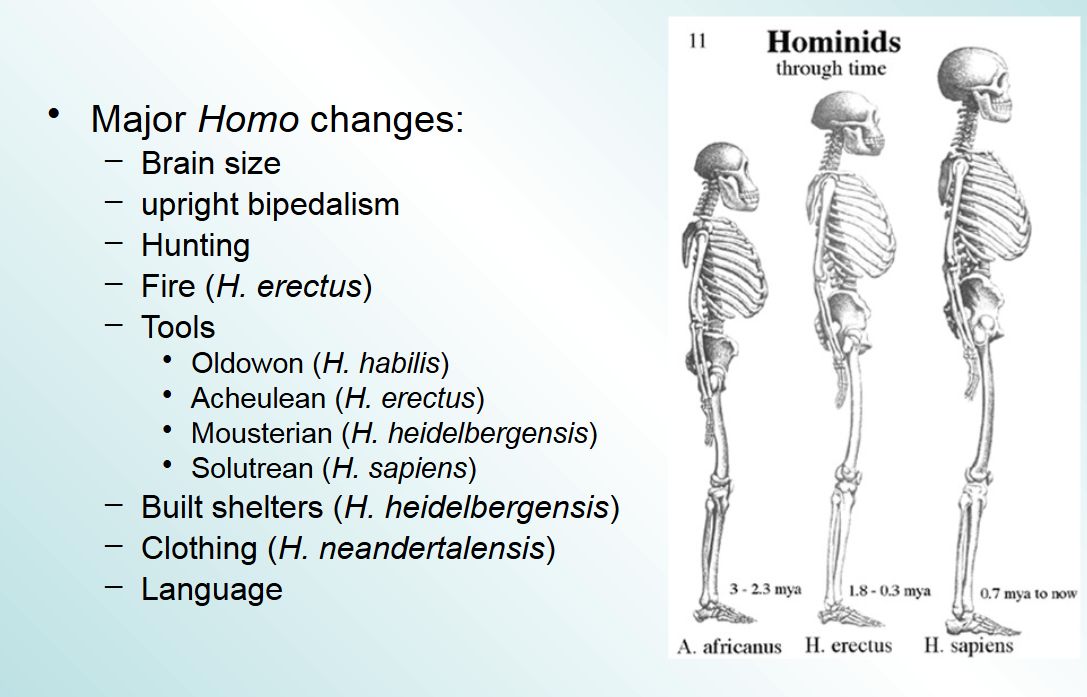
major homo changes
origin of homo sapiens
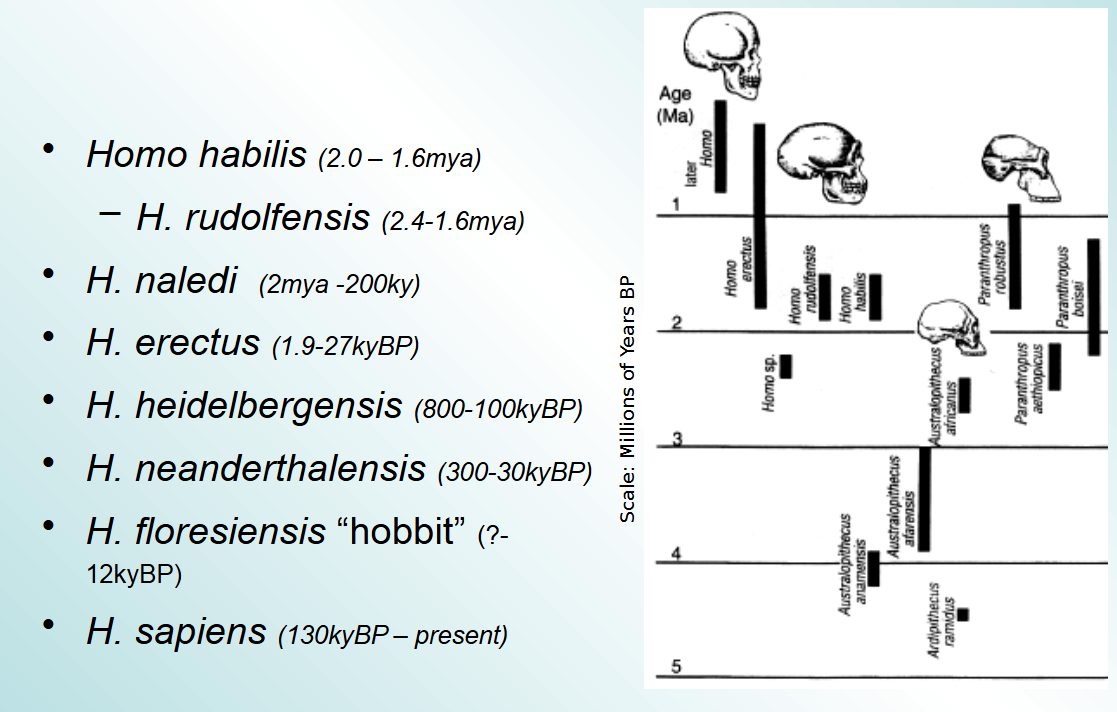
Homo habilis; a specific species of hominin, which are a group of primates including modern humans and all extinct human species
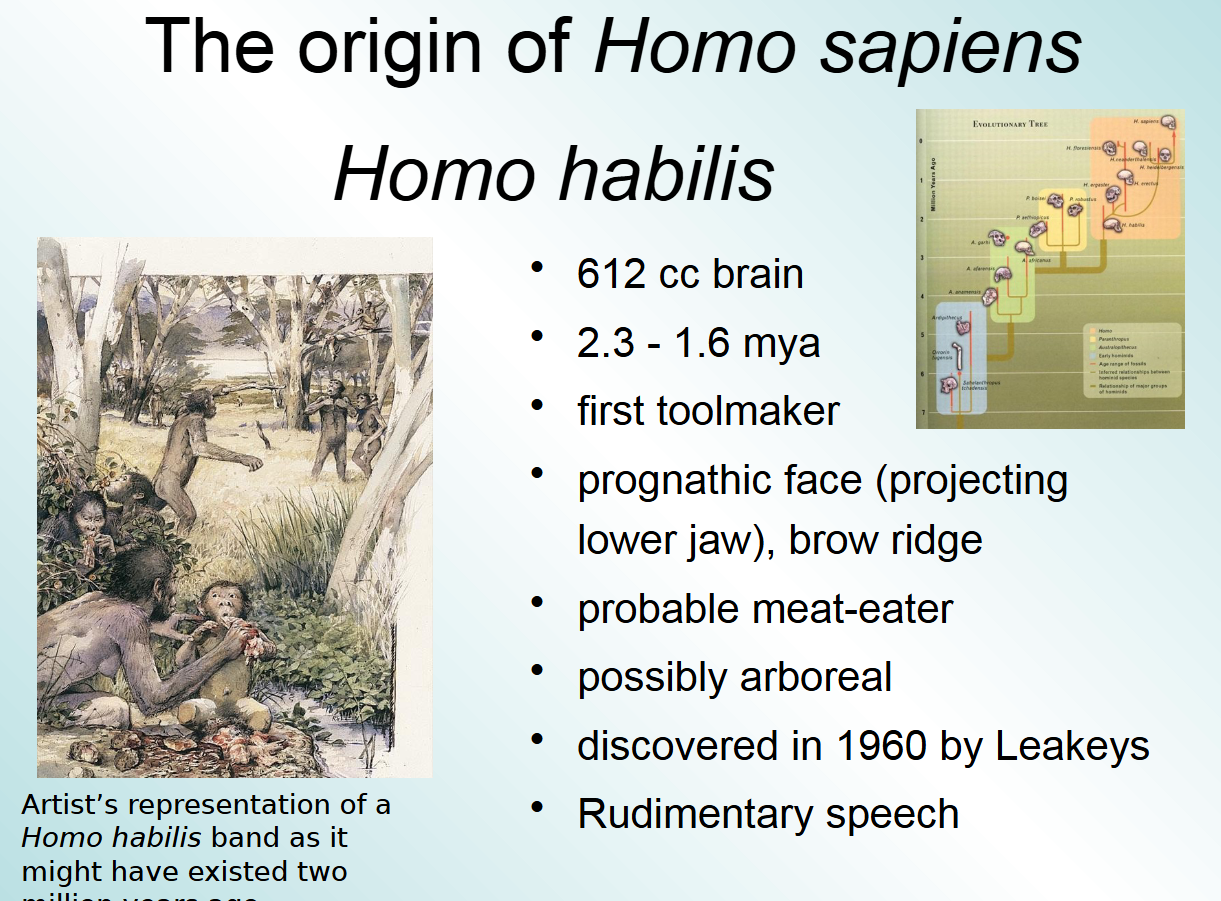
H. habilis vs. H. erectus
H. erectus was considerably taller and had a larger brain than H. habilis

tools of hominids
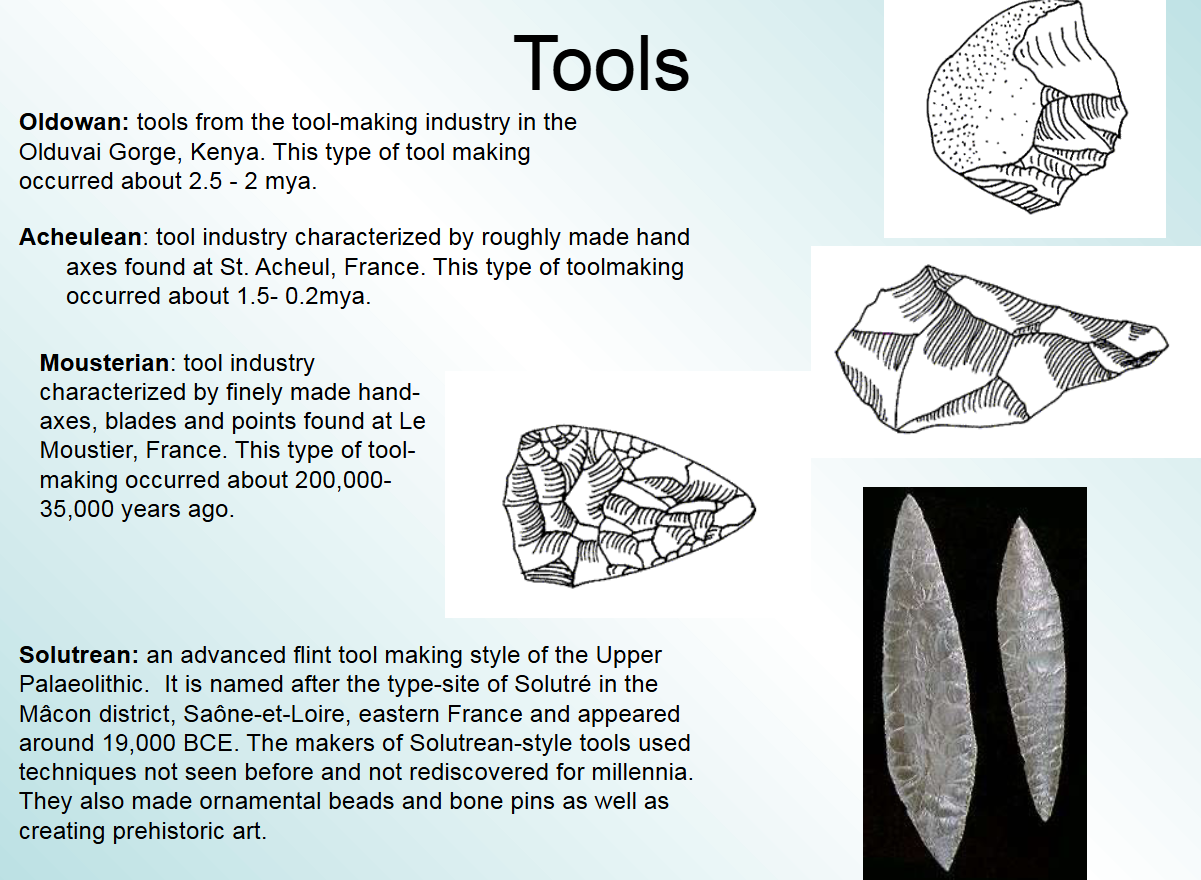
main reason for success of homo erectus

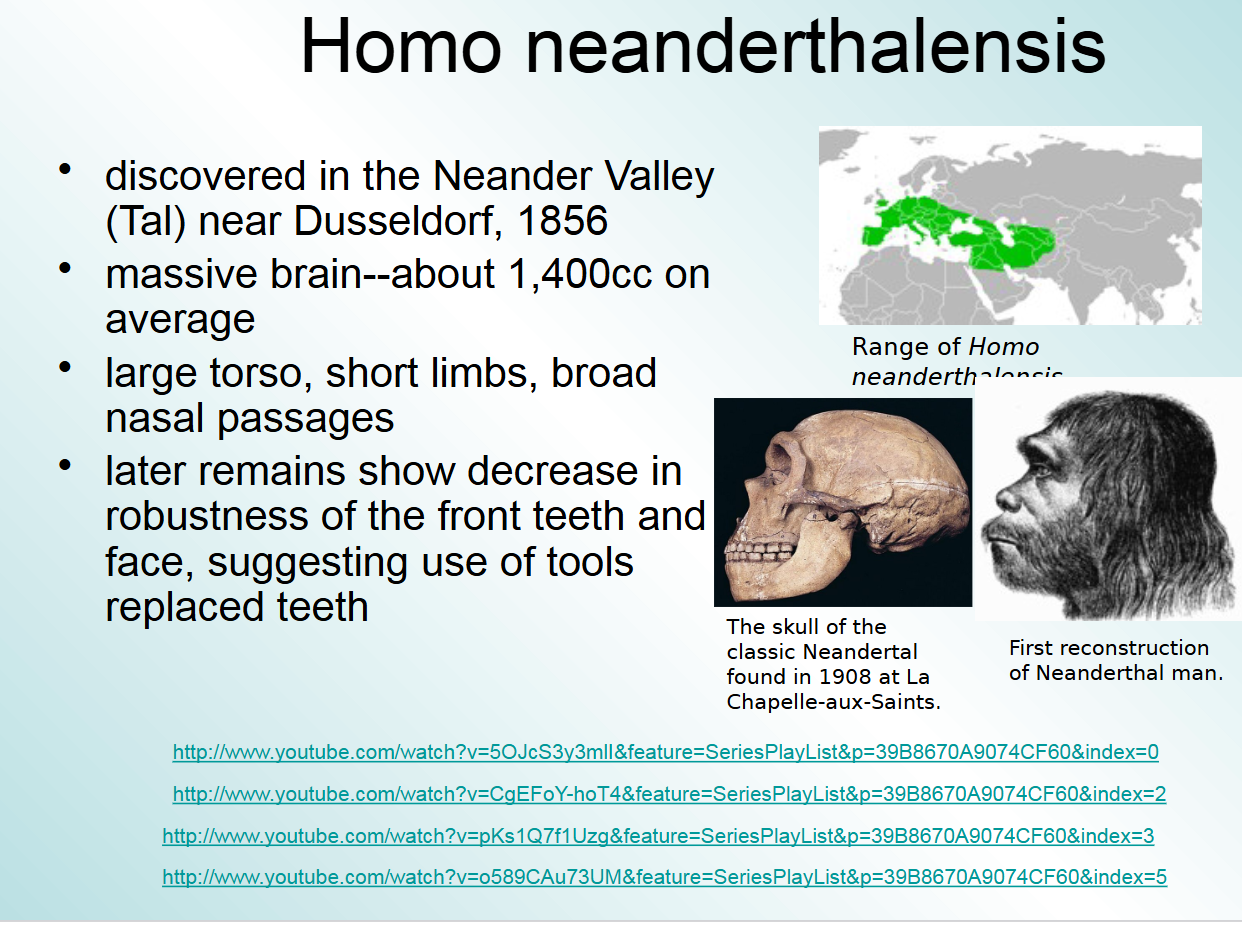
homo neanderthals found in
neander valley
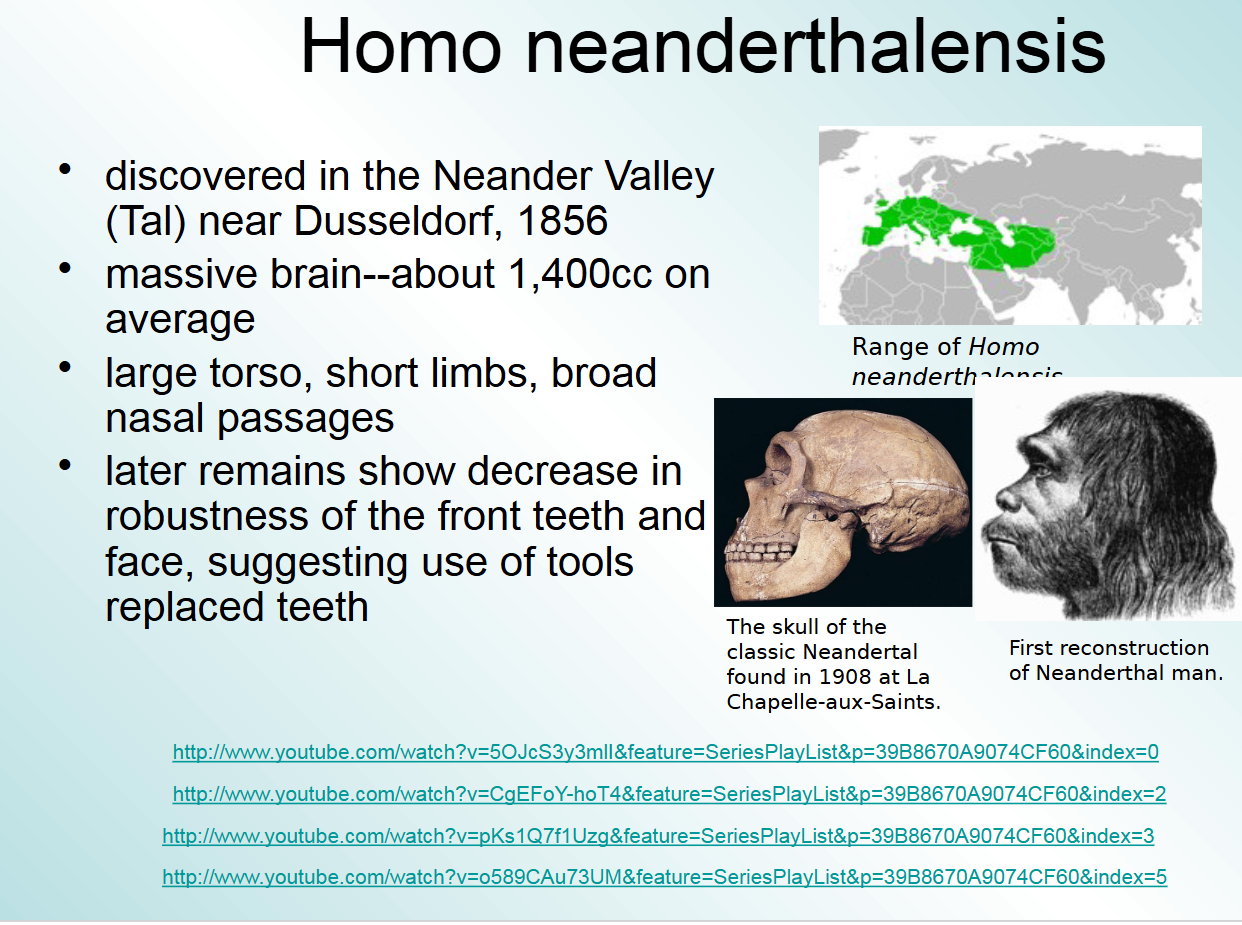
later remains show decrease in robustness of the front teeth for homo neanderthals and face, suggesting
use of tools replaced teeth
homesites
In caves, also in the open (near rivers, framed with wood and covered with skins)

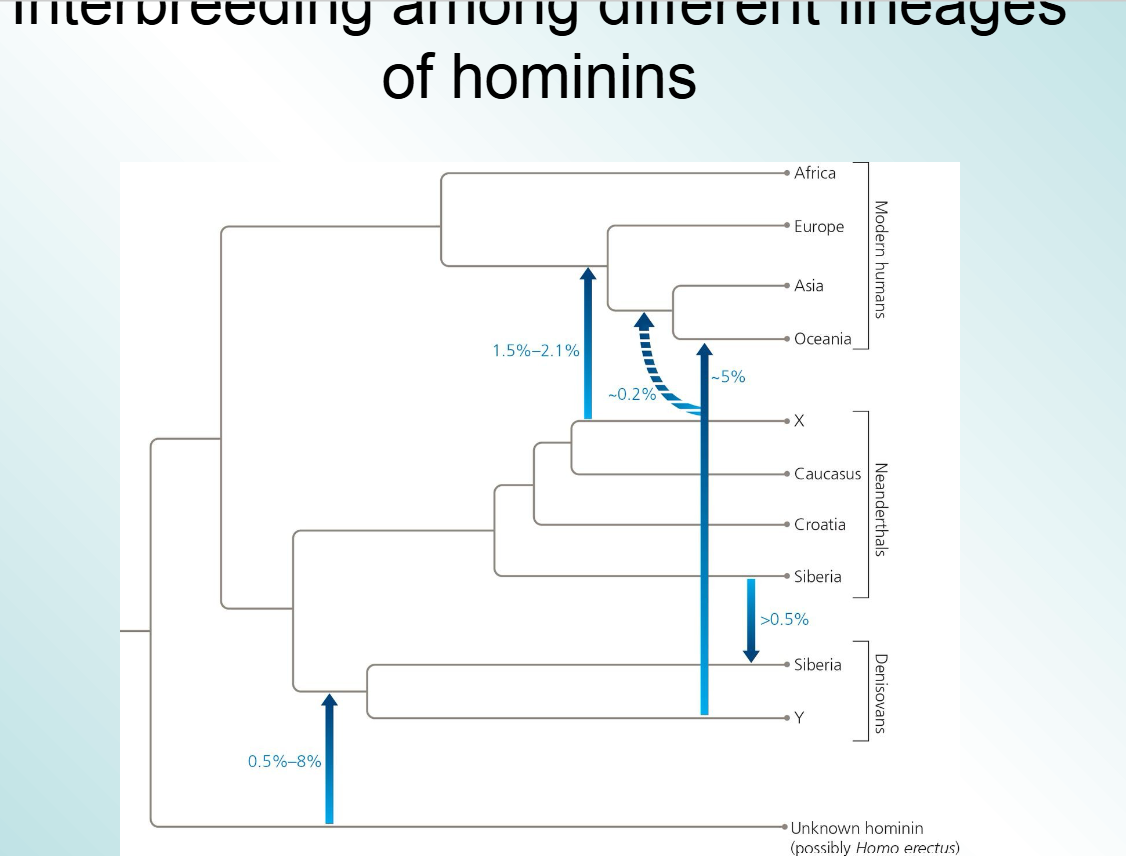
what happened to homo neanderthals
they interbred with homosapiens and were killed off by them maybe due to disease or competition

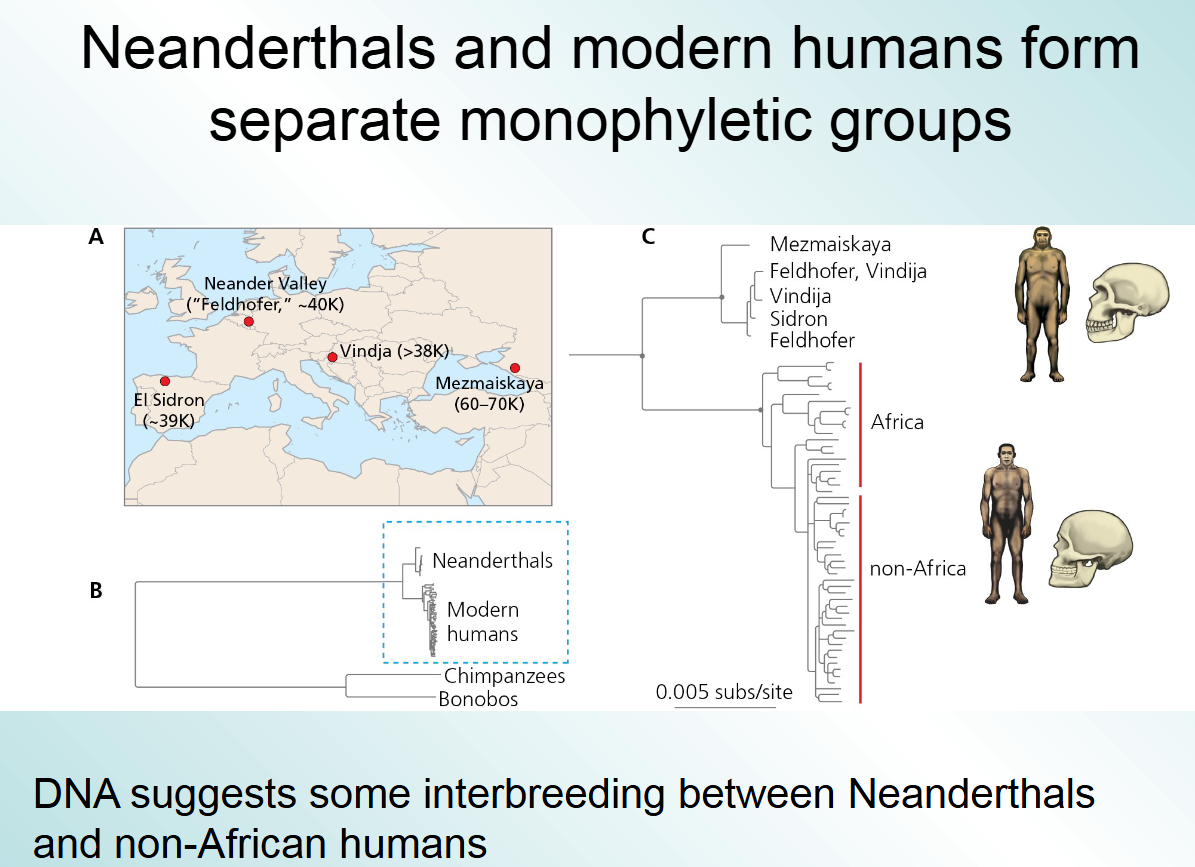
are neanderthals and modern humans separate monophyletic groups?
yes
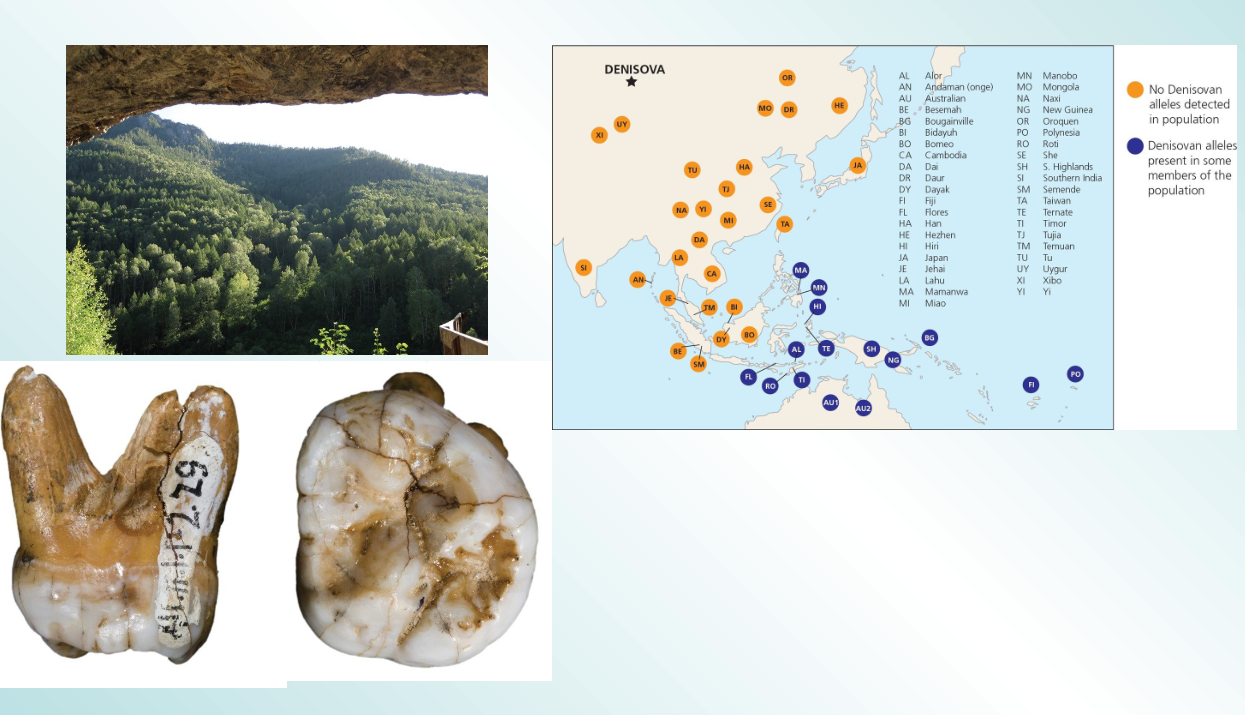
Denisovans
close relatives of Neanderthals also interbred with humans
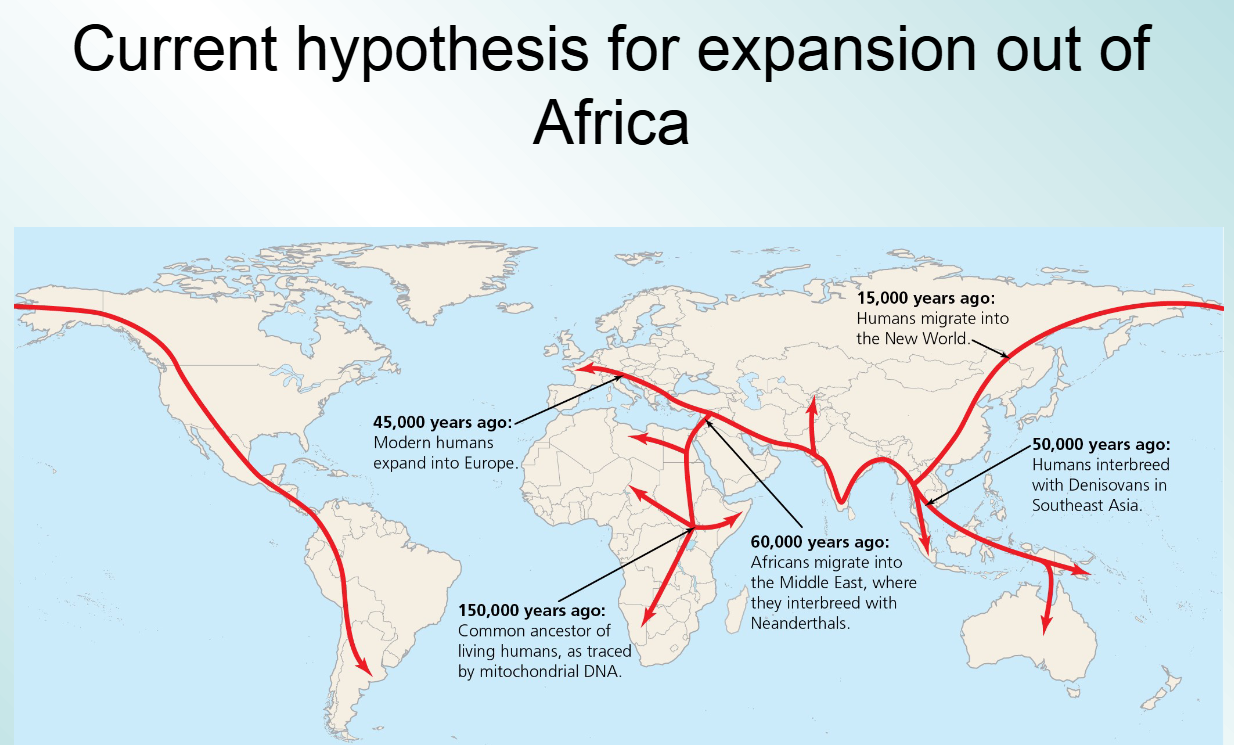
hypothesis for expansion out of africa in order
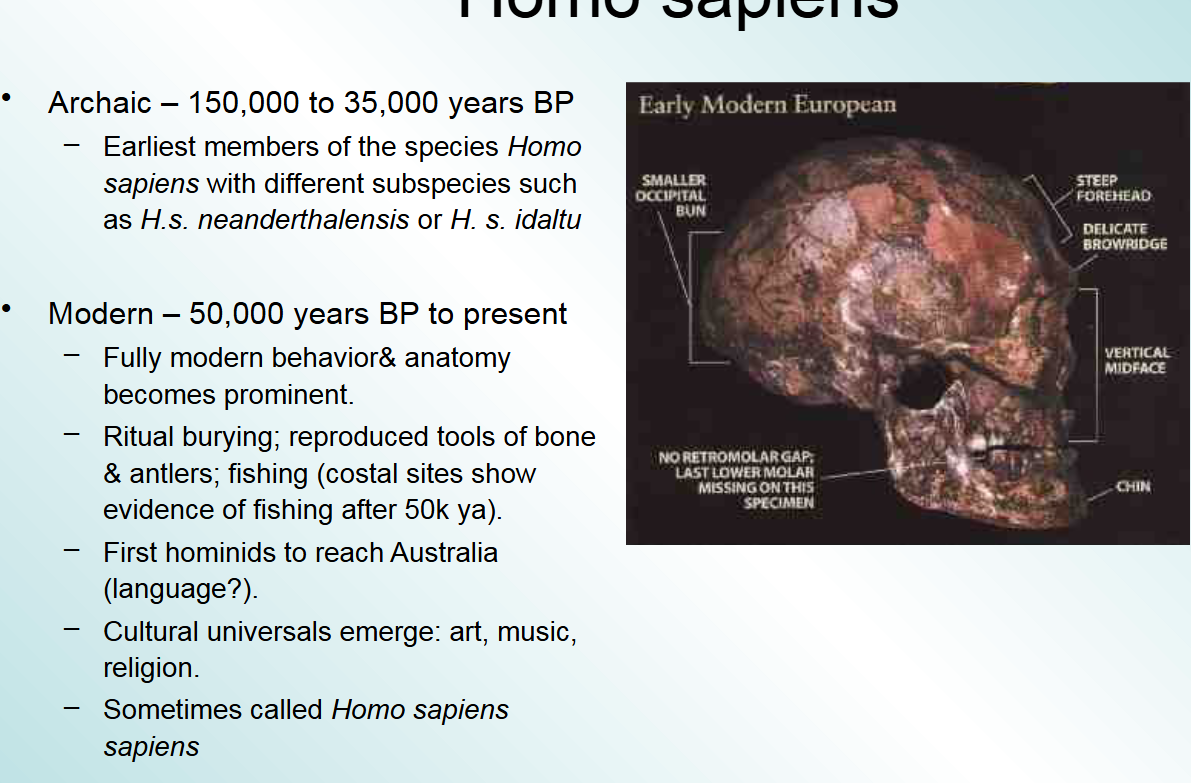
archaic vs modern homo sapiens
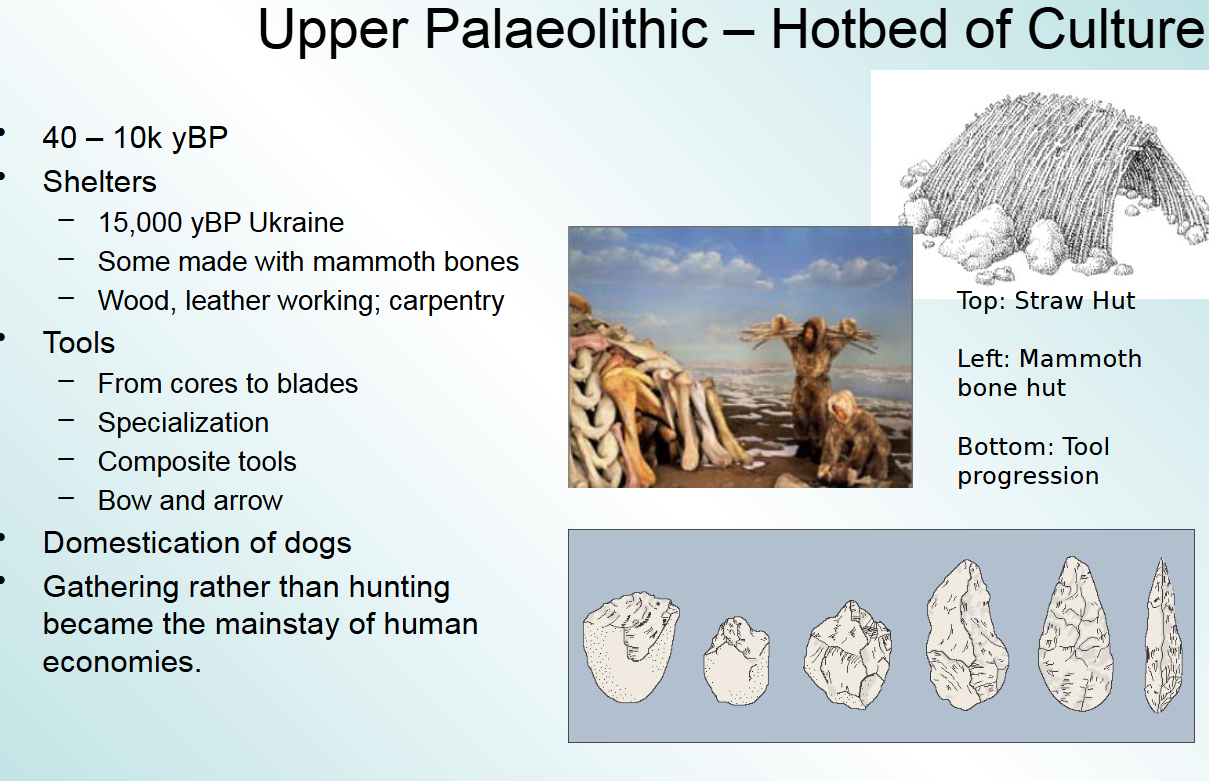
early shelter and tool progression
started gathering rather than hunting; shelters made of mammoth bones and wool and tools got sharper
Venuses art

why did archaic homo sapiens not draw other humans

last place colonized by hominids
