Exam 4
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
Tissues
groups of similar cells that perform a common function
Types of Tissues
Epithelial
Connective
Muscle
Nervous
Epithelial Tissue (Epithelium)
tightly packed sheets of cells that cover organs and outer surfaces, as well as line hollow organs, vessels, and body cavities
Anchored on one face, but free on another
Free side exposed to body fluids or the external environment
Can be single layer or many layers
Constantly sloughing off; replaced by cell division
Functions of Epithelial Tissue (Epithelium)
Protection
Secretion
Absorption
Connective Tissue
loosely organized and composed of cells embedded in a matrix of protein fibers and ground substance
Usually binds T organs or tissues to one another
Types of Connective Tissue
Loose connective tissue
Adipose tissue
Blood
Fibrous connective tissue
Cartilage
Bone
Loose Connective Tissue
connects epithelia tissues, holds organs in place, pads skin
Most widespread tissue in animals
Loose Connective Tissue Structure
matrix composed of collagen fibers for strength and elastin fibers for stretching
“Loose” due to loosely woven fibers
Adipose Tissue
fat tissue
Connects skin to underlying structures
Insulates and protects organs
Makes and stores energy-rich reserves of fat
Primarily cells; small amount of matrix
Blood
Connective tissue that circulates throughout the body via blood vessels
Composed of…
Liquid Portion/Matrix: plasma
Solid Portion: red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets
Blood Stem Cells
Stem cells in bone marrow produce cellular components of blood
Red Blood Cells
carry oxygen from lungs to body
Small, pinched shape provides large surface area to volume ratio for rapid oxygen diffusion
No nucleus or other organelles
How are new red blood cells made?
Body knows when you need more through negative feedback: low blood oxygen levels
Made in bone marrow
Stems cells divide to make one new stem cell (replacement) and one new RBC
Hemoglobin
a protein in red blood cells that transports oxygen to the tissues and carbon dioxide to the lungs
Made of four different protein chains, each with an iron atom that binds with oxygen
White Blood Cells
fight infection/attack invaders
Remove toxins, wastes, and damaged cells
Less white blood cells than red blood cells
Have nuclei
Platelets
work with proteins to clot blood
Fibrous Connective Tissue
forms tendons and ligaments
Matrix is densely packed collagen fibers running in parallel
Tendons
connect muscles to bones
Ligaments
connect bones to each other at joints
Cartilage
Connects muscles with bones
Composed of chondrocytes
Matrix rich in collagen and other structural proteins
Allow for shock absorption
Cushions joints
No blood vessels, so slow to heal
Bone
Rigid connective tissue composed of branched osteocytes
Matrix composed of collagen and minerals
Supports and protects other tissues and organs
Reservoir of calcium and minerals if dietary levels are too low
Muscle Tissue
highly specialized tissue capable of contracting
Composed of long, thin cylindrical cells called muscle fibers
Fibers contain specialized proteins, actin and myosin
Cause contractions when signaled by nerve cells
Types of Muscle Tissues
Skeletal
Cardiac
Smooth
Skeletal Muscle
usually attached to bone
Striated
Voluntary movements
Exercise increases size of skeletal cells
Cardiac Muscle
found only in heart tissue
Striated
Involuntary movements
Undergoes rhythmic contractions to produce heartbeat
Branched, interwoven cells help contraction signal to propagate
Smooth Muscle
Not striated
Involuntary movements
Comprises the musculature of internal organs, blood vessels, and the digestive system
Contracts more slowly than skeletal muscle but remains contracted longer
Nervous Tissue
Composed of neurons that conduct and transmit electrical impulses
Found in the brain, spinal cord, and nerves
Most nerve cells do not undergo cell division to repair damage
Nervous Tissue Functions
Senses stimuli
Processes stimuli
Transmits signals from the brain to the body
Organs
structures composed of two or more tissue types working together for a specific function
Organ Systems
organs that interact to perform a common function
Liver
Found on the right side of the abdomen below the diaphragm
Divided into four lobes, subdivided into lobules
Contain a central vein that allows blood to reach all of the liver
Hepatocytes filter toxic materials from blood
Associated with the gallbladder
Organ Systems of the Liver
Circulatory System
Digestive System
The Circulatory System and the Liver
Synthesize blood-clotting factors
Detoxify harmful substances in the blood
Regulate blood volume
Destroy old red blood cells
The Digestive System and the Liver
Produce bile
Metabolize and store nutrients
Stores and releases excess glucose
Liver Transplants
usually because liver failure:
Hepatitis C
Chronic alcohol use
Liver can come from living or dead donors: small piece of liver can be transplanted and will regenerate in donor and recipient
Organ Failure
failure of one organ can affect one or more systems (liver failure affects circulatory and digestive systems for example)
Compromises body’s overall ability to maintain a steady state
Homeostasis
The ability to maintain a consistent internal environment under changing conditions
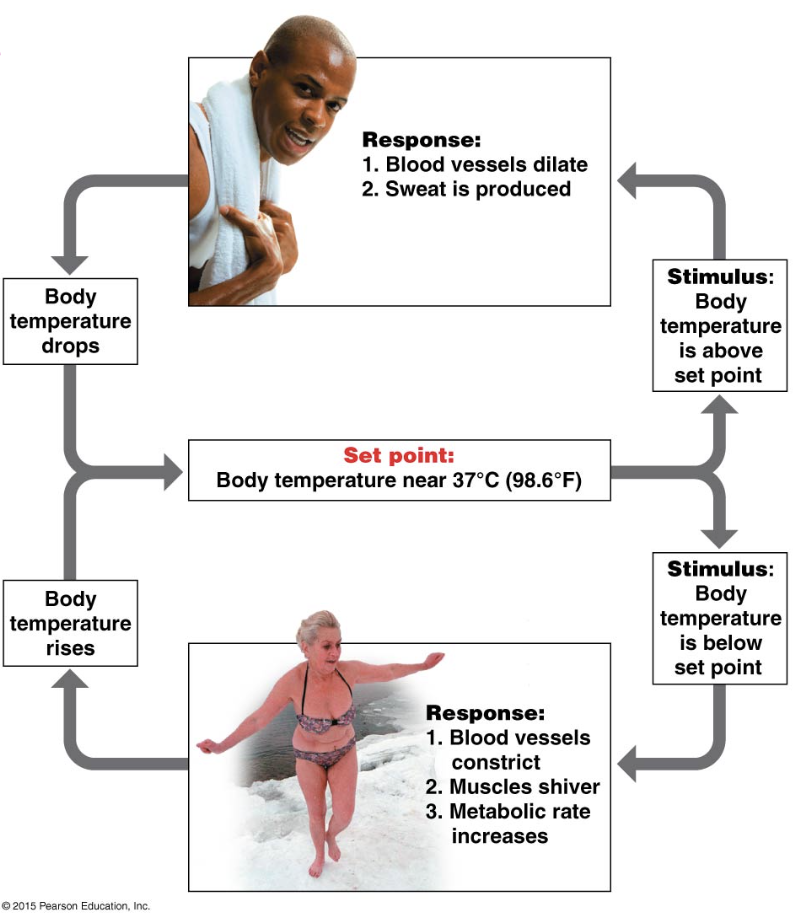
Negative Feedback
the product of the process inhibits the process (reverses a change)
Controls thermoregulation and blood glucose level regulation
Positive Feedback
the product of the process intensifies the process
Labor and childbirth: hormones release during childbirth that cause contractions to birth the baby
The Digestive System
Breaks down food to be used for energy by the body
Alimentary Canal
AKA the digestive tract
Where absorption and elimination occur
Steps of food in the Digestive Tract
Ingestion: taking food into the digestive tract
Digestion: breaking the food into small units
Absorption: bringing the food from the tract into the cells of the body
Elimination: expelling the unusable parts of the food from the digestive tract
Absorption Steps
Small nutrients are absorbed into the circulatory or lymph systems
Nutrients and water diffuse from blood and lymph into the cell
Digested nutrients are absorbed into the bloodstream
Villi and Microvilli
Increase the surface area of the small intestine for nutrient absorption
The Small Intestine
Most absorption takes place in small intestine
Many folds and projections give it the approximate surface area of a tennis court
Minute projections called villi (singular: villus) cover the entire folded area
Villi move back and forth in chyme
Each cell of villi has microscopic projections called microvilli
Elimination
Any material not absorbed move through large intestine/colon and are eliminated through feces
Feces mainly consists of indigestible plant fibers
Types of Digestion
Mechanical digestion
Chemical digestion
Mechanical Digestion
grinds down food to increase surface area
Mechanical Digestion Steps
Begins in the mouth (oral cavity)
Teeth chew and grind food into smaller pieces
Tongue forms a bolus (ball of food) and pushes it to the back of the mouth
Bolus moves to pharynx and esophagus
Peristalsis: smooth muscle contractions push food through esophagus to stomach
Chemical Digestion
secretions help convert polymers into subunits
Chemical Digestion Steps
Begins in the mouth
Salivary amylase breaks down sugars
In the stomach
Forms chyme: a slurry with digestive enzymes (gastric juices)
Pepsin breaks down proteins
In the small intestine
Intestinal enzymes and pancreatic enzymes break down all nutrient types
Accessory Organs in the Digestive System
Outside of the alimentary canal but produce or secrete substances for digestion
Pancreas
Liver
Gallbladder
Pancreas in the Digestive System
produces secretions to neutralize stomach acids and enzymes to digest nutrients
Liver in the Digestive System
produces bile to help dissolve fats
Gallbladder in the Digestive System
stores and concentrates bile to be released into the small intestine
Alcohol and the Digestive System
Alcohol relaxes the muscles for peristalsis: food spends more time in digestive tract = more enzyme exposure = diarrhea
Food in the stomach slows the rate of alcohol absorption in the small intestine
Liver metabolizes toxins including alcohol
Pancreatitis: inflammation of the pancreas prevents secretion of digestive enzymes
The Urinary System
Removes waste while retaining materials to be reused and recycled
Organs:
Kidneys
Ureters
Urinary bladder
Urethra
Kidneys
filter and cleanse circulating blood
Paired organs located behind the liver and stomach
Contain nephrons (looped tubules)
Supplied with blood by the renal arteries
Nephrons
Functional unit of the kidneys (removes toxins and produces urine)
Process waste in four phases:
Filtration
Reabsorption
Secretion
Excretion
Effects of Alcohol on the Urinary System
Alcohol is a diuretic: Promotes the formation of urine and increases the volume of urine released from the bladder
Alcohol acts on the pituitary gland to lessen antidiuretic hormone (ADH) secretion: Kidneys reabsorb less water and produce more urine
Alcohol is a depressant: slows down brain function
Environmental Tobacco Smoke
secondhand smoke emitted by a lit cigarette combined with smoke exhaled by active smokers
What is the most abundant gas in tobacco smoke?
Carbon monoxide
Diaphragm
Dome-shaped muscle
Separates respiratory system from the digestive organs
Ventilation
Consists of inhalation and exhalation
Your brain responds to levels of CO2
High levels of CO2 –> increases ventilation
Increases the level of O2
Removes the CO2
Inhalation
Diaphragm contracts
Air flows in
Exhalation
Diaphragm relaxes
Air flows out
Lungs
Air enters the lungs through bronchi which branch into bronchioles
Alveoli
Tiny sacs at the end of bronchioles
Contain the respiratory surface (size of tennis court)
Supplies O2 and removes CO2 waste
Total amount of respiratory surface can be destroyed by smoke —> shortness of breath and wheezing
Gas Exchange
Process that acquires O2 from the environment and expels CO2 from the body
Necessary for cellular respiration
Occurs by simple diffusion between the alveoli and surrounding capillaries
Surfactant covering surfaces may be negatively affected by tobacco smoke
Hemoglobin and Smoking
Hemoglobin binds to carbon monoxide (which comes from smoking) more strongly than to oxygen
Causes oxygen shortages in tissues
How do lungs expel and remove foreign objects?
Coughing: response to large particles in trachea
Mucus traps smaller particles
Cilia move trapped particles to nose and mouth
Mucus is coughed up, expelled from nose or mouth, or swallowed
Effects of particles in tobacco smoke
Increases mucus production
Damages cilia in bronchi: more difficult to expel mucus and particles
Bronchitis: inflammation of bronchi
Abundant mucus production
Lasting cough
Asthma: allergic response resulting in muscular constriction of bronchial walls
Emphysema: lung disease cause by damage to alveoli walls
Reduces surface area for gas exchange
Permanently damage alveoli
Lung Cancer
The Cardiovascular System
distributes gases and other materials around the body
Three main components:
Circulating fluid (blood)
Pump (heart)
Vascular system (blood vessels and capillaries)
Vascular/Circulatory System
blood vessels that carry blood to and from the heart
Composed of…
Arteries
Capillaries
Veins
Arteries
Move blood away from the heart
Thick muscular walls
Ability of these muscles to dilate and constrict aids in the maintenance of blood pressure
Constricted arteries = faster flow
Relaxed arteries = slower flow
Arteries —> arterioles —> capillaries
Arterioles
Connect arteries and capillaries
Very small
Capillary Networks
Designed so materials can move in and out easily
Located next to every cell in your body
Capillaries
contain thin, porous walls to exchange gases and other materials
Capillary bed: network of capillaries found in highly used tissues
Materials forced out due to higher blood pressure near arterial end of capillary bed
Veins
Carry the oxygen depleted (not always) blood back to the heart
Blood is under lower pressure than arteries from large diameter and less muscle
Valves are used to ensure the one way flow of blood
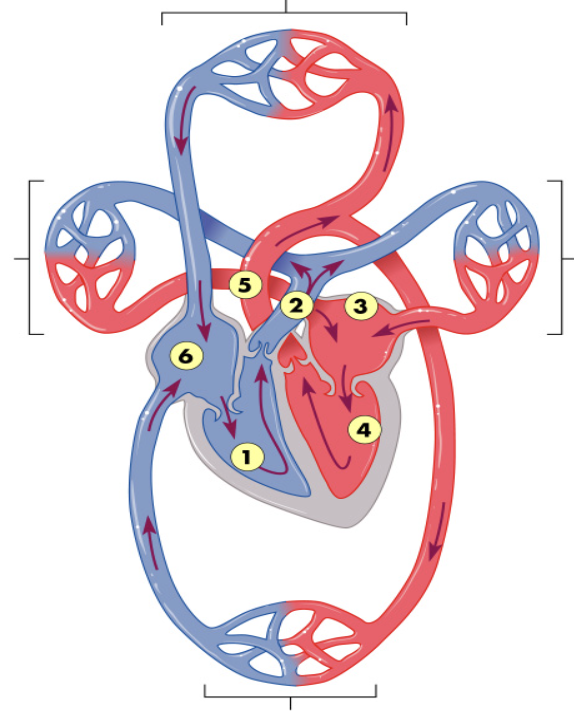
Heart
Consists of two muscular pumps and four chambers
Right and left atria
Right and left ventricles
Right side receives oxygen-poor blood from the body and sends it to the lungs
Pulmonary circulation
Left side receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs and sends it to the body
Systemic circulation
The Circulatory/Vascular System Pathway
Right ventricle: Pulmonary semilunar valve
Pulmonary arteries: Lungs, Pulmonary veins
Left atrium: Left atrio-ventricular valve
Left ventricle: Aortic semilunar valve
Aorta
Right atria
The Heartbeat
Systole: Atria and ventricles contract, blood is pushed out
Diastole: Atria and ventricles relax, heart chambers fill
Sound comes from the closing of the heart valves
How is the heartbeat controlled?
pacemaker cells located in the sinoatrial node in right atrium
Signals the atria to contract —> pause as impulse moves to the atrioventricular node —> Signals the ventricles to contract
Cardiac Output
The volume of blood per minute that the left ventricle pumps into the systemic circuit
The amount of blood pumped by the left ventricle each time it contracts times the heart rate
Heart Valves
Made of flaps of connective tissue
Prevent backflow: valves close when ventricles contract, keeping blood from flowing back into the artria
Heart Murmur
a stream of blood squirts backward through a valve
High Blood Pressure
hypertension
Affected by epinephrine and norepinephrine
Leads to arteriosclerosis (hardening of the arteries)
Blood Clots
result from an increase in the stickiness of platelets and formation of fibrinogen
Can occur from smoking
Types:
Thrombosis
Embolism
Thrombosis
blood clot in blood vessel blocks blood flow
Embolism
blood clot breaks free and becomes lodged in another blood vessel
What do most deaths due to smoking result from?
Cardiovascular disease