KNES 259 LECTURE MIDTERM
1/487
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
488 Terms
Homeostasis
Keeping internal environment constant despite a changing external environment
The hypothalamus is the body's __________ _________
Control centre
Two functions of the hypothalamus regarding homeostasis
- Receives input from sensory receptors
- Controls hormones (endocrine system)
What do we keep constant in the body?
- Nutrients/Wastes
- O2/CO2 levels
- pH
- Water/electrolytes
- Temperature
- Blood volume
- Blood pressure
_______ nerve innervates the plantar surface of the foot
Tibial
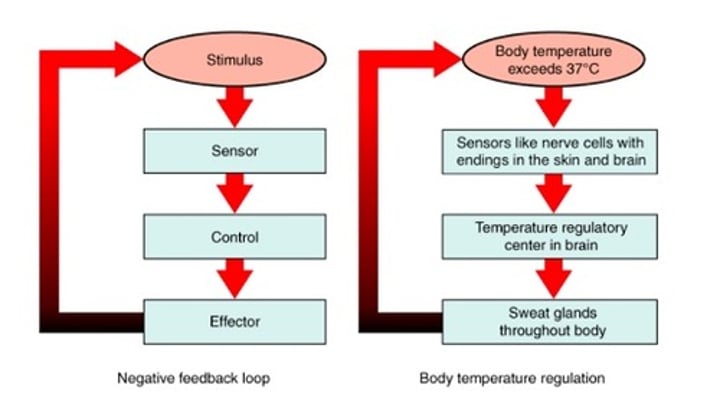
Negative feedback loop
- A feedback loop that works to oppose the stimulus that triggers it
i.e. sweating to counteract an increase in body temperature
Positive feedback loop
- A feedback loop that works to reinforce the stimulus that triggers it
i.e. childbirth or bleeding
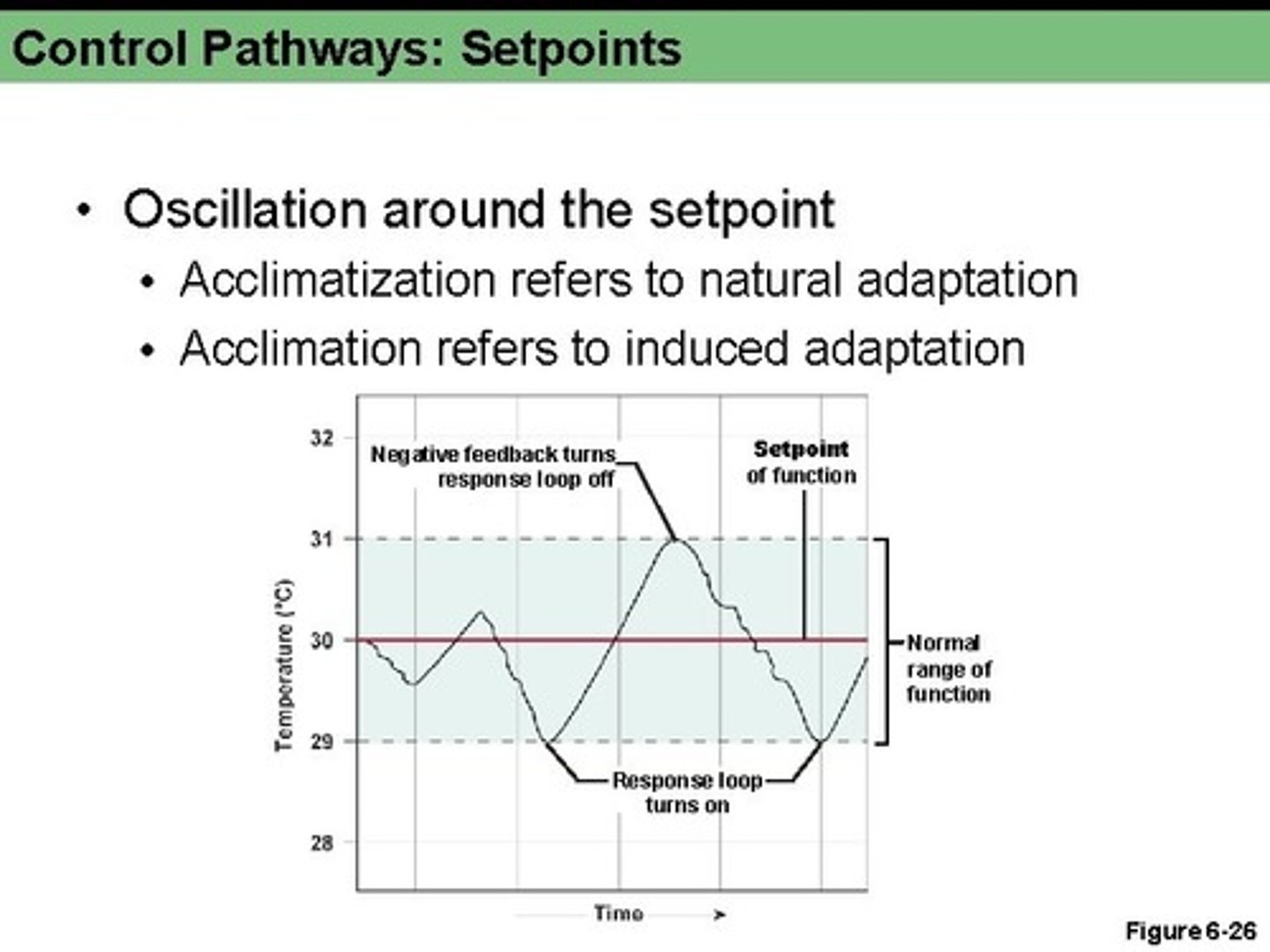
Negative feedback causes ____________ around the set point function
Oscillation
The three parts in which the cell can be divided into.....
- plasma (cell) membrane
- Cytoplasm (cytosol 'goo' and organelles)
- Nucleus (chromosomes and genes)
Nucleus function
- Stores DNA and genetic material for cell replication + repair
- Coordinates the cell's activities (growth, metabolism, etc.)
There is usually one nucleus per cell, what are the exceptions?
- Red blood cells, which are made in the bone marrow (no nucleus)
- Muscle cells (multi-nucleated)
Ribosomes
Make/synthesize proteins
Ribosomes can be either _________ or ___________.
- Free (make proteins for the cell)
- Attached (make proteins for export)
Free ribosomes are found primarily in what organ?
Muscle, makes actin and myosin
Smooth ER Function
- Calcium storage
- Steroid production
Smooth ER that specializes in calcium storage can be found in which organ?
Muscle
Smooth ER that specializes in steroid production can be found in which organ?
Ovaries, testes and adrenal glands
Rough ER function
- protein production for export + protein folding
- ribosomes attached
Rough ER is found primarily in what organ?
Anterior Pituitary
Golgi Complex function
Re-packages RER proteins into a vesicle that can leave the cell
Golgi complex organelle can be found primarily in which organ?
Anterior pituitary
Peroxisomes Function
Oxidative enzyme which detoxifies various waste products and harmful substances/free radicals
EX. alcohol
Organ which contains numerous peroxisomes?
Liver hepatocytes
Lysosomes Function
Sac of digestive enzymes which are used for repair and removal of foreign matter
Where would we see a lot of lysosomes in the body?
White blood cells
Proteosomes
Large protein complexes that digest tagged proteins (proteins that are damaged, incorrectly folded, or no longer needed)
Cytoskeleton
A complex protein network that helps maintain the shape + structure of the cell
Three distinct elements of the cytoskeleton
- microtubules
- microfilaments
- intermediate filaments
Microtubules function
- Transport secretory vesicles
- Form mitotic spindles during cell division
- eg. Tubulin
Microfilaments Function
- Muscle contraction
- Mechanical stiffeners (structural)
-Cleavage furrow in cell division
- Eg. Actin and Myosin
intermediate filaments function
- Help resist mechanical stress + bear tension
- hair, skin, nails
- eg. Keratin
Centrosomes
Microtubule-organizing centers of the cell (contains the centrioles)
Centroiles
Cylindrical structures composed of microtubules that form the mitotic spindle fibres during cell division
Cilia + Flagella
- Composed of microtubules that aid in cell movement (locomotion)
i.e. sperm = flagella (long 'tail-like' structure)
i.e. cilia lining the trachea (short 'hair-like' structure)
Mitochondria Function
- Site of ATP production (renew and recycle energy)
- Enzymes for TCA cycle and ETC
Liver contains lot of ______________
Mitochondria
Cellular Diversity
- 200 different types of cells
- variety of shapes and sizes
- differing lifespans
- organize into complex tissues and organs
Specialized functions of cells relate to:
- shape of cells
- arrangement of organelles
As we age our cells...
- lose function
- # of body cells lowers
- cannot respond to stress
- lose integrity of extracellular components
Free radical aging theory
• Damage from byproducts of cellular metabolism
• Radicals build up and damage essential molecules of
cells (i.e. OH from smoking, air pollution, UV light, etc.)
Mitochondrial aging theory
The decrease in the production of energy will weaken cells
Genetic aging theory
aging is programmed by genes:
- with each replication of DNA, nucleotides are lost (cells cannot divide indefinitely
- telomeres (the end caps of 'junk DNA' that protect the important parts of the chromosome) get shorter with each replication, which results in aging
Telomeres
Repeated 'junk' DNA sequences that protect the ends of chromosomes by shortening every time the cell divides
Telomerase
An enzyme responsible for the lengthening/maintenance of telomeres
Plasma membrane function
- physical barrier
- gateway for exchange
- communication
- cell structure
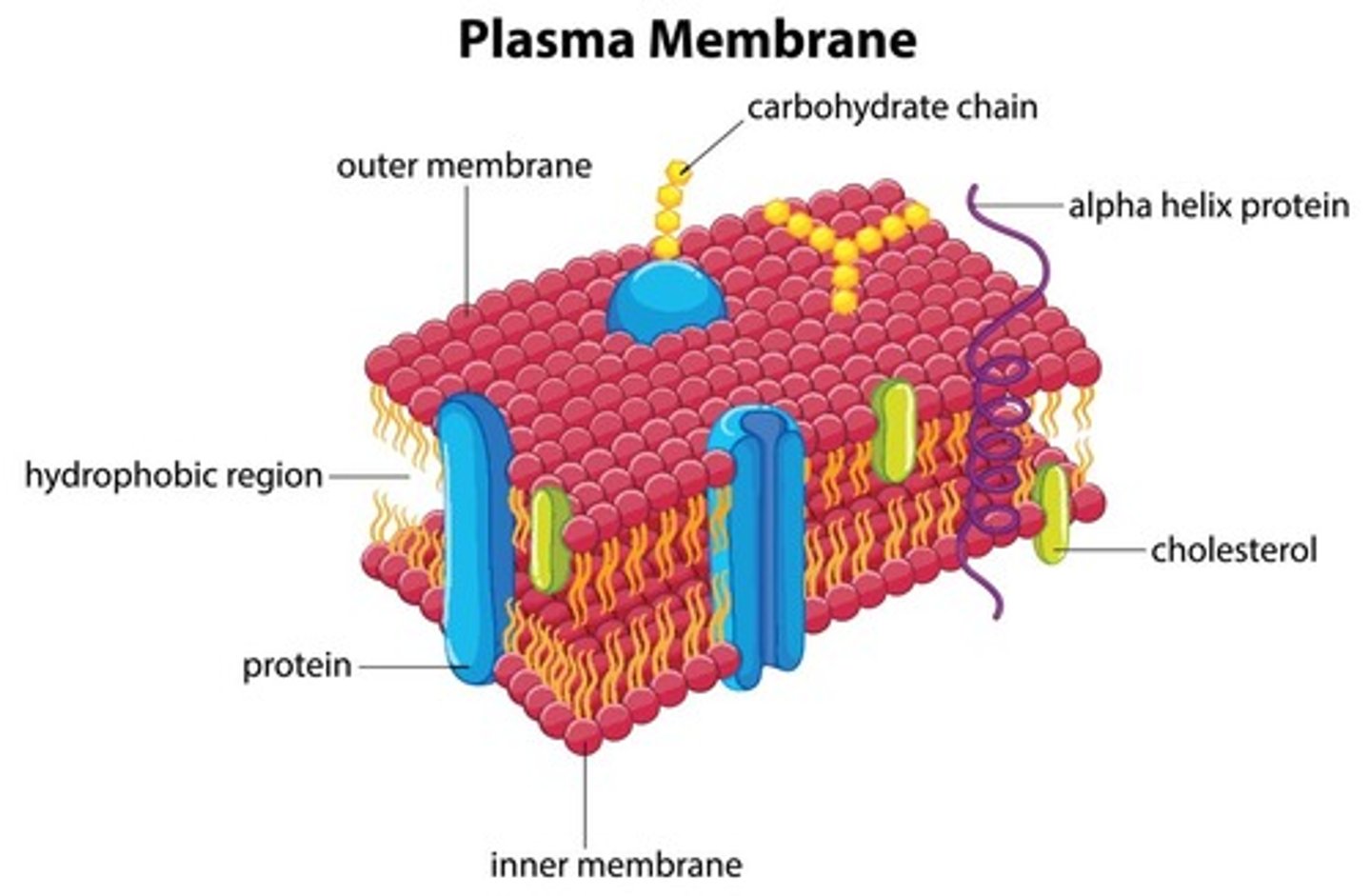
Plasma membranes are __________ permeable
selectively
The cell membrane is made out of:
Phospholipids and cholesterol
Phospholipids
- hydrophilic (water-soluble) head
- hydrophobic (lipid-soluble) tail
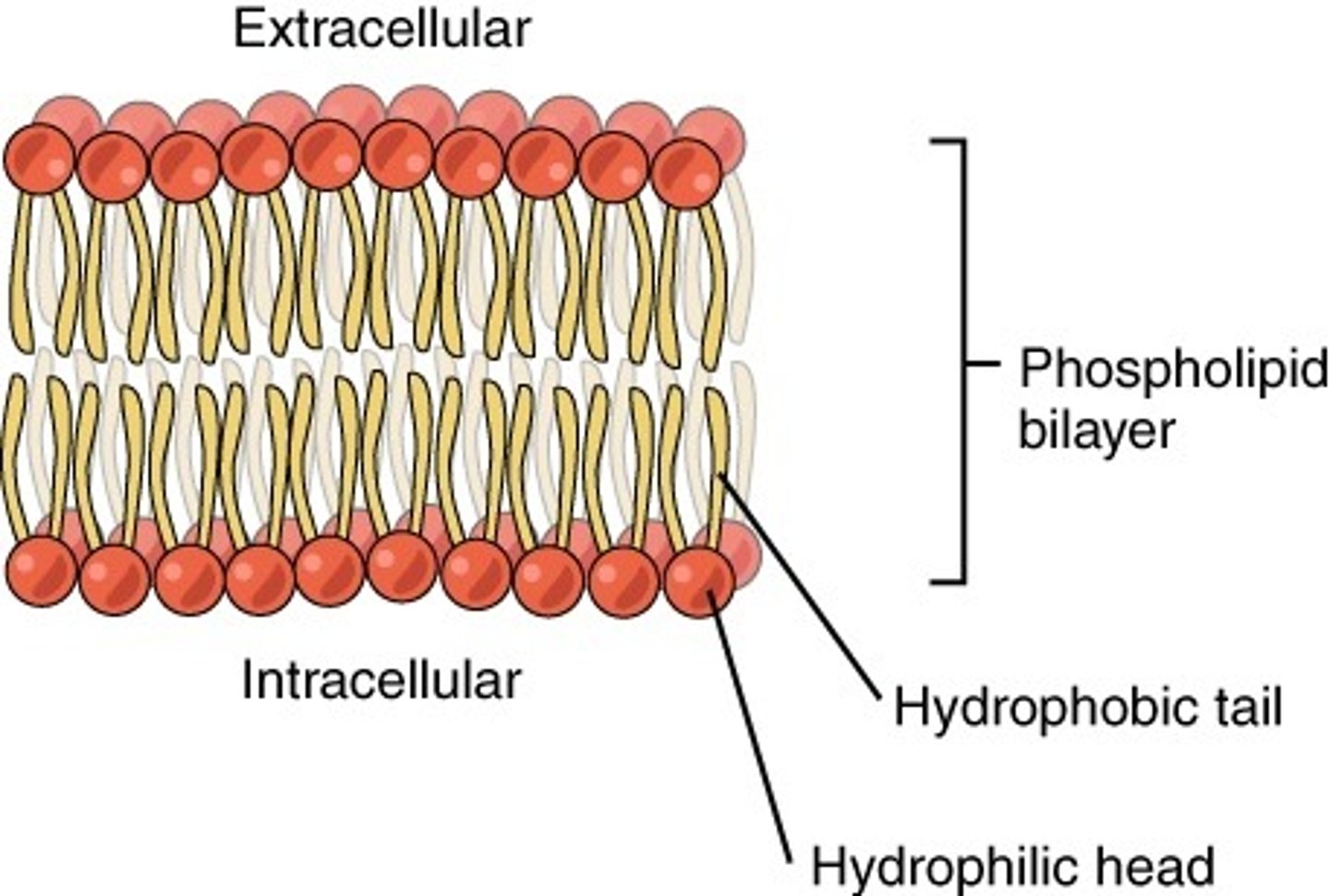
Function of phospholipid tails in the cell membrane
Creates barrier for flow
Glycocalyx
- a network of glycoproteins and glycolipids found on the surface cell membranes
1. cell recognition + interaction
2. cell orientation
3. allows the cell room to grow (keep cells from touching so that they have room to grow in the future)
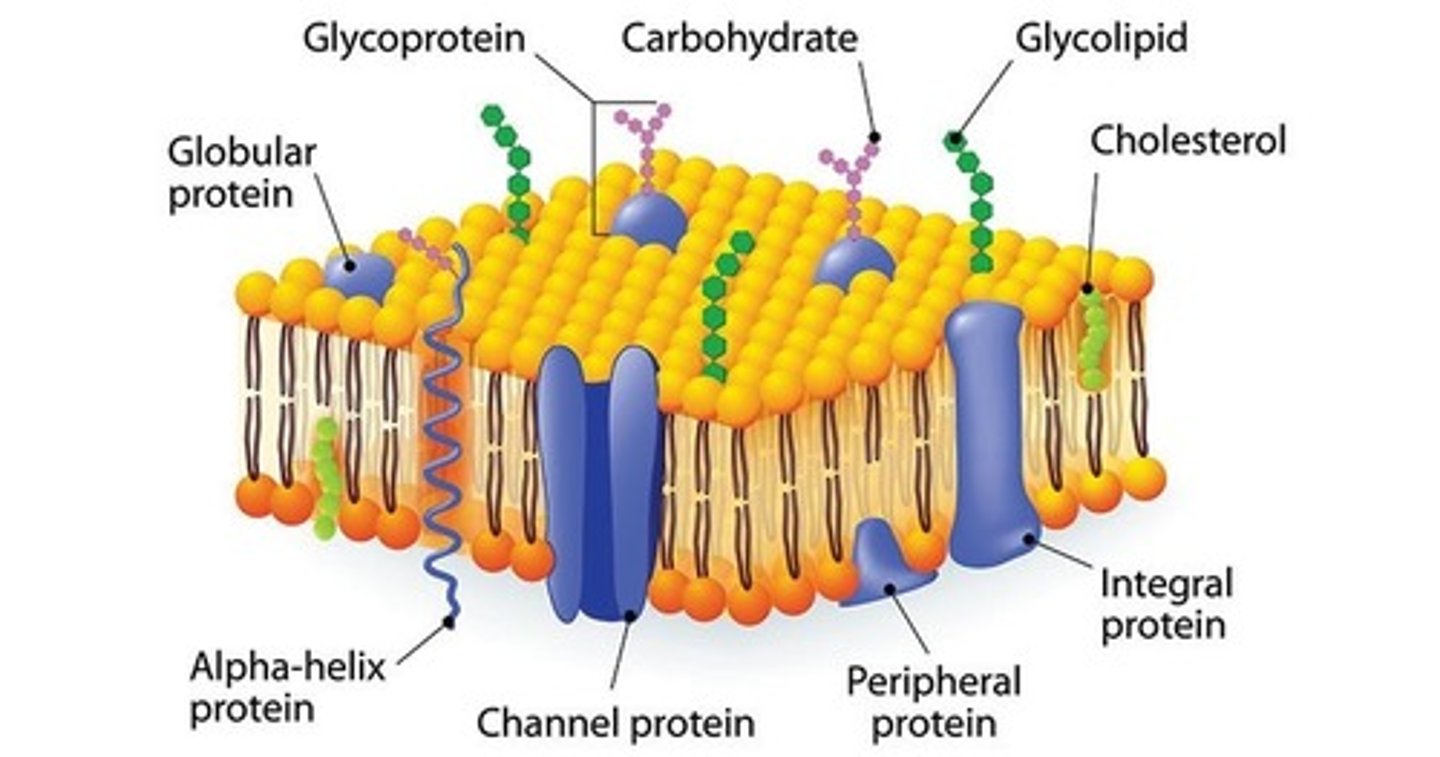
What are the two types of membrane proteins?
Integral (transmembrane) proteins
- permanently embedded within the membrane
- goes through the membrane (found on both sides)
Peripheral proteins
- detachable from the surface (doesn't go through) of the plasma membrane
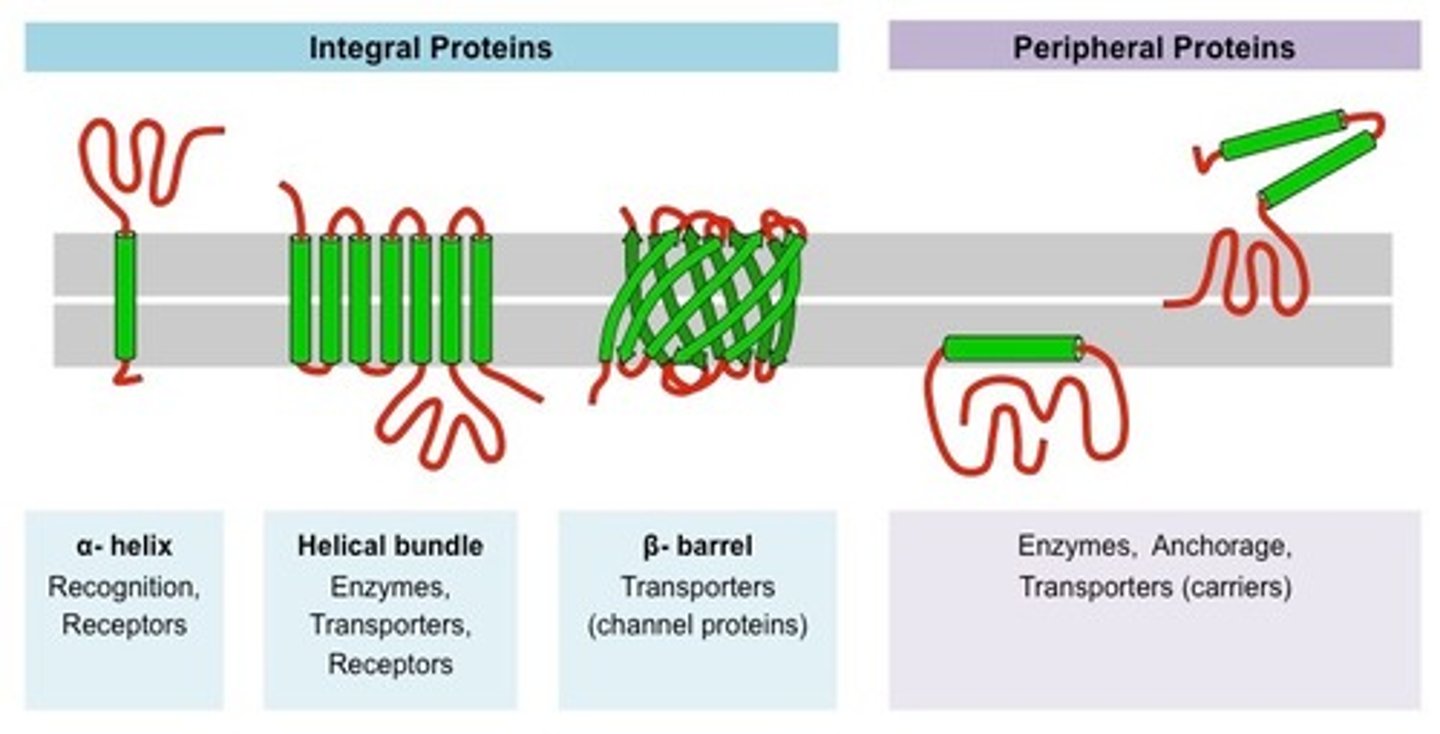
Functions of membrane proteins
- Ion channels
- carriers
- receptor sites
- enzymes
- pores
- structural
- Cell adhesion (cell junctions)
Plasma membranes are permeable to:
small, uncharged, non-polar (lipid soluble) molecules
Plasma membranes are non-permeable to:
large polar (water-soluble) molecules and ions
Transmembrane proteins
act as channels or transporters that move polar molecules into the cell (since the plasma membrane doesn't let them through on their own)
Categorize the passive processes of membrane transport

passive vs active transport
Passive transport = movement of molecules from high concentration to low concentration without the use of energy
Active transport = movement of molecules from low concentration to high concentration that requires energy
Categorize the active processes of membrane transport
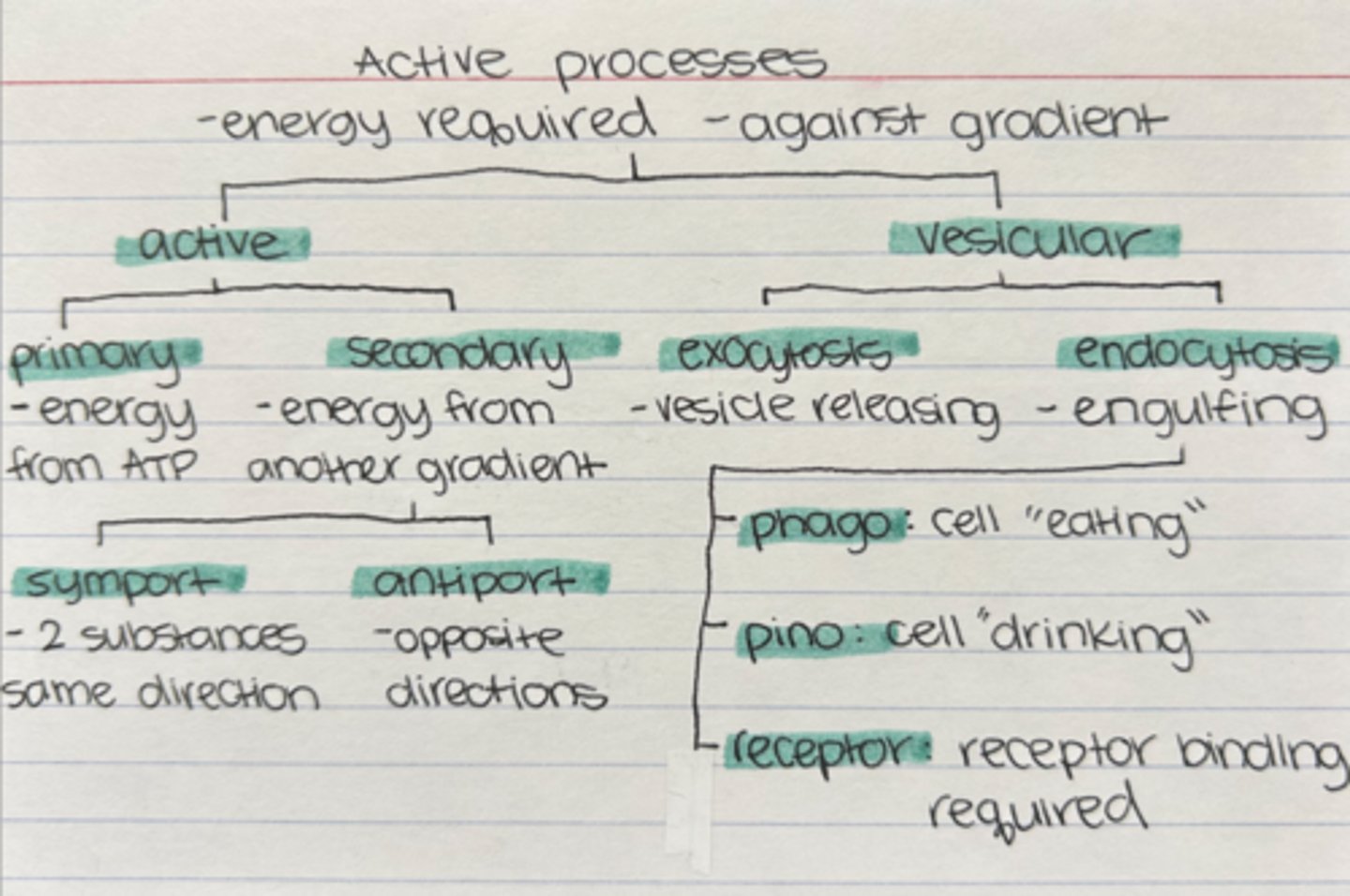
Active processes of membrane transport (Uses ATP)
- against the gradient
- active transport
- vesicular transport
Three different kinds of membrane gradients
- Concentration gradient
- Electrical gradient
- Electrochemical gradient
Concentration gradient
A difference in the concentration of a substance across a membrane
Electrical gradient
Difference in charge or concentration of ions across a membrane
Electrochemical gradient
Combination of electrical and concentration gradients
Simple diffusion
Net diffusion (flow in one direction is greater than opposite direction) from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration without any assistance from membrane proteins
Examples of simple diffusion in the body
- oxygen transfer from lungs to blood
- Steroids
Rate of diffusion depends on:
- temperature
- concentration gradient
- diffusion distance
- mass of diffusion substance
Diffusion across a membrane depends on:
- permeability
- surface area
- gradient
- temperature
Osmosis
Net diffusion of water from an area of high concentration to low concentration determined by tonicity
Tonicity
how an extracellular solution can change the volume of a cell by affecting osmosis
Hypertonic solution
Solute concentration is greater than that from inside the cell; cell loses water
isotonic solution
a solution whose solute concentration is equal to the solute concentration inside a cell
- no net osmosis
Hypotonic solution
Solute concentration is less than that inside the cell; cell gains water
Facilitated diffusion
the transport of substances through a cell membrane along a concentration gradient with the aid of specialized proteins:
1. channel mediated
2. carrier mediated
Channel mediated facilitated diffusion
- involves the use of channel proteins that create hydrophilic holes in cell membranes (like a tunnel) which allows the target molecules/ions to pass through by the process of diffusion
- only transports ions
- the shape of the channel protein remains fixed and doesn't change (can only open and close)
Example of channel mediated facilitated diffusion
Na+ and K+ channels
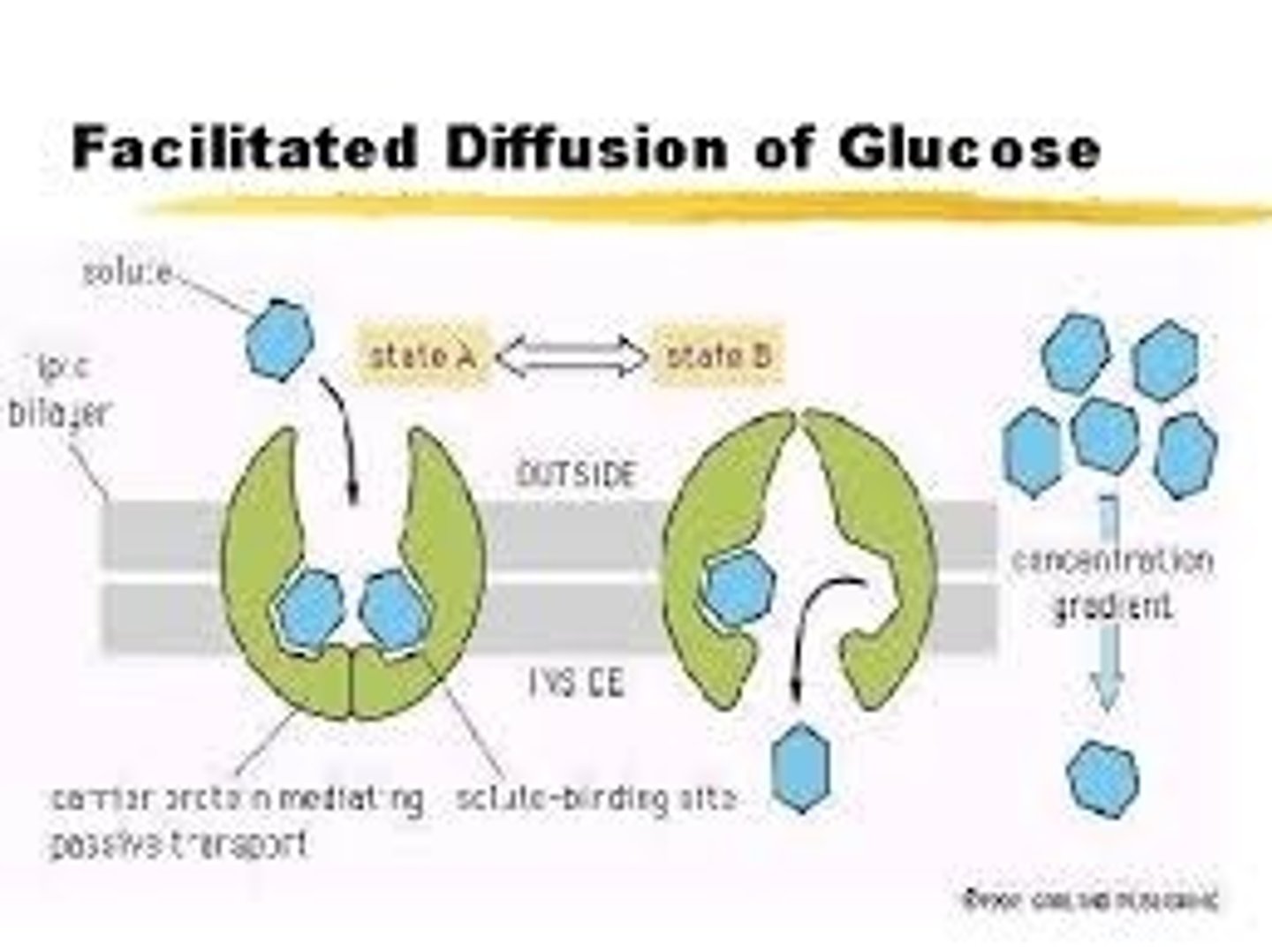
Carrier mediated facilitated diffusion
- involves integral proteins that transport molecules across the membrane by binding to target chemicals on one side of the membrane and altering their conformation in order to be released
- only transports small polar molecules
- the shape of the carrier protein will change
Examples of carrier mediated facilitated diffusion
Ex. Glucose carrier
Primary active transport
directly uses ATP to move molecules against their gradient
Example of primary active transport
Na+/K+ pump
The bigger the gradient, the ________ the movement
More
Secondary Active Transport (Co-transport)
- powered by electrochemical gradients established in primary transport (the concentration gradient of one solute moves the 2nd solute against its own gradient)
- uses symporters to transport
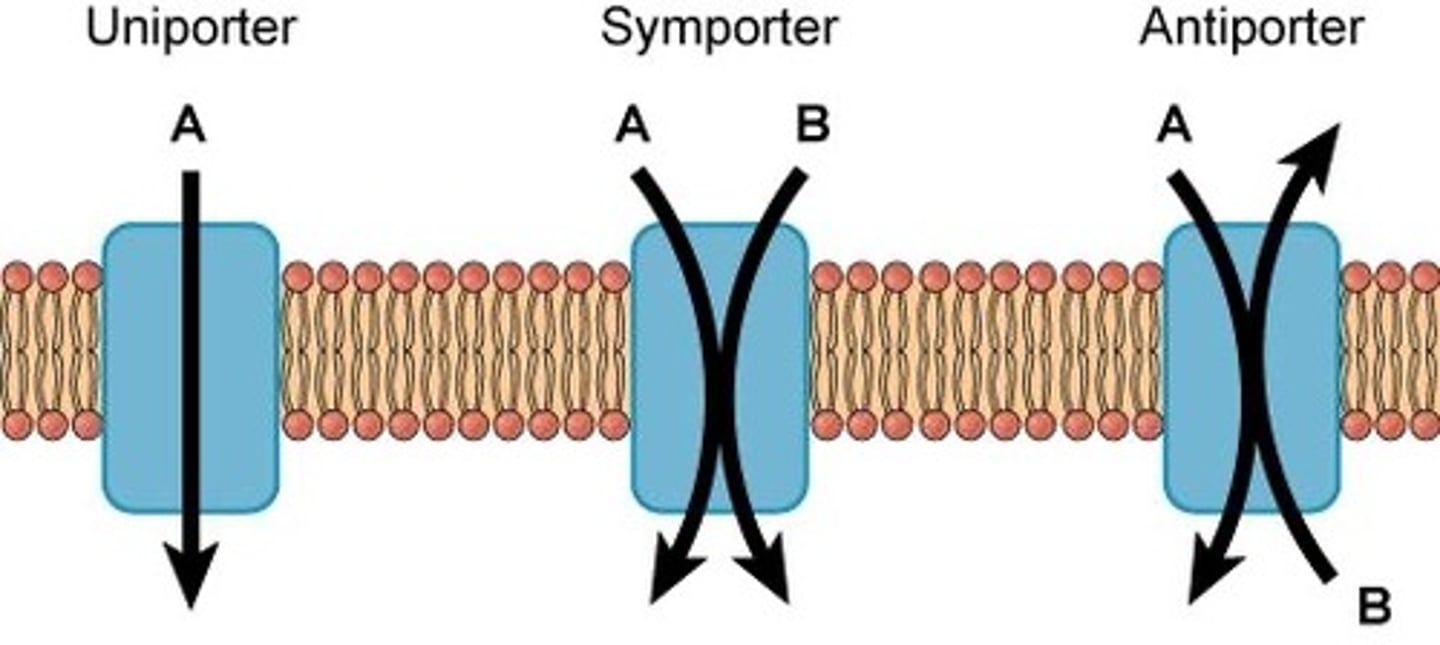
symporter
moves two substances in the same direction
antiporter
moves two substances in opposite directions
Difference between facilitated diffusion and active transport
FD has no limit while AT does
Countertransport
- Similar to co-transport but moves 2 or more substances in opposite directions at same time
- uses antiporters to transport
Endocytosis vs. Exocytosis (vesicular transport)
- endocytosis brings substances into the cell through the formation of vesicles:
1. receptor mediated
2. pinocytosis
3. phagocytosis
- exocytosis expels substances from the cell through the releasing of vesicles
Phagocytosis
A type of endocytosis in which a cell engulfs large particles or whole cells
Pinocytosis
A type of endocytosis in which the cell ingests extracellular fluid and its dissolved solutes.
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
- The use of receptor proteins on the cells surface to capture a specific target molecule + bind to it
- Once the receptors bind to their target molecule, endocytosis is triggered and everything is engulfed in a vesicle
which cells use phagocytosis
White blood cells bring bacteria inside them and break it down
Epithelial transport
-transport between body's internal and external environments and between different fluid compartments within the body (epithelial cells, blood vessels, etc)
- combines both diffusion and active transport for movement
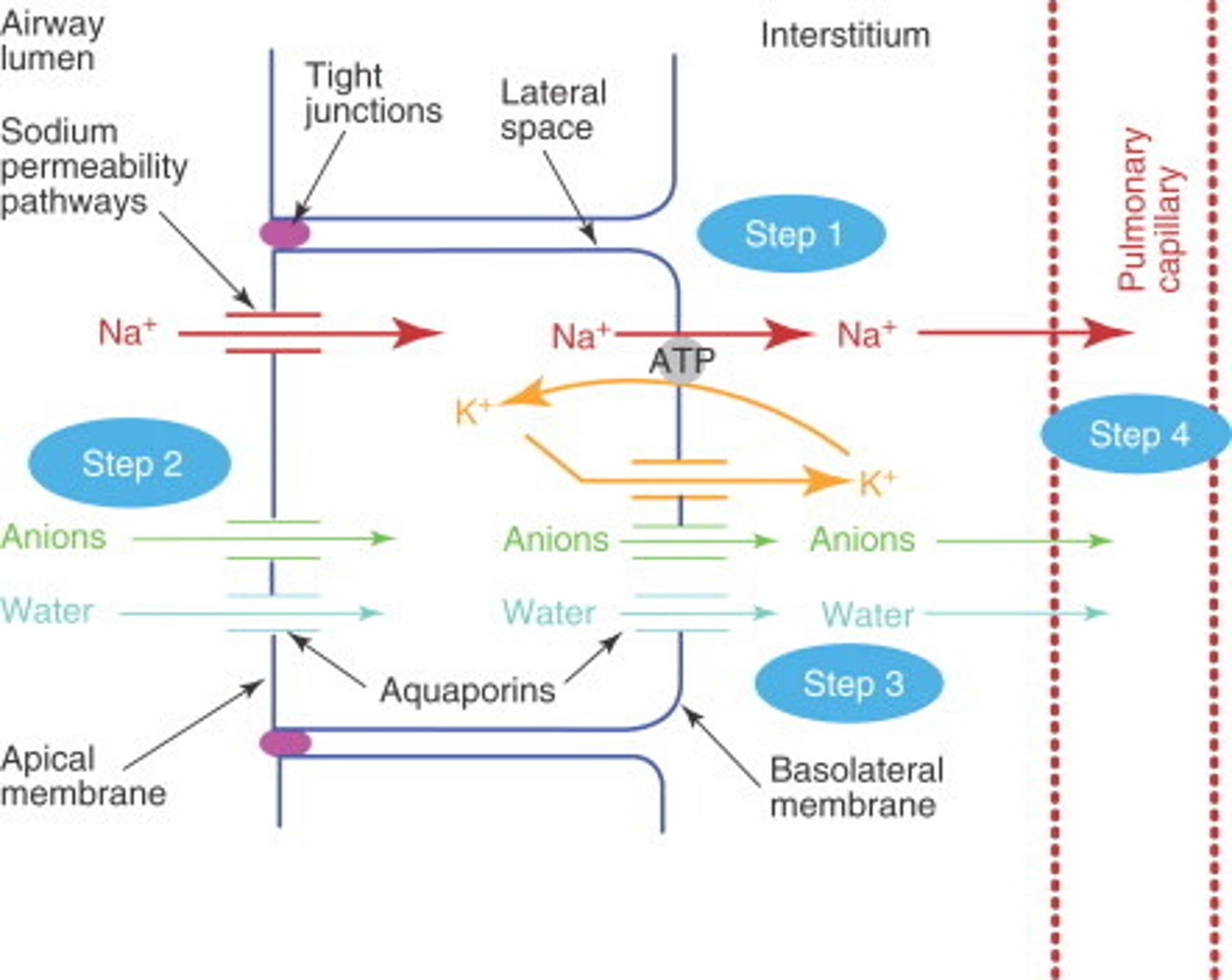
Where would we see epithelial transport in the body?
Gut and Kidney
cell communication through the 3 types of ligand receptors
cell communication uses ligands (molecules that bind to a receptor and act as "signalling molecules")
1. channel-linked receptors
2. enzymatic receptors
3. G protein-coupled receptors
Channel-linked receptors
- channels that open in response to a ligand binding
- helps initiate electrical changes in nerve + muscle cells
Enzymatic receptors
- cell surface receptors that act as an enzyme or are linked to an enzyme
- the binding of a ligand to this type of receptor will activate the enzyme and turn on its function
- involves protein kinase enzymes
Protein Kinases
enzymes that activate or inactivate other proteins by phosphorylating (adding a phosphate) them
G-protein coupled receptors
- indirectly activate protein kinase enzymes
- involves 1st and 2nd messengers
1st Messengers
- never enters the cell, simply binds to the receptor (aka the ligand)
- usually hormones or neurotransmitters
2nd messengers
- transmits the signal generated by the first messenger (from outside the cell) amongst the inside of the cell
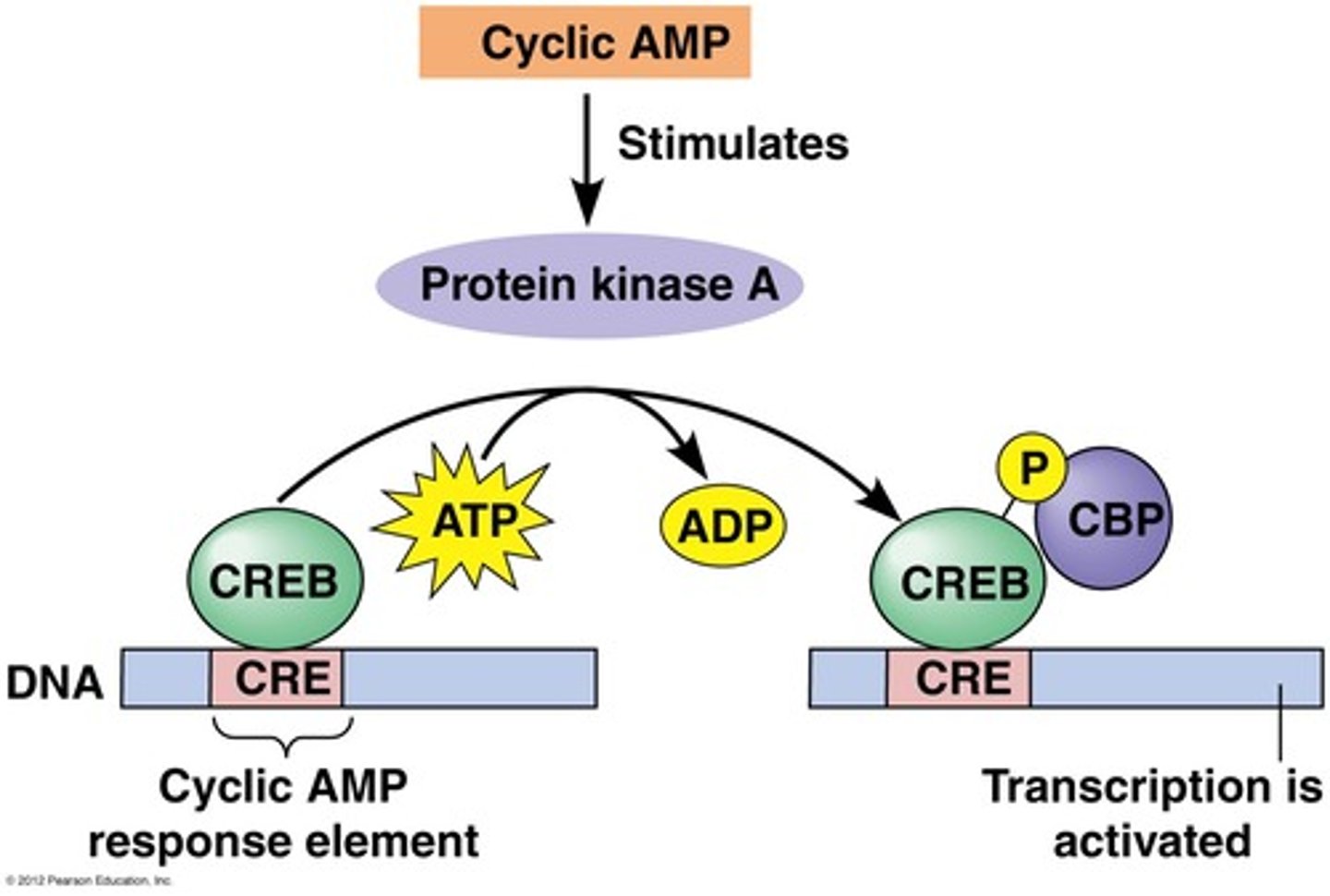
- i.e. cAMP (cyclic AMP)
cAMP response activates _________ _________
Protein Kinase