Optical Isomerism: General Exam Flashcards
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
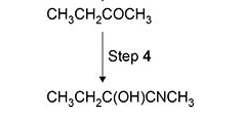
Explain why Step 4 produces a racemic mixture.(answer applies to this type of question generally)
Planar molecule
Equal chance of attack from above or below
Producing equal amounts of both enantiomers
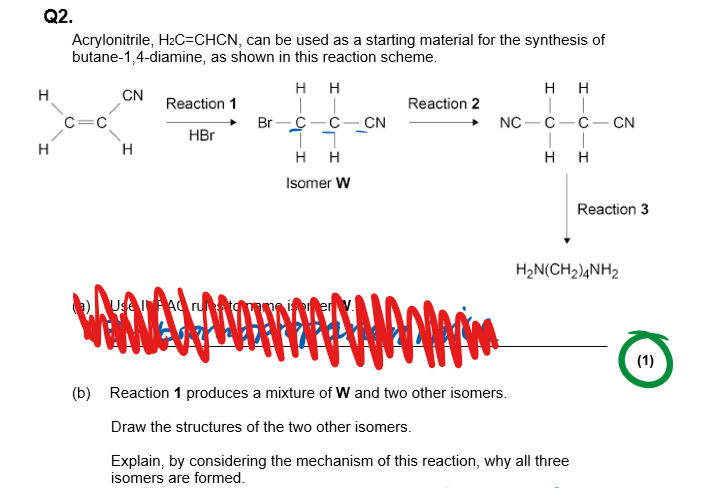
6 Marker
-First stage of the mechanism drawn out(H-Br to the organic molecule):
Produces two secondary carbocation intermediates
-Second stage of the mechanism drawn out(finish the mechanism)
So two different optical isomers created as can be attacked from above or below
-Draw the planar structure of the carbocation and show it being attacked from above and below

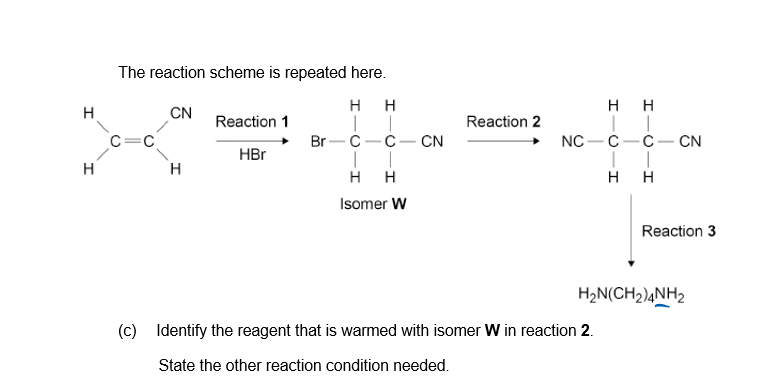
c) NaCN
Conditions: Ethanolic AND aqueous
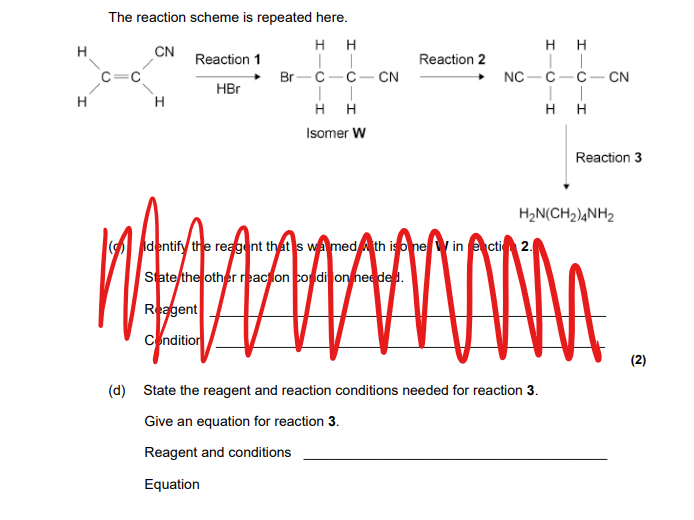
Hint: Involves reduction instead of substitution!
H² and LiAlH⁴ with dry ether
Equation: 2NCCH₂CH₂CN + 4H₂/[8H] → H₂N(CH₂)4NH₂
To remember how to balance:
All Cs not bonded to H get 2 Hydrogens each, which takes 4 away. This leaves 4(Creates two CH2
Then all the N gets two each, leaving none.
What is the general word equation for the hydrolysis of an Amide?
Amide + H₂O + H⁺ (acid) → Carboxylic Acid + Ammonium Ion
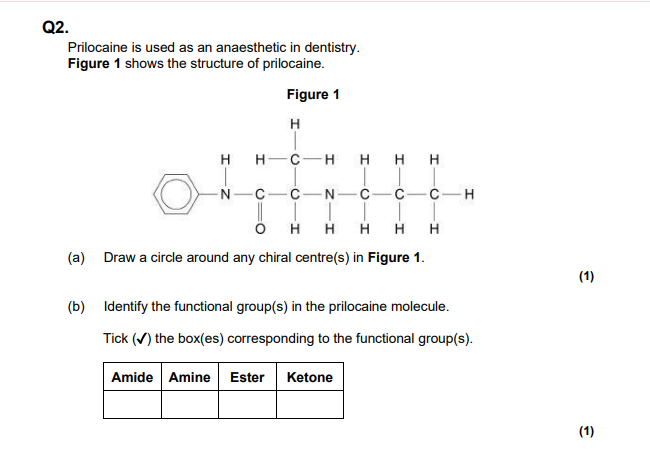
Amine group present(N-H)
Amide group present(CONH)
The C=O group is a part of the amide group, not a ketone!
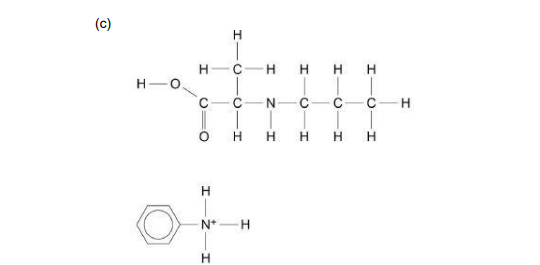
C-N bond broken in the amide
Leaving the Carboxylic acid as a product
And the phenylamine picks up 2 more H due to protonation, forms R-N⁺H₃(ammonium ion)
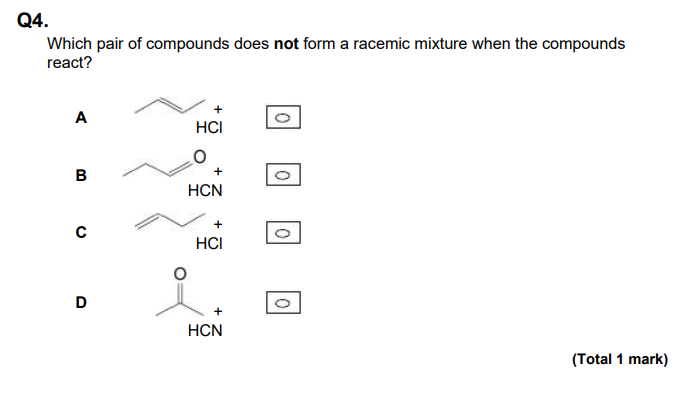
D
This is because it is a symmetrical ketone.
In these questions, look for symmetrical ketones,often right
2-Hydroxypropanenitrile displays optical isomerism. Draw three-dimensional representations of the two enantiomers of 2-hydroxypropanenitrile, showing how the two structures are related to each other.
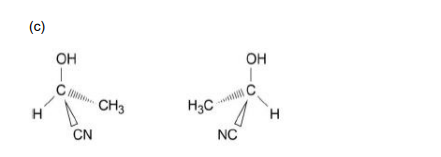
State the definition of racemic mixture.
Equal mixture of enantiomers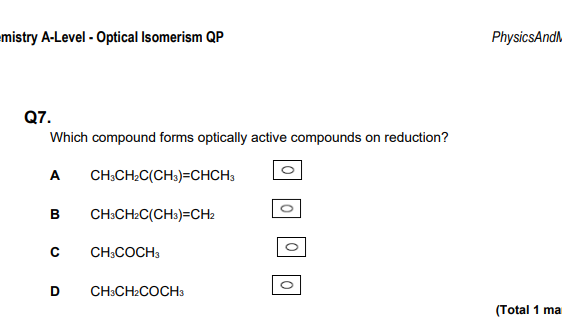
Reduction: Look for unsymmetrical ketones or aldehydes!