Psychology Ch 1-5, 8 exam 9/22 (copy)
1/72
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
structuralism
understanding the conscious experience through introspection
introspection
processing your own experiences to understand other experiences
What was the criticism of introspection and structuralism?
too vague and subjective
gestalt psychology (def)
focuses on humans as a whole rather then individual parts
Gestalt principles of perception (types)
figure-ground relationship, proximity, similarity, continuity, closure
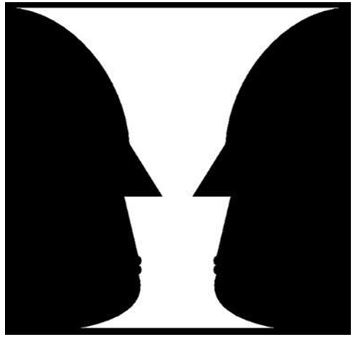
which principle does this picture represent
figure-ground relationship
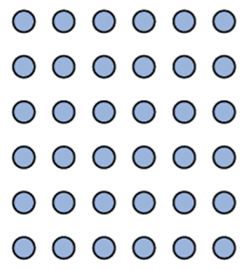
which principle does this picture represent
similarity
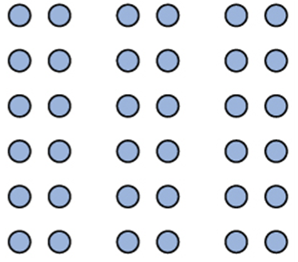
which principle does this picture represent
proximity
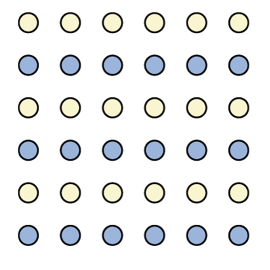
which principle does this picture represent
similarity

which principle does this picture represent
closure
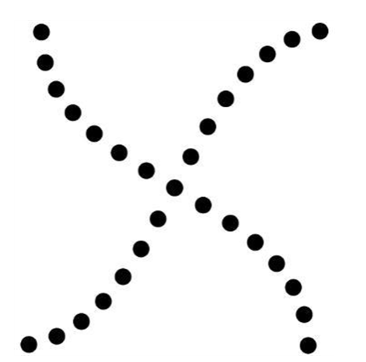
which principle does this picture represent
continuity
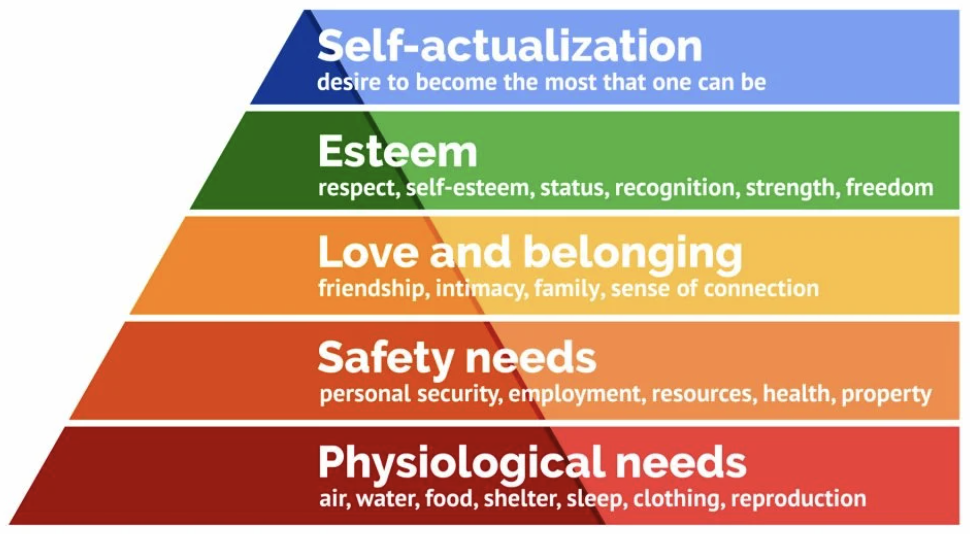
Who created this hierarchy of needs
Maslow
hierarchy of needs
self actualization, esteem, love and belonging, safety and needs, physiological needs
Therapists need 3 things:
unconditional positive regard, empathy, and genuineness
biopsychology
how structure and function of the nervous system determine behavior
sensation and perception
both physiological aspects of sensory systems and psychological experience of sensory information
personality psych
behavior and thought patterns that are unique to each individual
developmental
physical and mental attributes of aging and maturation
social psych
how people interact and relate with others and how interactions can affect behavior
health psych
how biology interacts with health
clinical psych
diagnosis and treatment of psych disorders
industrial-organizational psych
applies psychological theories, principles, and research to industrial and organizational settings
sports/exercise psych
psychological aspects regard sport and physical performance
forensic psych
deals with the justice system
inductive reasoning
tested through our personal observations to form conclusions
deductive reasoning
form hypothesis’s and theories
what are the types of research
clinical/case study, surveys, archival research, longitudinal/cross-section, naturalistic, and correlational
whats the risk with longitudinal studies
attrition
attrition
to drop out of long-term studies
independent variables
what you manipulate
dependent variables
what you are measuring
true random
everybody hs an equal chance at participating
quasi experimental
not everything can be controlled and it is not randomized
what can you not determine with a quasi experiment
cause and effect relationships
genotype
the genetics
phenotype
what you can see
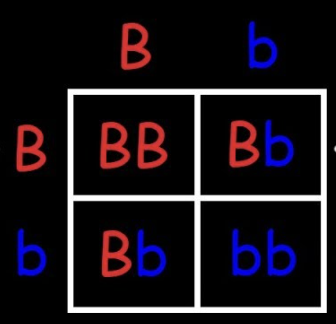
what is the genotype of 50% of the offspring
Bb
synapse
space between neurons
dopamine
mood/sleep/learning
seratonin
mood/sleep
2 major parts of the nervous system
central and peripheral
Central Nervous System
brain-spinal cord
peripheral nervous system
somatic/exterminates and autonomic/internal
central and peripheral job
bring the body to homeostasis
lateralization
left side or the brain controls the right side of the body
thalamus
serves as the relay center where most sense are routed before processing
Which sense doesn’t go through the Thalamus
smell
hypothalamus
links nervous system and endocrine system by controlling the pituitary gland and controls homeostasis
how much sleep should you be getting?
7-9, no more then 11 and no less then 6
what is mor addictive and why: crack or cocaine
crack because it is smoked not snorted
adderall
highly addictive and a stimulant
how does adderall work
gives brain dopamine which calms people with ADHD down
memory
set of process used to encode, store, and retreive information over different periods of time
whats the process of memory
encode→storage→retrieval
explicit memory
memory of facts
types of explicit memory
semantics and episodic
semantics
concepts and language
episodic
what/when/where, autobiographical
implicit memory
unconscious memory
example of implicit memory
riding a bike
implicit memory (taught?)
can be learned through emotional conditioning
explain sensory or emotional memories
higher emotional content in a memory makes it easier to remember, and sensory memories are recalled for seconds or minutes, if that
arousal theory
strong emotions form strong memories
flashbulb memories
memories that are affected by our emotional state
suggestibility
causes people to remember something that was just a suggestion from someone else
latent content
the unconscious wishes through expression in dreams or fantasies
transduction (conversion)
the action or process of converting something into another form
6 senses
vision, hearing, smell, touch, taste, balance
transduction
input of sensory information through transmittters
sensory adaptation
not perceiving a stimulus because you’ve grown use to it
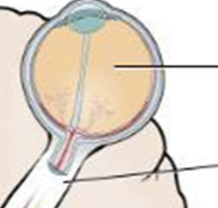
blind spot in vision (bottom line)
optic disc
optic chasm
where brain processes information
opponent-process theory
white dot theory, gives a negative after-image (continuation of visual stimulus)