EXAM 1: Intro to Clinical Microbiology
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
What are the key differences between eukaryotes and prokaryotes?
Eukaryotes- (Algae, fungi, protozoa) enclosed in a nuclear membrane, membrane-bound organelles
Prokaryotes- (bacteria) have a cell wall, don't have membrane-bound organelles
How do you correctly write an organism name using binomial nomenclature?
The first name is capitalized, the second is lowercase, and both genus and species are written. Example: Streptococcus pyogenes.
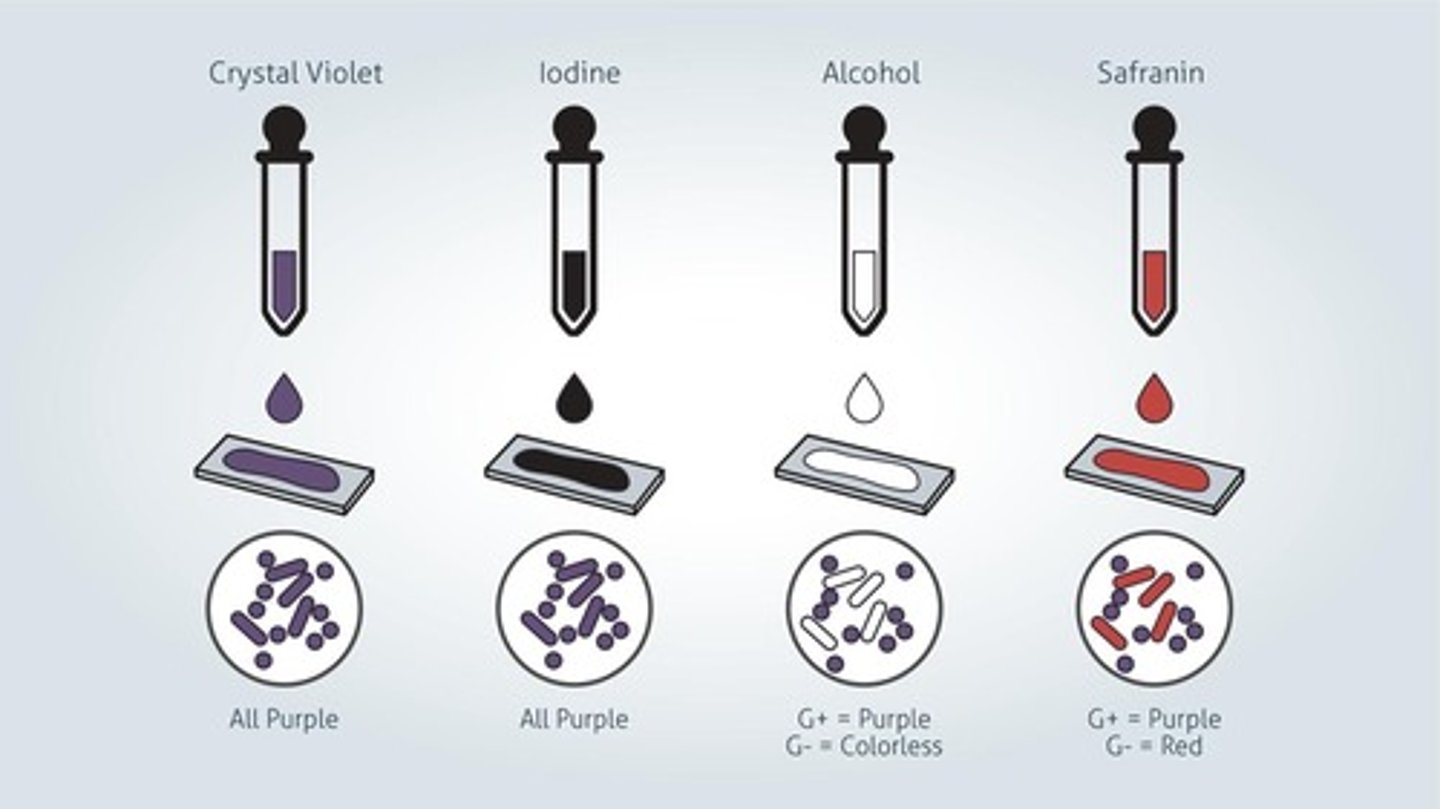
What is the principle of the gram stain?
Place a drop of sterile water on a dry slide, with a sterile loop, pick up a little bit and mix the water.
After the slide is dry, fix with methanol over the sink for 1 minute. Note heat fixing the slide will distort the specimen. Rinse.
Add crystal violet to the slide for 1 minute; this is the primary stain. It penetrates the cell wall and stains all bacteria purple. Raise.
Add Iodine for 1 minute; this is a mordant it enhances the reaction between the cell wall and the primary stain, making a complex. Rinse.
Add a decolorizer like ethyl/acetone, which damages the outer membrane if the Gram-negative cells, then the peptidoglycan layer is exposed. Rinse immediately or you will -decolorize.
Add Safranin for 30 seconds, which is a counterstain; this will color the gram-negative cells pink. Raise then pat dry and air dry, read them at 100x oil immersion.
Nonselective- supports growth of most nonfastidious organisms. Ex.BAP
- supports growth of most nonfastidious organisms. Ex.BAP
Differential- allow grouping of organisms by their ability to demonstrate phenotypic differences on the agar. Ex. BAP
- allow grouping of organisms by their ability to demonstrate phenotypic differences on the agar. Ex. BAP
Selective
- allow grouping of one organism but not another.
What are the atmospheric requirements of aerobes?
Aerobes grow in ambient air (78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, 1% other gases).
Enriched
- nonselective media that include additional growth enhancers to allow fastidious organisms to grow. Ex. CHOC.
obligate aerobes
- requires oxygen
obligate anaerobes
- cannot grow in the presence oxygen
facultative anaerobes
- can grow with/without the presence of oxygen
Microaerophiles- requires small amounts to grow
- requires small amounts to grow
What is the atmospheric composition and temperature of the ambient air incubator used in clinical microbiology labs?
78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, 1% other gases, and 35-37°C.
What percentage of CO2 is used in the CO2 incubator in the clinical micro lab?
5%-10% CO2.
What is doubling time?
The time required for one cell to divide into two.
Capnophiles
-require increased CO2
What are the end products of glucose metabolism via glycolysis?
Pyruvate, 2 ATP, and 2 NADH.
What is fermentation?
A process that allows glycolysis to continue without O2, producing ATP and converting pyruvate into other products.
Which metabolic pathways have a higher energy yield: Krebs cycle or fermentation?
Krebs cycle.
What is a plasmid?
A double-stranded, circular, self-replicating extrachromosomal genetic element located in the cytoplasm.
What is a complex transposon?
A piece of DNA that can move from plasmid replication or transfer or provide a specialized function.
What are standard precautions?
Guidelines that all patient samples are infectious and capable of spreading disease.
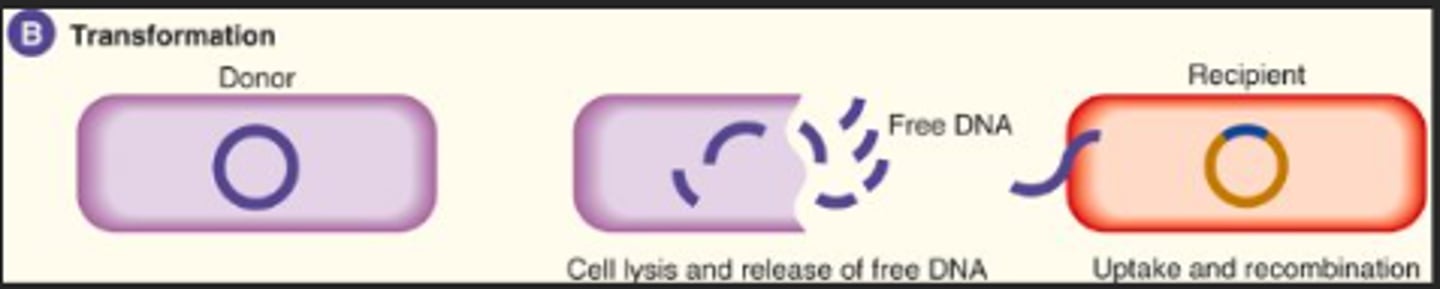
Explain Transformation
Transformation- bacteria take up free DNA from their surroundings and integrate it into their chromosomes.
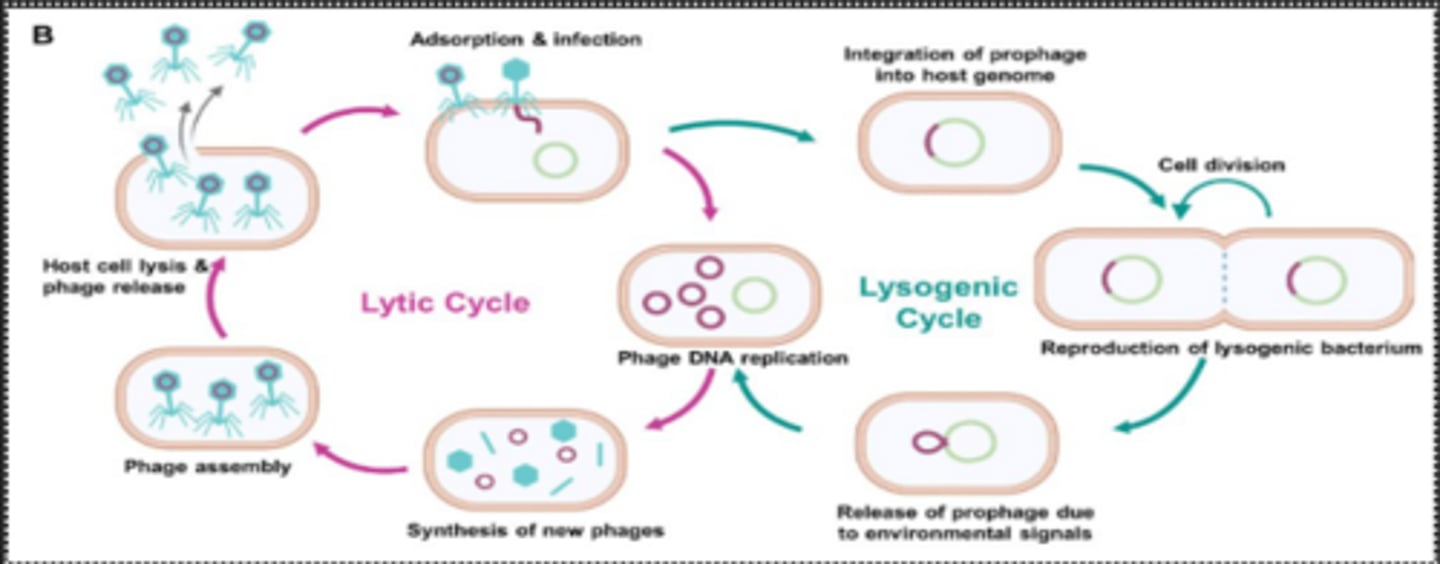
Explain transduction
Transduction- bacteriophage infects a donor bacterium and mistakenly packages up bacteria DNA into al particles, then the bacteriophage infects a recipient bacterium and transfers the donor bacterial DNA which may integrate into the recipient chromosome.
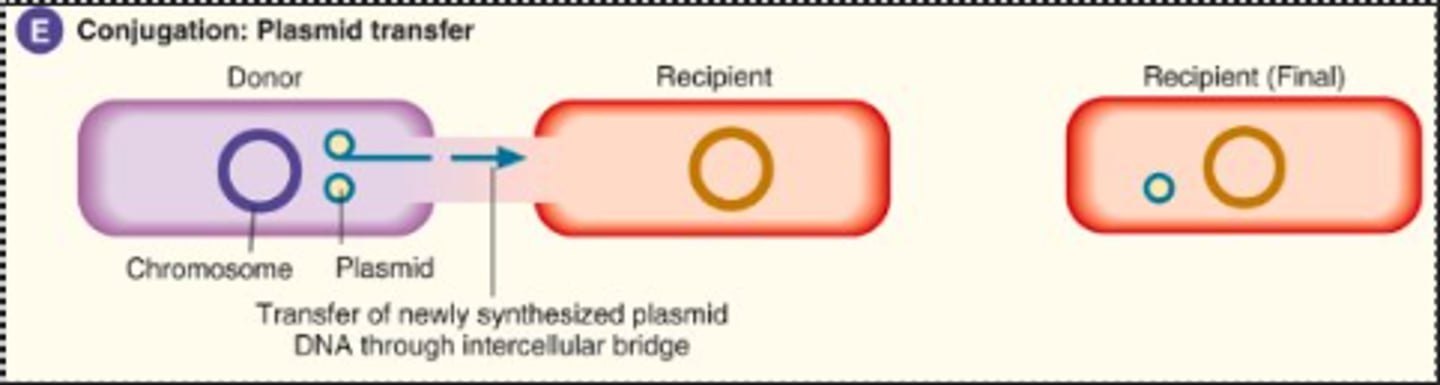
Explain conjugation
Conjugation- donor bacteria transfers plasmid via a pilus
Contact precautions
- direct/ indirect contact with patient or patient environment
Droplet precautions
- close respiratory contact or exposure of mucous membranes to respiratory secretions
How do you appropriately shut down a biological safety cabinet (BSC) after finishing work?
Clean with 75% ethanol, allow 15-30 mins before shutting off, and use UV light for cleaning.
Airborne precautions
- infectious agents that remain airborne and infectious over long distances
What are the differences between Class I, II, and III biological safety cabinets?
Class I has air entering and exiting as exhaust
Class II filters air before and after circulation
Class III is self-contained with HEPA filters.
What are the standard conditions for autoclaving?
121°C, 15 psi, for 15 minutes.
What is the difference between engineering controls and PPE?
Engineering controls- controls that isolate or remove the hazard from the workplace. Ex. Eyewash stations, emergency showers, plastic shield barriers.
PPE- personal protection equipment, equipment used to minimize exposure. Ex. gloves, lab coats, protective eye wear, mask, face shield.
What is the primary chemical disinfectant ingredient in household bleach?
Sodium hypochlorite.
What are the conditions for Biosafety Levels 1 to 4?
Level 1- minimal risk, on an open benchtop
Level 2- moderate risk, all precautions should be taken, BSC should be used when potential for aerosols
Level 3- aerosol transmission and potentially lethal consequences, specific training to handle, separate from other parts of the lab, have a negative airflow, and under a BSC
Level 4- high risk of causing threatening infection, isolated from other parts of the lab, noncirculating air filter, restricted access, positive pressure biohazard suits.
How often should gram stain quality control be performed?
Daily and as needed, using Staphylococcus aureus 25923 and Escherichia coli 25922.
What is the difference between sterilization and disinfection?
Sterilization- destruction of all forms of life
Disinfection- eliminates a defined scope of microorganisms.
What are the basic guidelines for specimen collection?
Collect early in infection and never collect after antibiotics
Use proper technique to minimize contamination from normal flora
Collect sufficient quantities
Collect and transport in container that will maintain organism viability
Label the specimen from where you got it, it's important.
Transport within 2 hrs and store in the proper environment
Labs need to be notified in advance if an unusual pathogen or bioterrorism is suspected
List information that should be included on specimen label
Full name, DOB, Identification number, room number or location, physician name, culture site, date/time of collection, initials of collector
What is the proper transport time for specimens?
Transport within 2 hours and store in the proper environment.
What two anticoagulants are acceptable for microbiological specimens?
Sodium polyanethol sulfonate (SPS) and heparin.
What are Level 1 critical specimens?
Amniotic fluid, blood, brain, cerebrospinal fluid, heart valves, pericardial fluid.
What are Level 2 unpreserved specimens?
Other body fluid, bone, wound drainage, stool, sputum, tissue.
What are Level 3 specimens requiring quantitation?
Catheter tip, urine, tissue from quantitation.
What are Level 4 preserved specimens?
Preserved stools, preserved urine, and swabs in holding media.
What is indigenous microbiota?
Microorganisms commonly found in or on body sites of healthy people.
Describe proper isolation technique (semiquantitative test)
1. Sterilize your inoculation loop, wait 7 seconds, take a colony from a pure culture, and inoculate a small circle on the media. Sterilize your inoculation loop, wait 7 seconds.
2. Place loop on the dot and drag it very slowly out in tight streaks. Sterilize your inoculation loop, wait 7 seconds.
3. Drag the inoculation loop 2-3 times in the prior inoculated section and drag out loosely. Sterilize your inoculation loop, wait 7 seconds.
4. Drag the inoculation loop 2-3 times in the prior inoculated section and drag it out even looser than the prior one. Sterilize your loop, name, date, and sign your plate. Place upside down to avoid condensation on the agar.
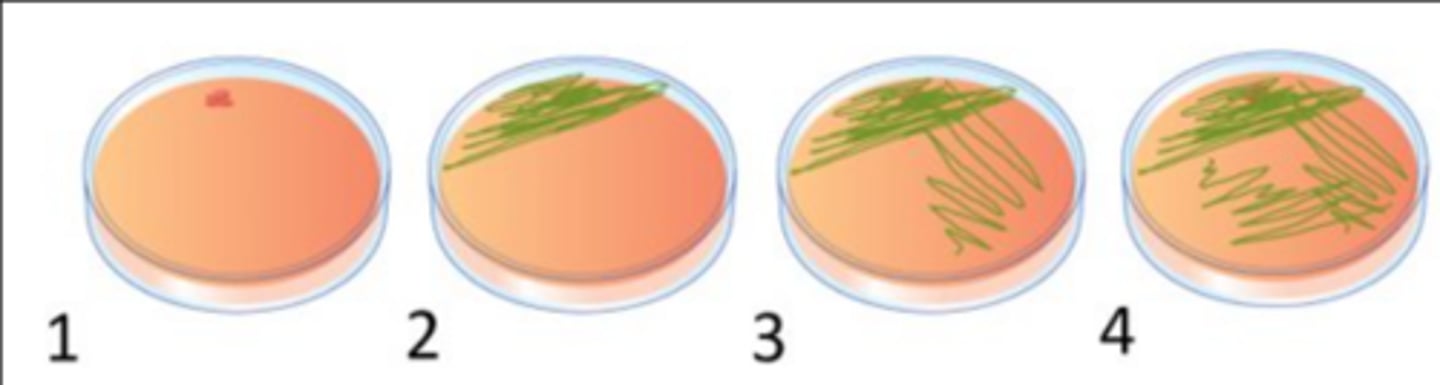
Describe the importance of knowing the specimen body site for interpreting culture results
The whole body has its own microbiota, and it is different on different body sites and can cause infection if it is displaced. So, it's important to know so we can tell if it's causing the issues.
What is the difference between resident and transient microbiota?
Resident- colonize an area for months or years.
Transient- present at a site temporarily.
What are some benefits of normal flora?
Help with nutrient metabolism, inhibition of colonization of pathogens by competition for nutrients and secretion of bacteriocins, and help develop the immune system.
What is an opportunistic infection?
caused by MO that doesn't normally cause infection unless displaced or immunocompromised.
What is an endogenous infection?
microbes from host's normal flora causes infection
What is an exogenous infection?
microbe from outside the host and enters the host and causes infection (environment).
What is virulence?
The degree of pathogenicity that allows pathogens to evade host defenses and cause disease.
What is an iatrogenic infection?
occurs as a result of medical treatment or procedure
What is a nosocomial infection?
healthcare-associated infection.
What is a community-acquired infection?
infections acquired outside a healthcare environment
What is the difference between a true pathogen and an opportunistic pathogen?
True pathogen- causes disease in healthy individuals
Opportunistic pathogen- caused by MO that doesn't normally cause infection unless displaced or immunocompromised.
What methods do bacteria use to avoid phagocytosis?
Capsules- mask the cell surface structures, preventing recognition by phagocytic cell receptors, prevents binging of complement proteins, inhibiting complement activation.
Bacterial cell wall- may interfere with phagocytosis
Bacterial toxins- kill phagocytes, inhibit the movement to sites of tissue damage.
What are adhesion factors?
Factors that help them stick to things
Fimbriae(pili)- contain adhesion proteins on their tips that bond to cell surface receptors.
Biofilms- sticky and adhere.
What occurs to bacteria in the humoral immune response?
Bacteria get opsonized, lysed, and a memory B cell is made.
What is the difference between exotoxins and endotoxins?
Exotoxins -gram -/+ inside bacterial cells and excreted upon lysis, species specific, heat labile, low dose is fatal.
Endotoxins- gram - from LPS, not specific to species, cause fever, hypotension, septic shock, activates complement, initiates coagulation, heat stable, requires higher dose.
For which type of microbes is the cell mediated adaptive immune response particularly important?
Intracellular bacterial infections and viral infections.
What are components of the innate immune system?
Nonspecific response, no memory, natural
Skin, mucous membrane, acidic pH and enzymes, normal flora, phagocytosis, inflammation, NK cells
What is the principle of MALDI-TOF?
Breaks down to fragments and reads the time of flight with a laser.
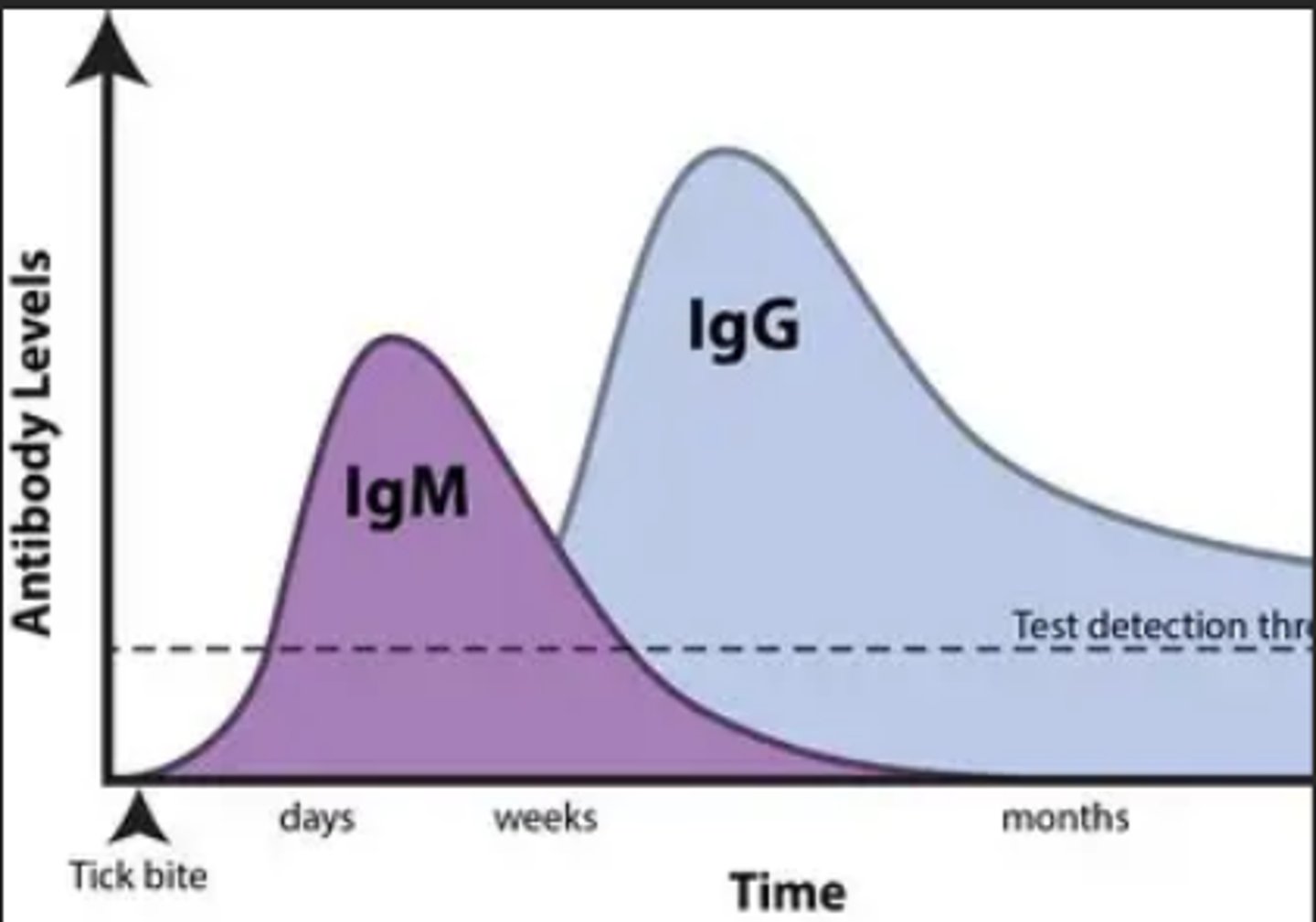
What are the differences between IgG and IgM?
IgG- is small, can cross the placenta, appears after IgM as a secondary response, and it is produced first in the second response. (warm)
IgM- large, cannot cross the placenta, appears first after initial exposure then second on second exposure. (Cold)
What is the principle of PCR?
Primers attach to the target section, nucleic acids are added, and DNA is amplified.
What is the difference between primary plating and subculturing?
Primary plating- inoculation of clinical specimen onto lab culture media.
Subculturing- bacterial colonies are selected for further testing and inoculated to other plates.
What is sensitivity in testing?
How well a test can detect a pathogen or specific amount.
What is specificity in testing?
How good the test is at detecting what it is supposed to.
What can cause false negative results in serology testing?
False negative- not waiting a significant time after onset to see antibody response, variation in host immune response (immunocompromised), hook effect
What can cause false positive results in serology testing?
False positive- cross-reactive antibodies
What is a monoclonal antibody?
Monoclonal- one type of antibody that binds to specific epitope
(high specificity), rarely occurs naturally anda are manufactured to be used commonly in lab testing
What is paired sera testing?
Testing for optimal diagnosis of current infection
Acute is collected when disease is first suspected
Convalescent is collected 2 weeks after acute phase
Diagnosis requires a four-fold or two doubling dilutions between the acute and convalescent
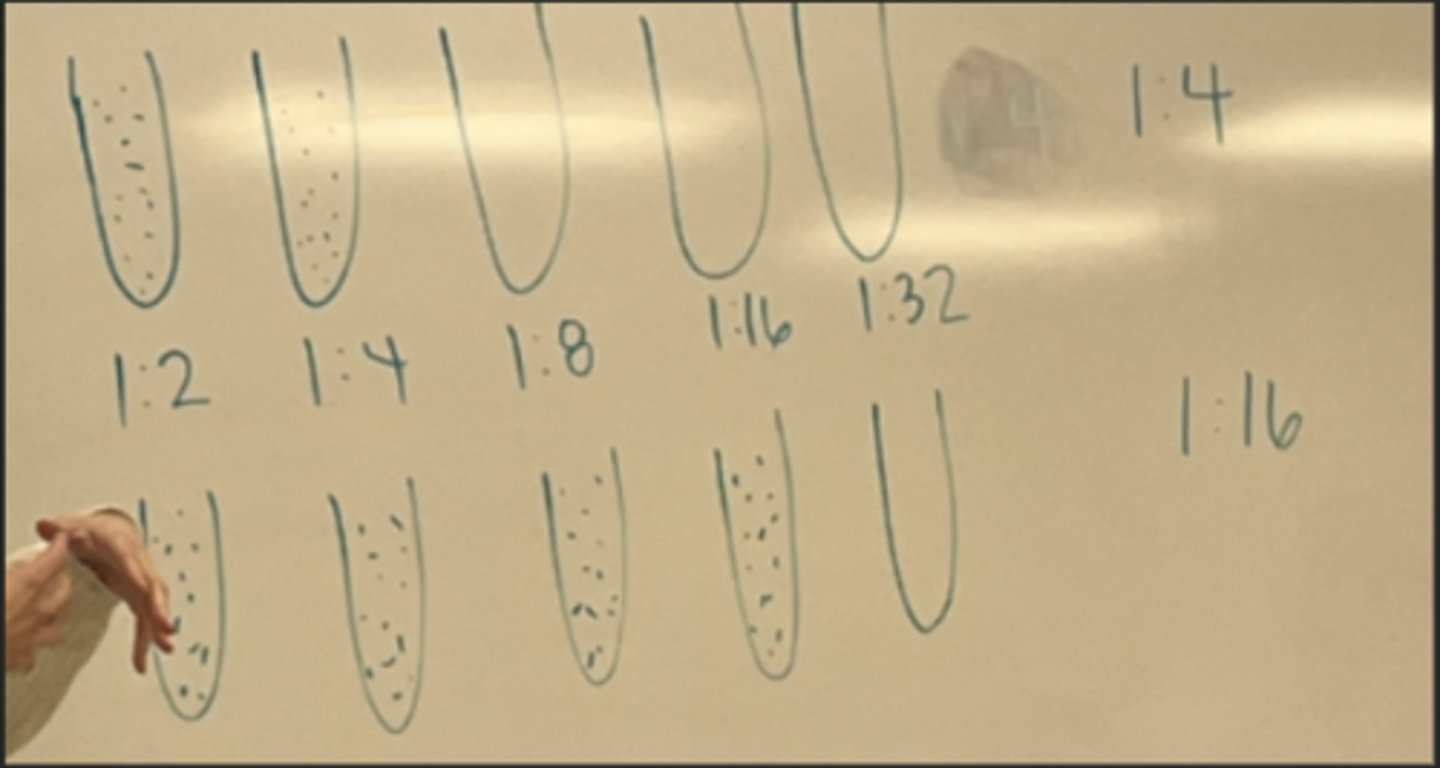
When is it okay to test a single serum specimen for antibody titer?
Yes, in the case of assessing immune status, testing for IgM in congenital infection, and infection that are rare (rabies).
What is a precipitation test?
Soluble antigen and antibody diffuse through agar liquid and a visible precipitate forms when they combine.
What is the principle of an agglutination test?
Clumping of particles coated with antigen-antibody complexes
-Sensitization and lattice formation.
What is the difference between competitive and noncompetitive assays?
Competitive is inversely proportional
noncompetitive is directly proportional.
What is the principle of a lateral flow enzyme immunoassay test?
Antigen or antibody bound to enzymes that catalyze a reaction, measured by catalyze reaction. Capillary action moves the liquid through it.