Forecasting (Severe Weather & Winter Weather)
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
What is the criteria for a severe thunderstorm?
Wind gust of 58 mph or greater, produces hail an inch or greater in diameter, or produces a tornado
What are the two types of severe thunderstorms that produce a majority of storm reports?
MCS, Supercells
What is a Mesoscale Convective System?
This is a group of thunderstorms (multicellular) with each member in one phase of thunderstorm development (cumulus, mature, dissipating)
What are the configurations of MCS?
Cluster, Line, Bow
What is a multicell thunderstorm?
Isolated storms (3-4) that are neither part of a larger group nor contain a mesocyclone. Composed of general or pulse thunderstorms.
True or False: Associated with moderate instability and unidirectional shear (winds have the same direction with increasing height)
True
What is an MCS Squall Line?
Linear configuration of thunderstorms in various stages of development. Shear vectors are typically parallel to the forcing mechanism.
True or False: MCS - Squall Lines are better organized than the multi-cell cluster
True
How do MCS - Squall Lines develop?
With a linear forcing mechanism
True or False: MCS - Squall Lines are both severe and non-severe squall lines that usually have significant directional shear
False: Unidirectional shear
What are the keys of maintenance for an MCS - Squall line?
Cold pool strength; some dry air is required for evaporative cooling.
What is a Bow Echo?
Radar signature indicating the descent of strong winds to the surface. The winds result in a portion of the line moving ahead of the rest of the line forming a bow or backwards C shape.
What kind of atmosphere environment do Bow Echoes form?
Moderate Wind Shear, moderate to strong instability, and mid-level dry air
What is the primary severe weather threat of a bow echo?
Damaging straight-line winds which are commonly found on the apex of the bow
True or False: For a Bow Echo, tornadoes are a lesser threat and tend to be found in the cyclonic vortex and to the south of the apex.
False: North of the Apex
What is a Derecho?
A series of downbursts associated with a bow echo, or a series of bow echoes. They can persist up to 24 hours.
What is the primary hazard of derechos?
Straight-line winds, sometimes eclipsing 100mph
When do Derechos primarily occur?
March and August but can occur year-round
What are supercells?
Large, long duration thunderstorms that are typically discrete from other storms.
What are the four types of supercells?
High Precipitation, Low Precipitation, Classic, and Mini
What can you use to determine the type of supercells?
Anvil Level (9-11 km) relative winds, along with sounding
True or False: Supercells are most prominent component is the mesocyclone.
True
What are the characteristics of Low Precipitation?
Anvil winds (60+ kts), relatively little precipitation (evaporates before reaching the ground); hard to detect on radar. Rarely produces tornadoes, but large hail is likely. Found along the dry line and semi-arid environments.
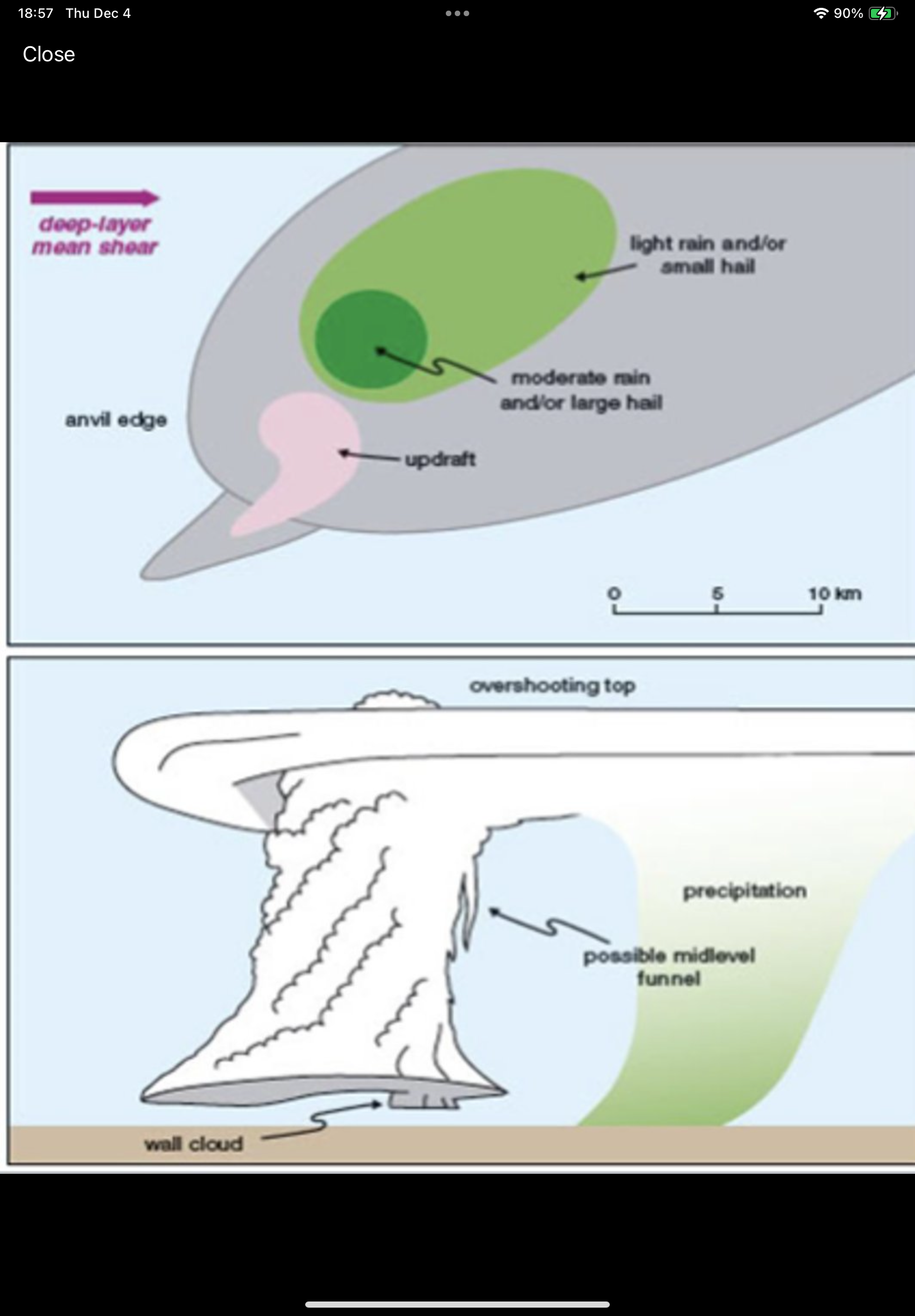
What type of Supercell is this image?
Low Precipitation
What are the components of a Classic Supercell?
Anvil level winds (40 - 60 kts), most of the precipitation falls in the FFD, common to the Great Plains, radar signature includes a hook echo, usually located on the SW flank of the storm. Balance between updraft and downdraft leads to longest duratino supercells.
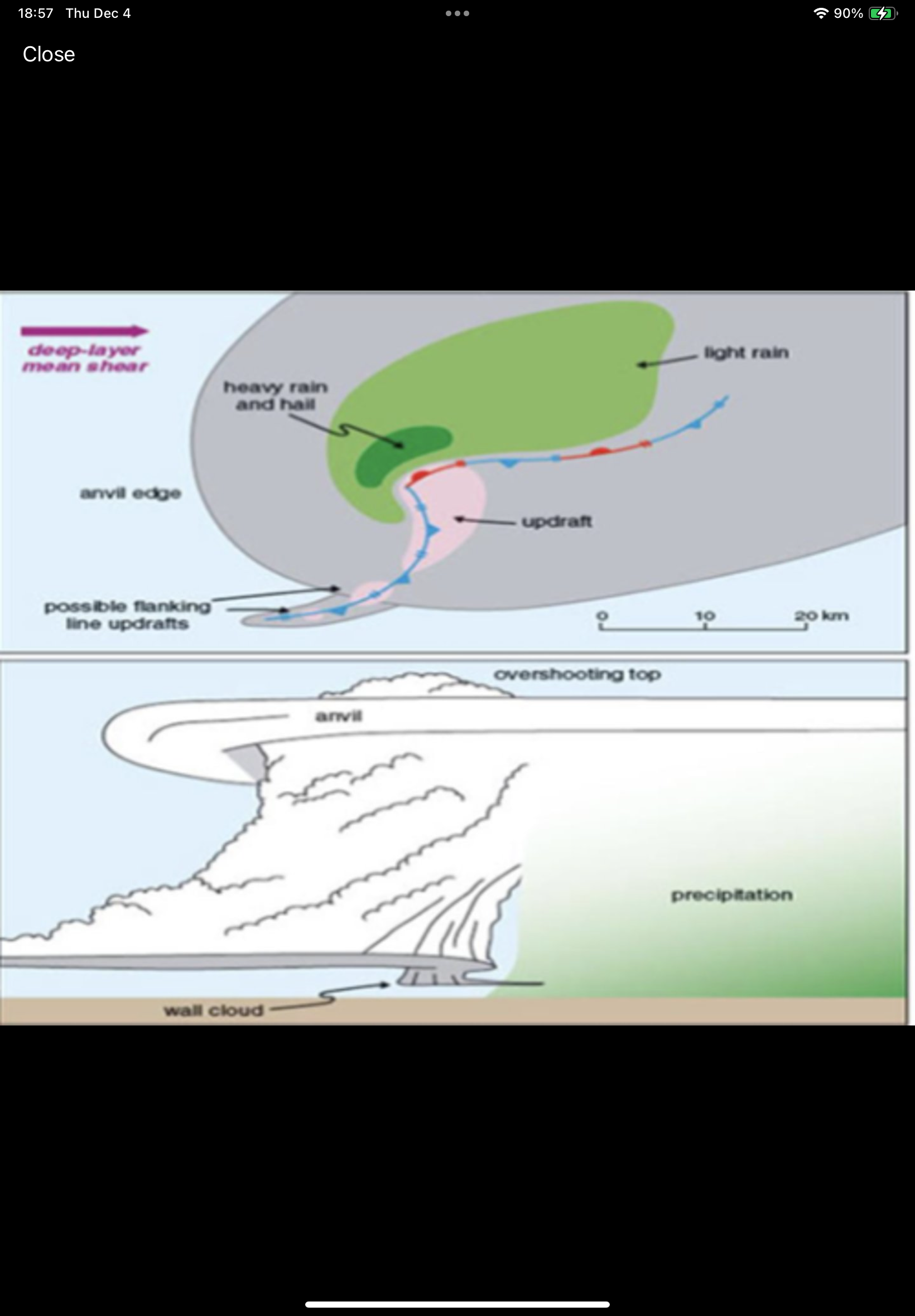
What type of supercell is this image?
Classic
What are the components of the High Precipitation Supercells?
Anvil level winds less than 40 kts. Abundant precipitation throughout; often obscures the mesocyclone visually but is still apparent on a radar—more of a kidney-bean-shaped echo than a hook. Very common, especiaily in humid areas of the U.S. (SE)
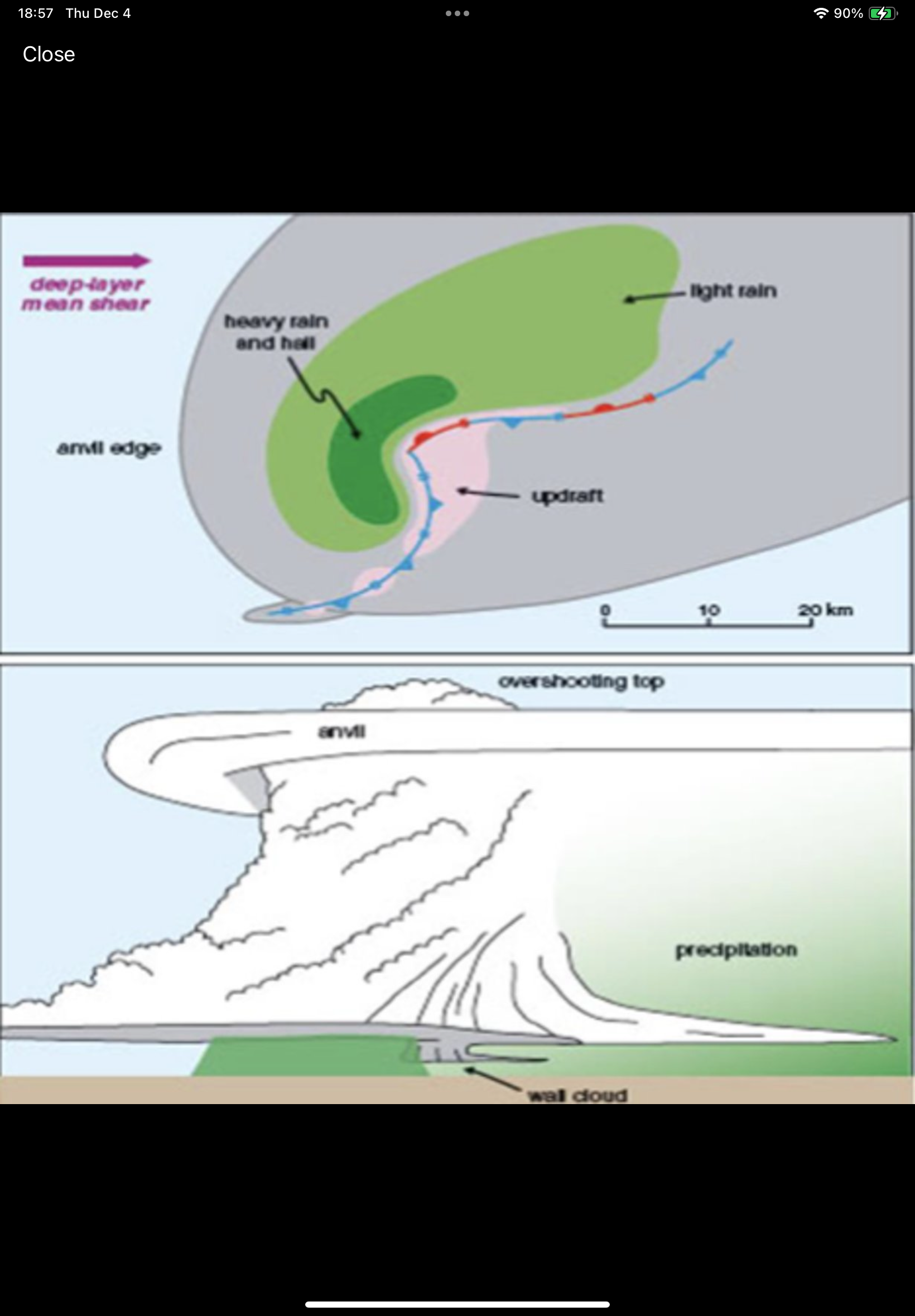
What type of Supercell is in this image?
High Precipitation
True or False: in an HP Supercell, they are often updraft dominant which limits tornado production.
False: Downdraft Dominant
What allows transitions from HP to Squall Lines, and possibly derechos?
Strong Outflow
What are the ingredients for severe weather?
Shear, Lift, Instability, and Moisture
What is shear?
Changes in wind with height; it can be either speed or directional
What does shear do for storms?
Acts as a venting mechanism, removing mass and thus preventing collapse. Shear helps to seperate updraft and downdraft so that both can persist.
What is positive shear vorticity?
Generated by either an increase in wind speed with increasing height or by a clockwise change in wind direction with increasing height.
True or False: Shear generates rotation that can be ingested by thunderstorms and lead to the development of mesocyclones.
True
How can shear be analyzed?
Viewing wind barbs at each level, but it is best visualized using the hodograph
What is 0 - 6 km Bulk Shear?
Assesses the potential of the atmosphere for organized convection.
What values for 0 - 6 km Bulk Shear indicate potential for downdraft/updraft seperation?
Greater than 35 kts
What is deep-layer shear?
Wind shear vectors can be used to assess storm mode. Specifically, their orientation relative to the initiating boundary.
When are the discrete convective modes likely?
When vectors are approximately 60 degrees.
What do perpendicular vectors lead to?
Splitting Supercells
What do environments with unidirectional shear with increasing height lead to?
Generation of splitting supercells, assuming instability levels are high
What is Storm Relative Helicity?
Measures the potenital for rotating updrafts. This is a direct estimate of the amount of horizontal vorticity generated by the ambient shear.
What are the categories of SRH?
0-1km, 0-3km, and Effective Inflow
What is the SRH value equal to?
To the area under the curve swept out in the given layer, relative to the storm motion vector.
What is the storm motion vector?
Mean of the 0 - 6km winds
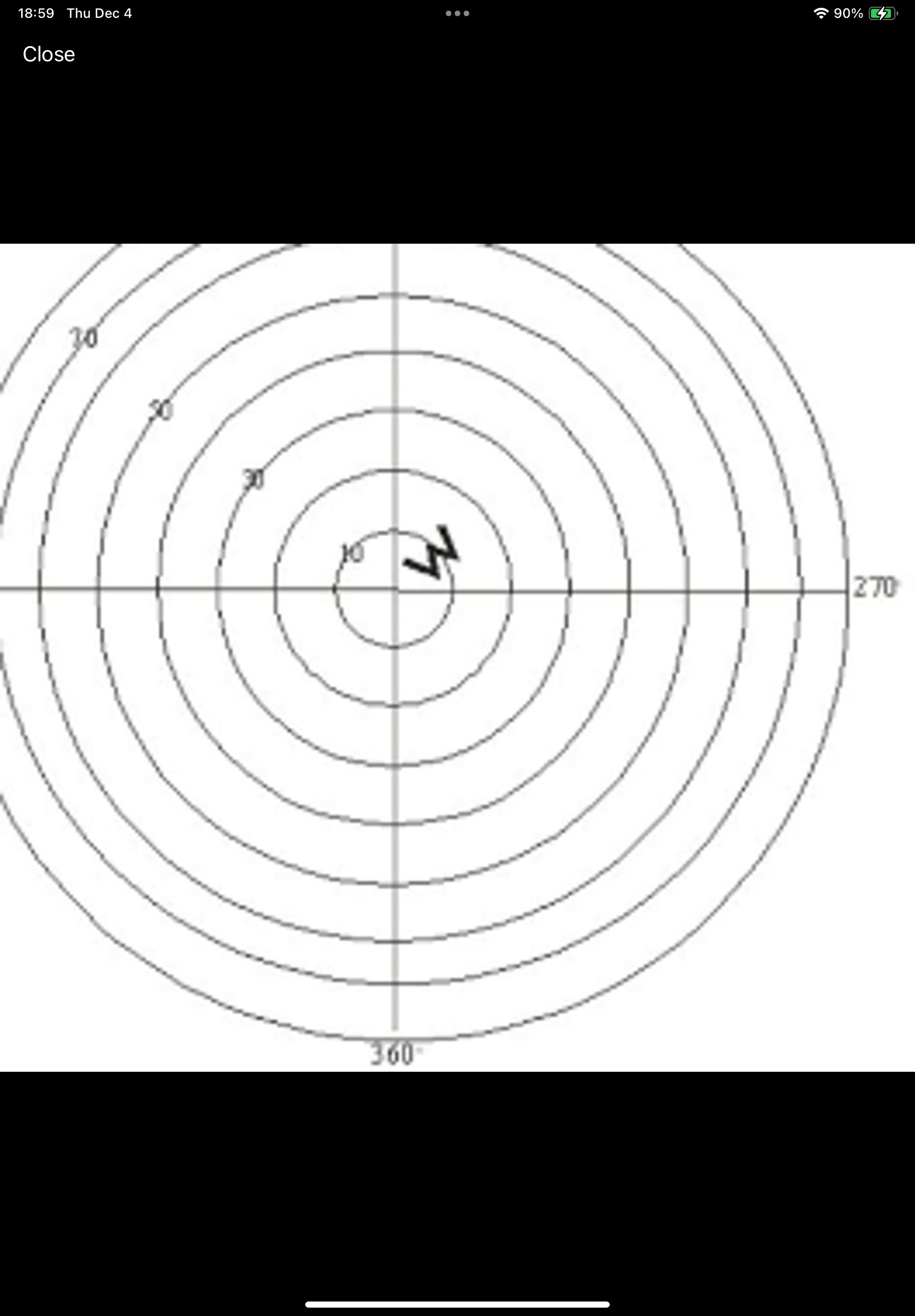
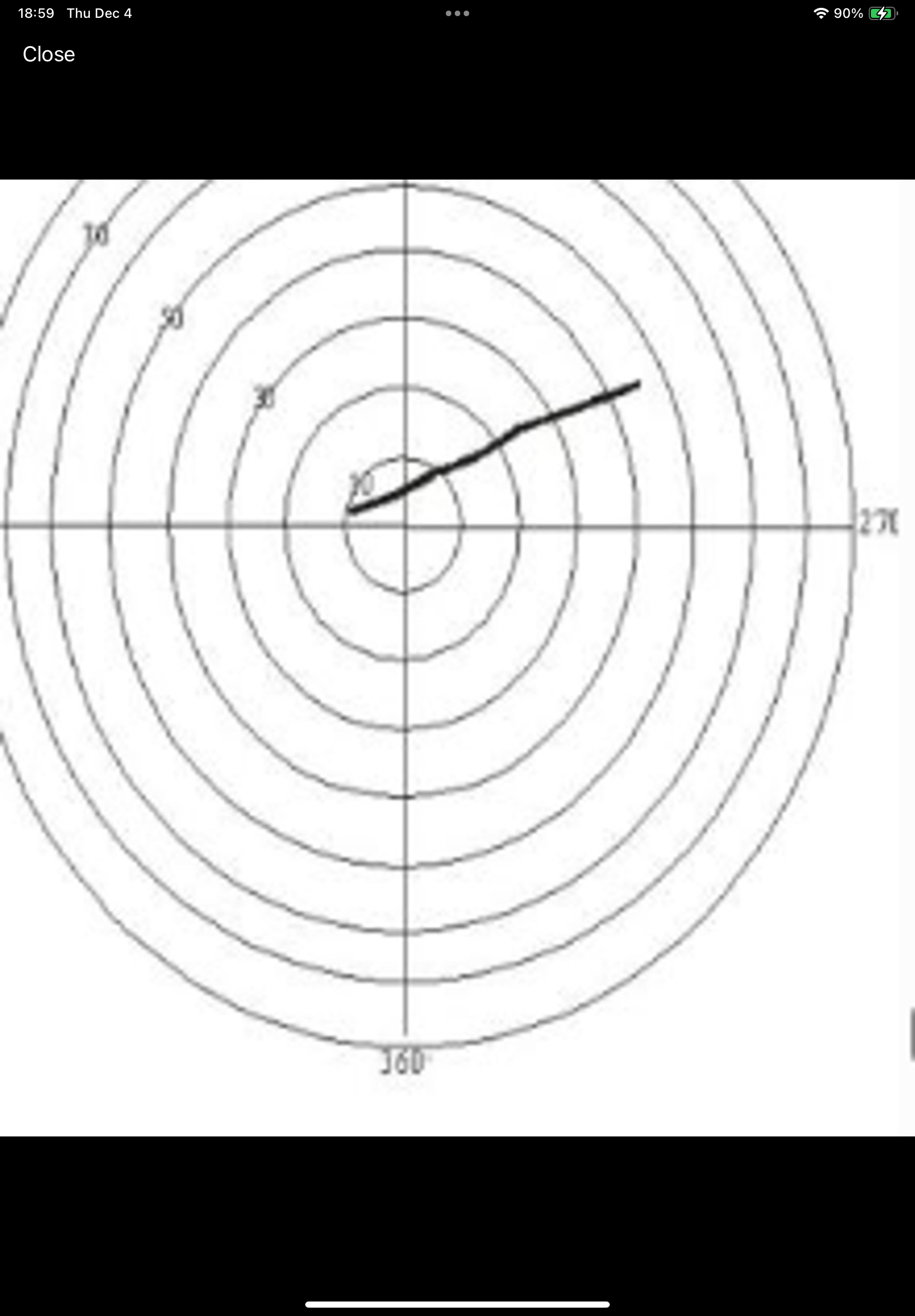
What type of storm is this hodograph?
Pulse Storm
What type of storm is this hodograph?
Multicell/splitting Cell Storm Type
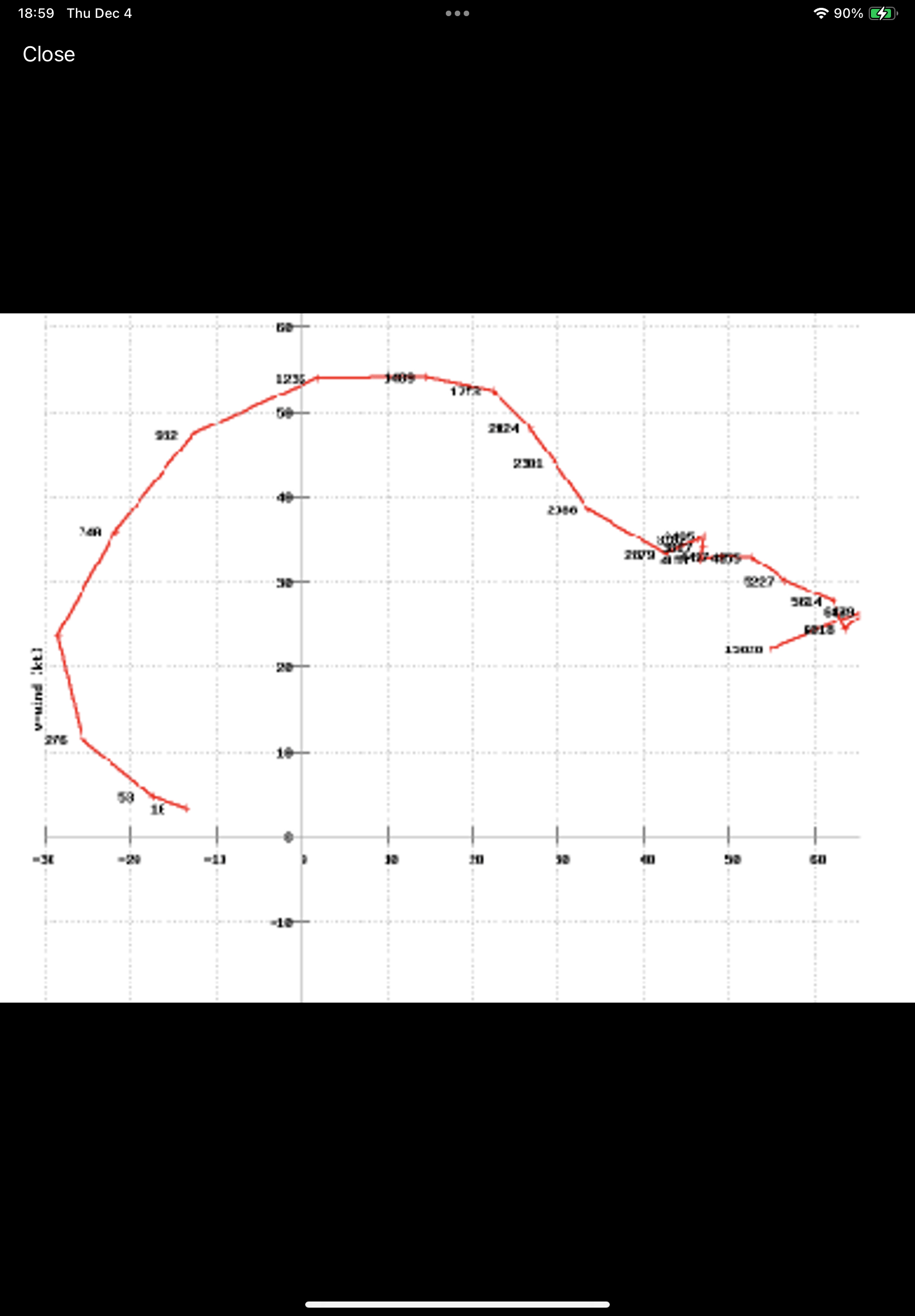
What type of storm is this hodograph?
Supercell
What does Effective SRH use?
CAPE and CIN to determine the SRH that exists within the inflow layer of the storm.
What is Effective SRH better at?
Discrimminating between non-significant and significant tornado environments
What is the range of SRH?
0-1km: 100 m2/s2
0-3km: 250 m2/s2
When does tornadic potential increase for helicity?
Concentrated between 0-1km; allows for greater vortex stretching, a tighter circulation, and faster rotation of the mesocyclone.
What is lift?
Any mechanism that generates upward movement (mechanical/dynamical forcing).
What are examples of boundaries for lift?
Fronts, outflow, orography, dry line
What are examples of Upper-level factors for lift?
DPVA, Jet Streaks, Divergence, Diffluence
True or False: Convergence in the lower-levels will contribute to uplift?
True
What does instability promote?
Density differences which lead to rising air
What is CAPE?
Convective Available Potential Energy
What are the types of CAPE?
Surface, Mixed-Layer, and Most Unstable
What is surface-based CAPE?
Uses parcel lifted from the surface
What is Mixed-Layer CAPE?
Uses the average parcel from the bottom 100mb of the troposphere. Generally, the most accurate. Accounts for boundary layer mixing.
What is most-unstable CAPE?
Most Unstable Parcel
What are some generalized CAPE instability guidelines?
0 - 1000 J/kg: Marginally
1000 - 2500 J/kg: Moderately
2500 - 3500 J/kg: Very
3500+ J/kg: Extremely
What are other forms of CAPE?
0-3km, Normalized, Downdraft
What is 0-3 km CAPE?
The portion of the CAPE found between the surface and 3km. This is important as the larger the amount in the lower levels, the greater the stretch of the streamwise vorticity in the vertical. This increases the rotation rate of the mesocyclone.
What is normalized CAPE?
This is the amount of CAPE divided by the depth of the buoyancy later. Used to gauge the shape of the CAPE; a small value implies a tall, thin profile. Leads to gradual parcel acceleration and reduced severity. A high value indicates a tall, thick profile. Suggests the possibility of more robust updrafts and increased severity.
What is downdraft CAPE?
Measure of the negative buoyancy. Leads to acceleration of downdrafts towards the surface. Increass with the presence of dry air. Values greater than 1000 have been associated with damaging outflow winds.
What do Lapse Rates express?
The change in environmental temperature with increasing height. Higher values indicate a more rapid change in temperature and a less stable atmosphere.
What are lapse rates depicted as?
Low-level (850-700mb) and mid-levvel (700-500mb)
What are stability values for lapse rates?
Stable: 5.5 - 5.0 C/km
Conditional: 6.0 - 9.0 C/km
Unstable: >9.5 C/km
What is the most reliable measure of moisture?
Mixing Ratio
At what rate does dew point change?
2 C/km in the vertical, but mixing ratio remains constant
True or False: For severe weather considerations, it is important not only that significant moisture be present, it should also be present in a shallow layer.
False: Deep Layer
If the moisture is shallow, what is there a chance of?
Mixing that will lower the dew point at the surface. This will lead to higher LCL heights and a lower tornado potential
What does the return flow of moisture make the difference between?
Tornadic threats and wind threats
If the wind trajectories originate from the Gulf what will happen to the moisture?
It will return as forecasted
If the wind trajectories are from a source with drier air, what will happen to the moisture?
It is likely the models will be overdone on the strength of the moisture.
What is "The Cap"?
In many severe weather scenarios, a capping inversion will exist in the low-to-mid levels
What if the cap is too weak?
Several storms will develop at once. Competition for resources will lead to weaker storms on average.
What if the cap is too strong?
Storms won't be able to form
What does an inversion of modest strength allow?
Allows for instability to build and will limit the number of storms that develop. A few very strong storms
What is Convective Inhibition?
Represents the negative energy on the Skew-T diagram below the LFC. The environment is warmer than the parcel and will keep the parcel from rising
What is the Level of Free Convection?
The height in the atmosphere where the parcel first becomes warmer than its environment and will rise unaided.
What are the Storm Relative Wind categories?
1. Low-Level (0-2 km): Sustained supercells > 15 kts
2. Mid-Level (4-6 km): Tornadic Supercells > 15 kts
3. Anvil-Level (9-11 km): Supercell type
What is Supercell Composite?
Incorporates the Most Unstable CAPE, Effective Storm Relative Helicity, and Effective Bulk Wind Difference
What is Significant Tornado Parameter?
Combines Bulk wind Difference, 0-1 km SRH, Surface-Based CAPE, Surface-Based LCL (Fixed Layer)
What is EHI?
Combination of surface-based CAPE and SRH int he selected layer.
What is the critical angle?
The angle between the storm-relative wind at the surface and the 0-500m AGL Shear Vector
What is a critical angle near 90 degrees?
Infers streamwise vorticity near the ground, which favors stronger cyclonic rotation and dynamically forced ascent closer to the ground in a right moving supercell.
What are critical angles in the range of 45 to 135 degrees?
Near-surface vorticity is more streamwise than crosswise.
What is Tornadic 0-1 EHI?
Updated version of the 0-1 km EHI. Adds 0-3 km MLCAPE and 0-6 km bulk wind dfference as enhancing factors, and LCL/CIN as limiting factors.
What temperatures can ice form?
Below 0 C and if the air is supersaturated with respect to ice.
True or False: The saturation vapor pressure for ice is less than that of water?
True
What are two basic types of ice nucleation?
Homogeneous and heterogeneous
What is homogeneous nucleation?
Requires cloud temperatures to be -40C or less and for the supercooled water to be free of impurities.
What is heterogeneous nucleation?
Occurs when supercooled water droplets freeze directly on a nucleusm such as dust or pollen
True or False: For a substance to form an ice nucleus, it must have a molecular structure similar to ice.
True
What structure do ice crystals have?
Hexagonal
When does the maximum difference in SVP between ice and water occur?
-8 and 16 C