PPL Oral Prep
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Documents for flying
Pilot certificate, medical certificate, photo ID, aircraft registration, airworthiness certificate, operating limitations (POH), and weight and balance data. (14 CFR 61.3)
Maximum allowable BAC for pilots and how long must you wait until flying after last drink?
0.04 percent and 8 hours waiting (14 CFR 91.17)
Definition of 'Night for flight operations'
The period from 1 hour after sunset and 1 hour before sunrise at the location of aircraft (14 CFR 1.1)
Can a private pilot accept compensation for flight services?
No, a private pilot cannot accept compensation for flight services; however, they may share operating expenses with passengers pro-rata. (14 CFR 61.113)
What are the currency requirements for carrying passengers at night?
A pilot must have made at least three takeoffs and fullstop landings in the same category and class of aircraft within the preceding 90 days to carry passengers
Explain the term "pro-rata share" in relation to flight expenses.
Sharing flight expenses equally among all occupants, ensuring no profit is made from the flight. (14 CFR § 61.113)
Describe the procedure for recovering from a spin.
(PARE) Power Idle, Ailerons neutral, Rudder opposite to spin, Elevator forward.
What is the purpose of a transponder, and when is it required to be used?
A transponder provides aircraft position and altitude information to ATC radar. It's required in certain airspaces and above specified altitudes.
How does the pitot-static system function, and what instruments rely on it?
The pitot-static system measures air pressure to provide readings for the airspeed indicator, altimeter, and vertical speed indicator.
How do we keep our pilot certificate current?
Student pilot: with valid medical certificate
PPL: Flight review every 24 calendar months
(61.56, 61.57)
What are the currency requirements for carrying passengers?
3 takeoffs and landings within the preceding 90 days in an aircraft of the same category, class, and type if required. At night, these 3 landings must be made to a full stop.
(61.57)
What are the currency requirements for carrying passengers in the day
3 takeoffs and landings within the preceding 90 days in the aircraft (61.57)
Night definition? When can you perform required night landings?
Night = the time between evening civil twilight and morning civil twilight
Night landings can be logged 1 hour after sunset to 1 hour before sunrise (1.1, 61.57)
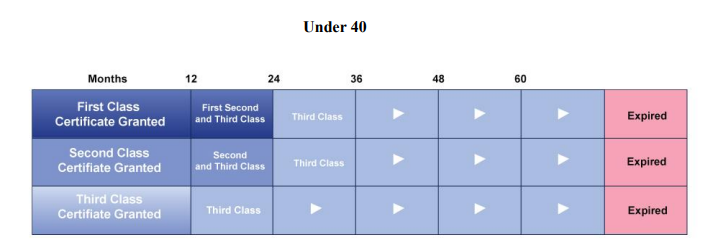
How long is a medical certificate valid for under 40?
(61.23)
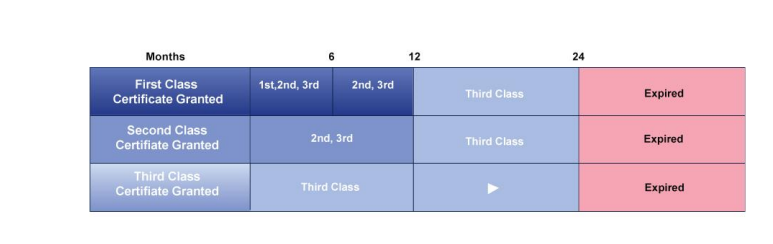
How long is a medical certificate valid for over 40?
(61.23)
What documents should be in the aircraft before flight?
A - Airworthiness Certificate
R - Registration
R - Radio License (required for international flight)
O - Operating Limitations (found in the POH)
W - Weight and Balance equipment list
ARROW (91.9, 91.203)
When will an aircraft registration certificate expire?
7 years
What factors will you consider for weather analysis when planning a cross-country flight?
METARs, TAFs, AIRMETs/SIGMETs, NOTAMs, and consult the National Weather Service. Consider weather at departure, en route, and destination.
What are the differences between AIRMETs and SIGMETs?
AIRMETs are for moderate weather phenomena, while SIGMETs warn of severe and hazardous weather for all aircraft.
How would you determine your course for a cross-country flight?
Use sectional charts to plot course, identify checkpoints, and address navigation aids. Plan for alternate routes or contingency plans.
What would you do if you experienced unexpected fuel starvation in-flight?
Switch tanks, possibly declare an emergency, and prepare for a safe landing.
What performance factors would you consider for takeoff, cruise, and landing?
Consult POH for takeoff and landing performance charts, adjust for weight, balance, density altitude, and weather conditions.
How does high density altitude affect aircraft performance, and what measures mitigate those effects?
It decreases performance due to less dense air. Reducing weight, flying during cooler times, and using longer runways can help.
How do you handle an inoperative instrument discovered in-flight?
Check if the item is required via MEL, KOEL, or 14 CFR Part 91.213, and determine steps to repair or land.
What steps would you take for a complete communication failure?
Cycle comms systems, check fuses, squawk 7600, use visual maneuvers, and follow light gun signals at towered airports.
What is a personal minimums checklist, and why is it important?
It's a pilot-specific list of conditions to ensure safety, including factors like health, weather, proficiency, and pressure.
Requirements for certification
Be 17, understand english fluently, Hold a US student pilot certificate (61.103)
You must notify the NTSB immediately if any of the following occur:
The aircraft sustains substantial damage, A person is killed or suffers serious injury,