exotics test 2
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
What type of housing is used for mice? (3)
Shoebox housing, metabolic caging, and micro isolation cages
What is the purpose of shoebox caging?
Female mice can be housed together in pairs or groups as well as males of the same litter

What is the purpose of metabolic caging?
Used to accurately monitor food consumption and waste products of the animal

What is the purpose of micro isolation cages?
Prevents pathogens from entering or exiting the cages

What is barbering?
Dominance behaviour where the dominant mouse pulls the hair from the other mice in the cage
These mice should be separated to avoid this progressing into fighting
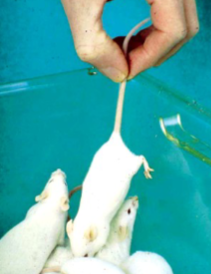
How to capture a mouse
Mice are alert but often nervous animals with quick reactions
They always try to avoid capture by running away
When cornered, bite
Grip the tail about midway down its length and lift it out of the cage
Calm and deliberate movements induce less stress and excitement in the house and you are less likely to be bitten
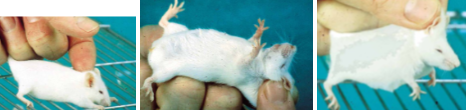
How to restrain a mouse
Need to alter grip
Let mouse grip with its fore feet onto a course surface
E.g. the sleeve of your lab coat, or the cage top
Fix the tail by crooking it in the last two or three fingers and let go with your thumb and fore fingers
Use your now free thumb and forefingers to grasp the scruff of the neck, this needs to be down in one smooth and deliberate action, hesitation may frighten the animal into biting
Enough loose skin must be gripped otherwise the mouse can twist its head and bite
If when taking the fold of skin you fail to take enough at the first attempt, then put the mouse down and restart
How do you sex a mouse?
Mice are sexed by comparing the ano-genital distance
It is always greater in the male but the prepuce is not always distinguished from the vulva
Testes are often retracted
It is easier to sex newborn puppies than 1 week old ones
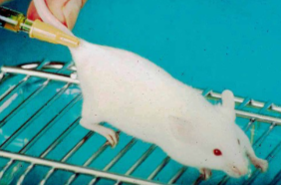
How do you perform a SQ injection on a mouse?
Made into folds of loose skin, most convenient site being over the lumbar area
Restrain mouse by tail and let it grip the surface with its feet
Push needle under skin from behind
Up to 1mL may be injected
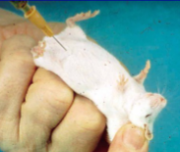
How do you perform a IP injection on a mouse?
Give intraperitoneal injections require restraining the animal in one hand with head lower than the hind legs
So all the abdominal organs fall away the injection sites
Place the tip of the needle slightly to side of the midline halfway between the rear edge of the breast bone and the front edge of the pelvis
Point the needle toward the centre of the abdomen
Push it in with sharp movement but go no further than 2-3 mm into the abdomen
How do you perform a IV injection on a mouse?
Tail veins are more clearly seen when the mouse is warmed for a few minutes
This is done by placing the cage under a heat bulb or a strong light
Albinos do not feel comfortable in strong light
A special restrainer is an advantage
Lit slit for illuminating the tail from below while warming the animal
Pull tail slightly towards you and rotate the tail 90 degrees to access either of the lateral veins
Pull the point of the needle through the skin at a shallow angle, it will then slide easily into the vein
Start injections at the caudal third of the tail, moving cranially for subsequent injections
A plastic tube could be also used to fix the tail
Make a slit for the tail in the rubber prop
SOME POINTS TO REMEMBER
Always inject in the lateral veins, not in the dorsal / ventral arteries
If the needle does not enter the vein then the injection is perivascular, and a diffuse white swelling occurs around the injection site
Use a syringe with a low resistance in the piston, so you can feel the difference between SQ (hard) and IV (no resistance to injection)
Start injecting as close to the tail tip as possible
It is easier to hit there, may closer to the tail base if you miss the first time
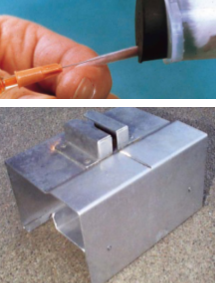
Methods for blood sampling of a mouse (3)
Saphenous vein, heart puncture, retro-orbital
How and what vein do you use for blood sampling in a mouse?
The best site from which a sample of adequate volume and quality can be taken is from the saphenous vein
Effective restraint is essential
A tube of approx 2cm diameter is used
Perforated 50ml lab tube
Shave the leg along the saphenous vein from the heel to the knee
The mouse will climb into the tube if you let the top of the tube turn upwards after the head is in the tube
To enter the vein, the venous return must be blocked, this is done by tightening the skin over the thigh while extending the shaved leg
Shave with a scalpel
Puncture the vein slightly above the heel with a needle about 1 mm deep
The cutting edge must be along the vein to avoid severing the vessel
Collect blood in a hematocrit tube or another collecting vessel
When you have collected enough blood, pull off the tube and bleeding will stop
Repeated sampling can be done by removing the clot (crust) by slight scrubbing with a swab

How do you perform a heart puncture for blood sampling on a mouse? How much blood can you take?
1-2ml blood can be collected from a mouse via cardiac puncture
General anesthesia is mandatory use of injectable agents, CO2, nitrous or other inhalation anesthetic via chamber is common
Although this is a terminal procedure, the longer the mouse’s heart is pumping, the larger the sample size that will be collected
Larger needle used with cardiac collection will avoid destroying the fibrinogen, allowing clotting for serum analysis as well as better cell quality
Locate the heartbeat with your index finger, about where the mouse’s left elbow touches the sternum, you may remove the skin with scissor for better visualization
As soon as you penetrate the skin or chest wall, apply a negative pressure in the syringe by gently pulling the plunger, as soon as you are inside the ventricle, blood will flow
Massaging the mouse body will increase venous return and give more blood
Transfer blood into desired blood containers for analysis

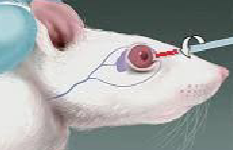
How do you get a blood sample from a mouse retro orbitally? How much can you take?
Can yield larger blood volume and higher quality samples than alternative methods in rodents
Generally used on mice and rats
Anesthesia is mandatory, may be a terminal or recovery procedure dependent on the blood volume required
Maximum of 1% of animal’s body weight can be withdrawn
Technique should be limited to once a week to a maximum of twice per eye as a recovery procedure
Standard heparinized or non heparinized micro hematocrit capillary tubes as well as traditional needle and syringe can be used
Animal is held by the back of the neck, and loose skin of head is tightened with the thumb and middle finger
Tip of capillary tube is placed at the medial canthus of the eye under the nictitating membrane
A short thrust past the eyeball will enter the slightly resistant membrane of the retro orbital sinus, the eyeball should remain uninjured
As soon as the sinus is punctured, blood enters the tubing by capillary action, it may be helpful to retract the tube slightly to facilitate blood flow
When the allowable amount of blood is collected, the tube is withdrawn and slight pressure with a piece of gauze on the eyeball is used to prevent further bleeding
Topical anesthetic can be administered to reduce the post procedural pain
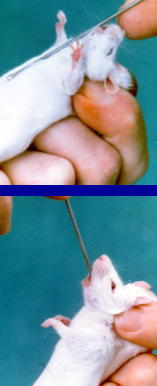
How and why would you gavage tube a mouse?
Accurate and reproducible oral dosing is done via a stomach tube
A blunt ended gavage needle about 10 cm long and 1-2 mm in diameter is suitable in mice
Start by measuring the distance from the nose to stomach/xyphoid process
Try to straighten the neck before introducing the needle
Wait for the pharyngeal reflex that brings the needle into the esophagus
It is not easy to get it into the trachea
Once you are in the stomach, give approx 1 mL of fluid
Fasting the mouse for 12 hours before the gavage will allow for a slightly larger volume
How do you house rats?
Generally housed in same manner as mine, but in larger cages
Females are housed in groups of 2-4
Mature males are housed individually

How do you sex a rat?
Same as in mouse, distance between anal and genital orifices is greater in the male compared to the female
How do you capture a rat?
Grasp the rat near the base of the nail and lift it from its cage
Important to grasp close to the body, grasping too close to the tip may result in tail degloving
Place the rat on your labcoat and pet to calm, rats are friendly and curious animals that can be quite cooperative when relaxed
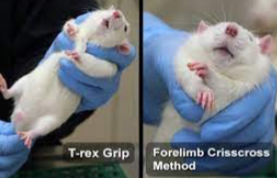
How do you restrain a rat?
Place your index and middle fingers down along the sides of the rat’s head for better control
Use your thumb and other fingers to support the chest lightly, hold the tail and support the lower body with your other hand
This method restricts the head movement but leaves an open pathway to the esophagus for gavaging
If a MORE SESCURE METHOD of restraining the rat’s head is needed, grasp the rat by the tail and press it down on a surface with your index finger directly over the back of the skull to stabilise the head
Slip your thumb and second finger under the rat’s forelegs, pushing them forward and parallel with the head
What is chromodacryorrhea in rats? What do you do if you notice is?
Rats are generally friendly and docile
Stress can be detected in a rat by the presence of porphyrin (“red tears”) secreted around the nostril and eye by the harderian gland
Porphyrin may appear as tiny red dots (like petechiae) on the nose, and progress into red fluid coming out of the eyes and / or nose
Flakes similar to flea dirt may be found in the coats of rats under chronic physical or environmental stress, as this is porphyrin that has been groomed away from the face
If you notice, STOP HANDLING RAT
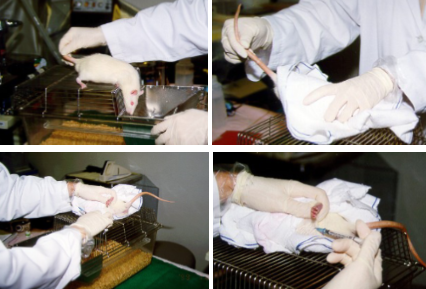
How do you perform an IP injection on a rat?
Let the rat relax on the top of the lid
Stretch the body of the rat by pulling up its tail and then cover the rat with a towel by your left hand
Fold the corners of the towel under the rat from all directions
Grasp up the left hind limb of the rat to expose the abdomen
The injection site should be in the lower left quadrant of the abdomen, because vital organs are absent from this area
Only the tip of the needle should penetrate the abdominal wall to prevent injection into the intestines
How do you collect blood from a rat? What vein?
TAIL VEIN USED
Optimal site of blood withdrawal in rats is around the distal ⅓ of the tail, since this part of the tails gives better visualization of the vessels
Generally, requires two people if rat is conscious, as a separate restrainer will be needed
Rotate the tail (the mouse) 90 degrees to access the lateral tail veins
When the needles penetrates the epithelium of the tail, pull back the plunger a bit to create negative pressure inside the syringe, then push the needle in the vein slowly until you see flashback
Using a scalpel to make a small wound on the tail is also an option for collecting blood from the tail vein, a pipette or hematocrit tube can then be used for collection
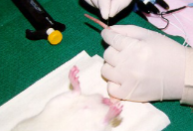
How do you gavage tube a rat?
Stomach tubing in rats may occur with a metal gavage needle or a red rubber feeding tube, if the red rubber feeding tube, care must be taken to avoid the rat’s teeth, and the possible biting off of the tube
Like the mouse, tube is measured from nose to the xiphoid process
Restrain the shoulders of the rat with your thumb and index finger, then support the lower limbs with your palm
A towel wrap could aid in proper restraint
It is preferable to have another person restraining the rat for the procedure
Introduce the ball tipped feeding needle from the pharynx into the esophagus when the rat is in the act of swallow, or slide the feeding tube from the left or right side of the mouth behind the teeth
Placement may be confirmed by injecting a small amount to see if there is a cough response OR palpating the throat for the presence of 2 tubes
How do you house rabbits?
Adult rabbits are housed individually shortly after weaning, fighting is common in both sexes even among littermates
Coprophagy is a normal behaviour in rabbits (night feces)
Important that housing enables this behaviour
NOT METABOLIC CAGES THATS FOR DAMN SURE
How do you capture a rabbit?
Rabbits are generally quiet, docile animals but they can be easily frightened as they are prey animals
Approach the animal slowly, provide reassurance by stroking it along its back
Grasp a handful of loose skin from the scruff of the neck and draw the rabbit towards you

How do you restrain a rabbit?
NEVER LIFT A RABBIT BY ITS EARS
ALWAYS SUPPORT THE HIND LEGS
Now slide your hand under the belly and between the hind legs, use your forearm to take most of its weight as you lift
A rabbit’s hind legs are very powerful, it is important to place your fingers and thumb firmly around each leg above the hock, with one finger between the legs so that you do not lose your grip
When you life the rabbit out of the cage, supporting its weight on your arm and keeping a firm grip on the hind legs, it is advisable to tuck its head under your arm, which has a calming effect
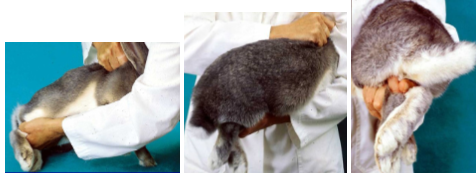
How do you return a rabbit to its cage?
Must go in backwards, if you put it in head first, it may leap forward and injure itself or you
Much care is needed to support a rabbits hind legs and preventing them kicking out, as they may easily attain spinal damage if not handled correctly

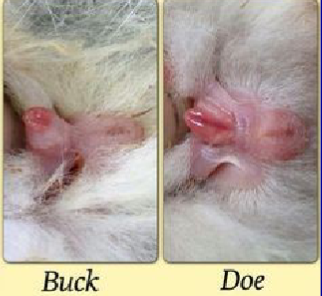
How do you sex a rabbit?
To sex a rabbit, keep your grip on the scruff and sit it upright on your knee, releasing the hindlegs, press with your forefingers in front of the genital opening
In the male, the penis is extruded, but in the female, only a vulval slit is visible
Testes are usually retracted in the male
VERY HARD TO DO
How do you give a rabbit an SQ injection?
Made into a fold of loose skin, most convenient being over the shoulder blades
With one hand, lightly restrain the rabbit using gentle pressure over the shoulders
The technique is the same as with a cat or dog

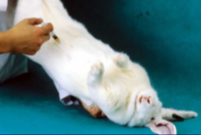
How do you give a rabbit an IP injection?
A restrainer is needed to position the rabbit with the head lower than the back legs
So abdominal organs fall away from injection site
Assistant holds animal by the scruff with the dominant hand, and the hind legs with the non dominant hand, allowing its body to rest on the forearm of the hand scruffing
Position the needle slightly to the side of the midline, halfway between the cranial edge of the pelvis
Direct the needle toward the centre of the abdomen, push it in with a sharp motion to penetrate the muscle, advancing no further than 1 cm into the abdomen
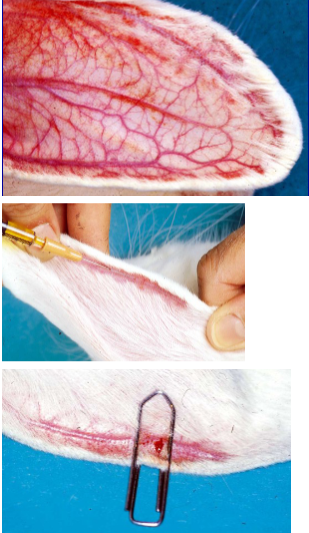
How and where do you give IV injections?
Usually given into an ear vein
Those in ear are prominent, especially after local heating
Lateral vessels are ear veins, central vessel is the artery
Find it easier to inject intravenously if someone holds the rabbit for you
Pluck or shave the injection site, then assistant “holds off” vein by restricting venous return at the base of an ear
Can use paperclip if alone
Insert needle, bevel up, at a shallow angle, and slide it into the vein
When the needle is in the vein, change your grip to fix the needle and ear between your finger and thumb
Tell your assistant to release the vein before you inject
If the needle has been positioned correctly, the blood in the vein will be washed away by the injection
When you withdraw the needle, use digital pressure to prevent any bleeding
Alternatively, use a paperclip half opened up and pushed halfway across the vein, BUT remember to remove it after a minute or two
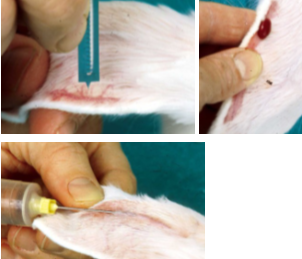
How and where do you collect blood from a rabbit?
Ear vessels are most commonly used for blood collection in rabbits
An assistant, commercial restraint device or a towel wrap can be used to retrain
Small blood samples can be collected from the lateral ear vein, shave or pluck the site and cut the vein longitudinally for about 1mm using a blood lancet or a small scalpel blade
A drop of blood can be collected with a capillary tube sufficient for microscopic smears or a micro sample
Small volumes can be collected with a needle and syringe
Samples larger than 5 ml may be collected by the use of a vacutainer in the central artery
Insert the needle with the bevel to the side, this prevents the arterial wall from occluding the opening to the needle
How do you insert a stomach tube into a rabbit and why?
Oral dosing or nutritional support in rabbits is done via a stomach tube
A gag prevents the rabbit from biting the tube, a cylindrical plastical device and about 1.5 cm in diameter works well
A red rubber tube catheter 2-4 mm in diameter works well as a stomach tube in rabbits
Estimate the length of the tube required to reach the stomach before insertion and mark it, using the measurement from the nose to the xiphoid process
Slide the gag in the side of the mouth behind the incisor teeth so that the hole is central and allows easy entry for the stomach tube
Moisten the tube with lubricant
Push it through the gag and with gentle pressure, the animal will swallow reflexively
Attach the syringe to the tube and give the solution slowly
Tube placement can be validated by the palpation of tube tubes in the throat and no air exiting the tube on exhalation
Aquisition of specimen, how do we choose them? What kind of sources (2) are there?
Animal models for human medical research are selected based on the similarity in the physiology and anatomy to a human in the applicable area
E.g. pigs are omnivorous and have similar GI function to humans - commonly used as models in gastroenterology research
3 R’s (replacement, reduction, refinement) principle should always be applied when selecting a model, for this reason, small rodents used whenever possible
Mice and rats also available with genetic alterations, creating a human disease state model
Transgenic (DNA added)
Knockout (genetic info removed)
Two legal ways to source research animals
Purpose bred
Random source
What are purpose bred animals?
The vast majority of lab research animals are purpose bred
Born and raised under controlled conditions and may be genetically manipulated
Purpose breeding of lab animals is becoming more and more common as researchers demand animals with particular genetic makeups
E.g. researchers investigating narcolepsy use dogs bred to be born with the condition
Charles River Laboratories and Jackson laboratories are the largest source of purpose bred research animals in Canada and the US
What are random sourced animals?
Live animals for research can also be purchased from random sources
Random sources include dogs and cats obtained from animal shelters (once all legal obligations of pound have been fulfilled) as well as animals purchase from farms or breeders
Random source animals must be legitimately / legally acquired and this process is outlined on the AUP
Random source animals are preferable to purpose bred in the case that no genetic modification or SPF status is required as the cost is significantly lower, additionally not all species are available from a research breeding facility (sheep)
Within the species, various breeds offer characteristics making them a more desirable research model for any particular experiment
Attributes such as
litter size, life span, ease of handling as well as genetic modification availability need to be considered when selecting the appropriate breed

RATS (Rattus norvegicus)
Strain (W)
Synonym
Colour
Characteristics
Wistar
Bkl:Wistar
Albino
|

RATS (Rattus norvegicus)
Strain (SD)
Colour
Characteristics
Sprague Dawley
Albino
|

RATS (Rattus norvegicus)
Strain (L)
Colour
Characteristics
Lewis
Albino
|

RATS (Rattus norvegicus)
Strain
Colour
Characteristics
Lister Hooded
Black and white
|

MICE (Mus musculus)
Strain
Synonym
Colour
Characteristics
C57BL/6/Bkl
Black/6, B6, C57 Black
Black
|

MICE (Mus musculus)
Strain
Colour
Characteristics
BALB/c/Bkl
Albino
|

MICE (Mus musculus)
Strain
Colour
Characteristics
SCID (Severely Compromised Immunodeficiency Mutation)
Available as hairless for tumor growth
|

MICE (Mus musculus)
Strain
Colour
Characteristics
Nude mouse
Hairless
|

GUINEA PIG (Cavia porcellus)
Strain
Colour
Characteristics
Hartley guinea pig
White
|

GUINEA PIG (Cavia porcellus)
Strain
Colour
Characteristics
IAF HAIRLESS GUINEA PIG
Hairless on albino background
|

GERBILS (Meriones unguiculatus)
Strain
Colour
Characteristics
Mongolian gerbil
Agouti with black
|

HAMSTERS (Cricetus circetus)
Strain
Colour
Characteristics
Syrian hamster
Golden / tan
|

RABBITS (Oryctolagus cuniculus)
Strain
Colour
Characteristics
New Zealand White (NZW)
Albino
|

RABBITS (Oryctolagus cuniculus)
Strain
Colour
Characteristics
New Zealand Red
Reddish brown
|

RABBITS (Oryctolagus cuniculus)
Strain
Colour
Characteristics
Californians
Black and white
|

RABBITS (Oryctolagus cuniculus)
Strain
Colour
Characteristics
Flemish giant
Non albino type, 7 different colour variations
|

DOGS (CANIS LUPUS FAMILIARUS)
Strain
Colour
Characteristics
Beagle
Tricolour
|