Human Biology
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Osteon
Structural unit of compact bone. They provide strength and rigidity to the bone and manage transport and allow for bone remodelling.
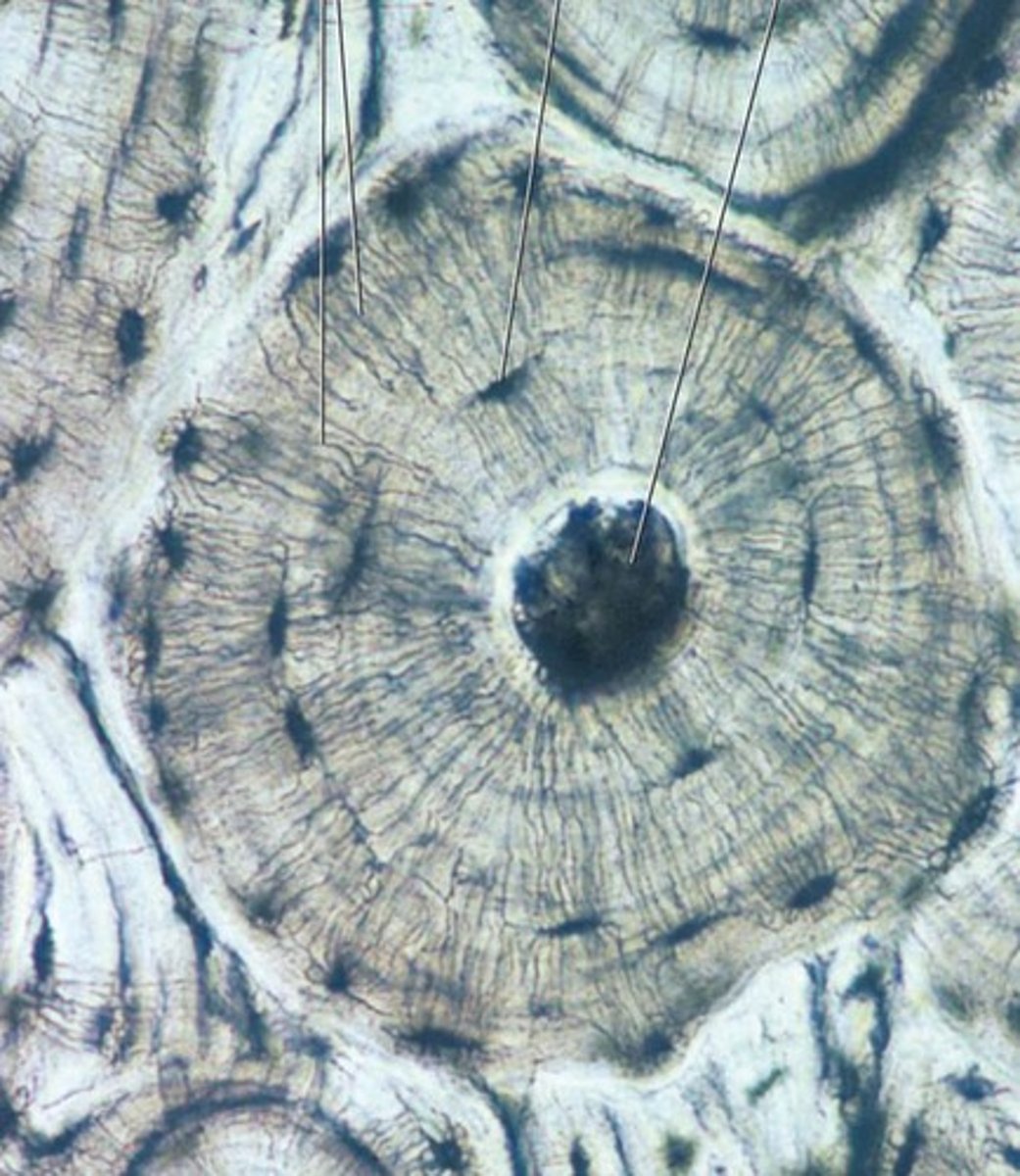
Haversian Canal
Provides a pathway for blood vessels, nerves and lymphatic vessels
Osteocyte
Regulate bone formation and control phosphate metabolism
Harbour communication between osteocytes.
Canaliculi
Lamellae
Provide Compact bone with its hardness and strength.
Osteoporosis
Weakening and brittling of bones.
Management for osteoporosis
Focus on preventing factures.
Osteoarthritis
Wearing down of joints over time.
capsule
Enclosing and sealing the joint allowing for an are for synovial fluid to reside.
Stabilise and reduce shock to a joint.
Meniscus
bursa
Cusions and reduces friction between tendons and bones.
The cruciate ligaments of the knee ________.
Provide joint stability
articular cartilage of synovial joint
Absorb shock and reduce friction
Synovial Joint
A fully moveable joint in which the synovial (joint) cavity is present between the two articulating bones. E.g. Knee
Fibrous Joint
immoveable and held together by ligaments only
ex. teeth in socket
Cartilaginous joints
allow only slight movement and consist of bones connected entirely by cartilage, e.g. ribcage.
Ball and Socket joint range of motion.
All ranges of motion including; flexion, extension, adduction, abduction, circumduction and rotation
Ball and Socket joint examples
Hip and Shoulder joints.
Hinge Joints range of movement
One planar movement, primarily flexion and extension
Saddle joint range of motion
A wide range of movement including, flexion and extension as well as adduction and abduction.
Gliding Joints move..
across two planes
Condyloid joint movement
Bi Planar movement, especially flexion and extension, as well as adduction and abduction.
Condyloid joint examples
Wrist and knuckle joints.
Hinge Joint examples.
Knee, elbow, ankle, interphalangeal joints
Saddle joint examples
carpometacarpal joint of the thumb
Gliding Joint examples
Carpals, Tarsals, Sternum & clavicle
hyaline cartilage location
Common and caps bones of synovial joints and is also found in bones and in the respiratory passage.
Toughest form, makes up the discs in the spine and in meniscus of the knee joint.
Fibrocartilage
Provide firmness and elasticity. Gives shape to the ear and epiglottis.
Elastic Cartilage.
What is cartilage?
A firm connective tissue.
What are the main components of cartilage?
Cartilage cells and matrix.
What is the composition of the cartilage matrix?
A firm gel with fibers embedded within.
cartilage function
Cap bones at joints to make movement easier, unites some bones and also provide shape to certain structures like the ear and nose.
metaphysis importance
important in the growth of the bone as they contain the growth plate of the bone.
Diaphysis importance
is important as storage for fat or transport for oxygen and other minerals as well as immune support.
Epiphysis
is important to form joints and distribute stress of the joint amongst the bone. Also houses the red marrow which creates blood cells.