Geometry Midterms
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
An __ is a transformation about a point with a given angle measure
rotation
Reflections, Translations, Rotations, and Glide Reflections are the four types of ___
Rigid Motions
A line that a figure is reflected across so that it maps onto itself is called an ___
Line of Symmetry
The Composition of a reflection and a translation is called a
Glide reflection
The set of points that a transformation acts on is the __
Pre-image
The result of a transformation is called the _
Image
A statement accepted without proof is a __
Postulate
Arriving at a conclusion by observing patterns is ___
Inductive Reasoning
A __ is the combination of a conditional and its converse
bi-conditional
According to the ___, if a conditional statement and its hypothesis is true, then its conclusion is also true
Law of Detachment
A conjuncture that has been proven is a ___
theorem
A statement of the form if not Q, then not P is a ___ of the conditional if p, then q
Contra-positive
You use ___ when you logically come to a valid conclusion based on given statements
deductive reasoning
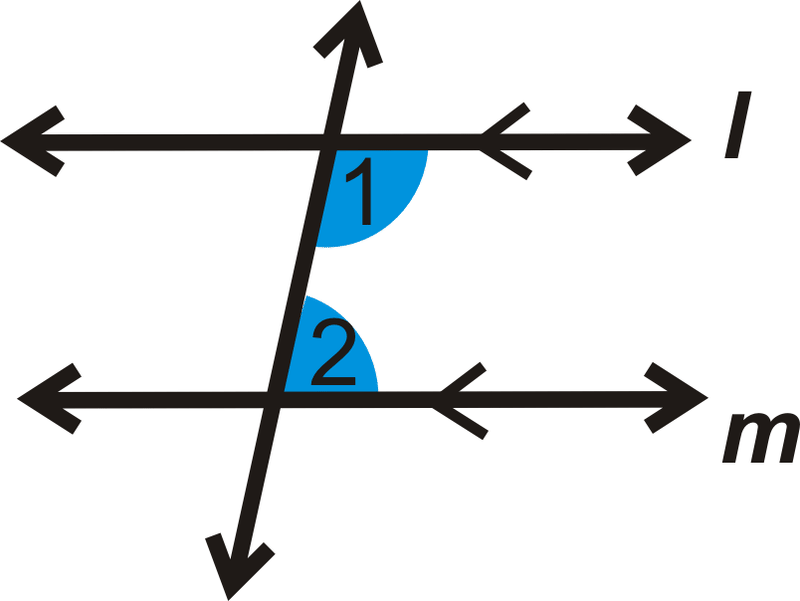
Angles that are outside the space between parallel lines and that lie on the same side of a transversal are __
Same Side interior Angles
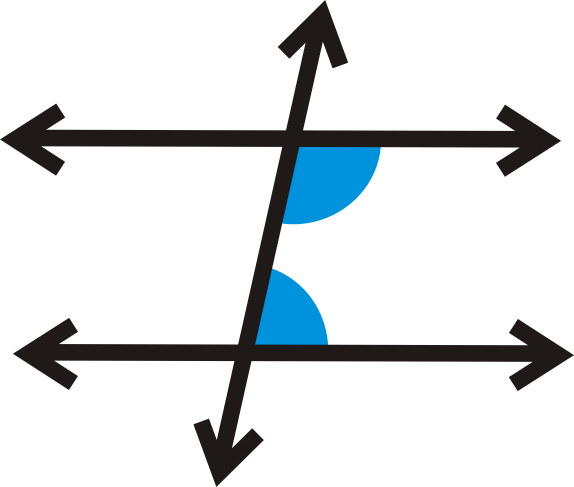
A ___ intersects co-planar lines at distinct points
transversal
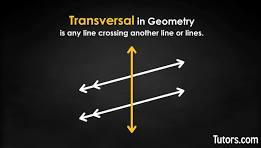
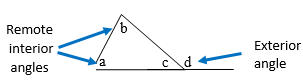
Two angles inside a triangle that correspond to the nonadjacent exterior angle are the
remote interior angles
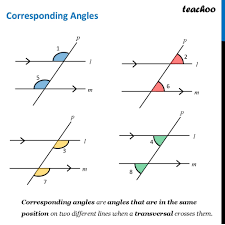
___ lie on the same side of a transversal of parallel lines and are in corresponding positions relative to the parallel lines.
Corresponding Angles
Angles between parallel lines that are nonadjacent and that lie on opposite sides of a transversal are
Alternate interior angles
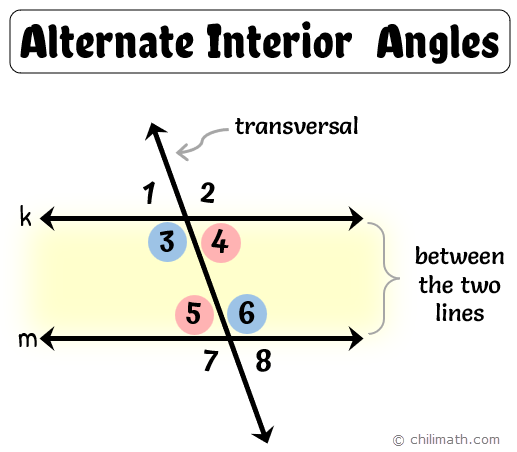
Angles Between parallel lines that are on the same side of a transversal are
Same-side interior angles
Figures that have the same size and shape are said to be ___
congruent
The side of an isosceles triangle that is opposite the vertex is called the _
Base
A rigid motion is sometimes called a __ because it maps a figure with the same shape and size
(congruence) transformation
The legs of a isosceles triangle form an angle called the
Vertex
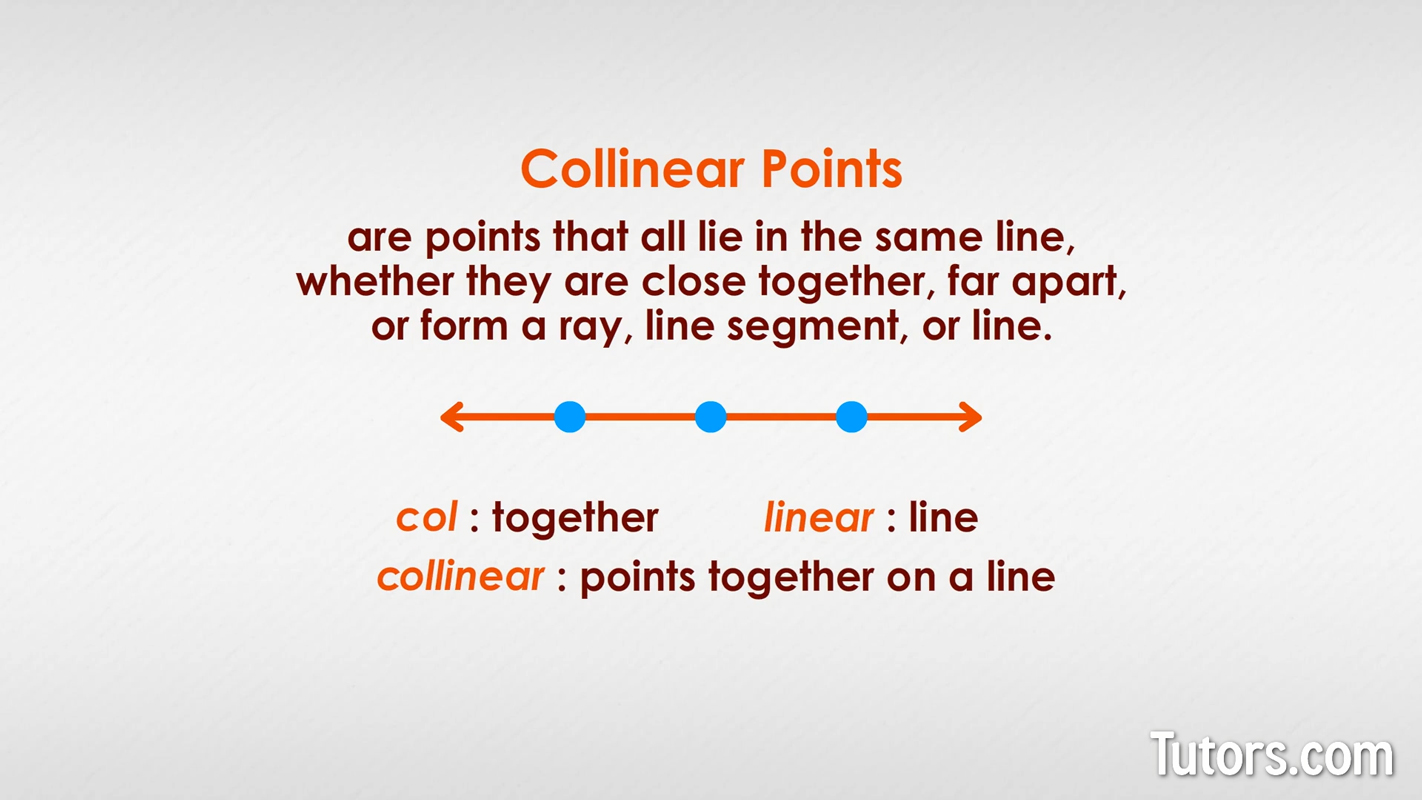
Colinear Points
Points that all lie on the same line
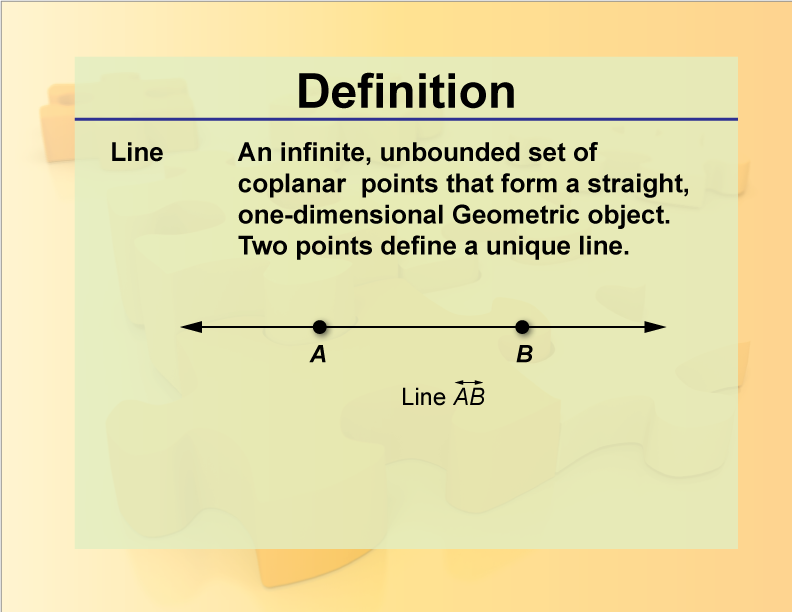
Line
A one-dimensional, forever going line. When two points are on it, they make a segment of the line.
Plane
A two dimensional surface with no boundaries
Point
A point in space
Segment Addition Postulate
AB+BC=AC
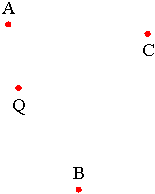
Angle Addition Postulate
m∠ABC+m∠DBC = m∠ABD
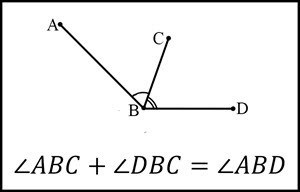
Angle Bisector
An angle bisector is defined as a ray, segment, or line that divides a given angle into two angles of equal measures.
Segment Bisector
A segment bisector is a line, a ray, a line segment, or a point that cuts a line segment at the center dividing the line into two equal parts.
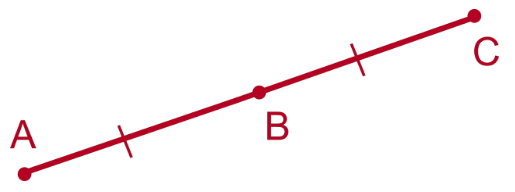
Midpoint
The midpoint of a line segment is the point at the exact middle of the line segment. The midpoint splits the line segment into two parts of the exact same measure
Midpoint Formula
(x1+x2 /2) , (Y1+Y2 /2)
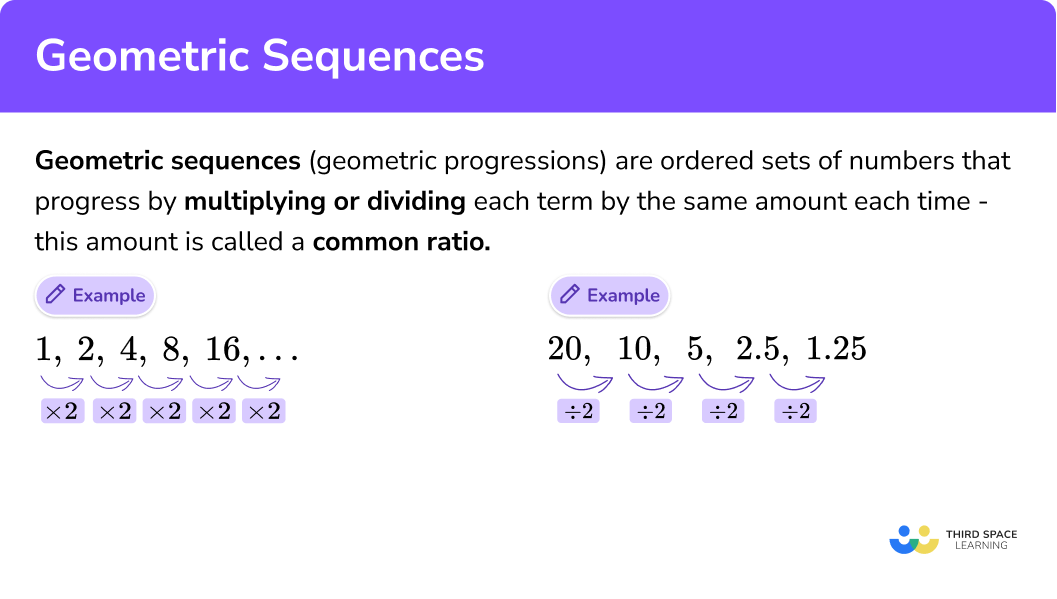
Sequence
A geometric sequence is a special type of sequence. It is a sequence in which every term (except the first term) is multiplied by a constant number to get its next term.
conjecture
An unproven guess.
Conditional
Conditional Statement: A statement with a hypothesis followed by a conclusion. Can be written in “if-then” form.
Converse
A statement where the hypothesis and conclusion of a conditional statement are switched.
Inverse
The inverse of a conditional statement is when both the hypothesis and conclusion are negated; the “If” part or p is negated and the “then” part or q is negated. The Inverse is referred to as ~p → ~q where ~ stands for NOT or negating the statement.
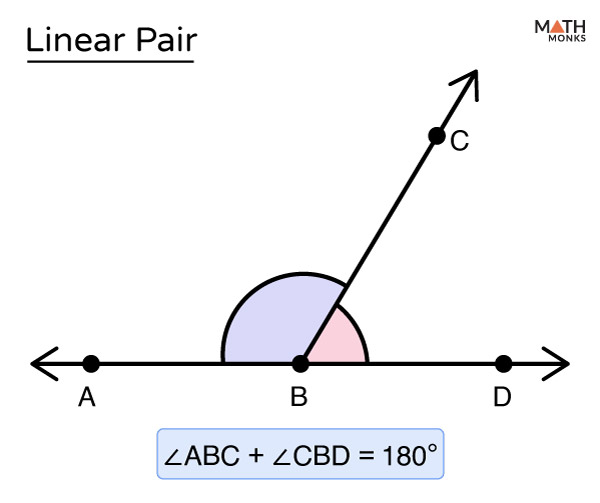
Linear Pair
The definition of a linear pair is two angles that make a straight line when put together. A linear pair also follows the linear pair postulate which says the angles add up to 180°.
Triangle Angle Sums
are always 180 Degrees
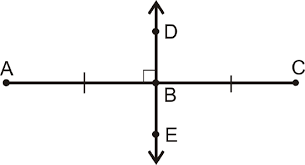
Perpendicular Bisector
A perpendicular bisector has two requirements: perpendicular and bisector. Perpendicular lines or line segments intersect at right, or 90 degree, angles.
Orientation
Orientation is how the relative pieces of an object are arranged