Teas 7 Anatomy Study Guide
1/242
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
243 Terms
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Consists of the extensive network of spinal nerves carrying sensory or afferent information towards the spinal cord and brain and motor or efferent information away from the brain and spinal cord.
afferent fibers
transmit impulses from organs to CNS
efferent fibers
transmit impulses to organs from CNS
somatic nervous system
voluntary control of skeletal muscles
ex: chewing food
autonomic (visceral) nervous system
involuntarily controls the visceral muscles of organ systems like the digestive and cardiovascular systems. Controls the contraction and relaxation of visceral reflexes.
ex: digestion, heartbeat
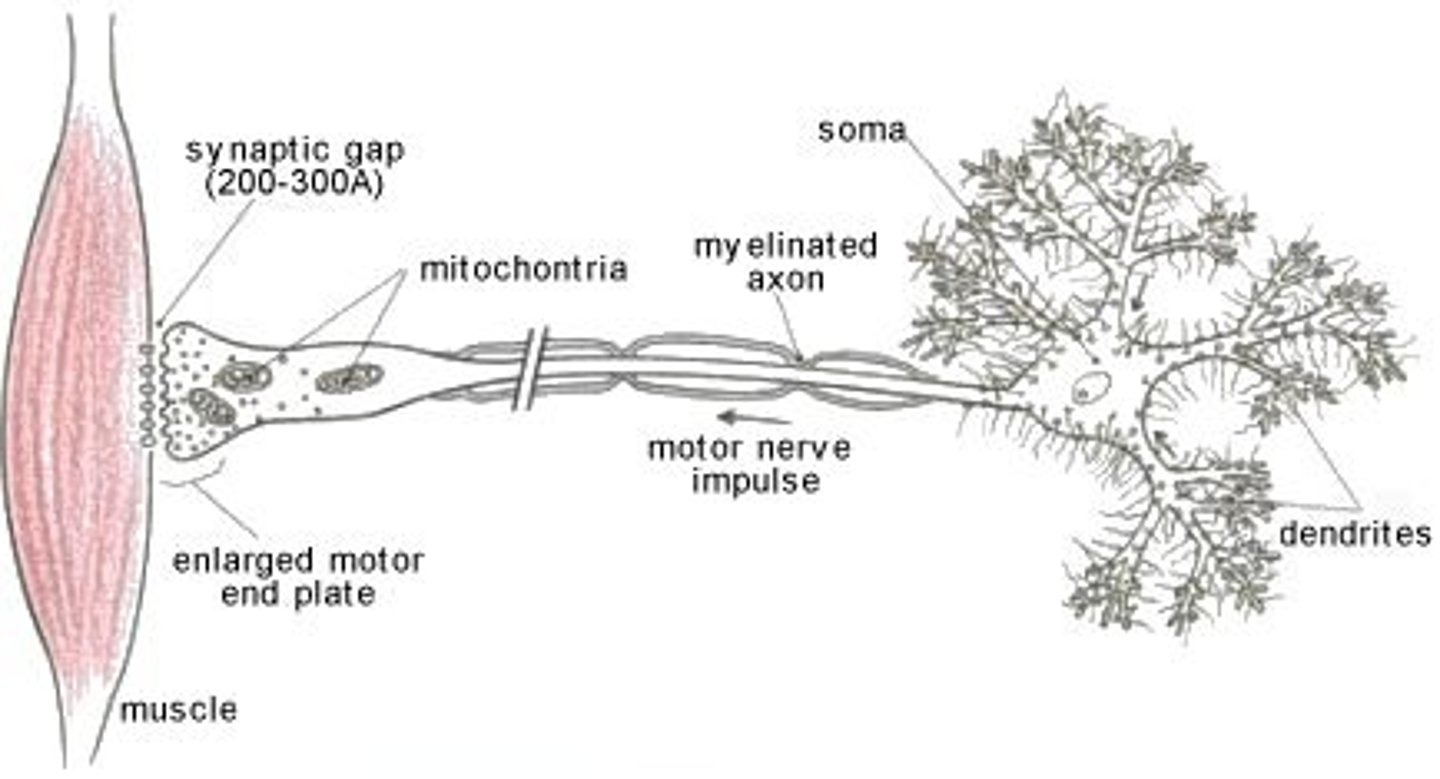
sensory neurons
gathers information and carries it to the CNS.
motor nerves
carry impulses away from the CNS to the effectors (muscles)
ventricles (brain)
canals in the brain that contain cerebrospinal fluid
cerebrospinal fluid
Fluid in the space between the meninges that acts as a shock absorber that protects the central nervous system.
cerebellum
part of brain found at the very bottom (near neck) of the skull and coordinates body movements, posture, and balance
brainstem
found between the thalamus and the spinal cord. Lowest part of the brain. Supports unconscious functions like breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure.
cerebrum
Largest part of the brain; responsible for interpreting touch, speech, reasoning, and emotions
cerebral cortex
grey matter that surrounds the entire cerebrum
gyri
ridges
sulci
shallow grooves
fissures
deep grooves in the brain
frontal lobe
processes high level cognitive skills, reasoning, concentration, motor skills, language.
parietal lobe
integration site for visual perception and sensory information such as touch, pain, and pressure
temporal lobe
Part of brain that controls hearing
occipital lobe
interprets visual information
limbic system
controls emotions and memory
Hypothalamus
plays role in regulating the autonomic nervous system. Primarily concerned with homeostasis and regulates activities such as hunger, anger and pain
amygdala
this produces feelings such as anger, violence, fear, anxiety
thalumus
sensory inputs come throught. Smell
hippocampus
helps convert short term memory to long term memory
neuron cell body is
largest part of a typical neuron; contains the nucleus and much of the cytoplasm and organelles
axon
the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons or to muscles or glands
myelin sheath
insulates the axon of some neurons and helps speed up neural impulses
epithelial tissue
A body tissue that covers the body surfaces, lines body cavities, and serves as a protective barrier
connective tissue
Connects other tissues to each other and serves to bind and support body parts
Muscle tissue
Moves the body and its contents by contraction
Nervous tissue
Receives stimuli from the internal or external environment and communicates through electrical impulses with the rest of the body
skeletal muscle
attached to bones and responsible for movement
~striated and very strong
~only voluntary tissue in the body
cardiac muscle
found in the heart and pumps blood throughout the body
~straited
smooth muscle
found in organ and vessel walls such as the stomach, intestines, and blood vessels
~not straited and the weakest
medial
towards the midline
lateral
away from the midline
Sagittal plane (aka median)
vertical plane that divides the body into right and left halves
frontal plane (aka coronal plane)
divides into posterior (back) anterior (front) division
Transverse plane (aka cross-sectional)
divides into superior (upper body) inferior (lower body) division
superior/inferior
towards the head; higher than/ towards the feet; lower than
anterior/posterior
toward the front and back of the body
distal/proximal
away from the point of reference (usually main part of body)/near the point of reference
ex. fingers are distal to wrist bc wrist is closer to main body
cephalic
head
cervial
neck
Antebrachial
forearm
Antecubital
front of the elbow
Pollex
thumb
crural
shin
tarsal
ankle
hallux
big toe
coxa
hip
Otic
ear
mental
chin
Occipital
base of skull
Acromial
shoulder
olecranal
back of elbow
sural
calf
coxa
hip
coccygeal
tailbone
perineal
area between anus and external genitals
inguinal
groin
femoral
thigh
crural
shin
sural
calf
pedal
foot
tarsal
ankle
hallux
great toe
cardiovascular system
closed system responsible for the movement of blood and lymph around the body, which permits nutrient distribution, waste removal, communication, and protection. Consists of the heart, blood vessels, blood, and lymphatic system
lymphatic system
open system where lymph that bathes the interstitial spaces b/t cells and circulates through lymph vessels
atria (heart)
superior chambers; receive blood from outside heart
ventricles (heart)
inferior chamber; pump blood
SA Node
60-100 bpm
AV Node
40-60 bpm
pulmonary system
right side of the heart pumps deoxygenated blood from the heart towards the lungs
systemic system
left side of the heart receives oxygenated blood from the lungs pumps it toward the rest of the body
arteries
Vessels that carry blood away from the heart. These vessels are muscular to withstand the force of a heartbeat and so feel pressure on their walls. Larger arteries branch into smaller arterioles, which connect to a bed of capillaries.
Capillaries
Small vessels that connect arterioles to venules and carry out gas exchange
veins
carry blood from body parts toward the heart. connected to capillary beds via smaller branches called venules. Both have thinner walls b/c they're farther away from the force of the heartbeat and so feel less pressure on their walls. Have one-way valves to prevent blood from flowing back into the system.
plasma
yellow liquid that contains water, immune proteins, and other nutrients.
blood
composed of plasma and formed elements, such as erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets
Leukocytes
white blood cells; defense against disease and function in immunity response
hemoglobin
protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen from lungs to cells and helps return CO2 from the cells back to lungs
Platlets
responsible for clotting
lymphatic vessels
linked to lymph nodes and lymphatic capillaries. vein-like.
lymph fluid
Clear fluid that moves throughout the lymphatic system to fight disease. filtered through hundreds of lymph nodes distributed throughout bodies.
lymphatic capillaries
entwined with cardiovascular capillaries and absorb excess tissue fluid and blood plasma that leaks from capillaries
lymph nodes
concentrated in neck, armpit, and groin and contain lymphocytes
Lymphocytes
Makes antibodies that target pathogens in lymph fluid so that other cells can destroy them
cardiac cycle
A complete heartbeat consisting of contraction and relaxation of both atria and both ventricles.
impulse within the sinoatrial (SA, pacemaker) node -> right and left atria causing them to contract and force blood into ventricles->impulse reaches atrioventricular (AV) node->travels through to the ventricles' walls causing them to contract->diastole (rest phase)
Systole
contraction of atria followed by ventricles (lub sound)
diastole
rest phase of the heartbeat (dub sound)
flow of blood from the body through the heart
pulmonary system receives deoxygenated blood into the right atrium from the body via the superior and inferior vena cava-> contraction of right atrium pumps blood through right AV valve into right ventricle-> contraction of right ventricle pumps deoxygenated blood into pulmonary artery through pulmonary semilunar valve-> lungs-> oxygenated blood through pulmonary veins into left atrium-> systemic system carries blood when left atrium contracts forcing blood through left AV into left ventricle-> contraction of left ventricle pumps blood through aortic semilunar valve-> body
Hypertension (high blood pressure)
can cause rupture of the smaller arterioles and capillaries possibly leading to a stroke
Atherosclerosis
buildup of plaque in blood vessels that reduces the flow of blood through the vessel.
embolus
A piece of plaque breaks off and travels through smaller vessels causing a blockage.
stroke
normal blood flow to the brain is stopped either by a blockage or by a rupture of a blood vessel, causing death of brain tissue.
heart attack (myocardial infarction)
damage or death of cardiac muscle tissue resulting from blockage
neuron
A specialized cell that conducts electrical impulses through the nervous system. Composed of cell body and nerve fibers that extend from the body
visceral
internal organs