Neurons
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
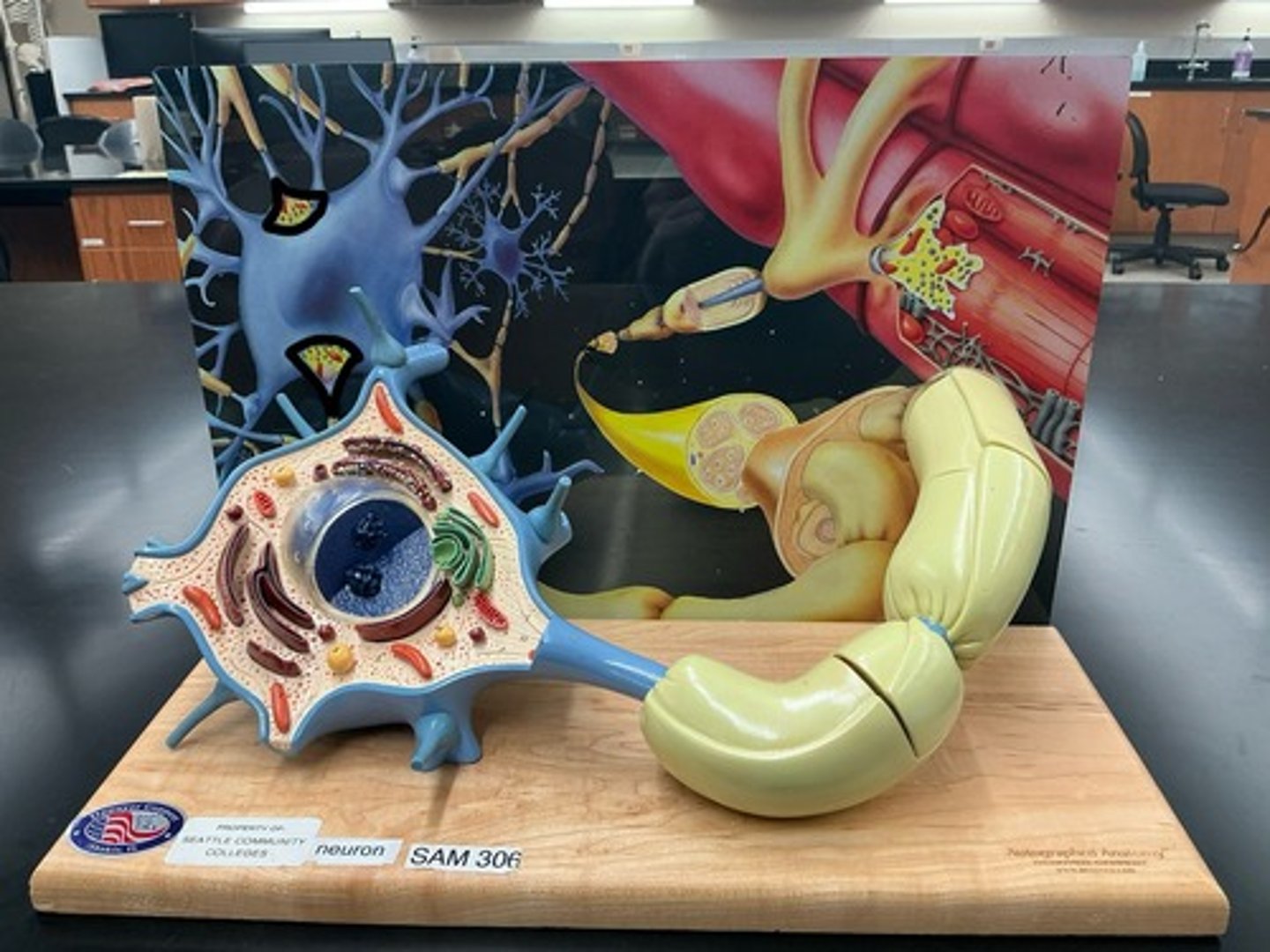
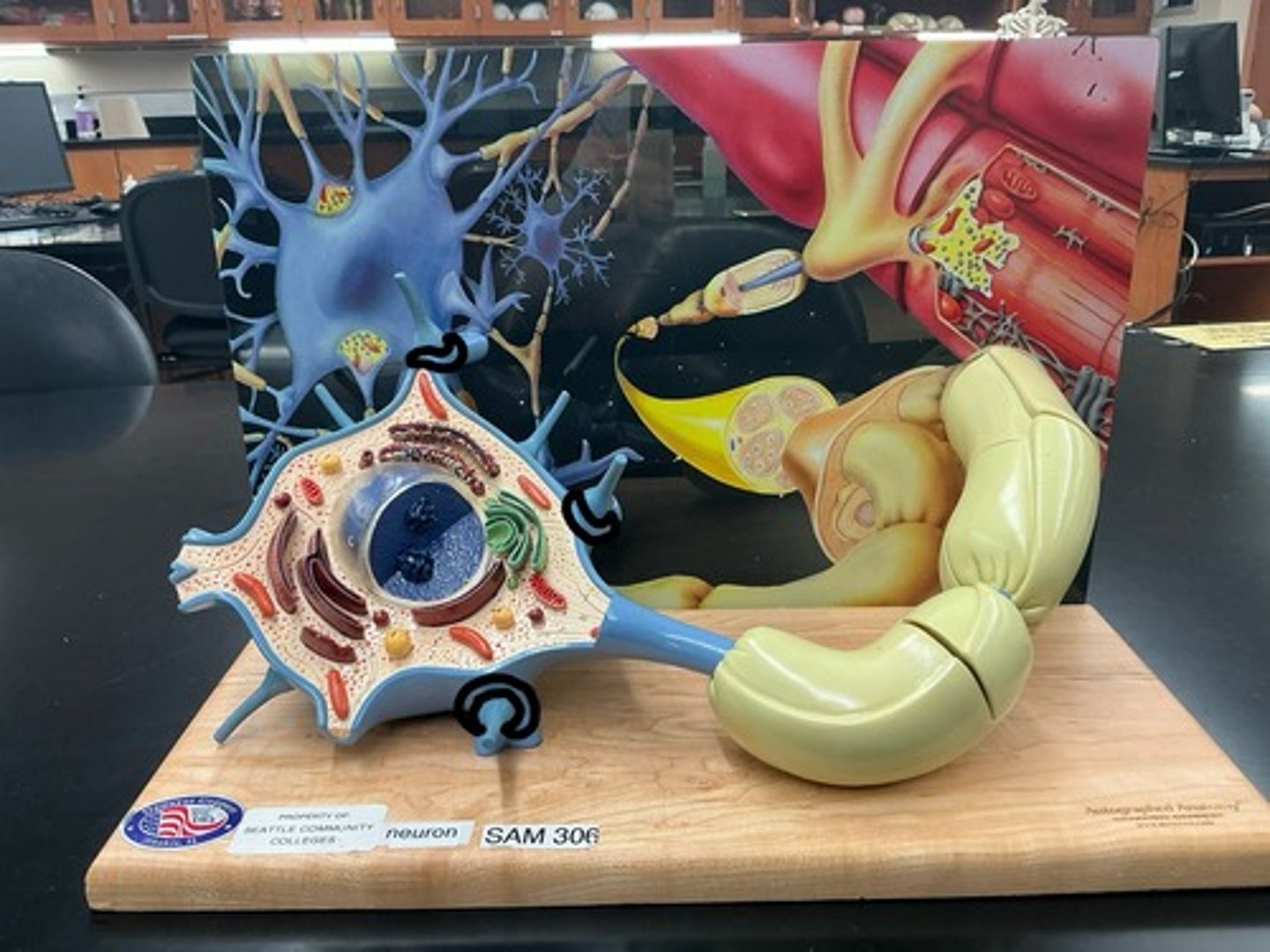
Soma (cell body)
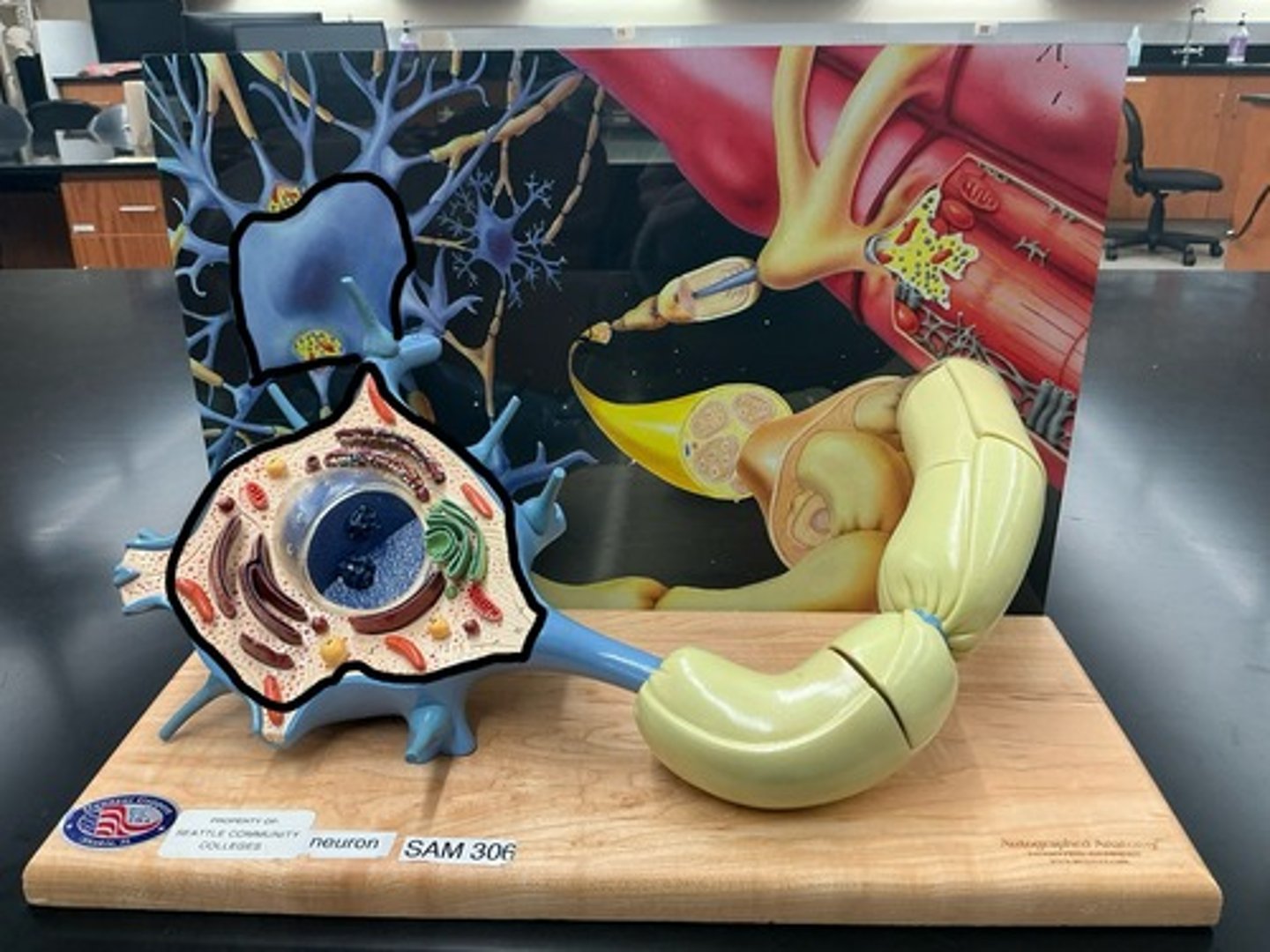
Dendrites
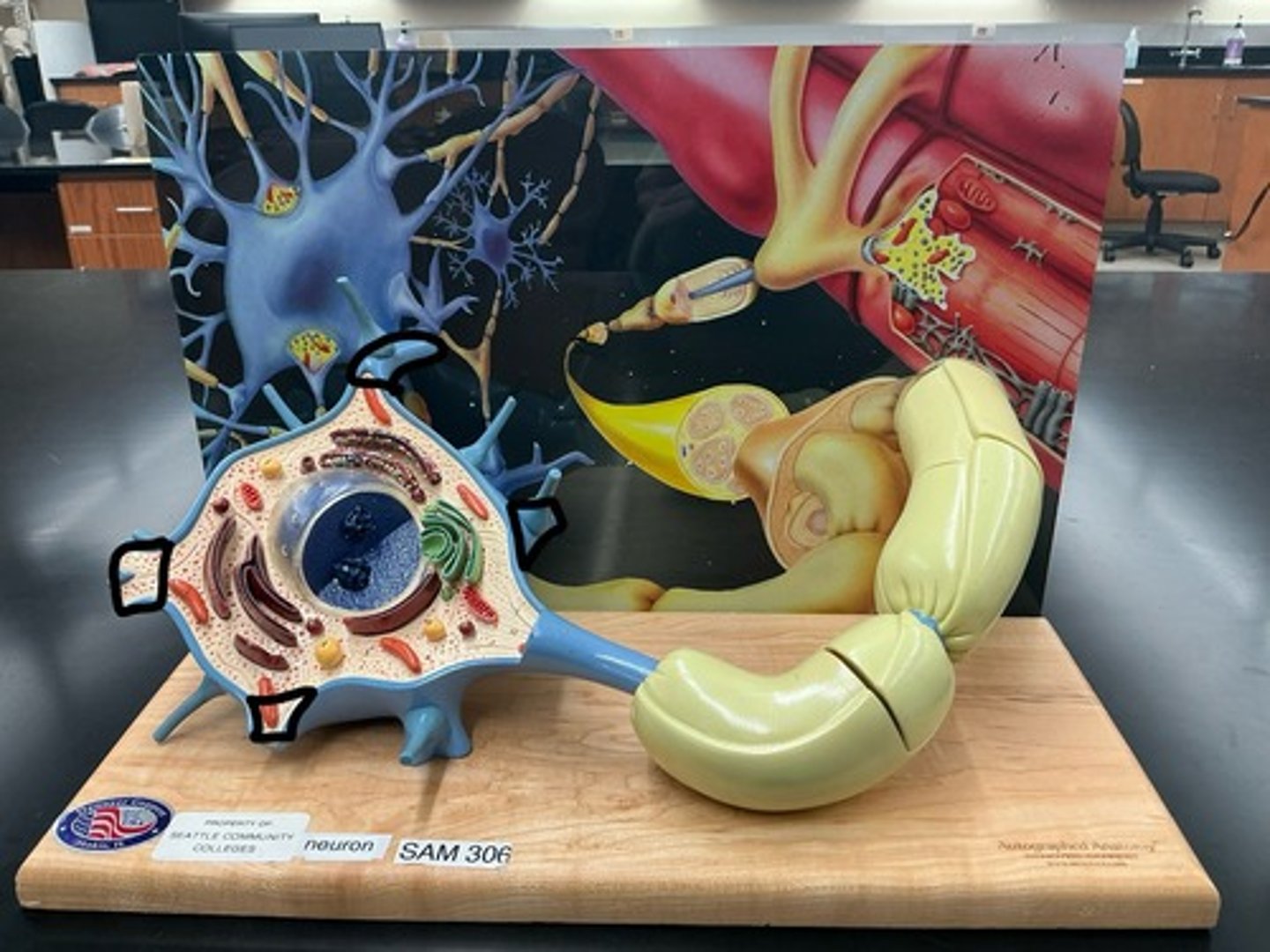
Axon
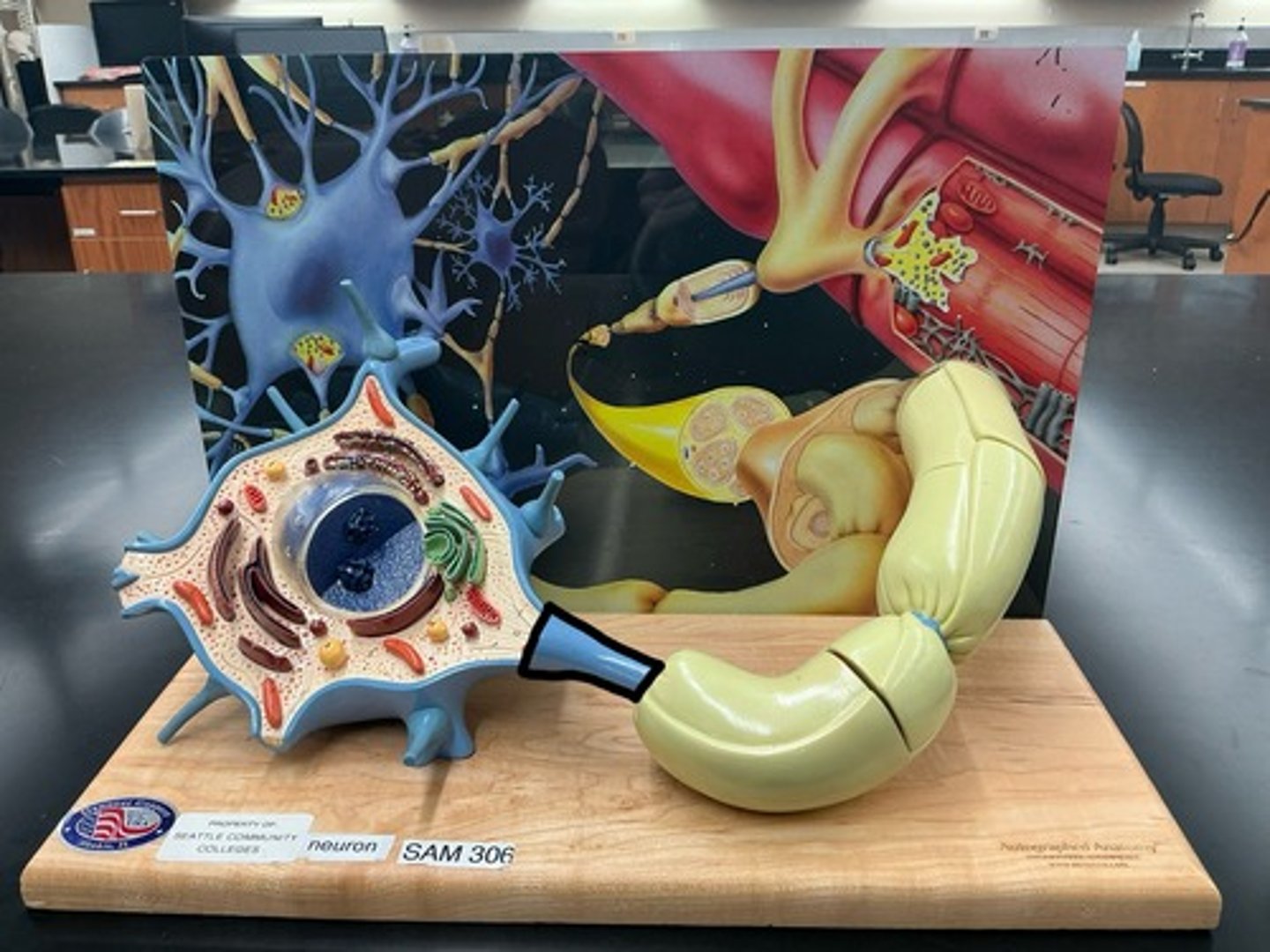
Axolemma
Plasma membrane of Axon
Axon hillock
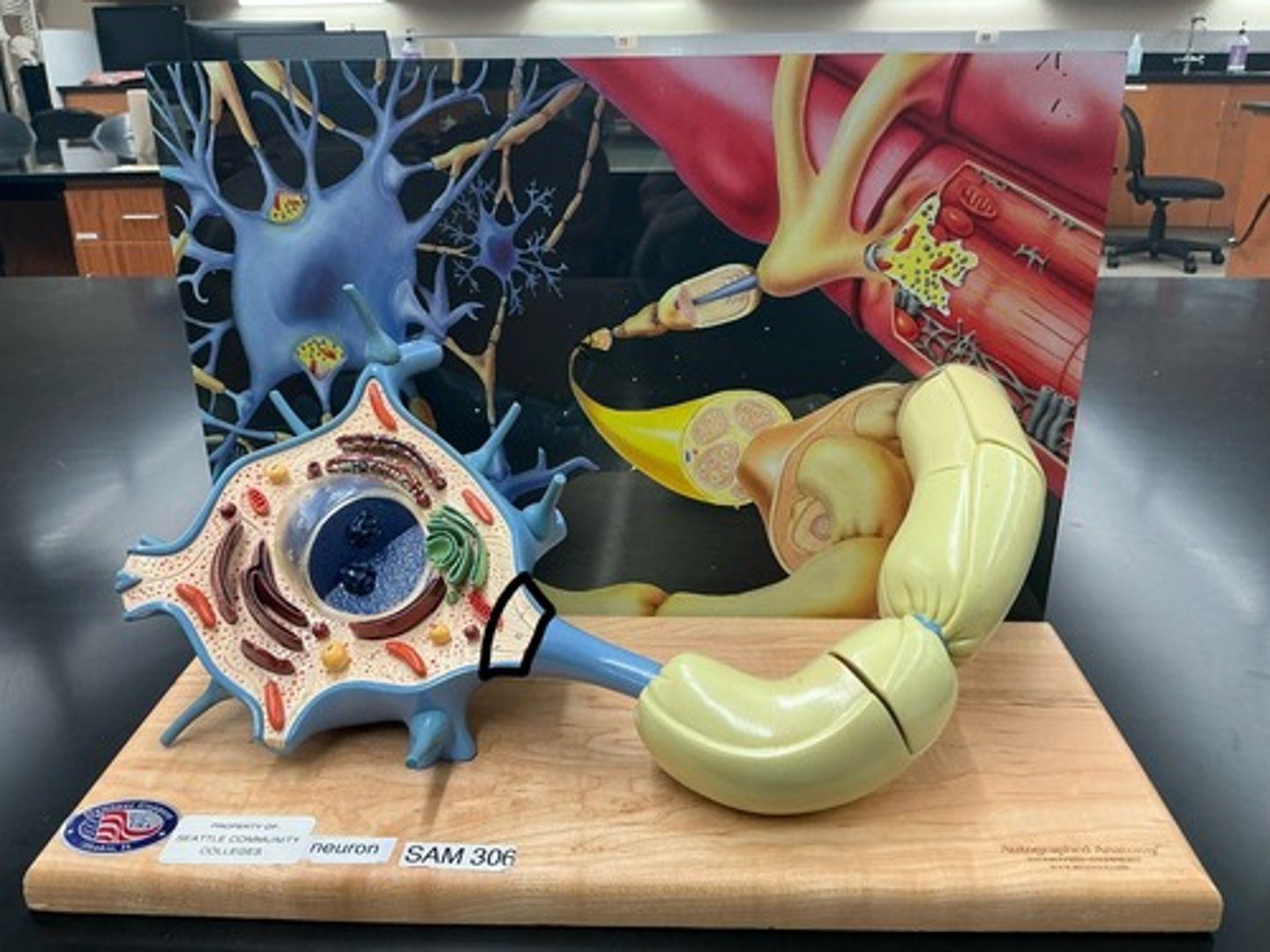
Telodendria
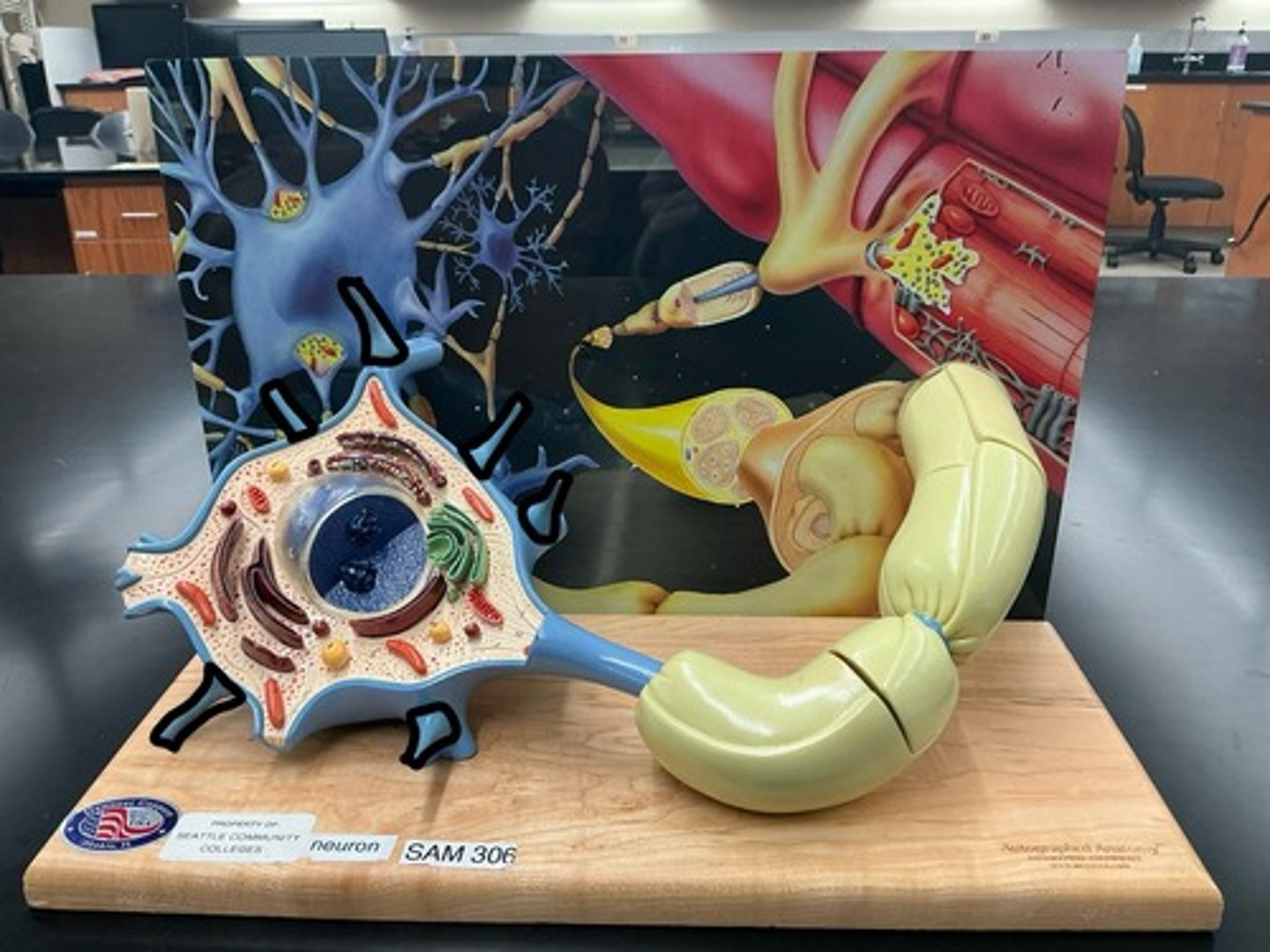
Neurofibrils
Cytoskeletal elements/protein fibers within neuron
Nissl bodies
Elaborate type of RER and ribosomes within neurons
Synaptic cleft
Space between presynaptic and postsynaptic terminals
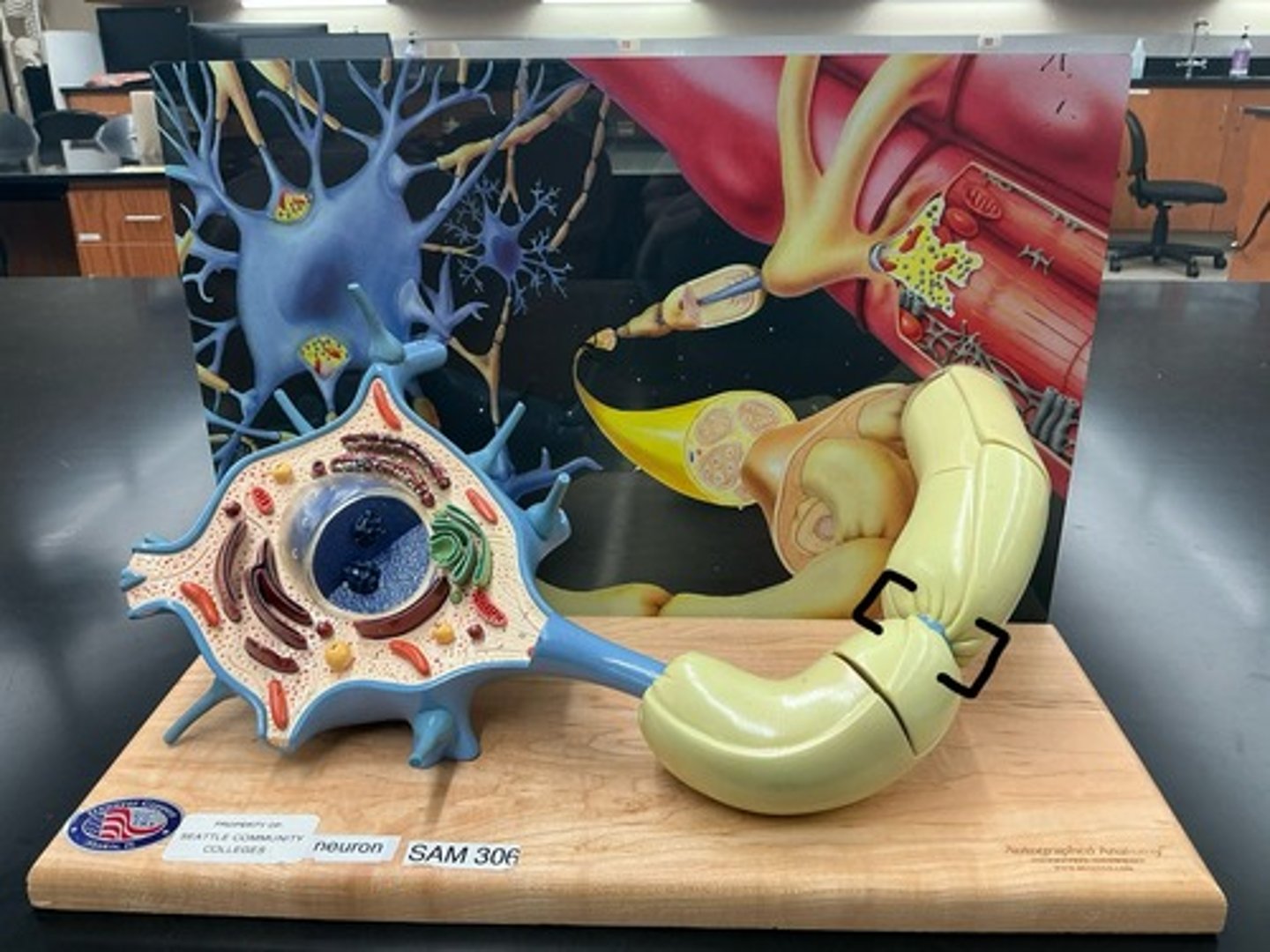
Myelin sheath
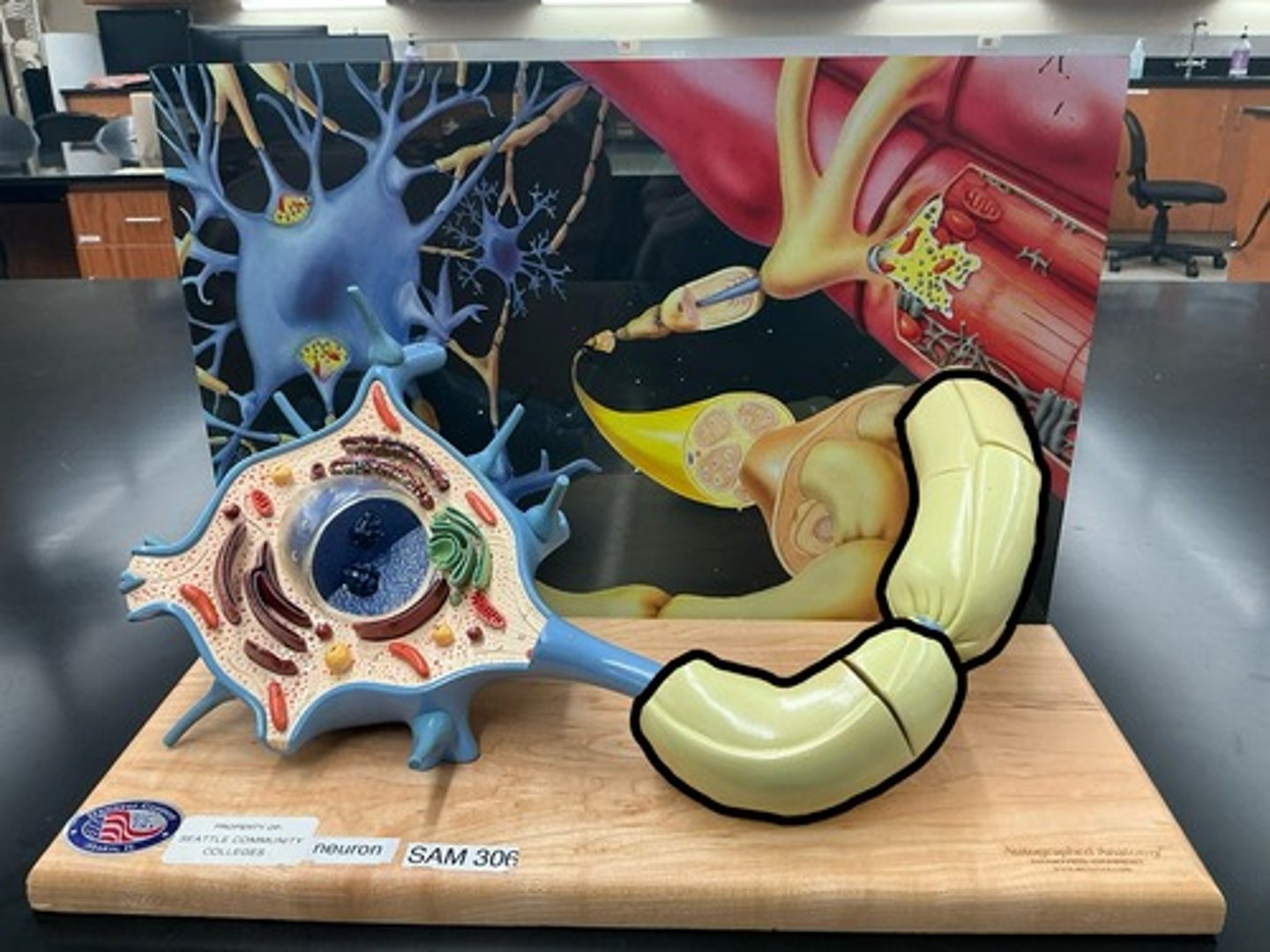
Nodes of ranvier
Neurotransmitter receptors
On Postsynaptic terminal (normally cell bodies and dendrites)
Connective tissue (CT) around entire nerve
Endoneurium
Presynaptic neuron
Releases NTs from synaptic vesicles
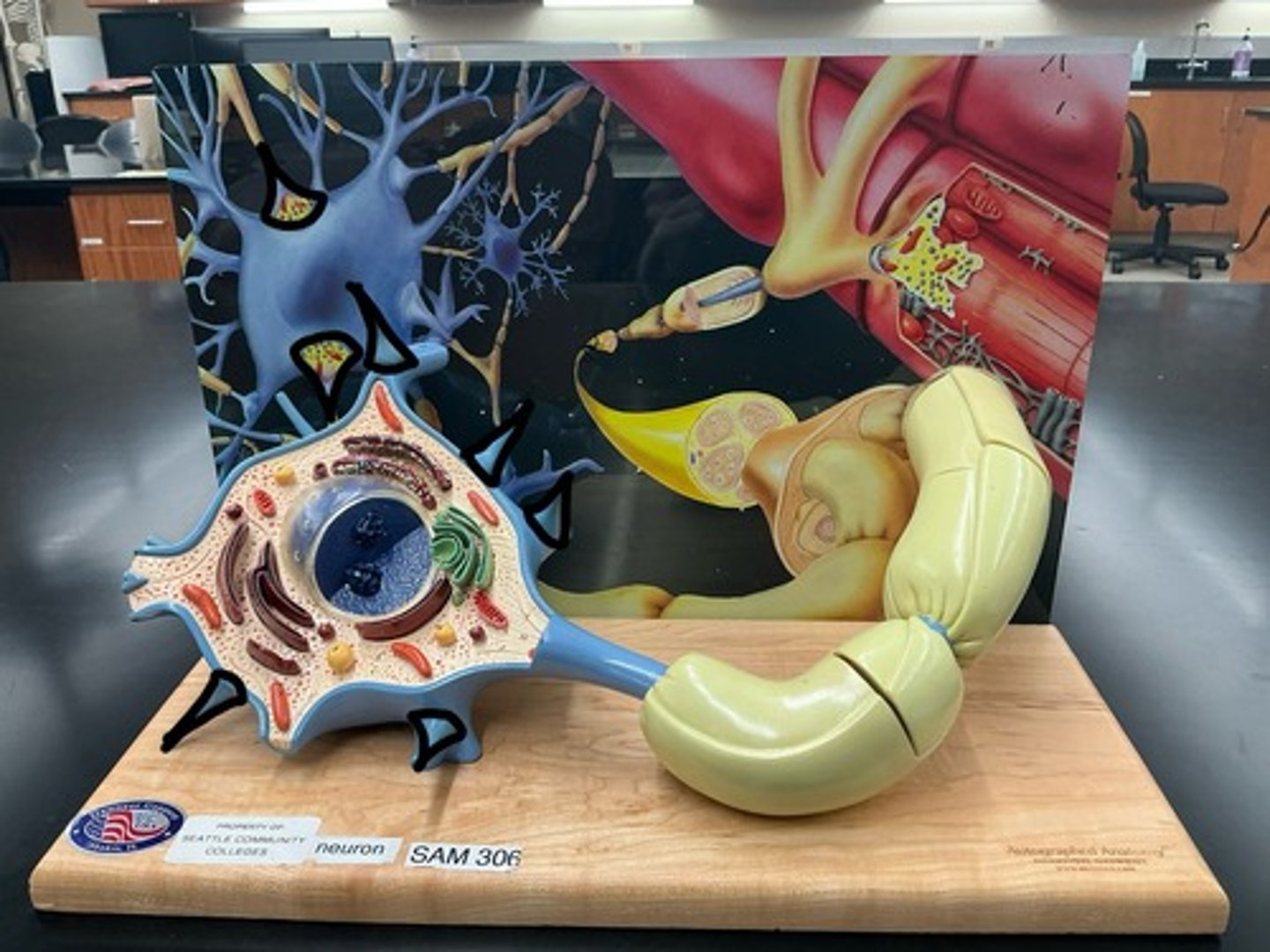
Axon terminal
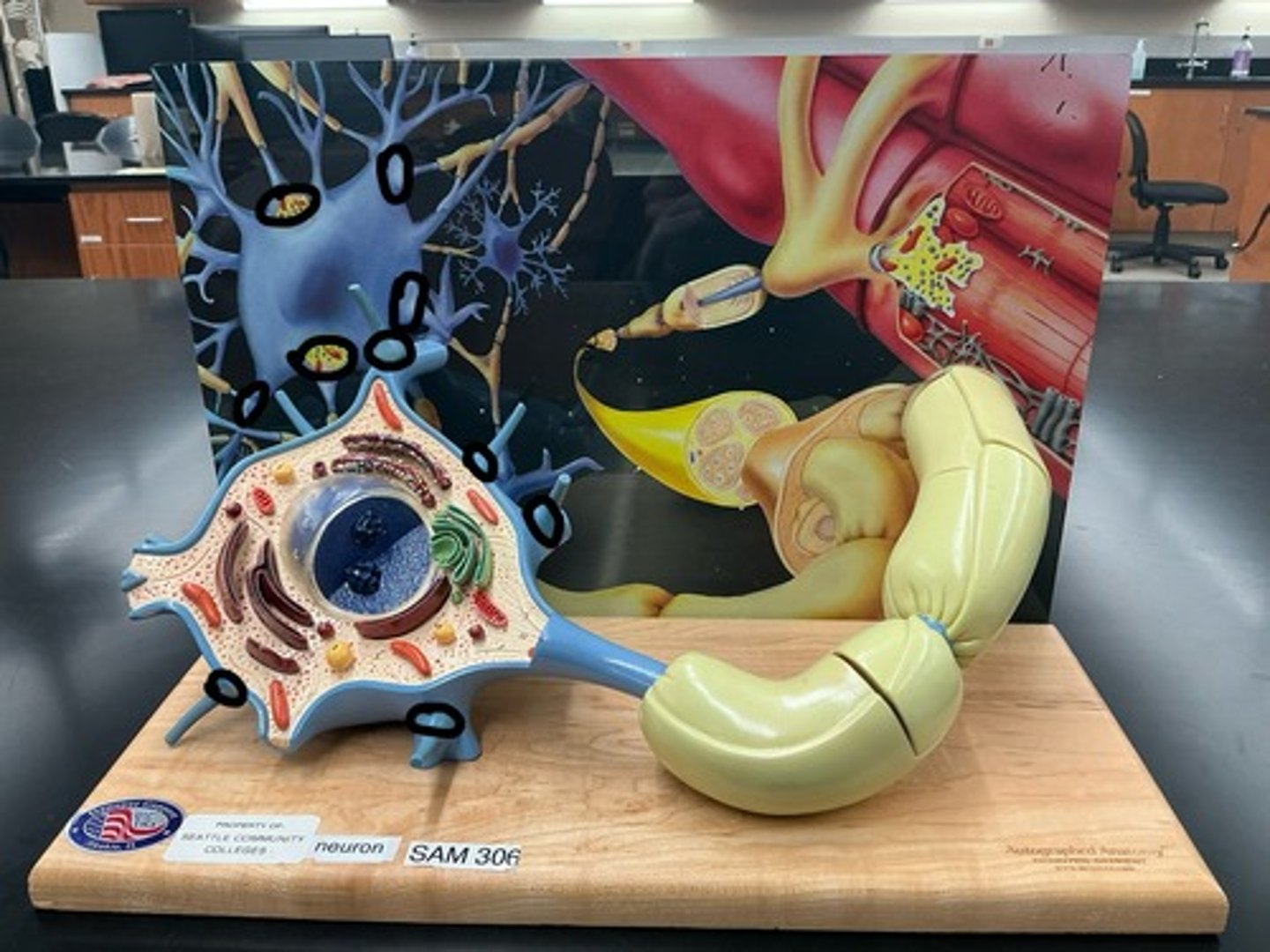

Synaptic vesicles
Filled with neurotransmitter/NT
Connective tissue (CT) around nerve fasicles
Perineurium
Postsynaptic neuron
Contains NT receptors that the NT binds to
Connective tissue (CT) around individual axons
Epineurium
Fasicles
Bundles of axons within a nerve
All spinal nerves
Mixed nerves
Carry information towards CNS
Sensory/afferent nerves
Carry information away CNS
motor/efferent nerves
1st cranial nerve
Sensory: from nasal cavity: smell
Olfactory
2nd cranial nerve
Sensory: from retina: vision (cross optic chiasma)
Optic
3rd cranial nerve
Motor: controls muscles that opens eyelid, constrict pupil, changes shape of lens and eyeball movement
Oculomotor
4th cranial nerve
Motor: controls superior oblique muscle (turns eye downward and laterally)
Trochlear
5th cranial nerve
Motor: controls muscles of mastication/chewing
Sensory: from face: touch and pain
Trigeminal
6th cranial nerve
Motor: controls lateral rectus muscle (turns eye laterally)
Abducens
7th cranial nerve
Motor: controls muscles of most facial expressions
Motor: stimulate glands: secretion of tears and saliva
Sensory: from tongue for taste and sensory from face and mouth
Facial
8th cranial nerve
Sensory: from inner ear: hearing and equilibrium
Vestibulocochlear
9th cranial nerve
Sensory: from tongue: taste
Motor: controls muscles of pharynx involved in swallowing
Glossopharyngeal
10th cranial nerve
Sensory: skin of head and neck and pharynx
Motor: muscles involved in speech and swallowing
Motor: to salivary glands
Motor: to most of thoracic and abdominal viscera (as main nerve of parasympathetic NS)
Vagus
11th cranial nerve
Motor: controls trapezius and sternocleidomastoid
Spinal Accessory or Accessory
12th cranial nerve
Motor: controls muscles of tongue movements
Hypoglossal
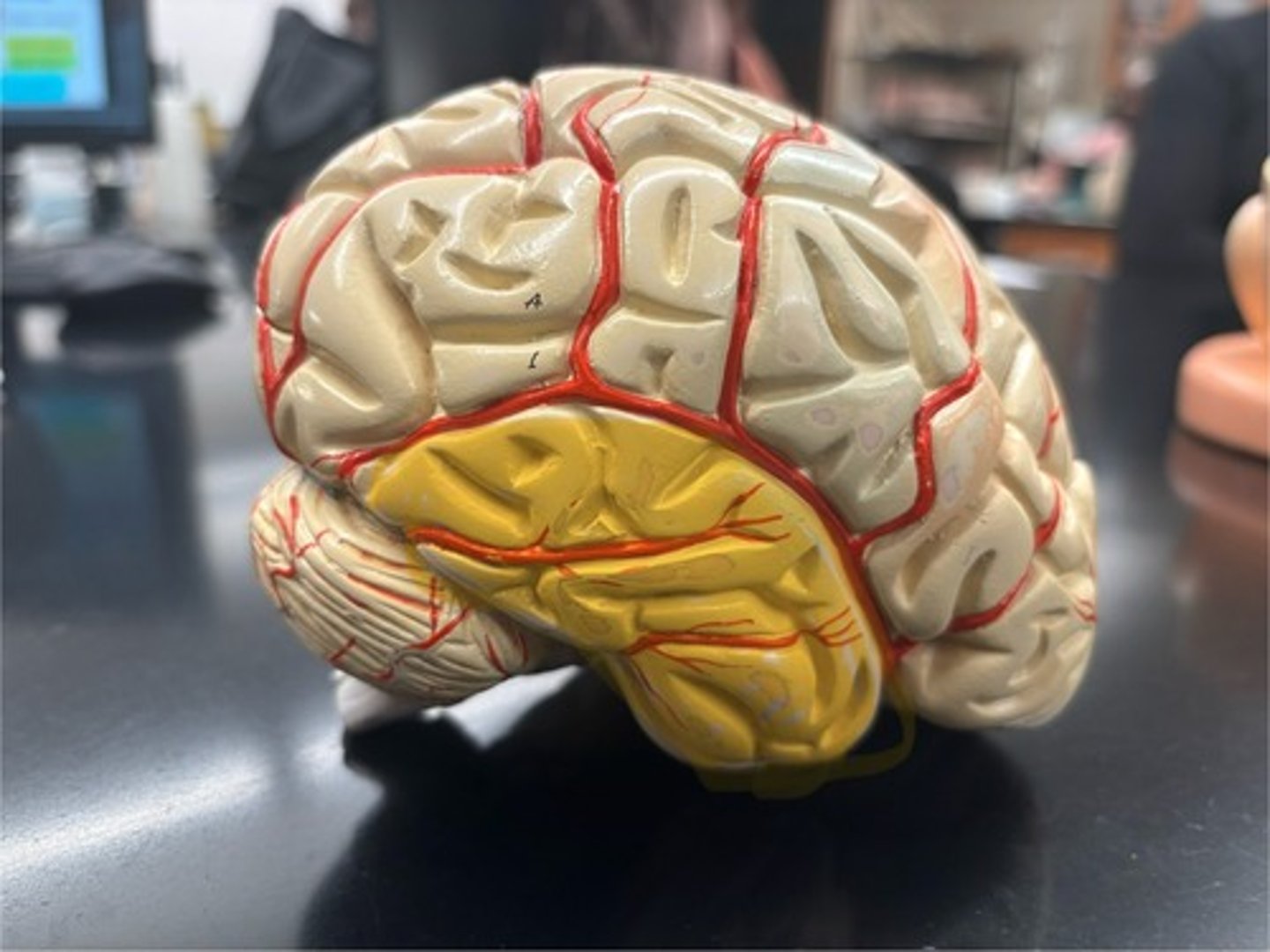
Frontal Lobe
Contains the motor cortex
Temporal Lobe
Contains the auditory and olfactory cortex
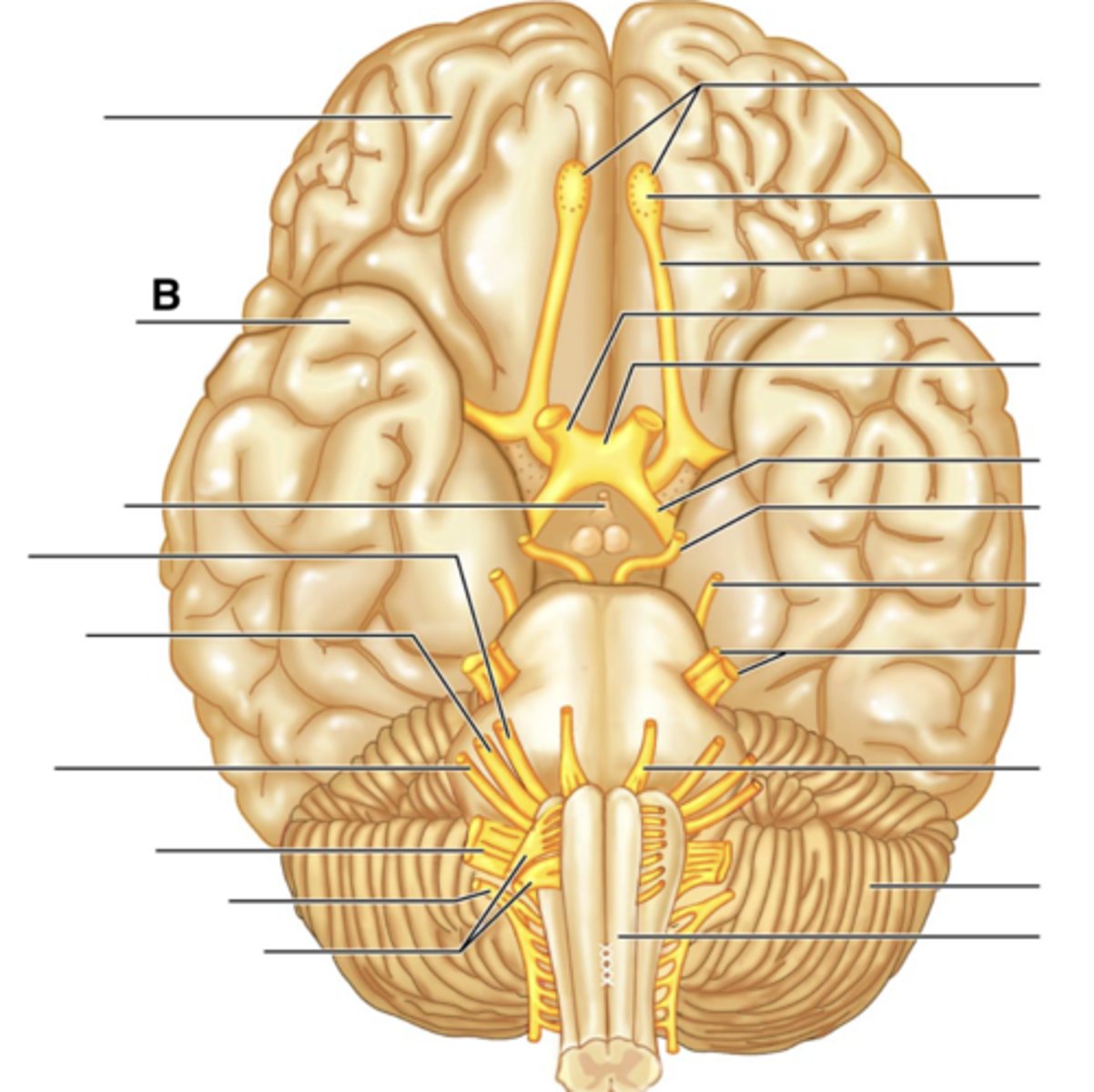
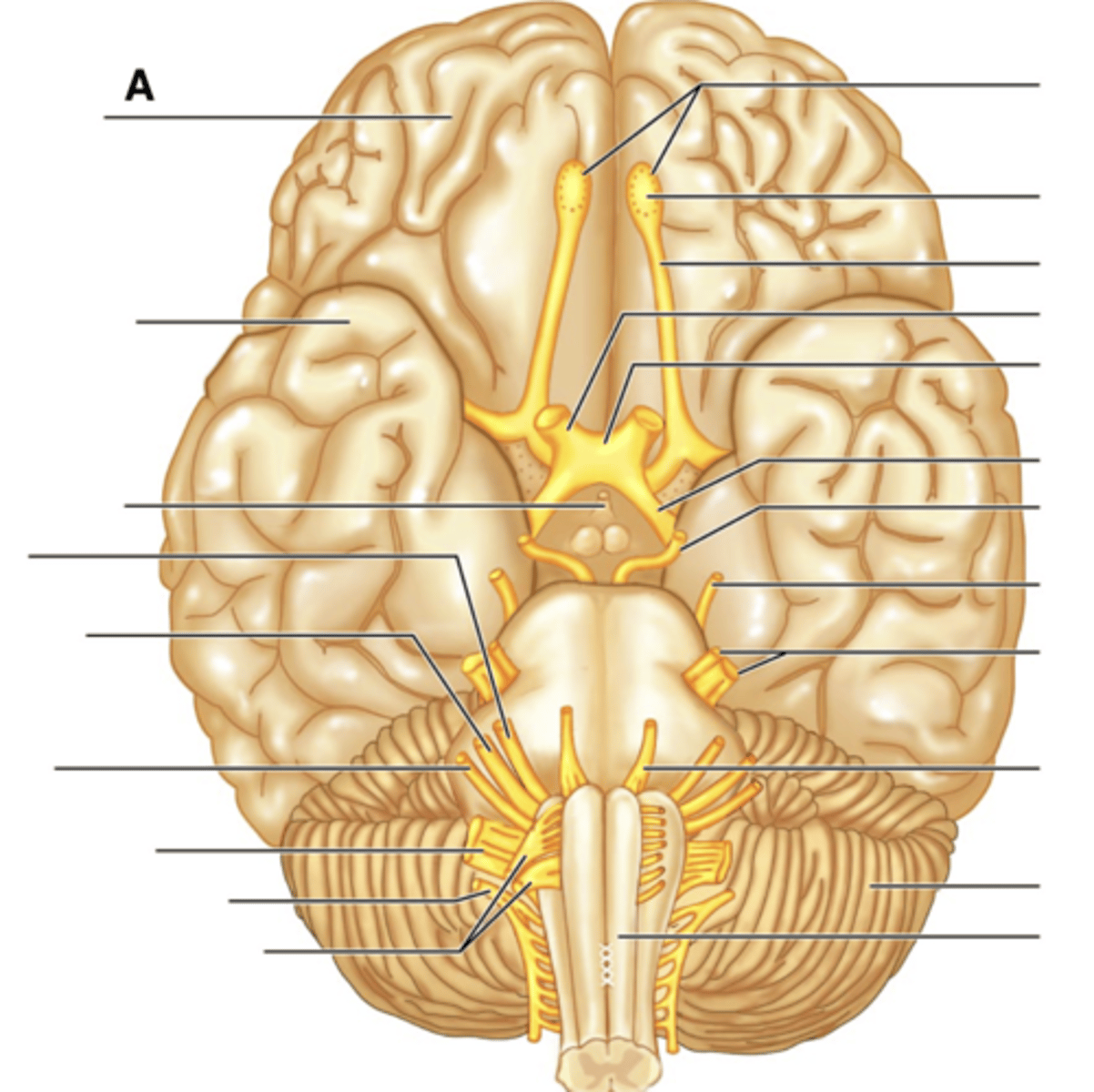
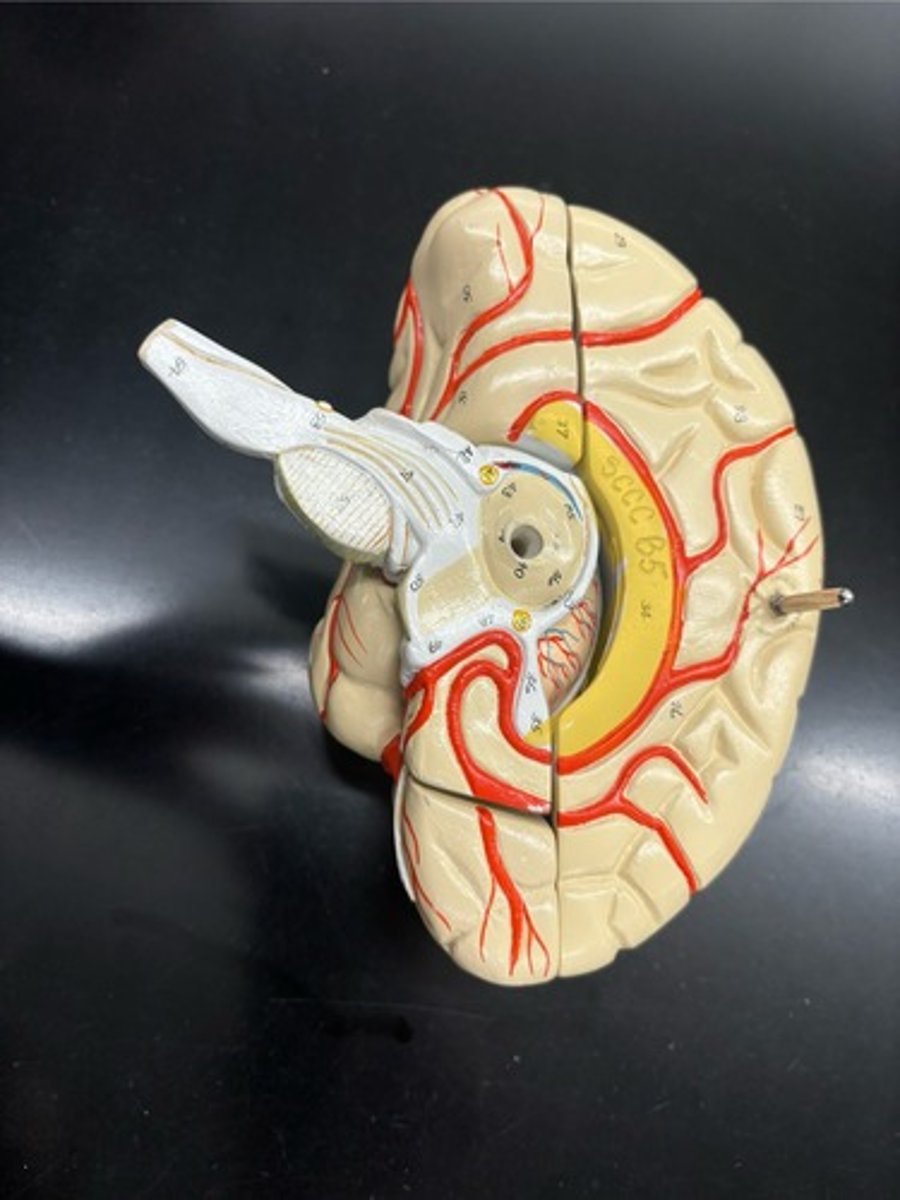
Infundibulum
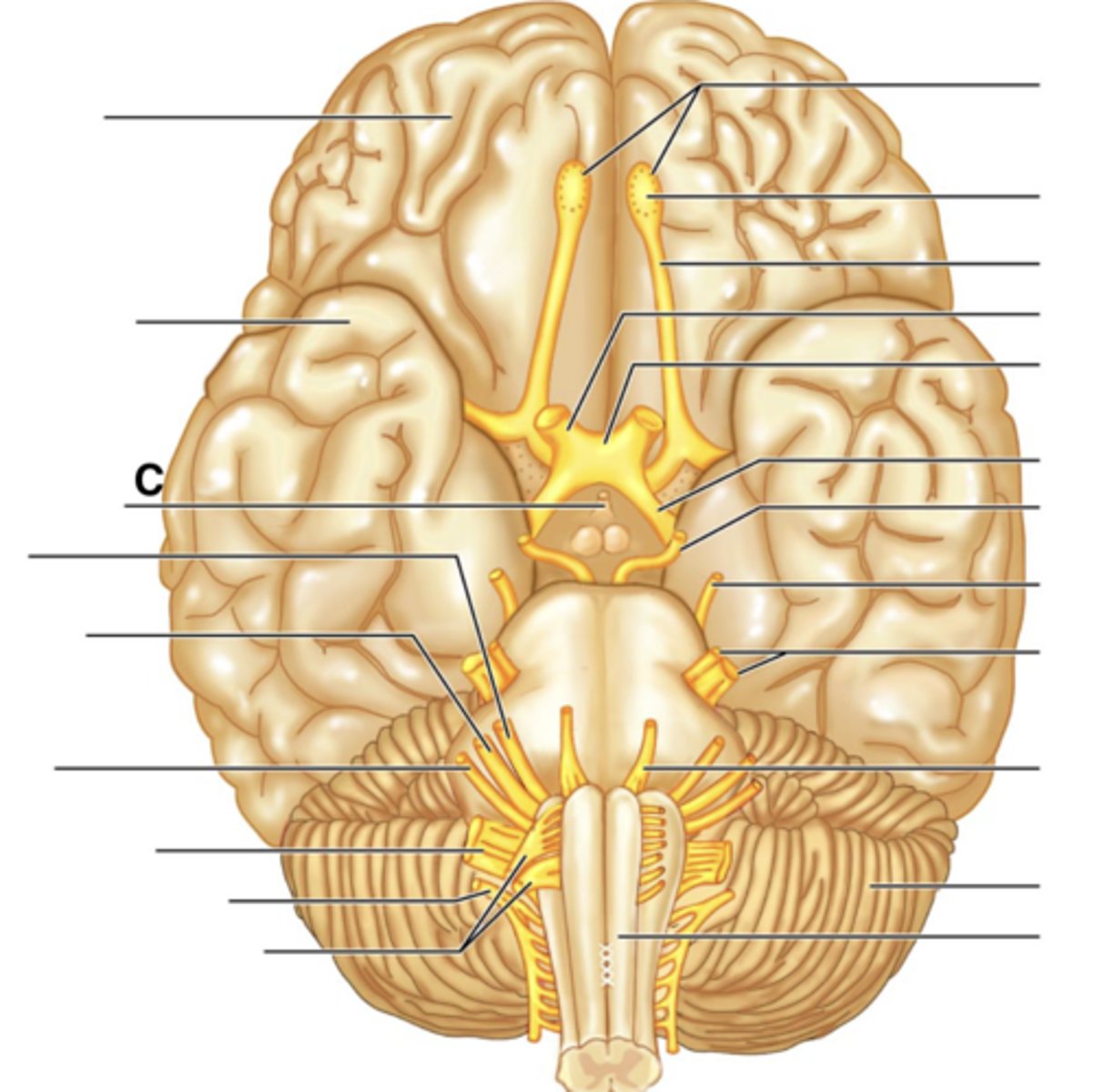
Facial Nerve (VII)
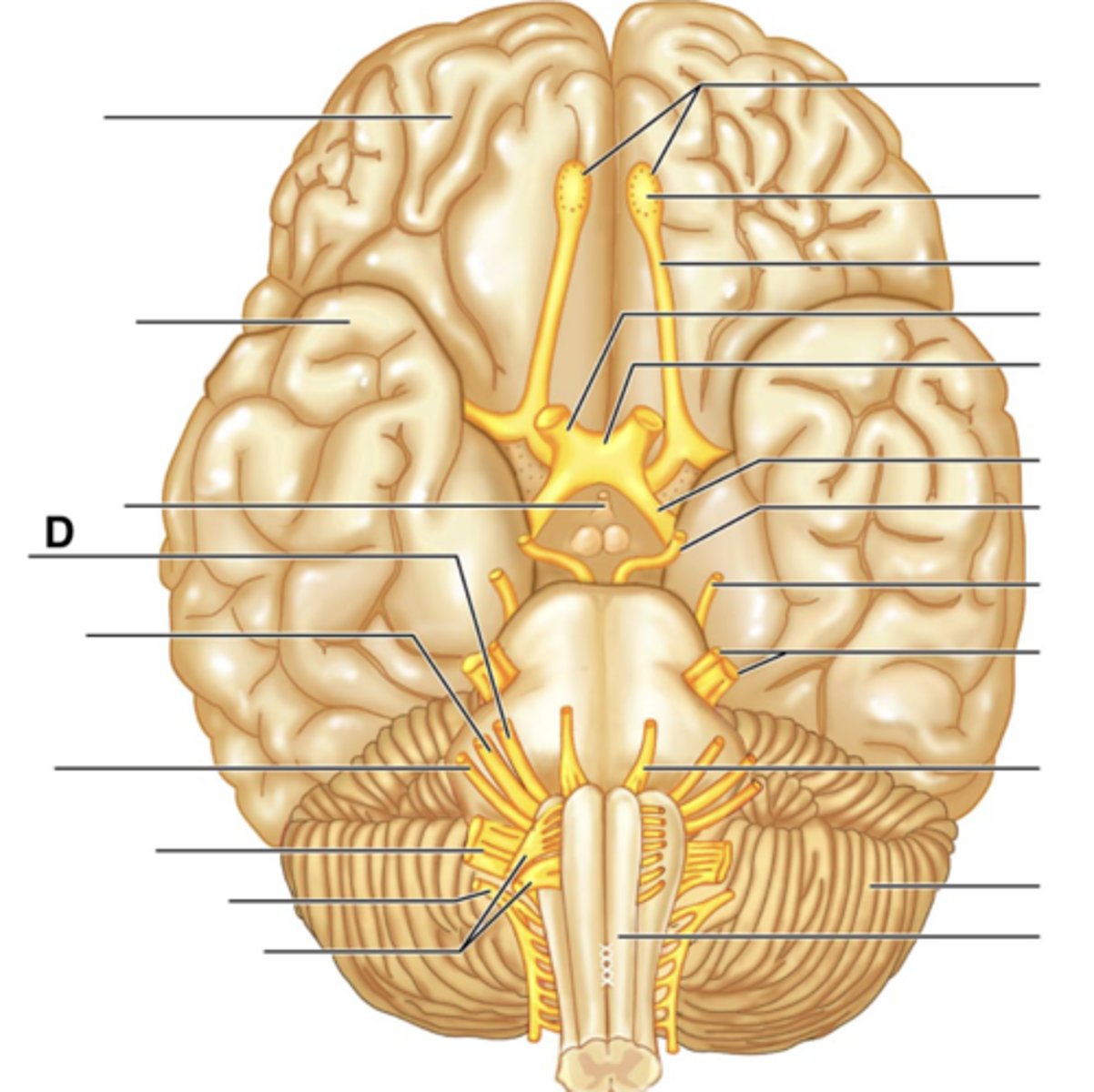
Vestibulocochlear Nerve (VIII)
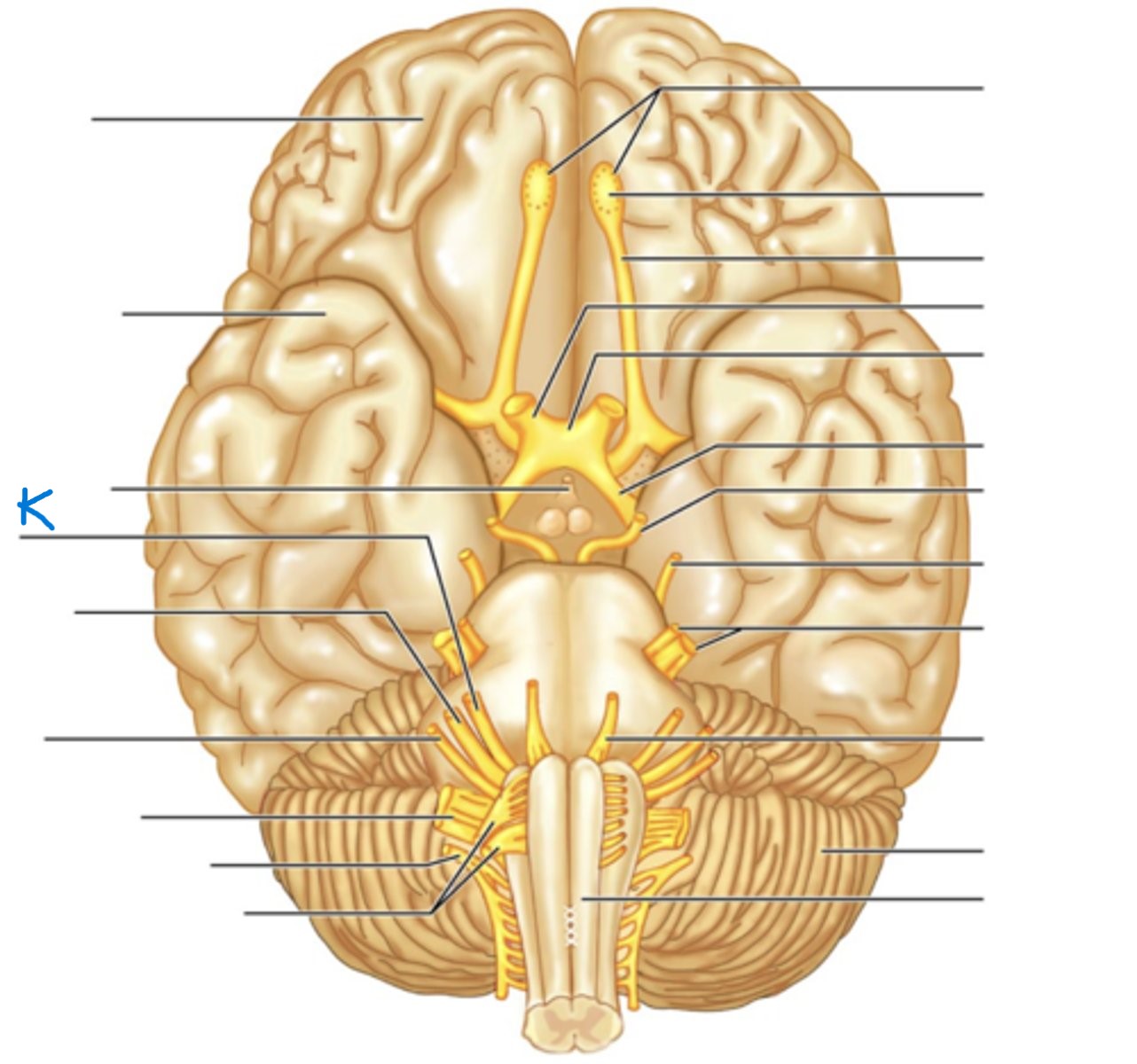
Glossopharyngeal Nerve (IX)
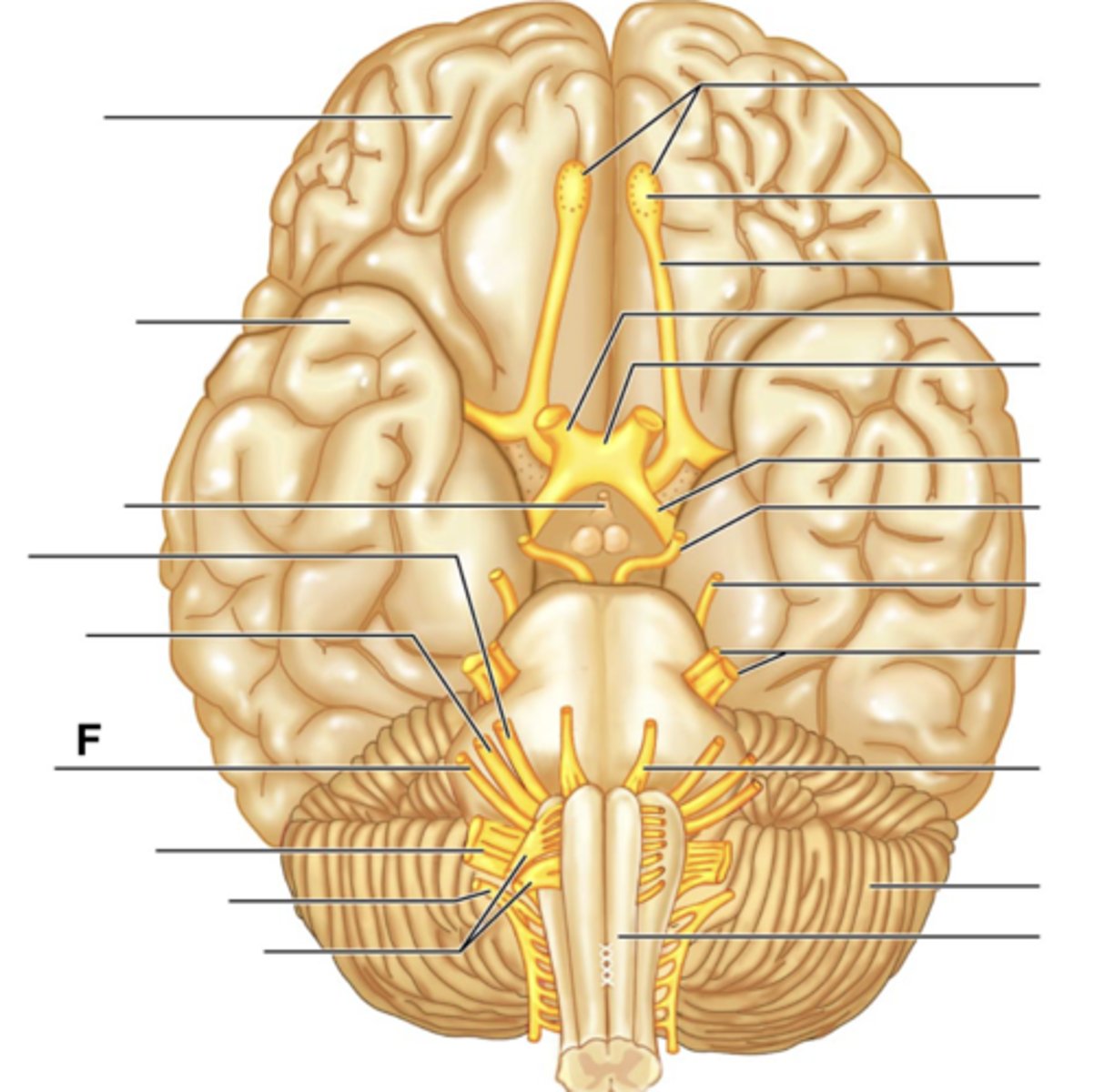
Vagus Nerve (X)
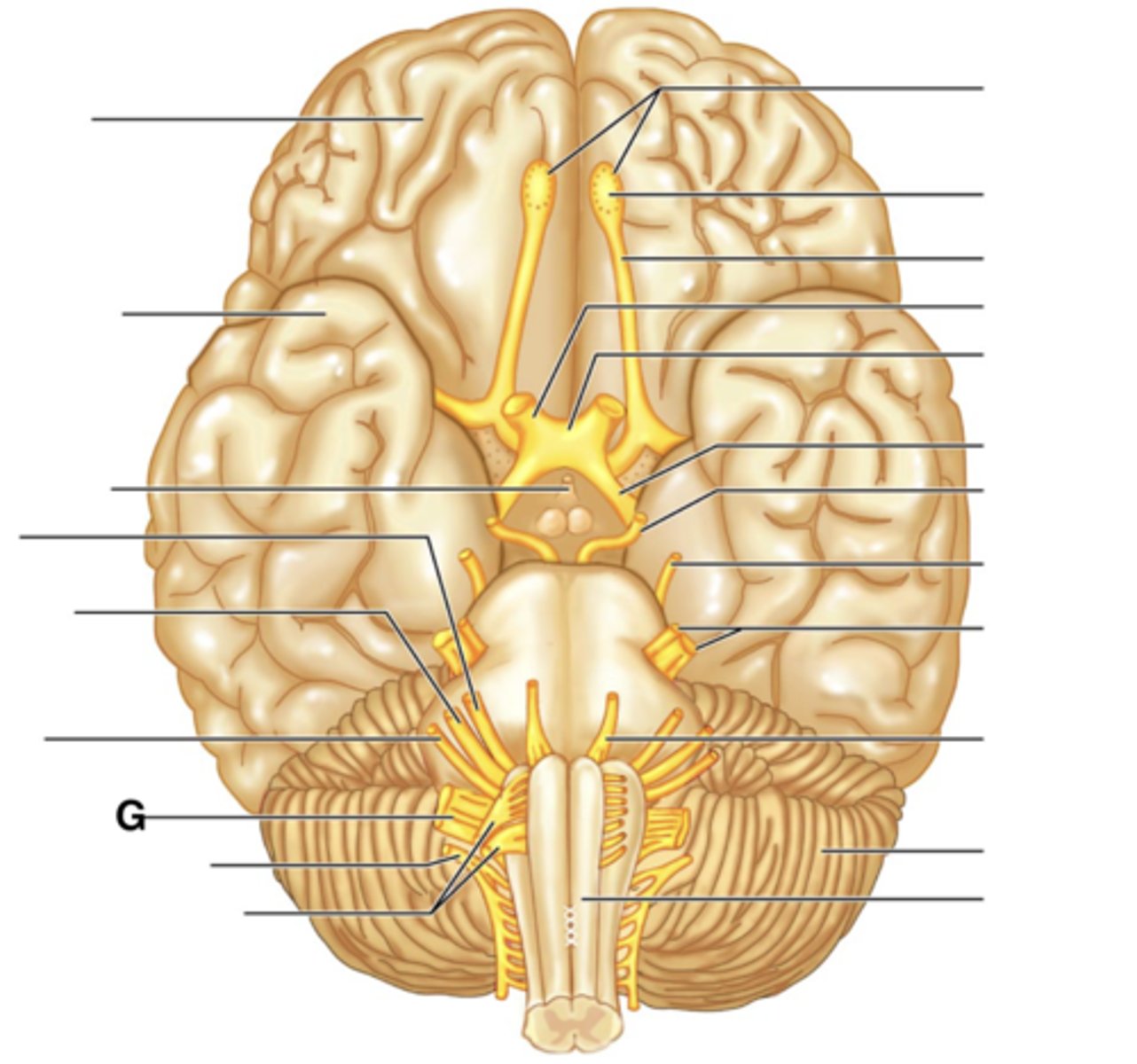
Accessory Nerve (XI)
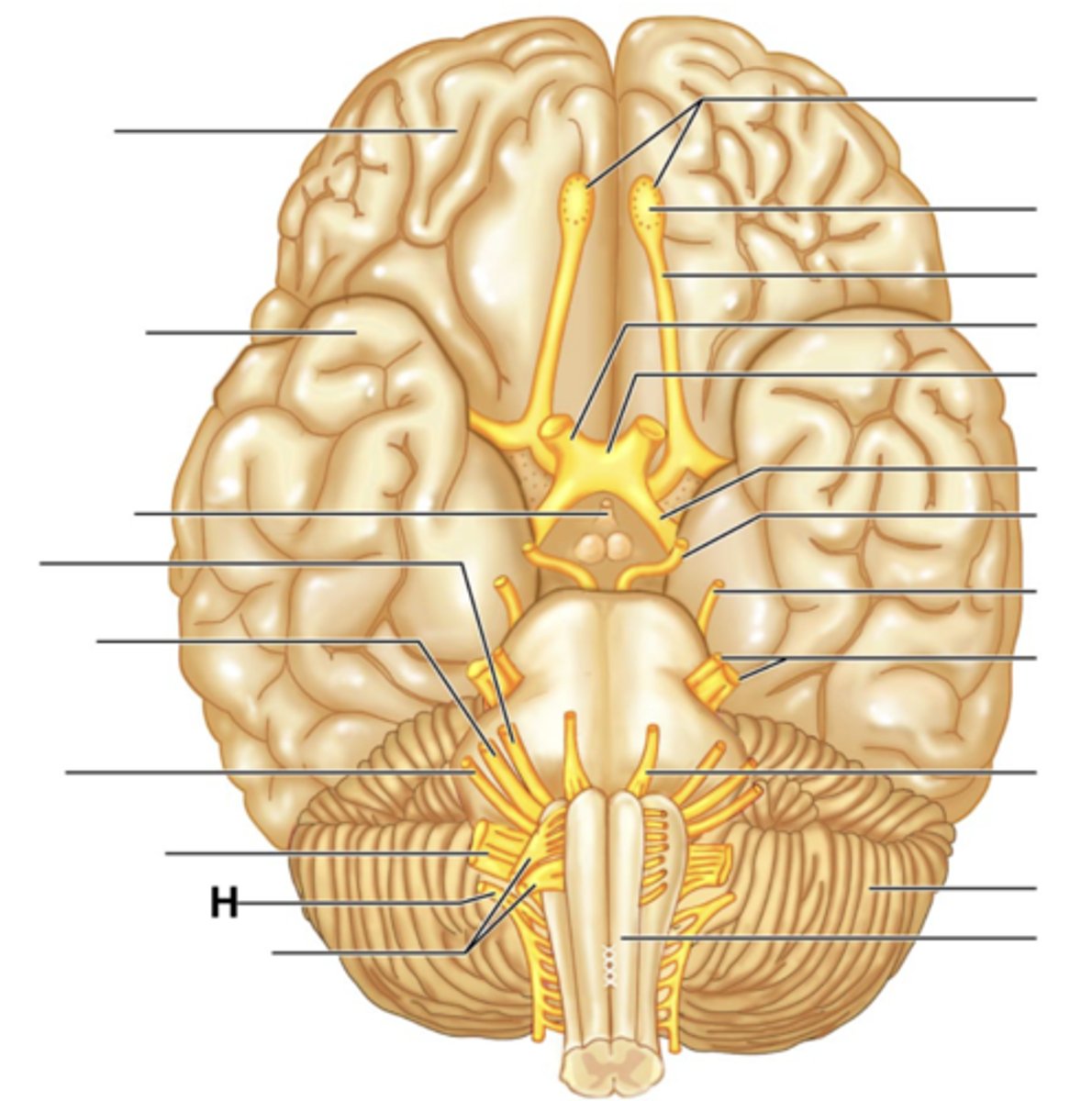
Hypoglossal Nerve (XII)
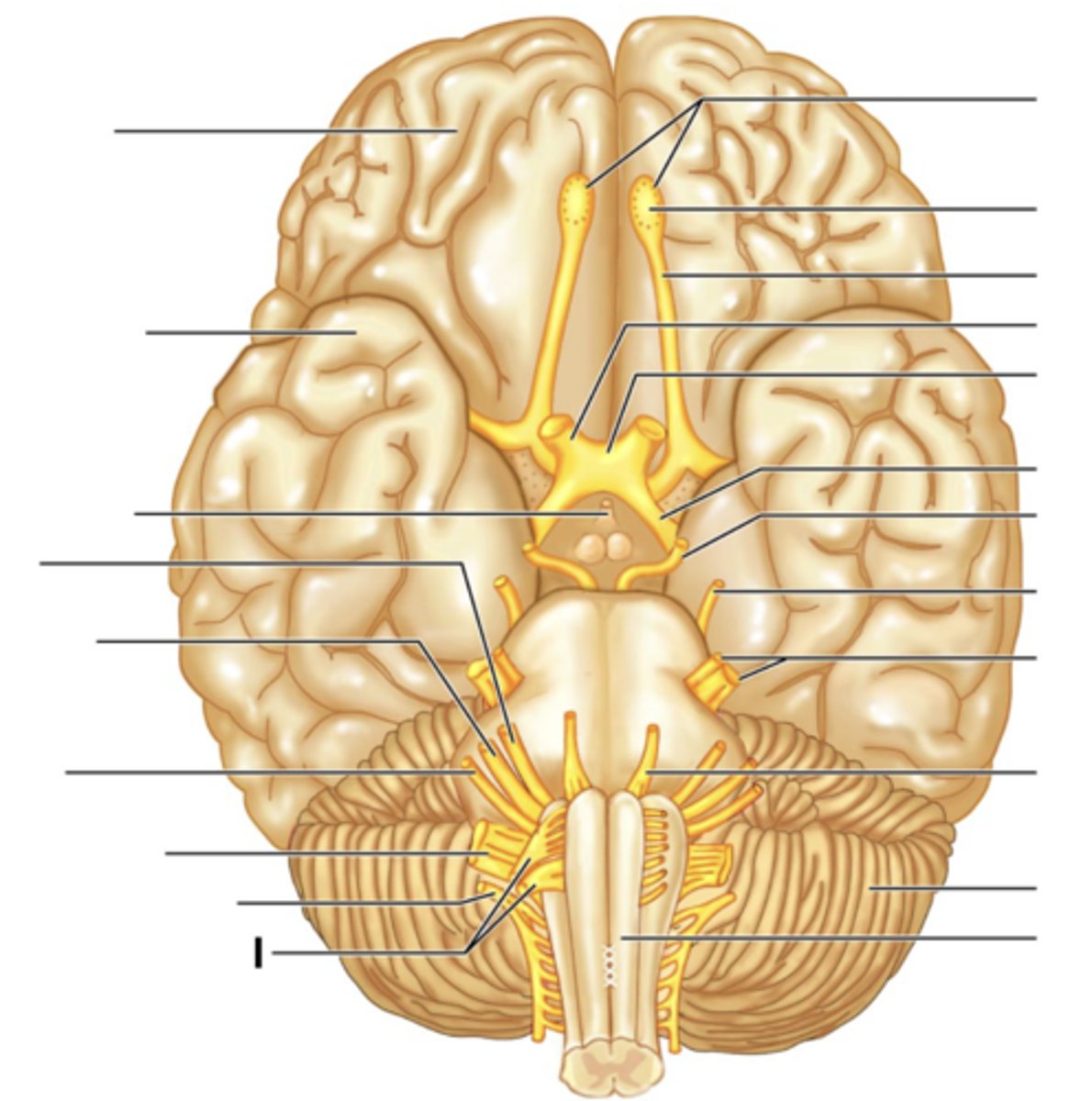
Filaments of Olfactory Nerve (I)
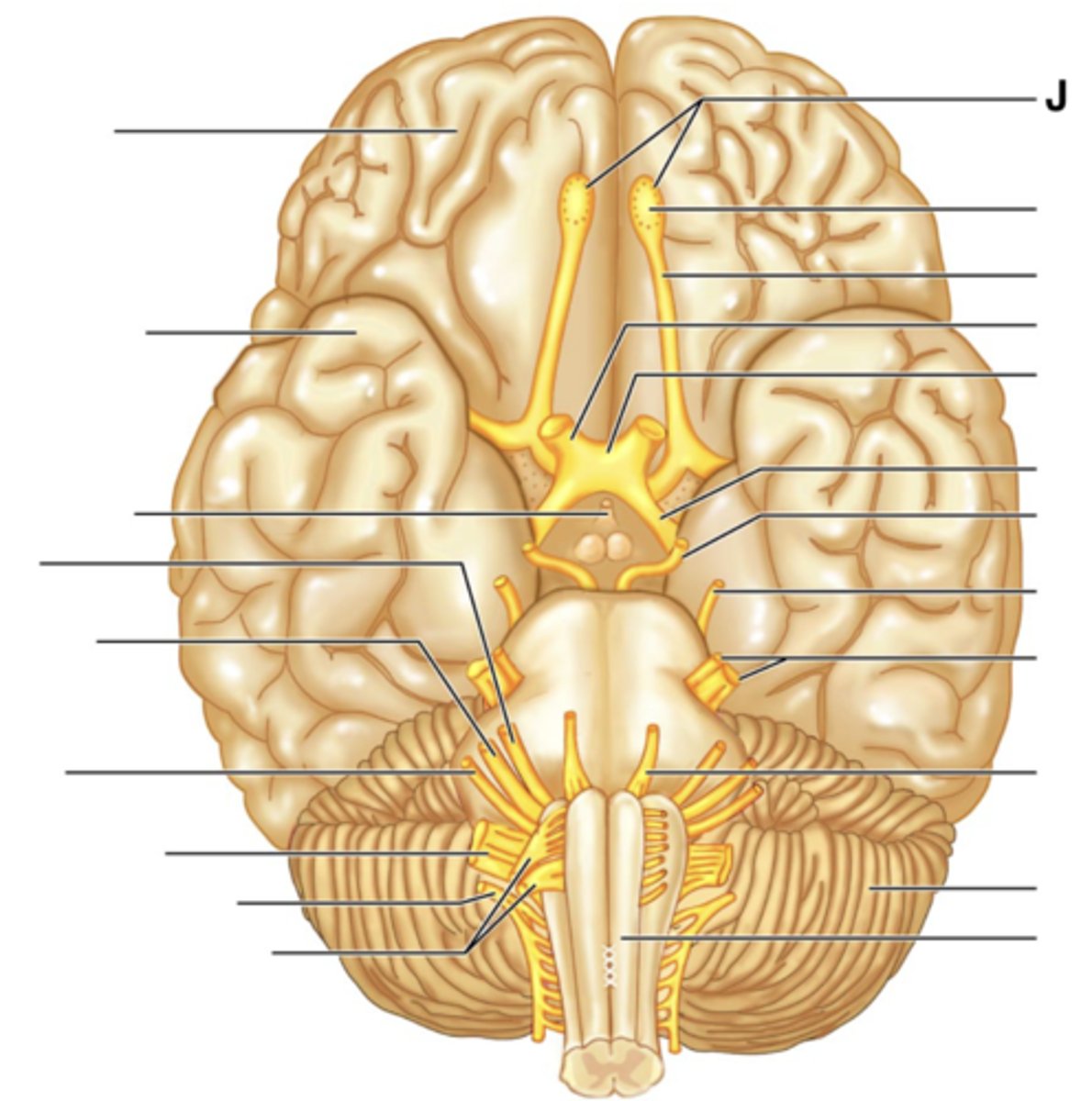
Olfactory Bulb
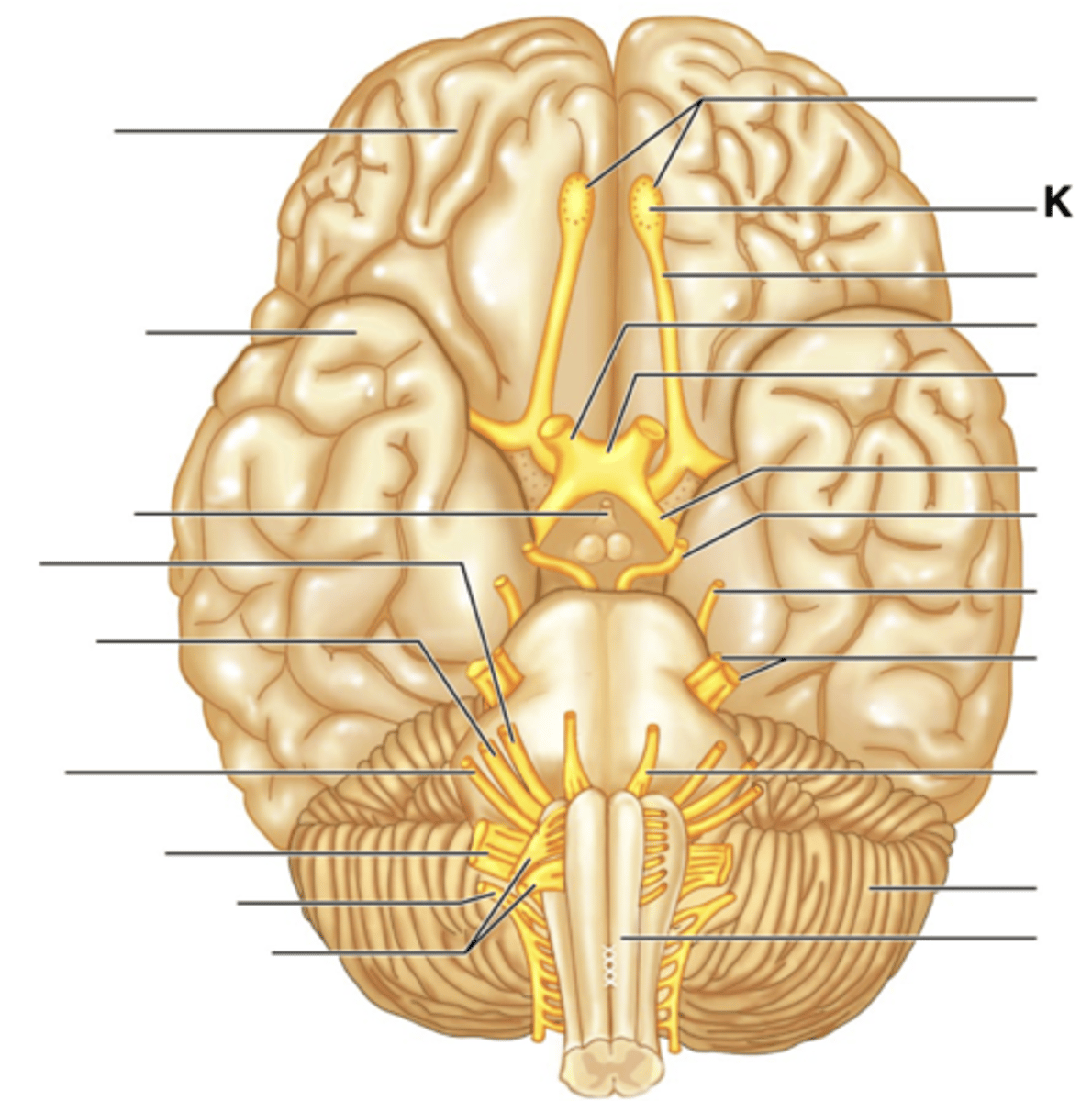
Olfactory Tract
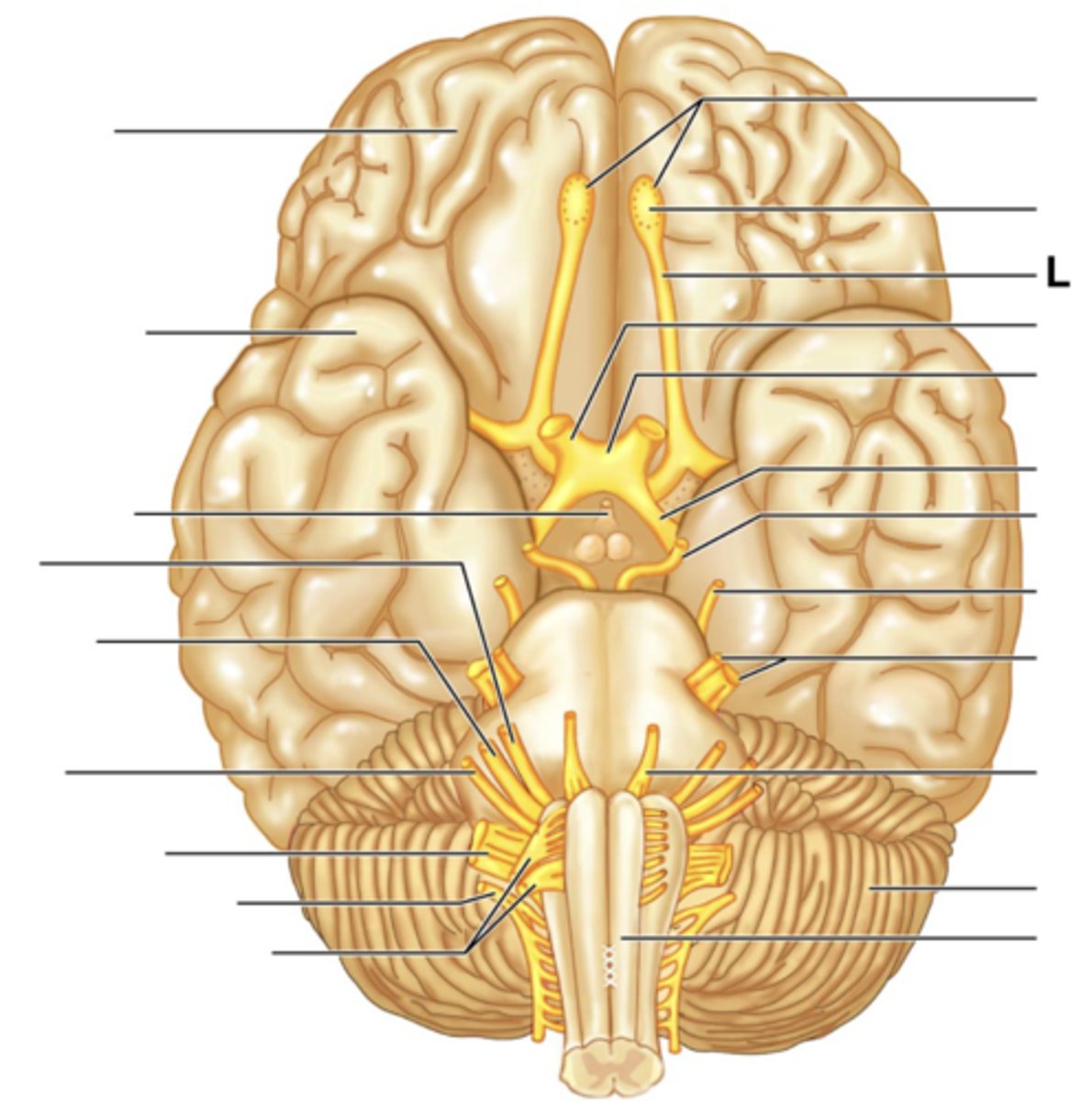
Optic Nerve (II)
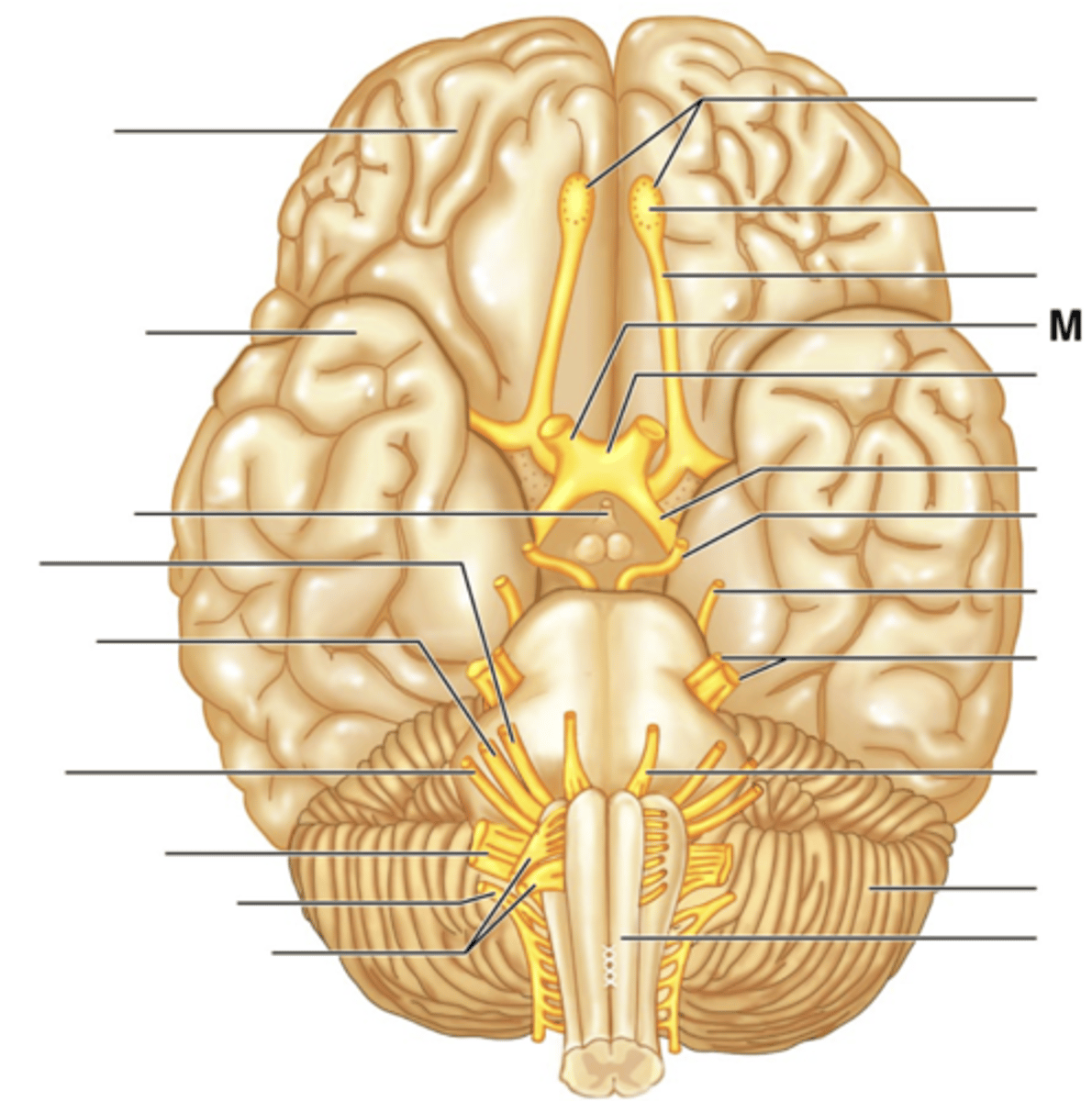
Optic Chiasma
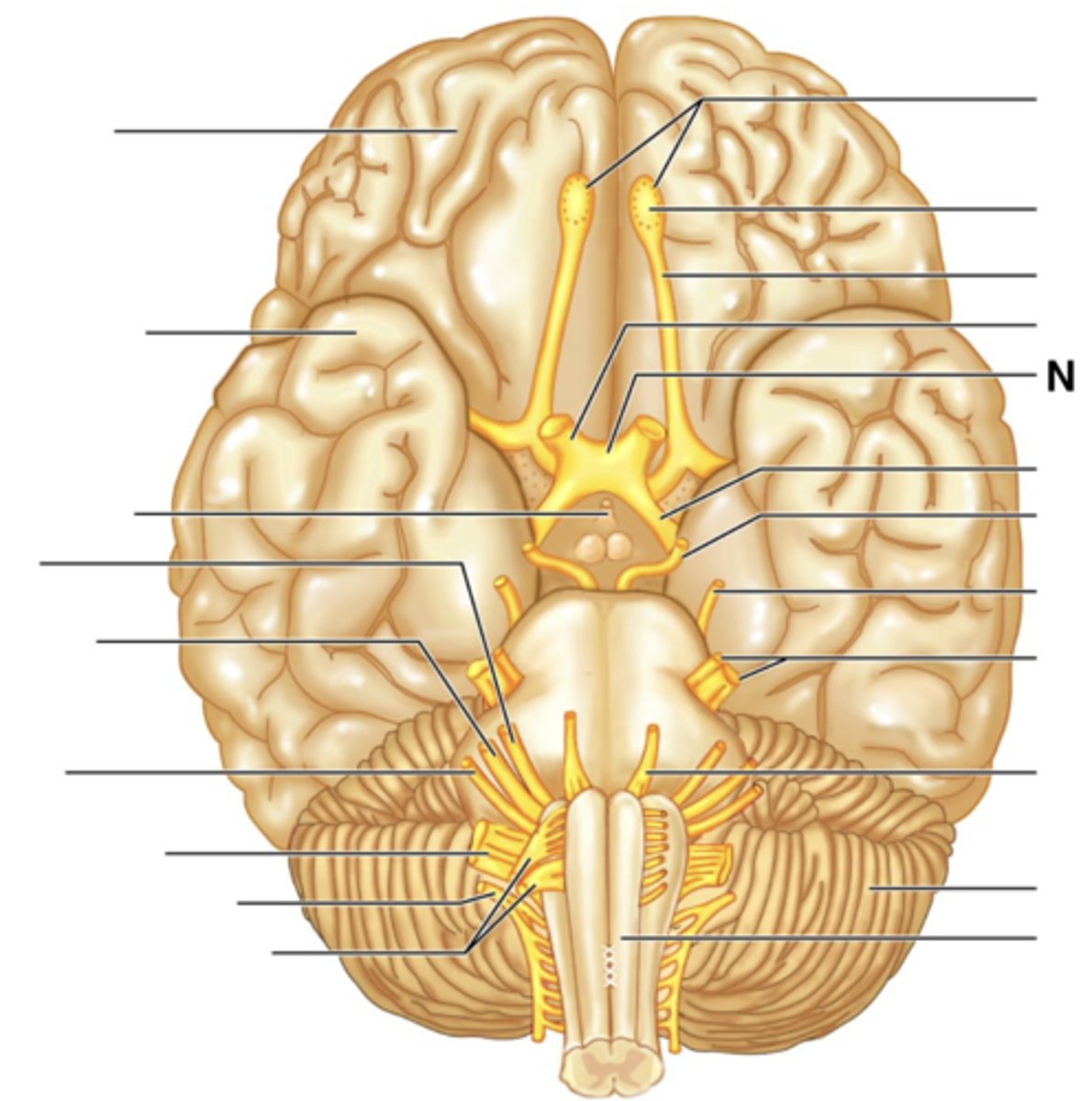
Optic Tract
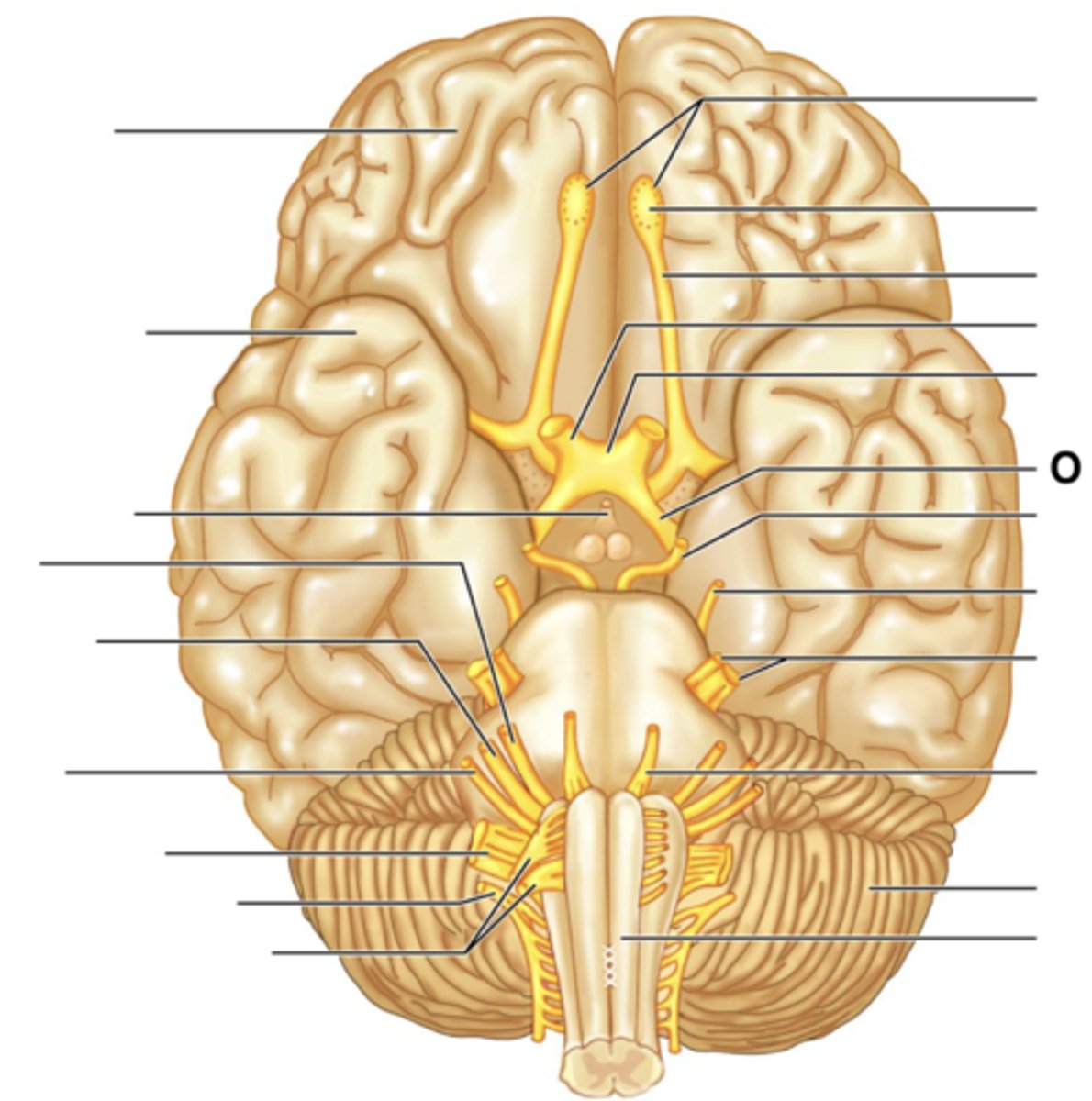
Oculomotor Nerve (III)
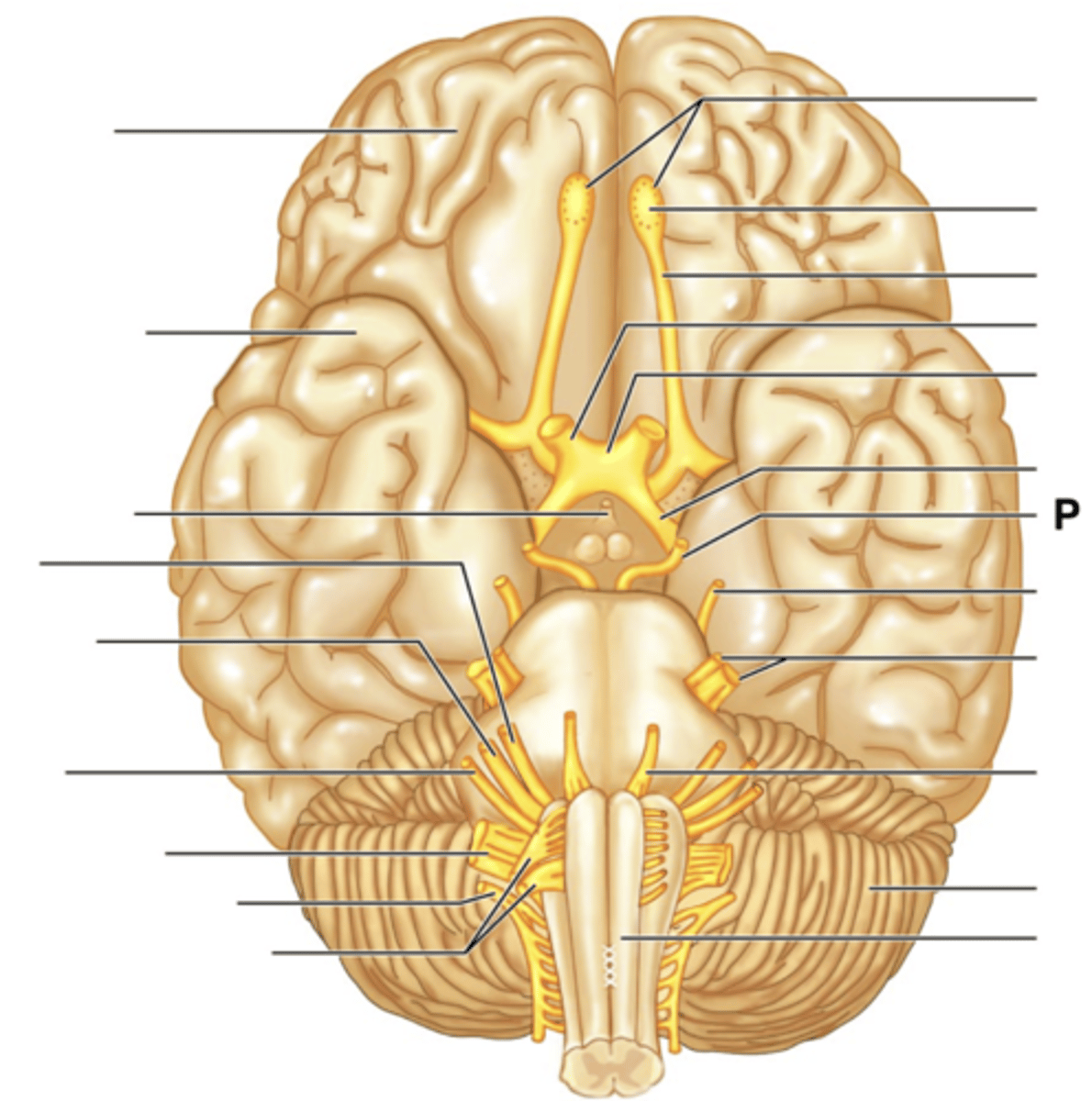
Trochlear Nerve (IV)
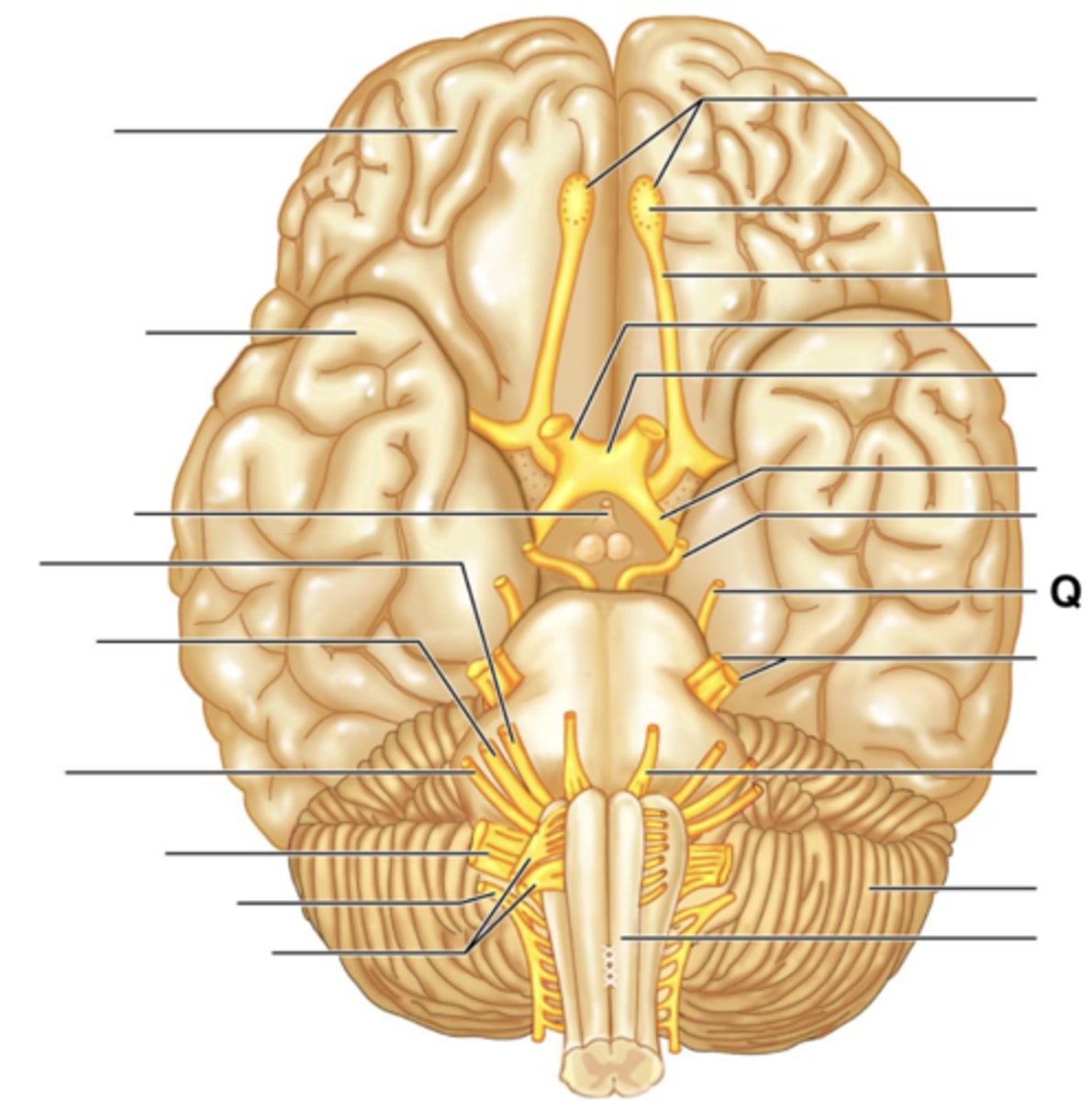
Trigeminal Nerve (V)
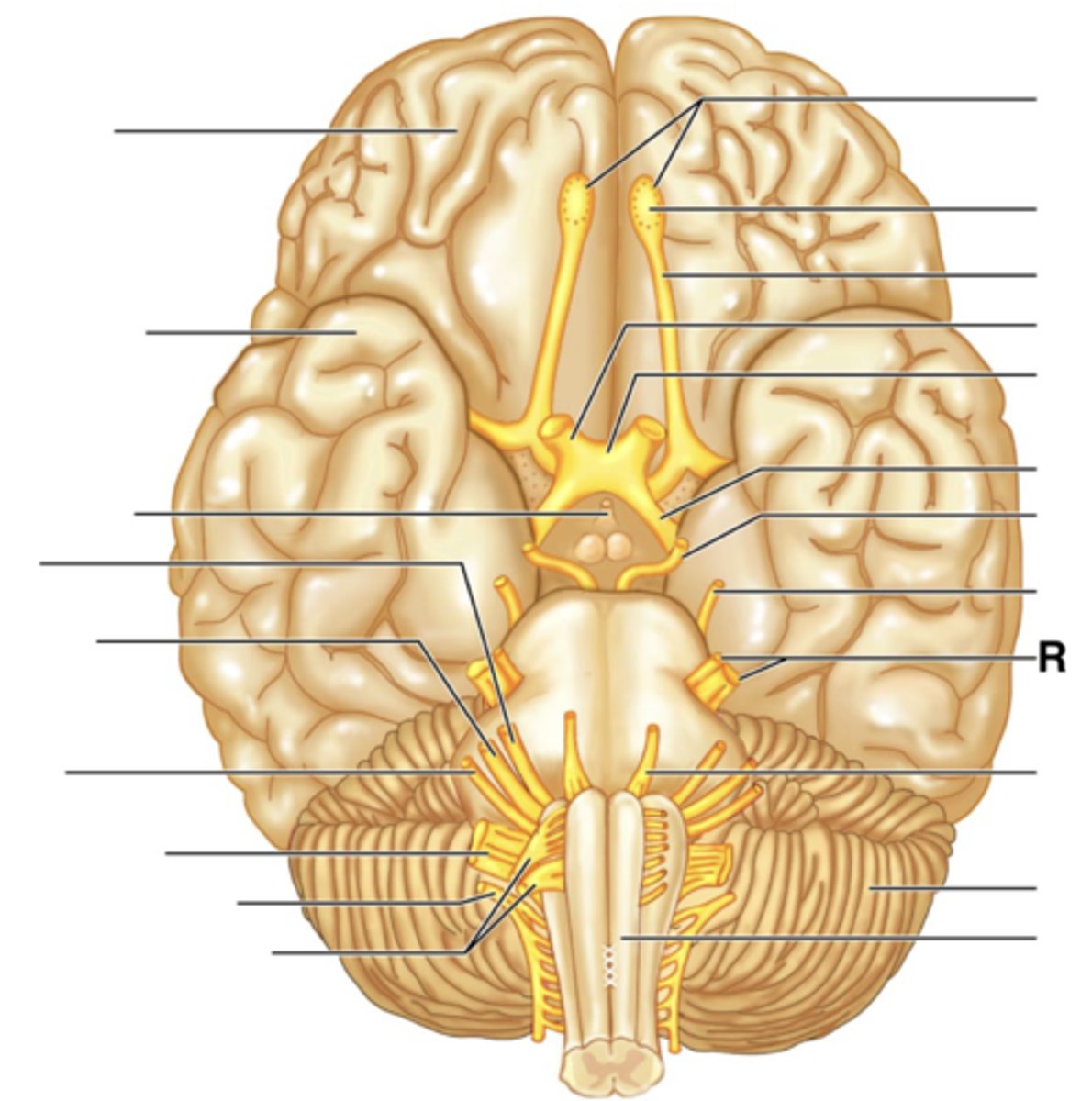
Abducens Nerve (VI)
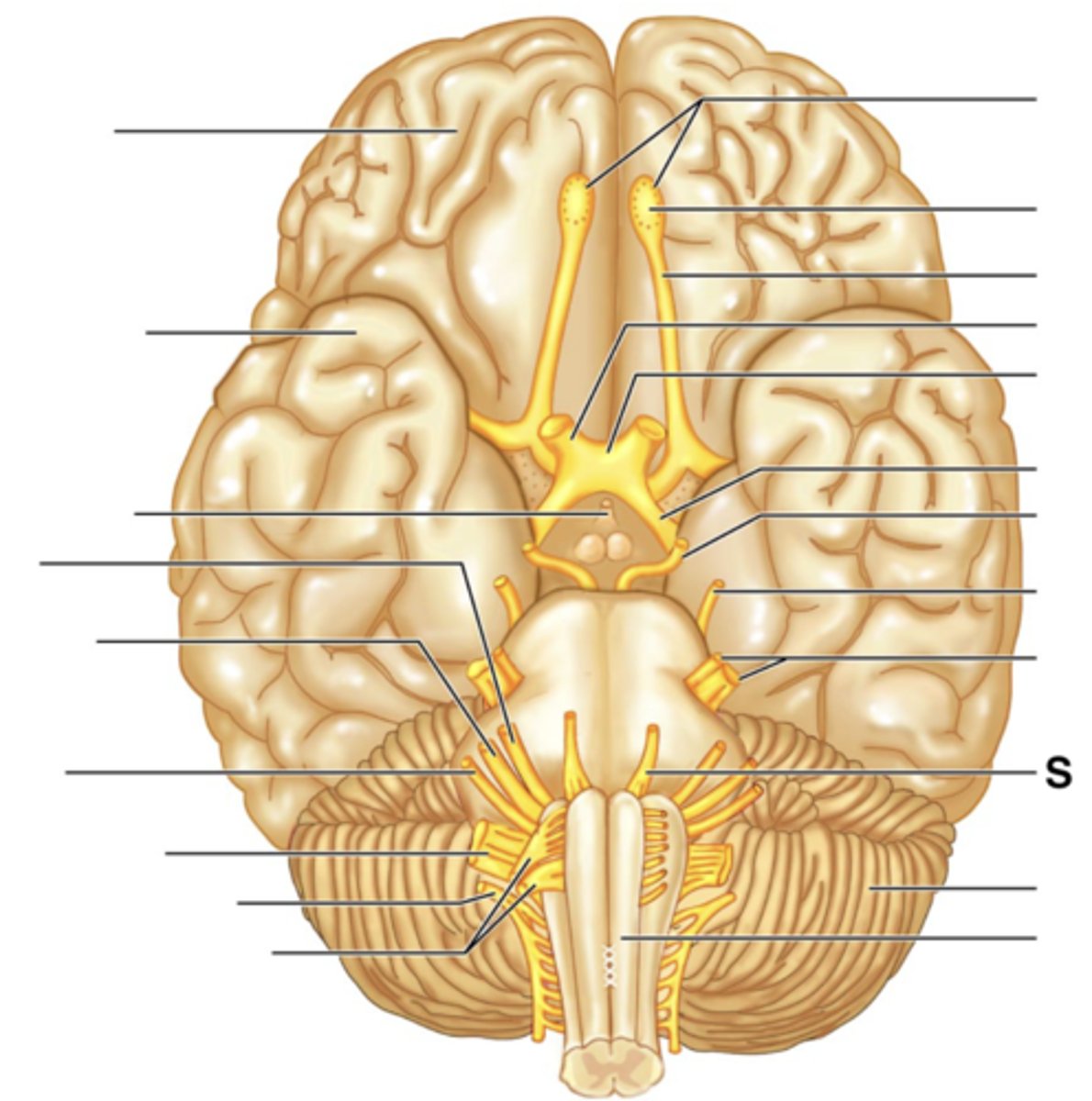
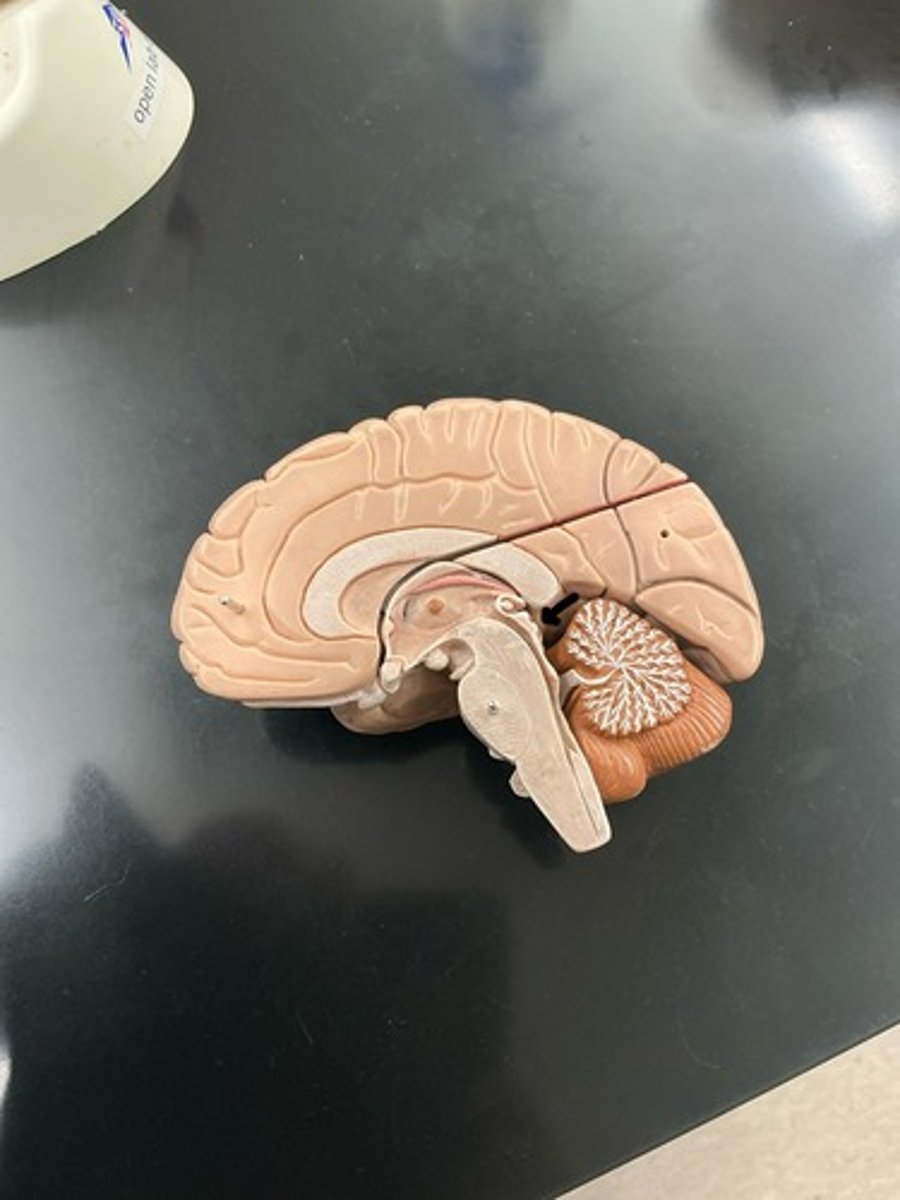
Cerebellum
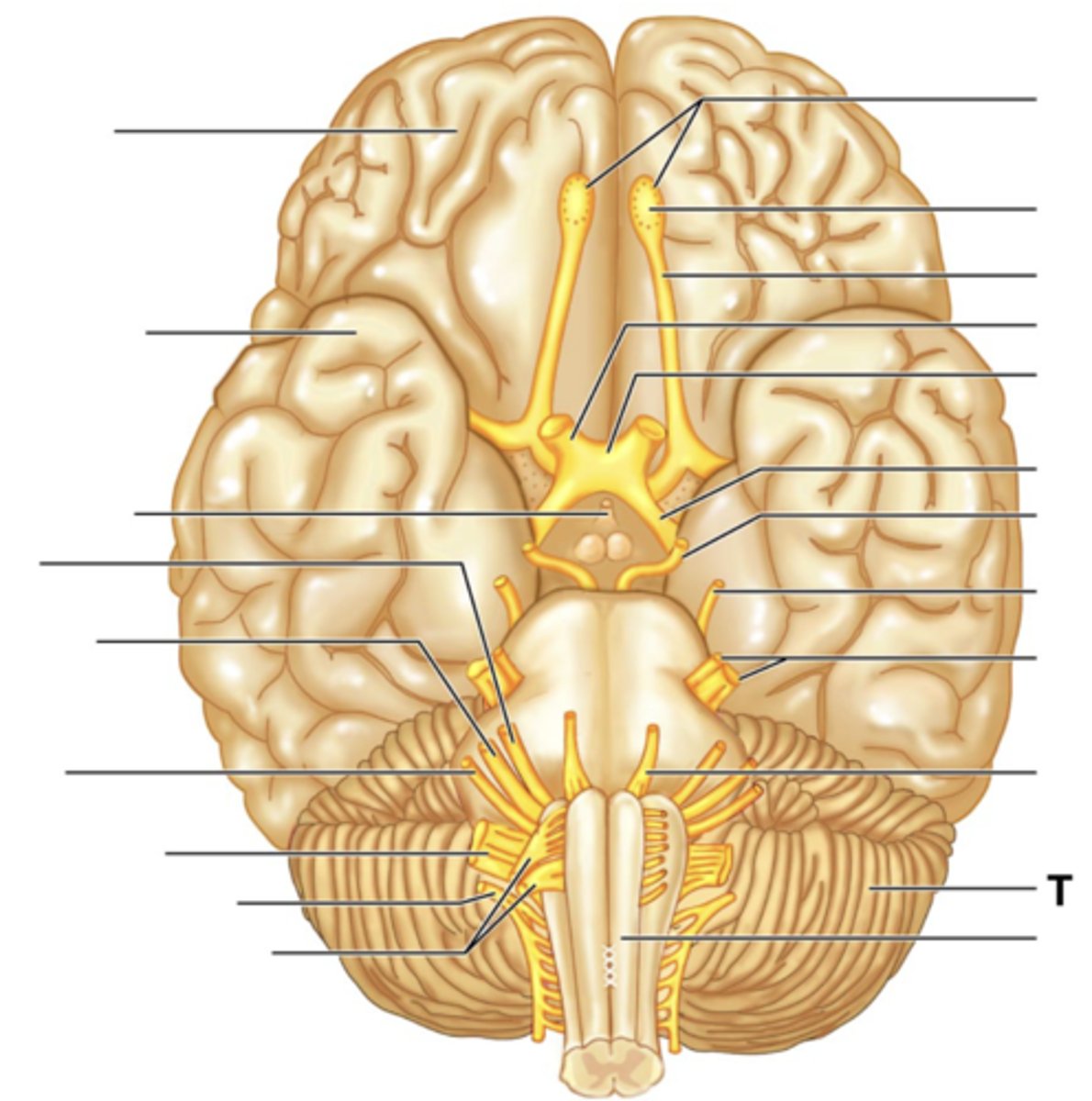
Medullua
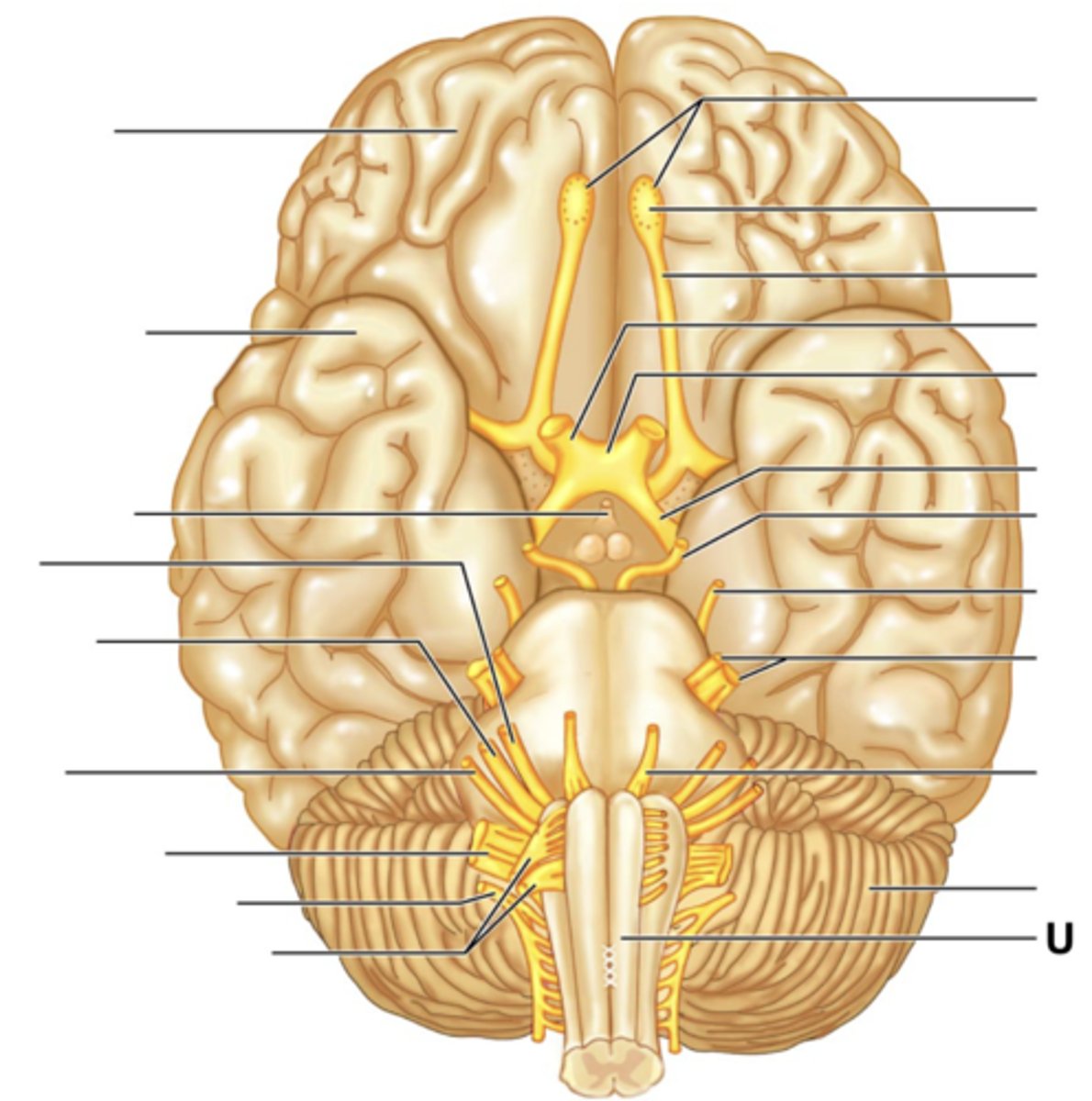
Shallow grooves
Sulci/Sulcus
separates frontal vs parietal lobes
Central sulcus
separates temporal lobe from others
Lateral sulcus
raised areas
Gyri/Gyrus
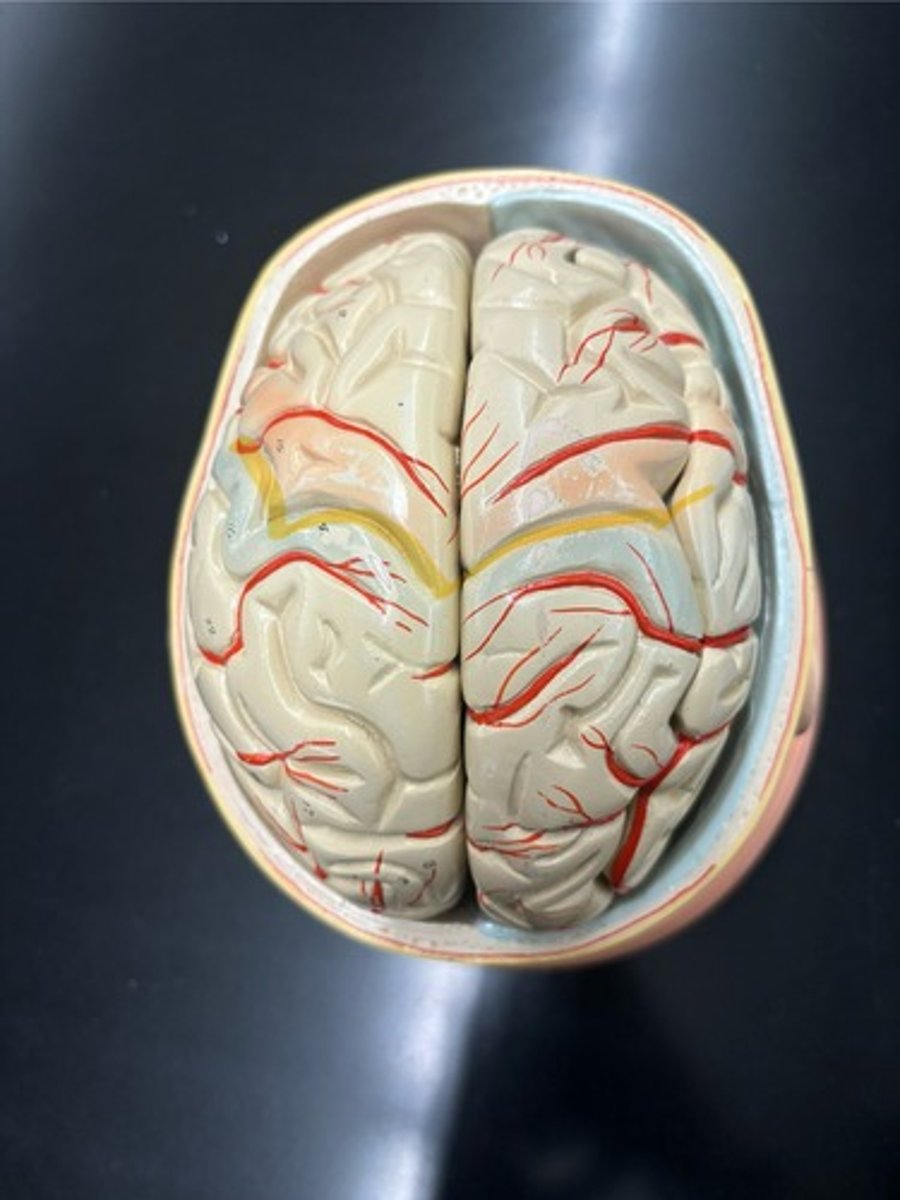
Location of the motor cortex
Precentral gyrus
Location of the somatosensory cortex
Postcentral gyrus
Postcentral gyrus
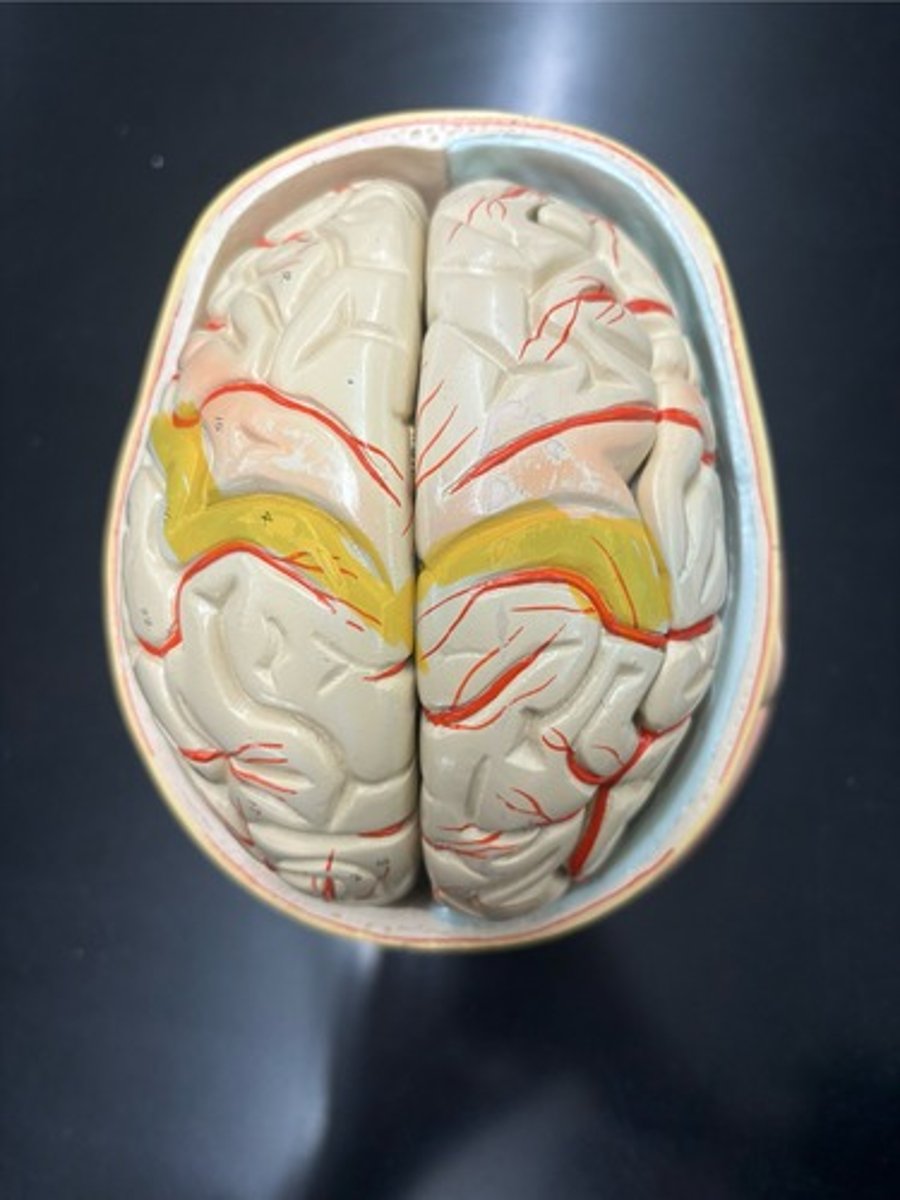
Precentral gyrus
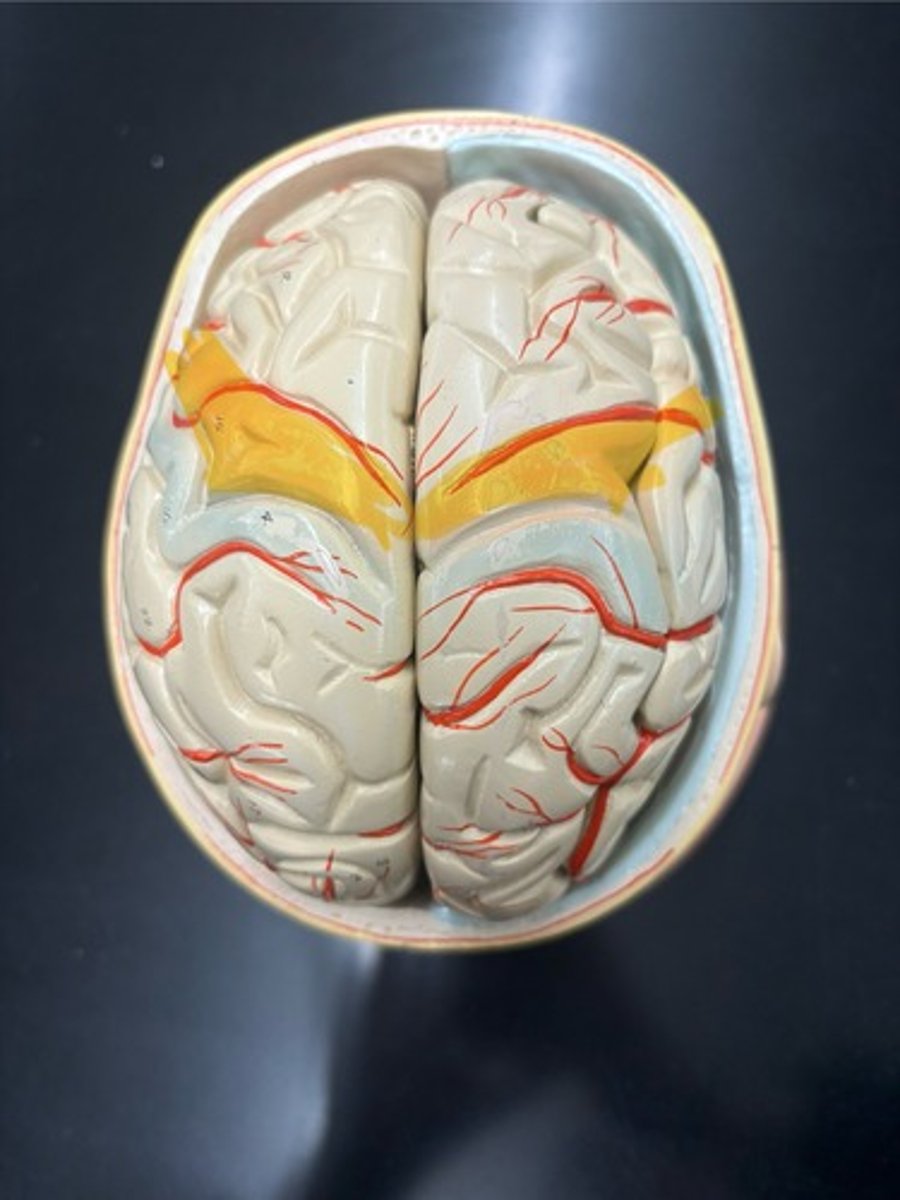
Lateral sulcus
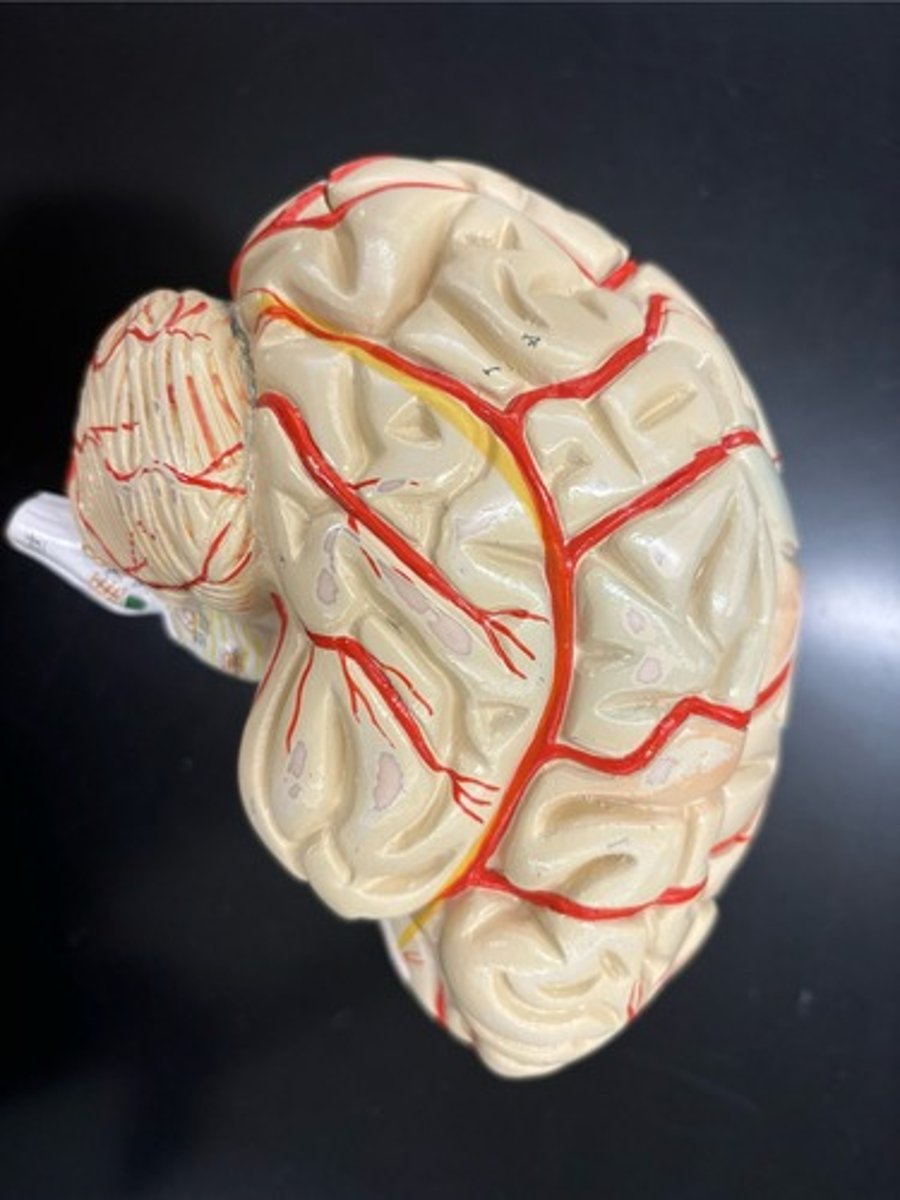
Central sulcus
Frontal (contains the motor cortex)
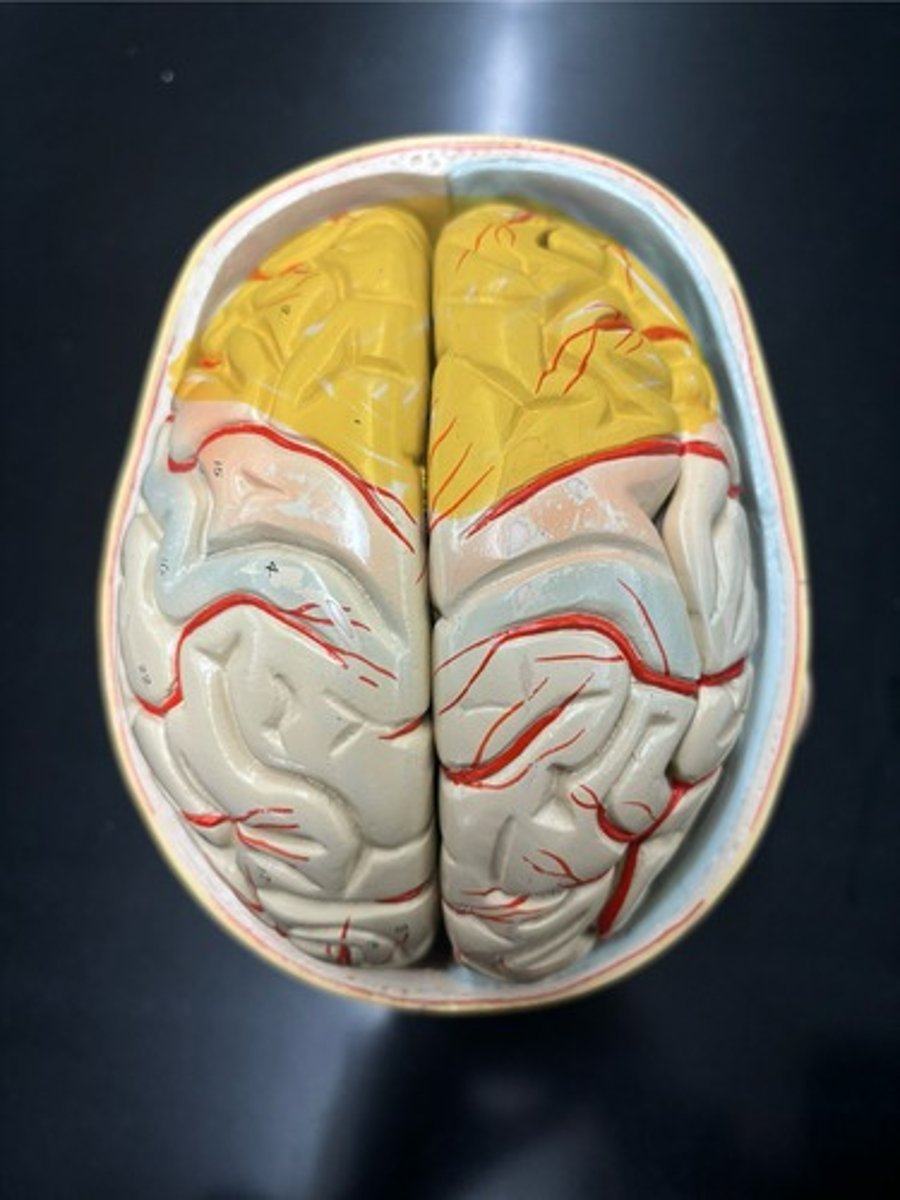
Parietal (contains the somatosensory cortex)
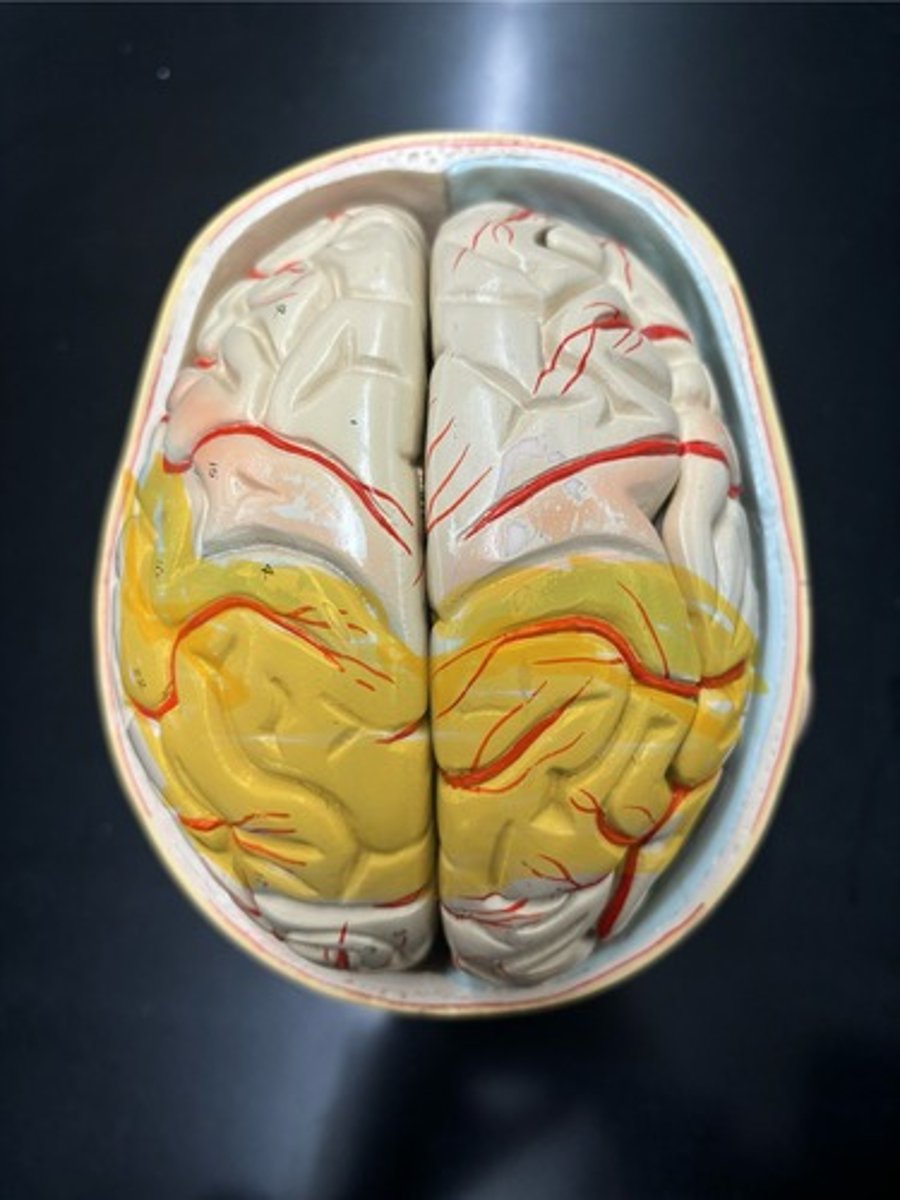
Occipital (contains the visual cortex)
Insula (contains the gustatory cortex)
Temporal (contains the auditory and olfactory cortex)
Corpus callosum: bundle of axons carrying info between hemispheres
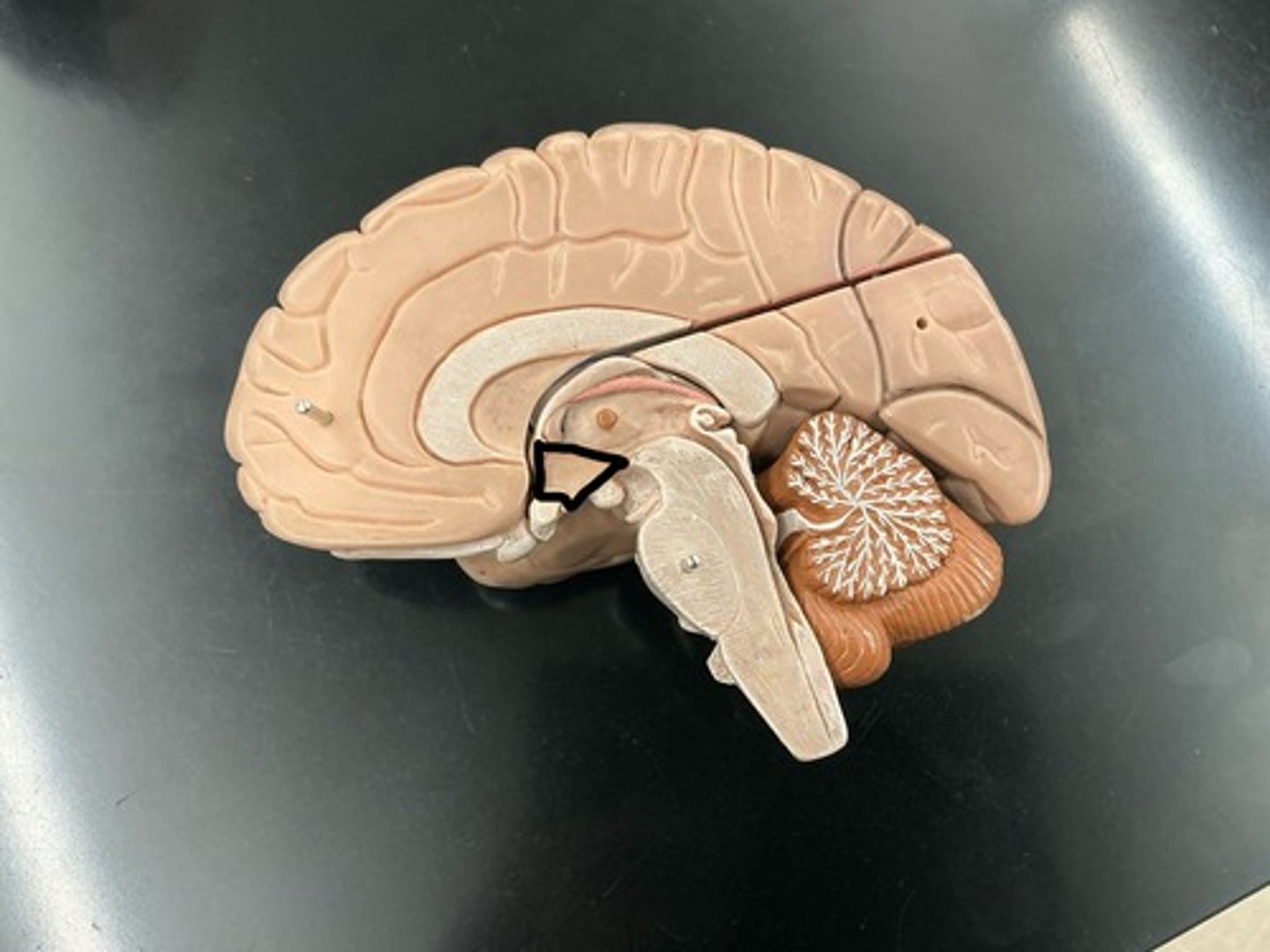
Optic chiasm: where optic nerves cross
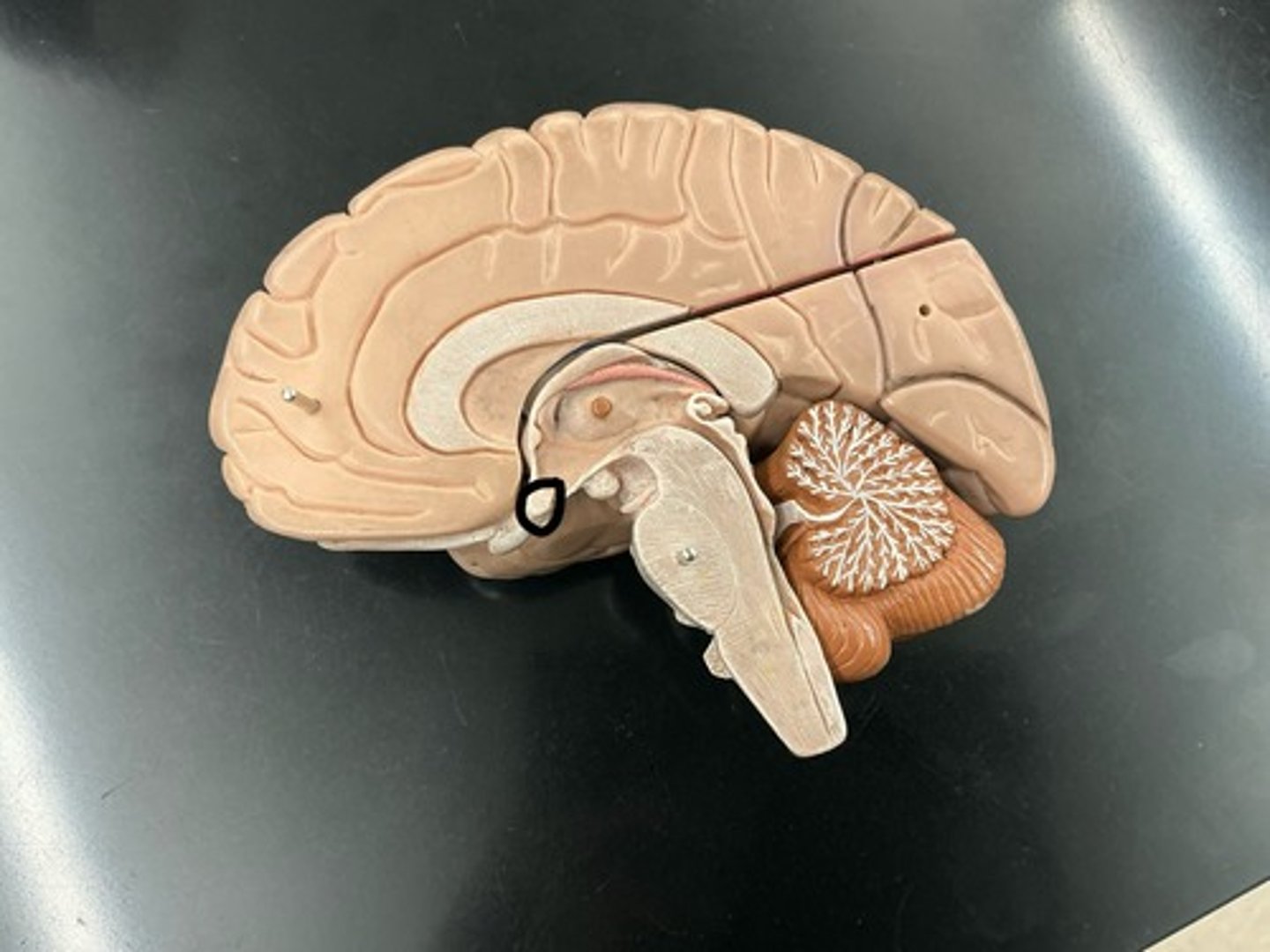
Hypothalamus: site of drives (hunger, thirst, rage, lust), temperature control counter, "seat" of ANS and controls the pituitary gland
Pituitary gland: major endocrine gland, releases 9 hormones
Deep grooves
Fissures
Mammillary bodies
involved in recollective memory and involved in feedings
behaviors - licking and swallowing
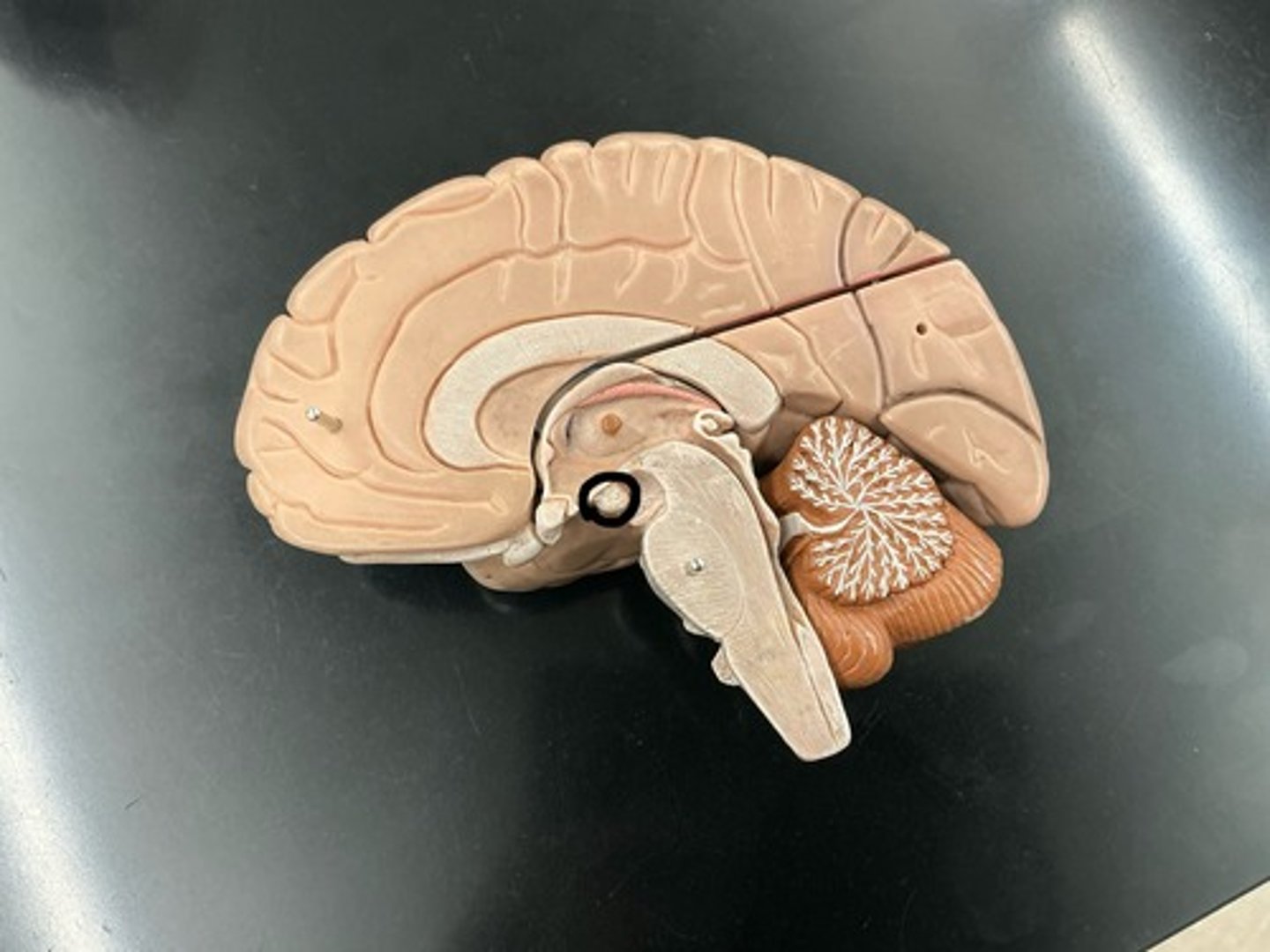
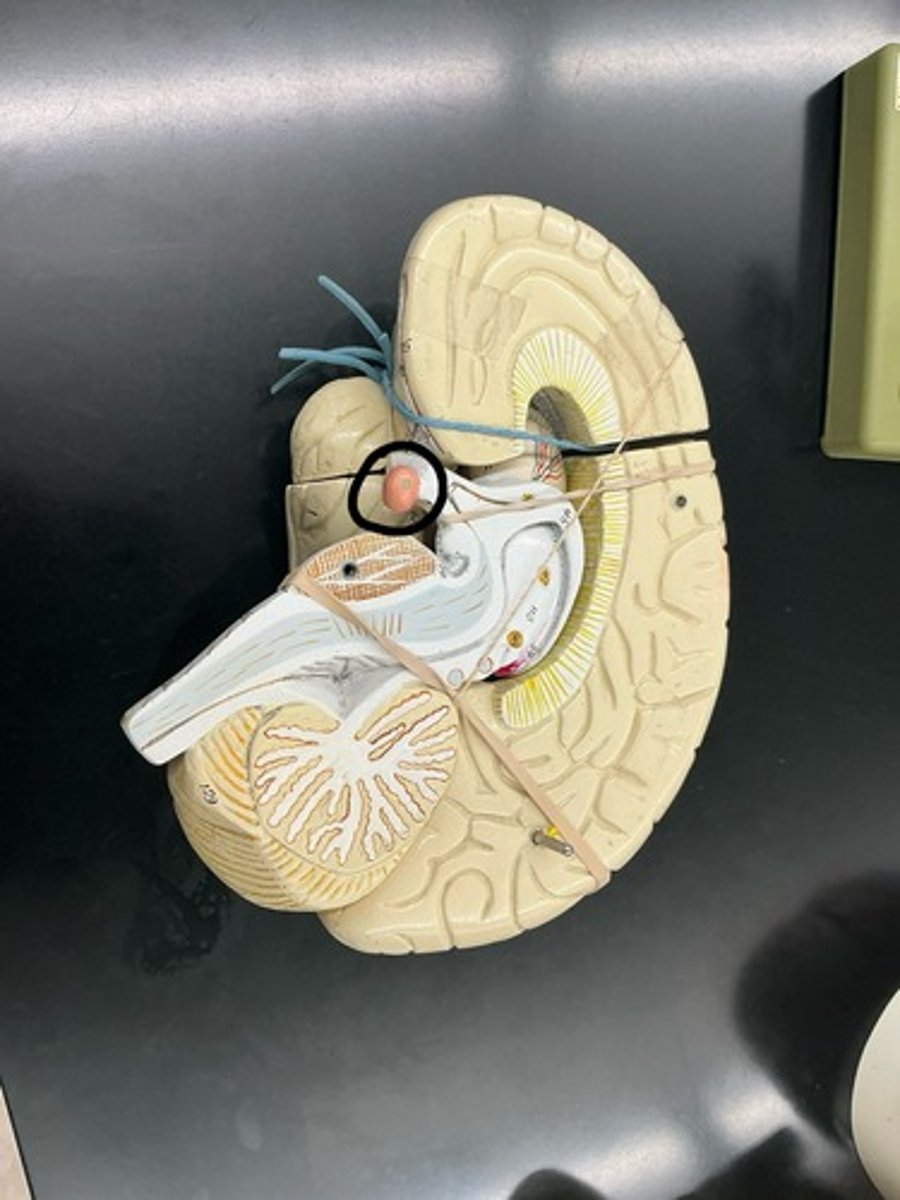
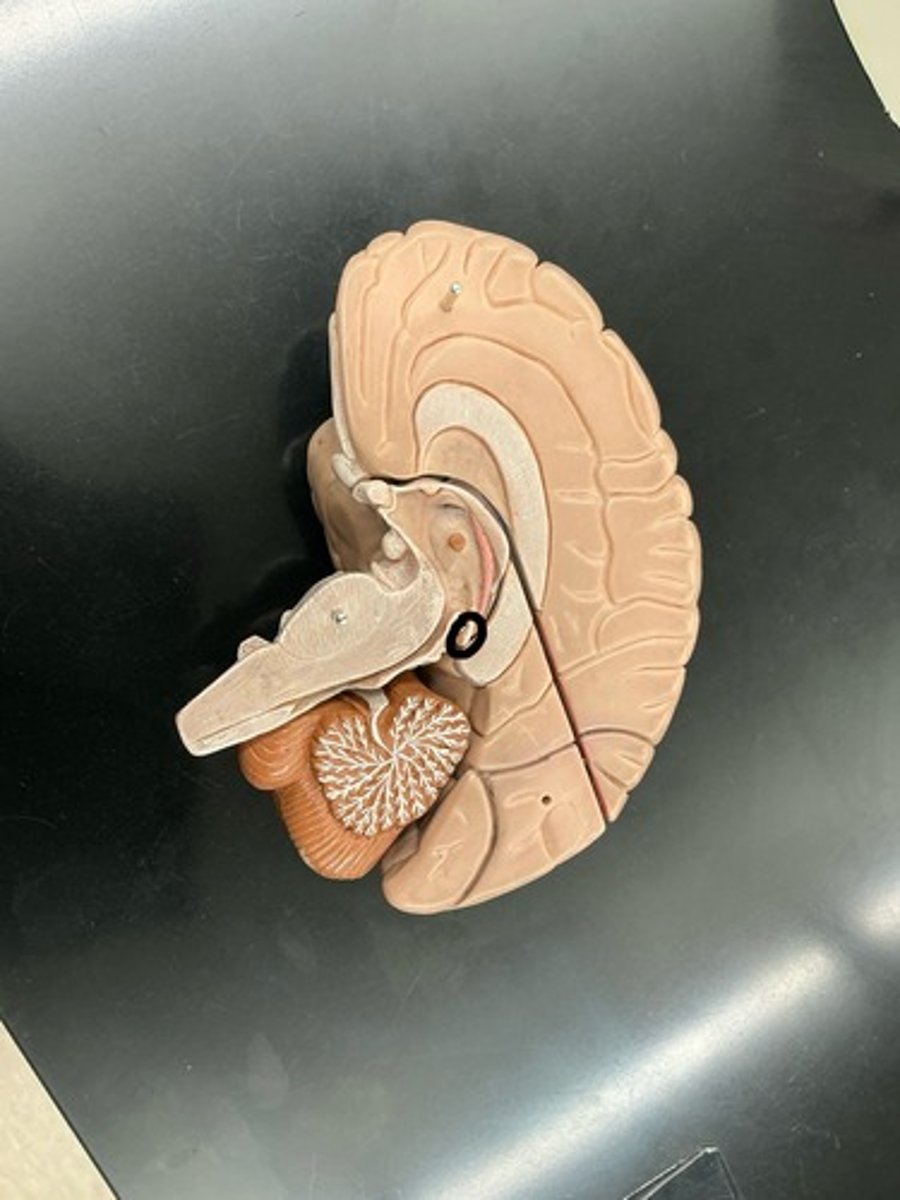
Thalamus: major sensory relay center for sensory information going up to the cerebral cortex
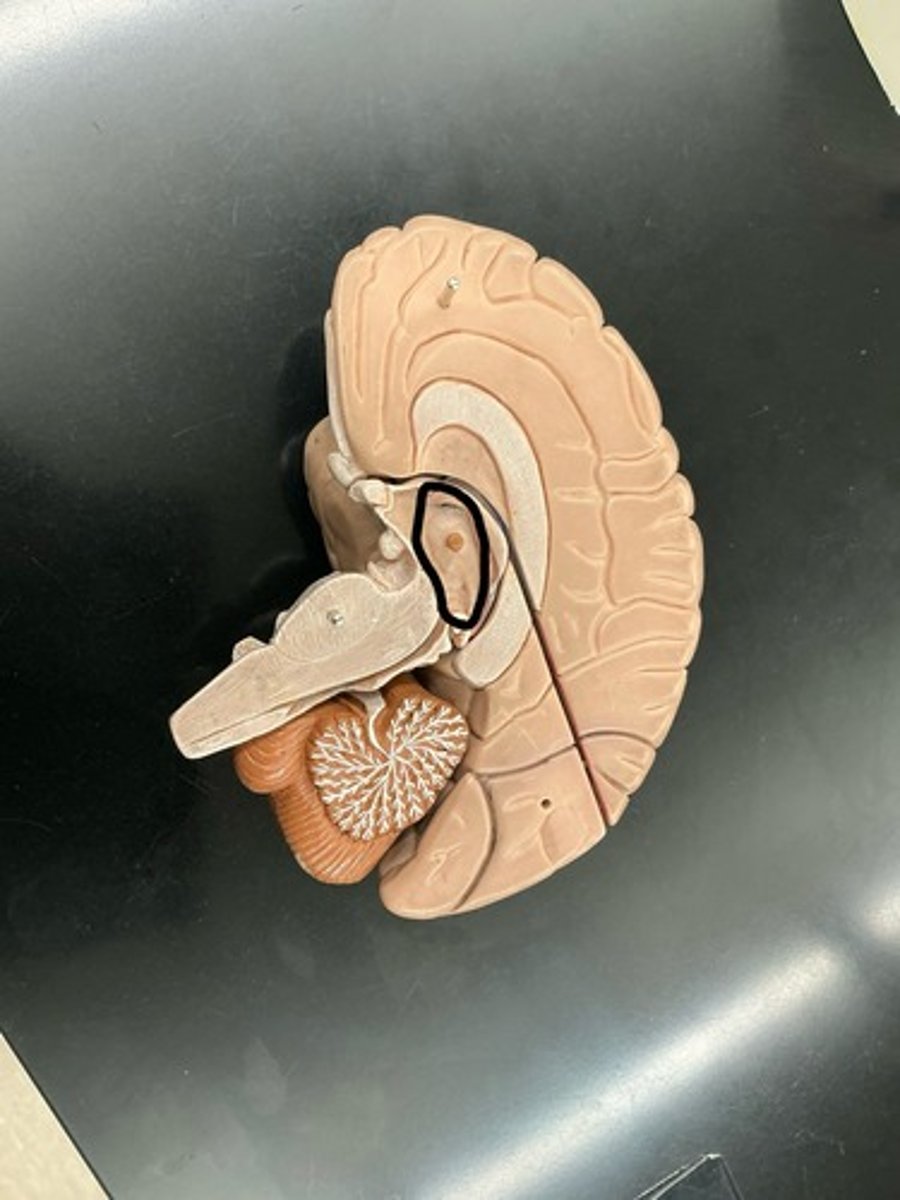
Pineal gland: releases melatonin (hormone that regulates day/night cycles)
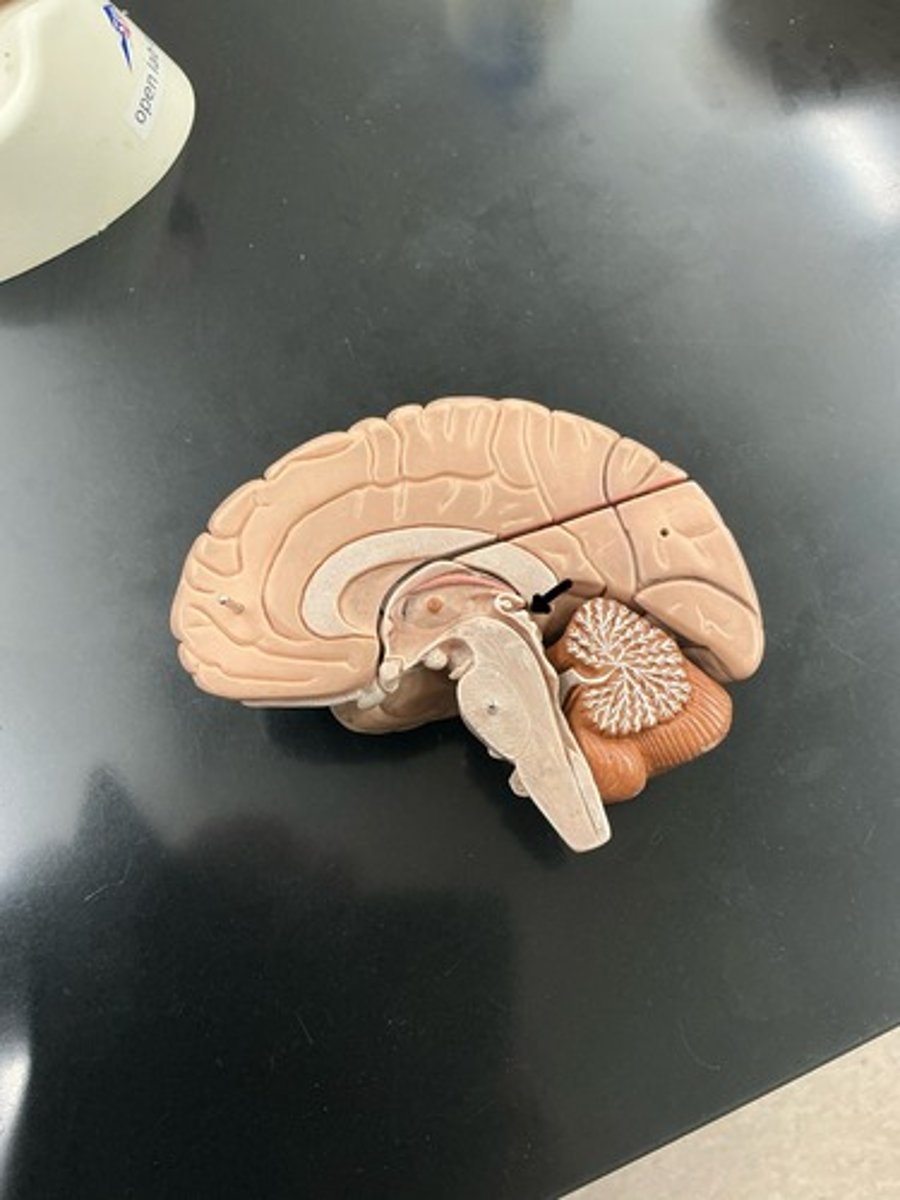
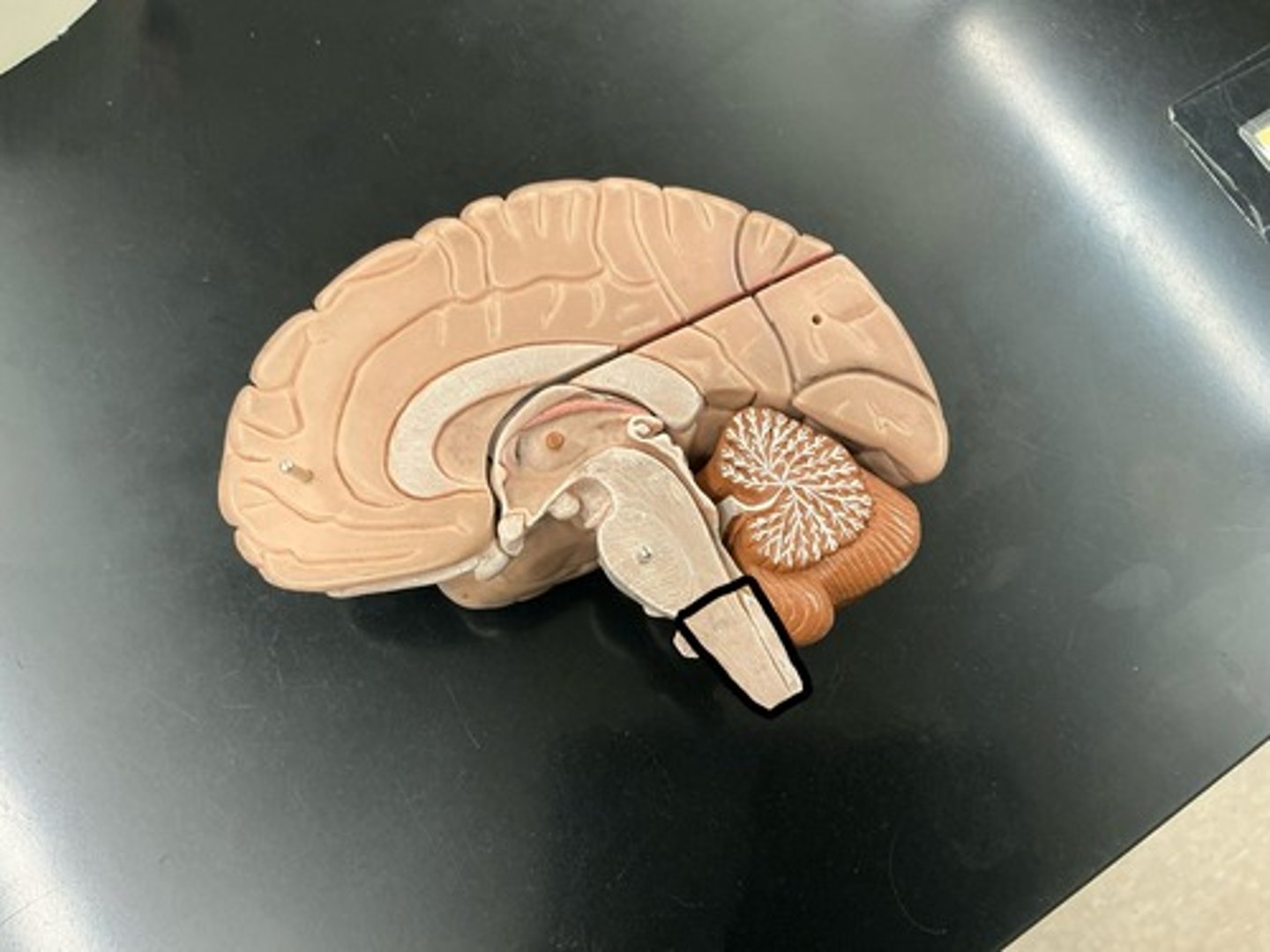
Midbrain/mesencephalon: superior part of brainstem
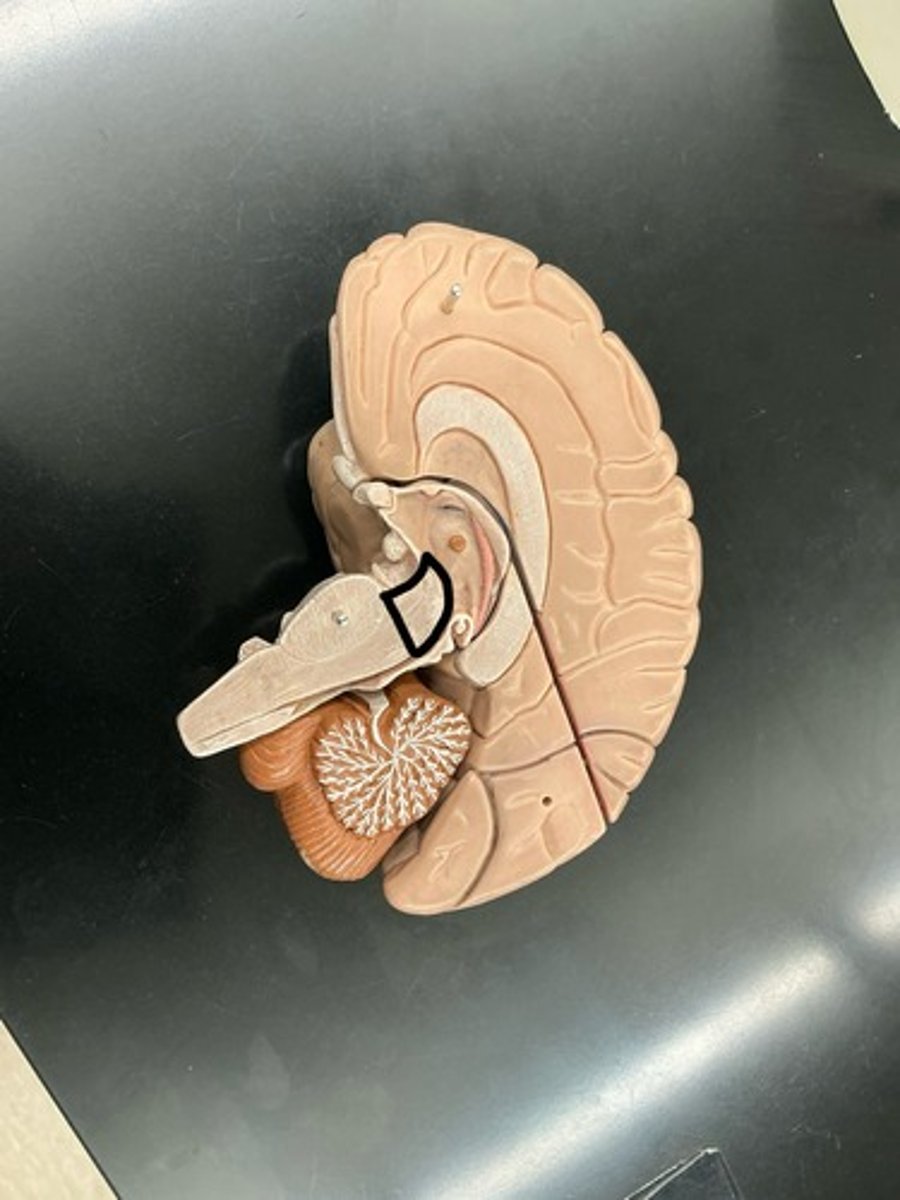
Superior colliculi: processing center for visual reflexes causing orientation towards the visual stimulus
Inferior colliculi: processing Center for auditory reflexes causing orientation towards the auditory stimulus
Pons: middle part of the brainstem
Relay centers for information going to and from cerebellum
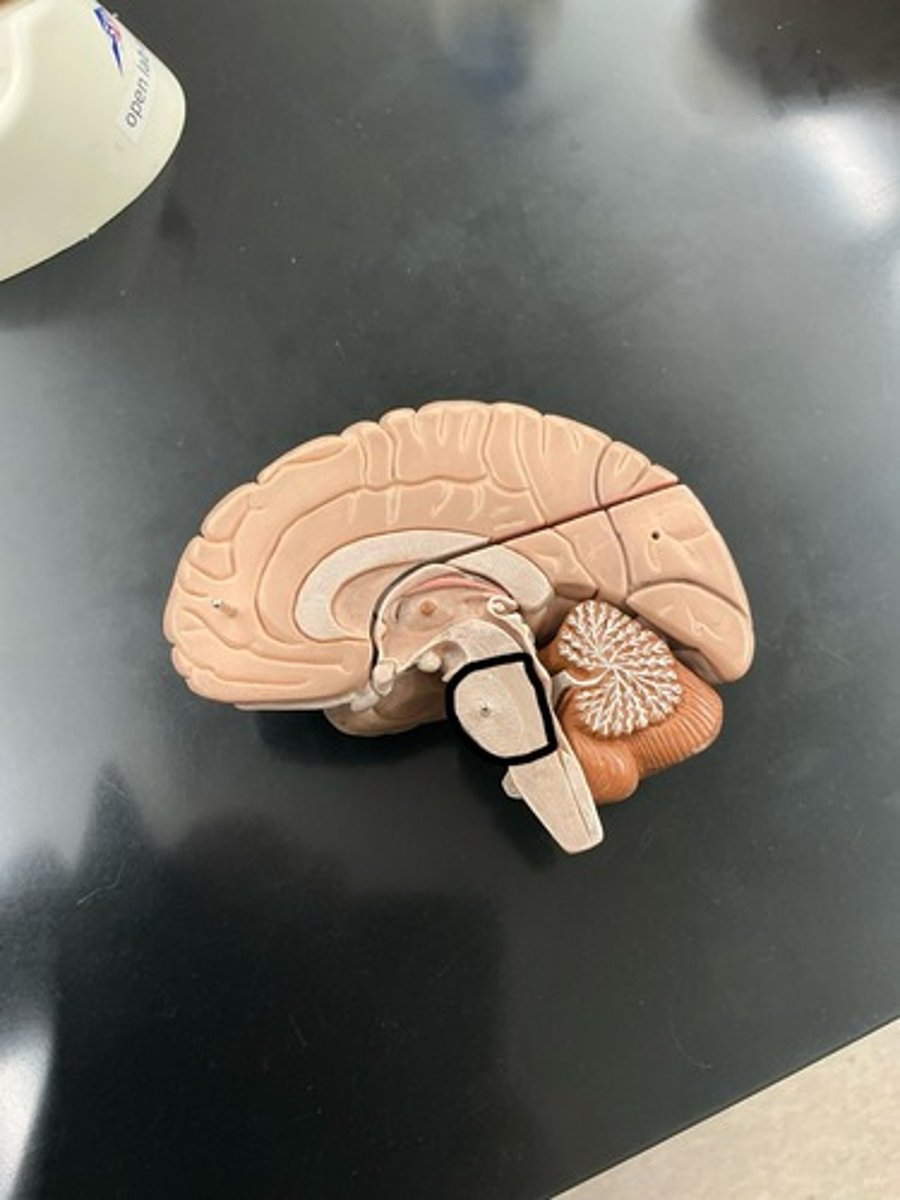
Medulla oblongata: inferior part of the brainstem
cardiovascular, vasomotor and respiratory centers
Longitudinal fissure: separates right and left cerebral hemispheres

Subdural space
Dura mater: outmost layer
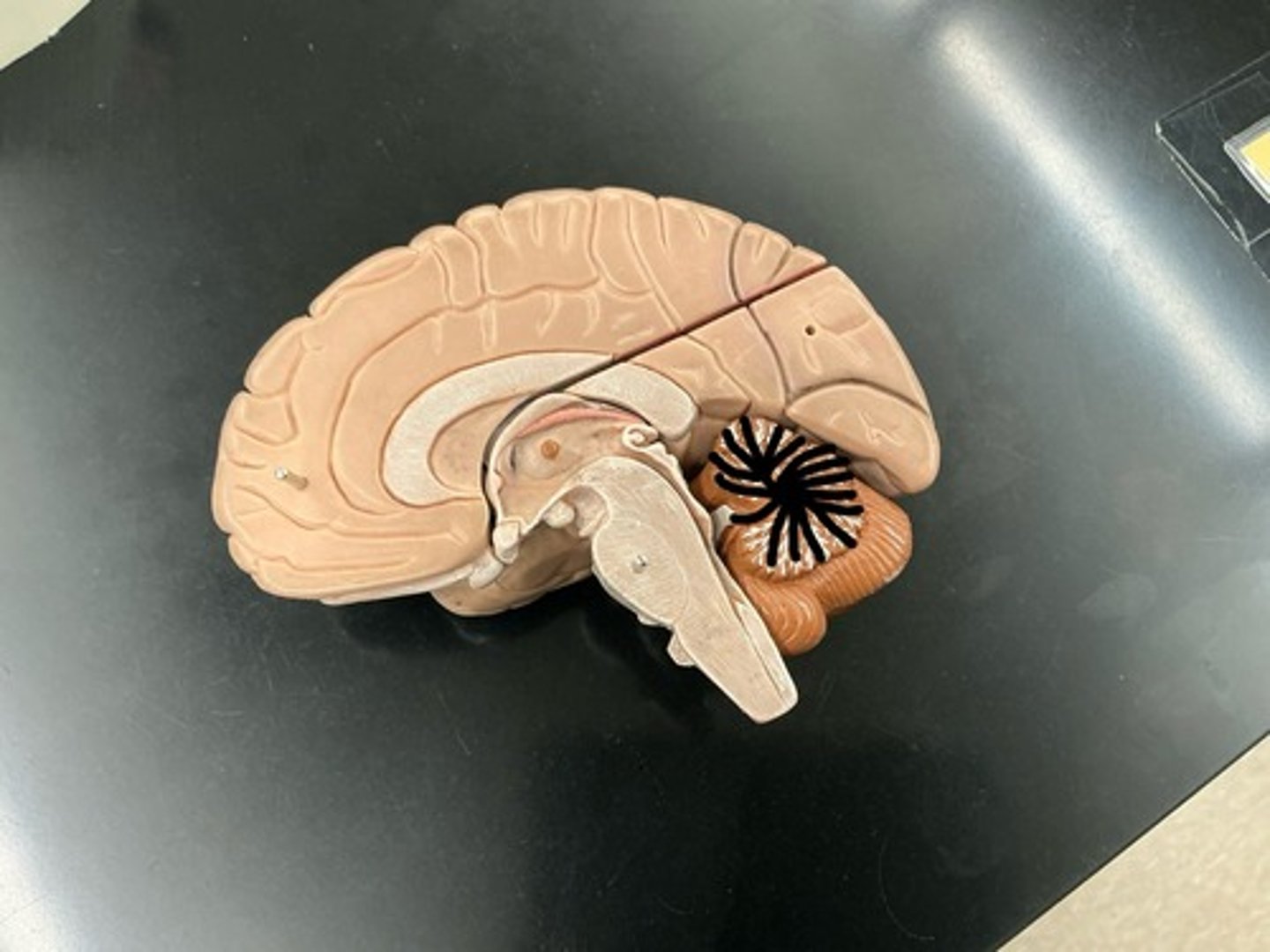
Arbor vitae: white matter within cerebellum
Arachnoid mater: middle layer
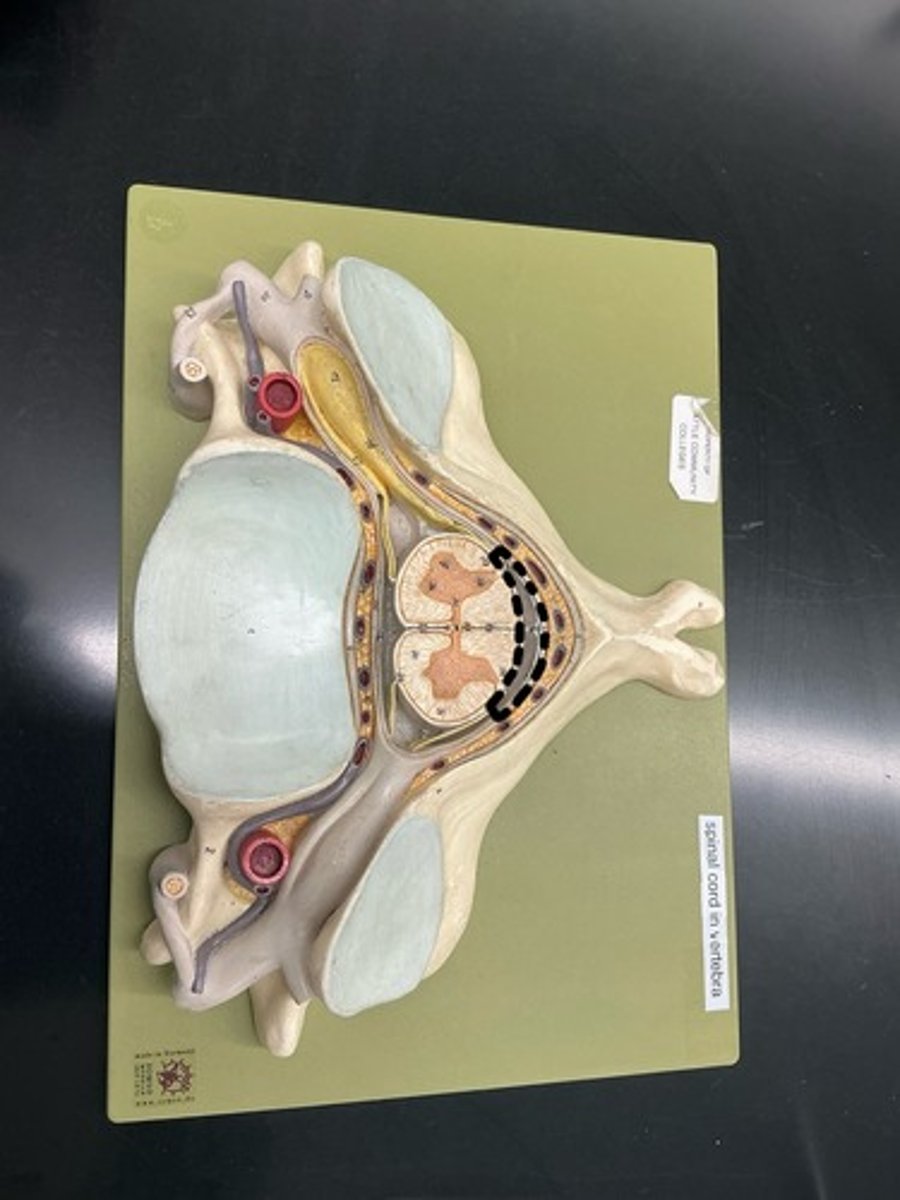
Choroid plexus: consists of combination of neuroglia and permeable capillaries, produces CSF, is found within all ventricles

Transverse fissure: separates cerebrum and cerebellum
Pia mater: innermost layer
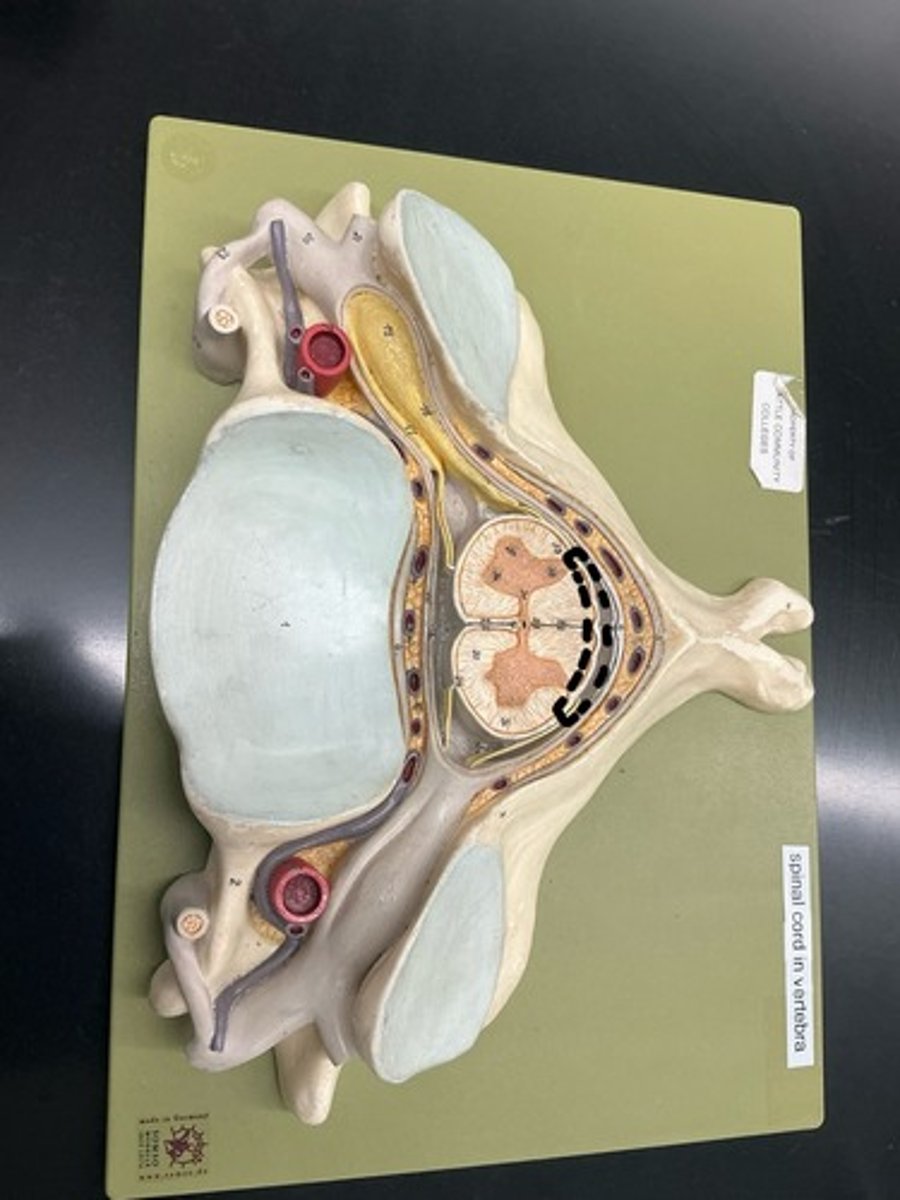
Subarachnoid space
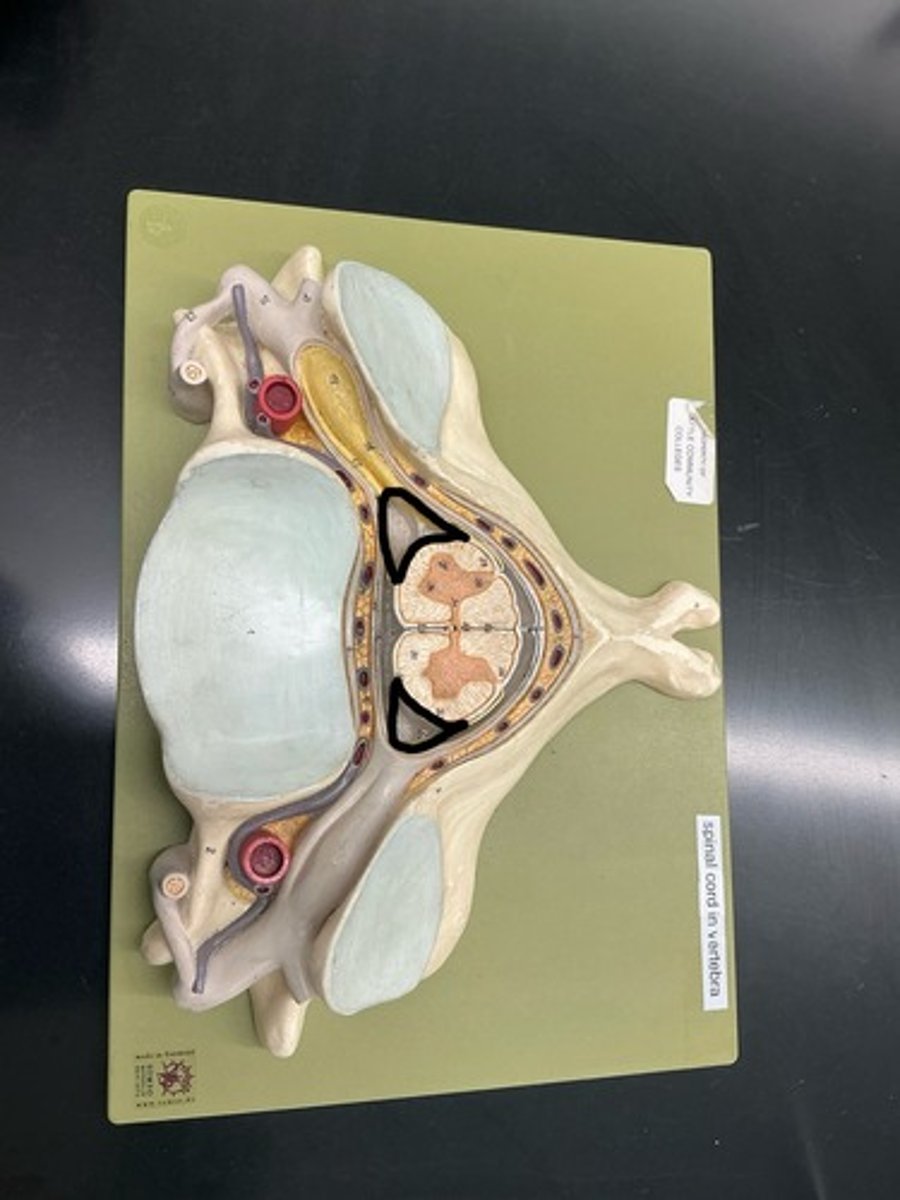
Lateral ventricles

Third ventricle
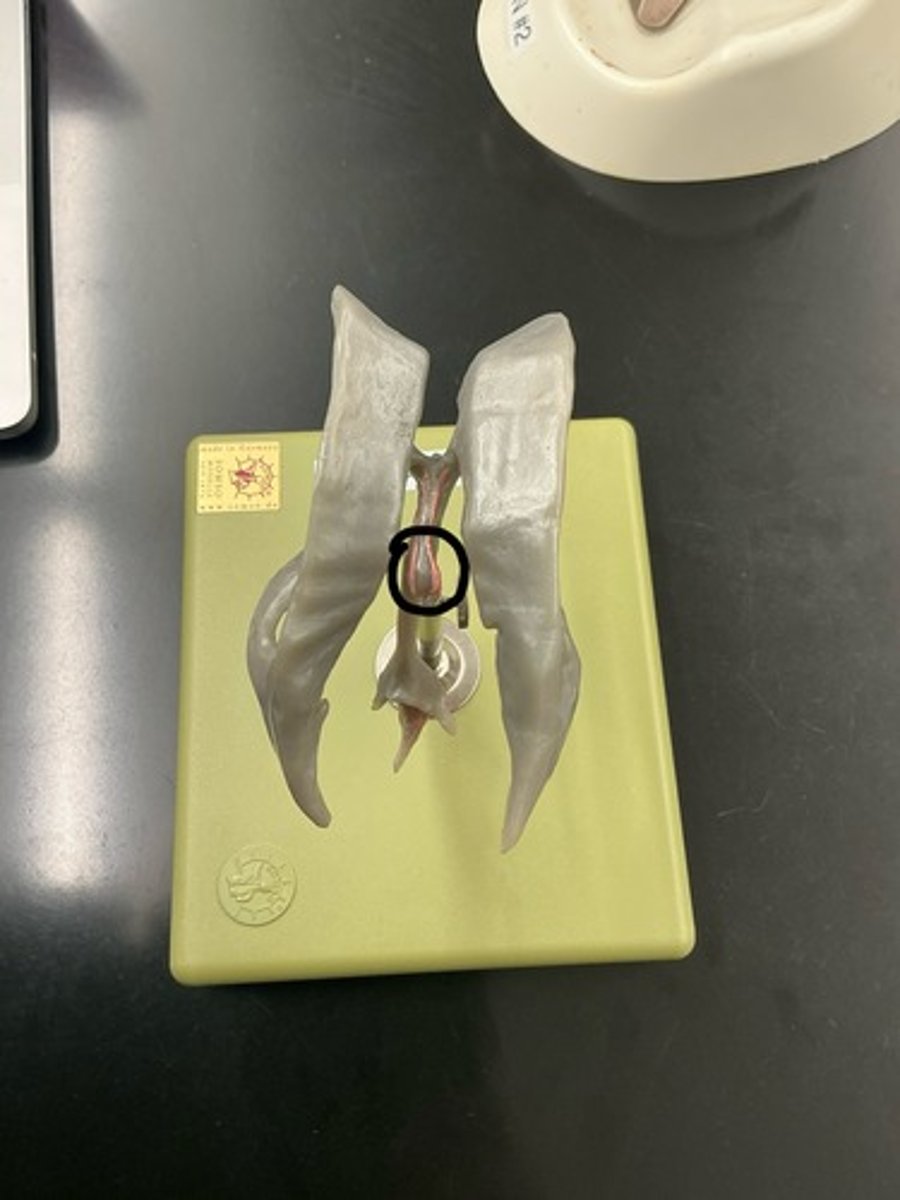
Cerebral aqueduct: is a passage way connecting 3rd ventricle to 4th
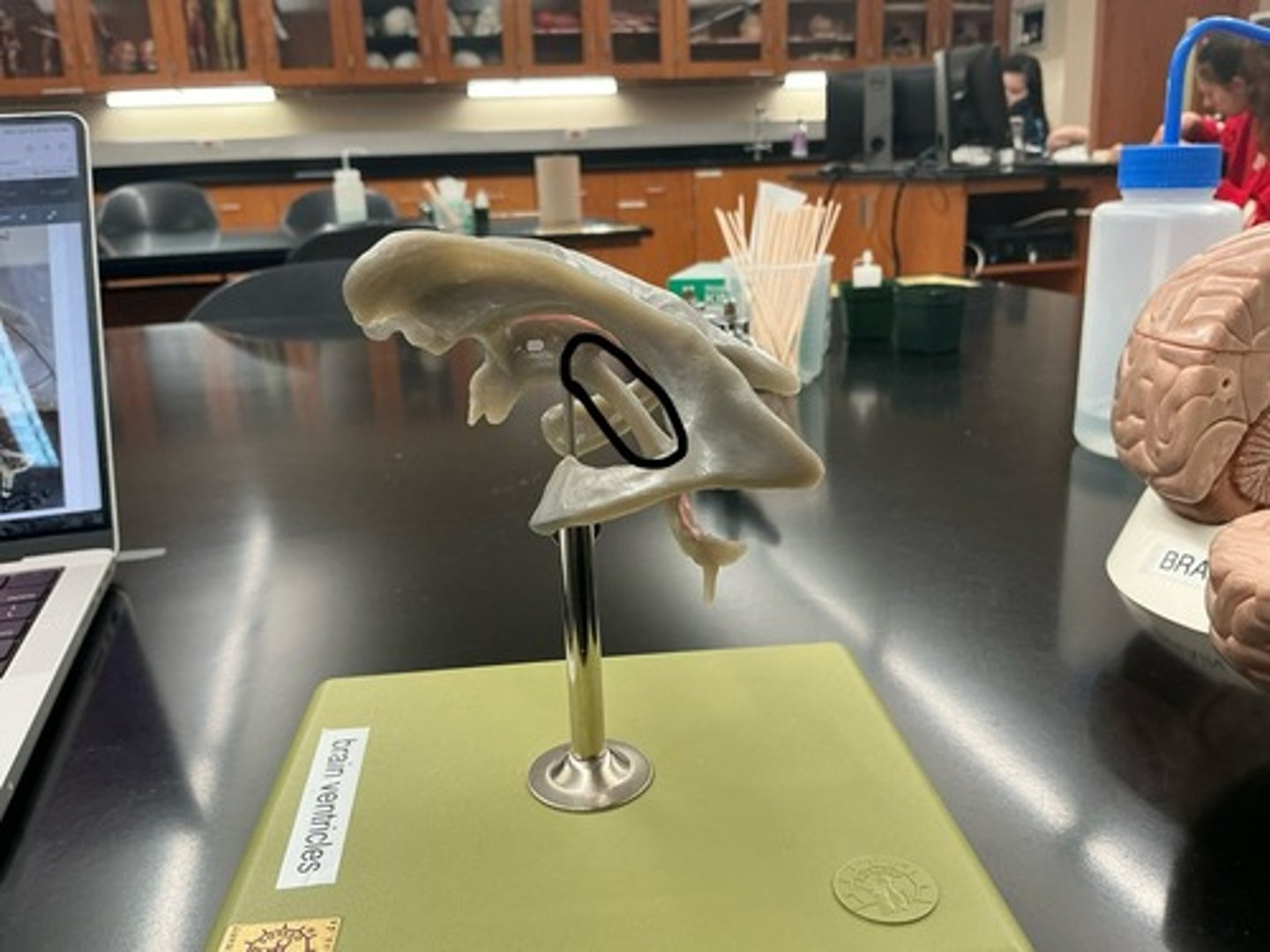
Fourth ventricle

Pia mater
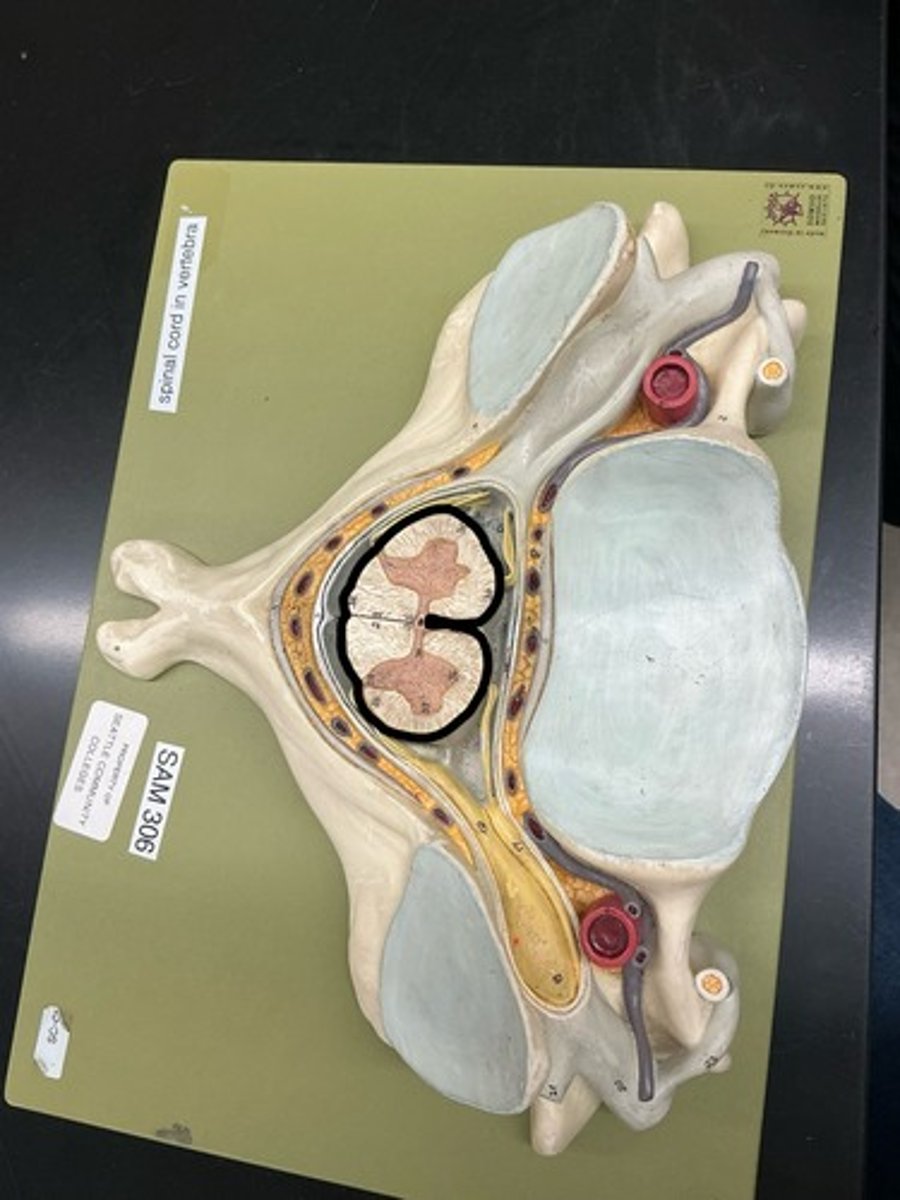
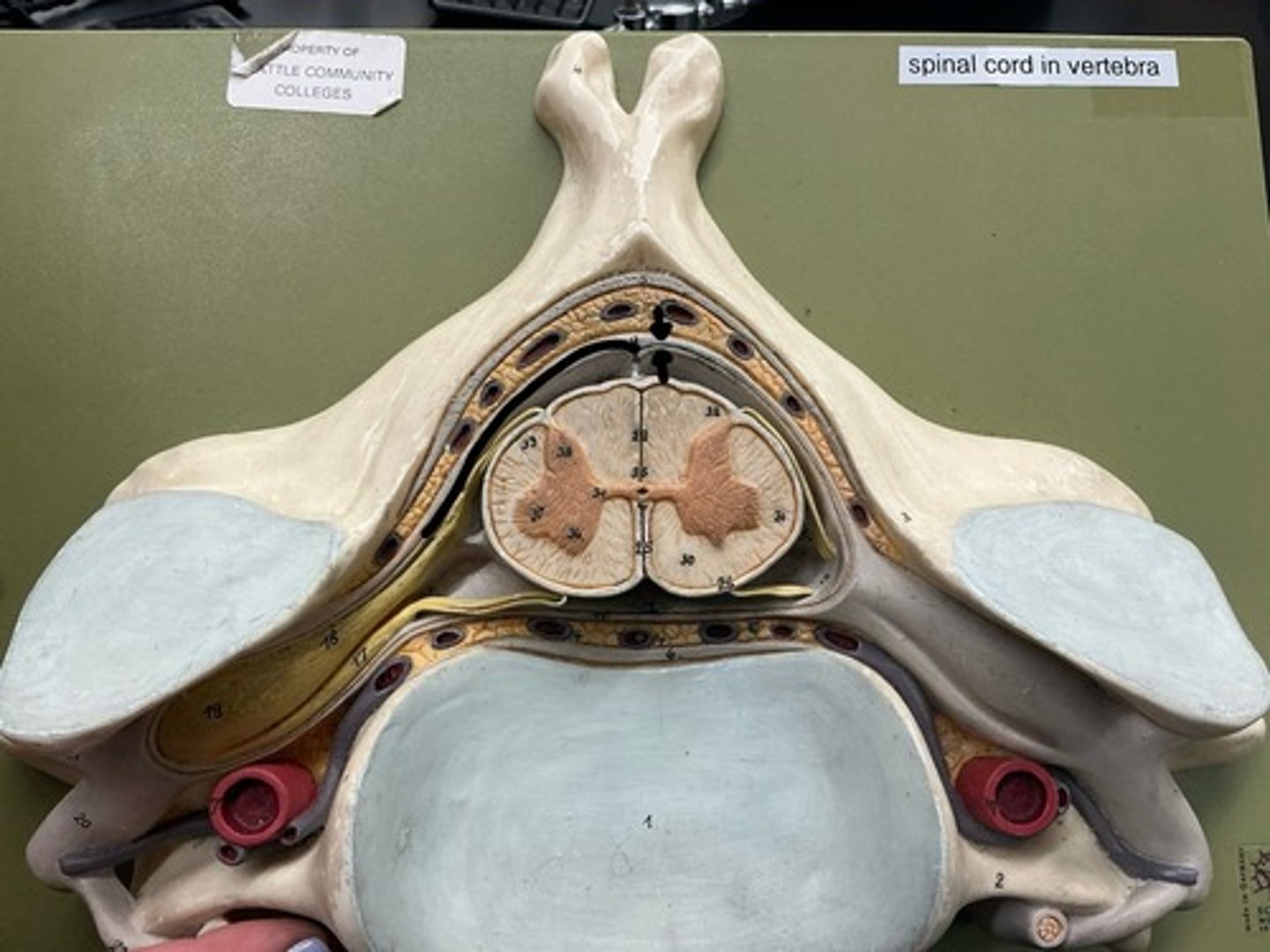
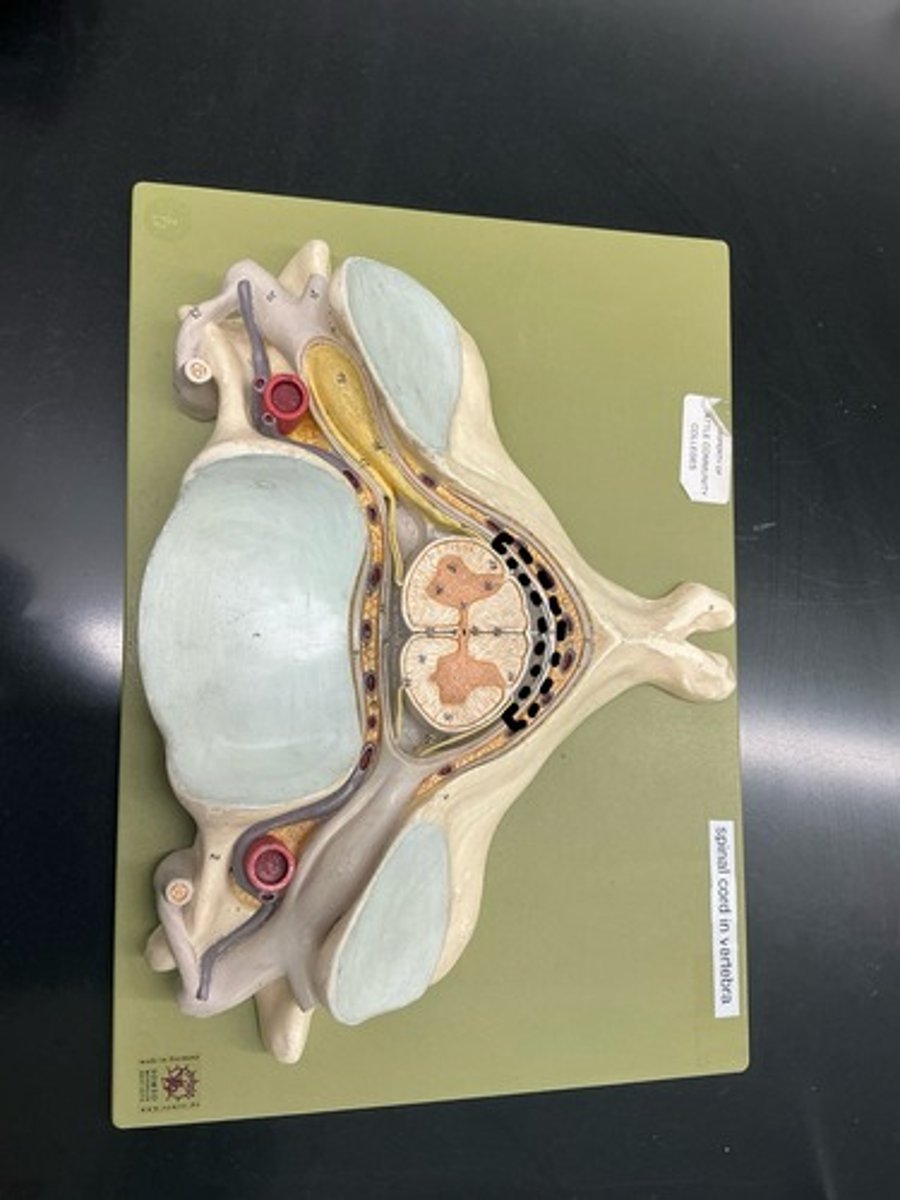
Denticulate Ligament
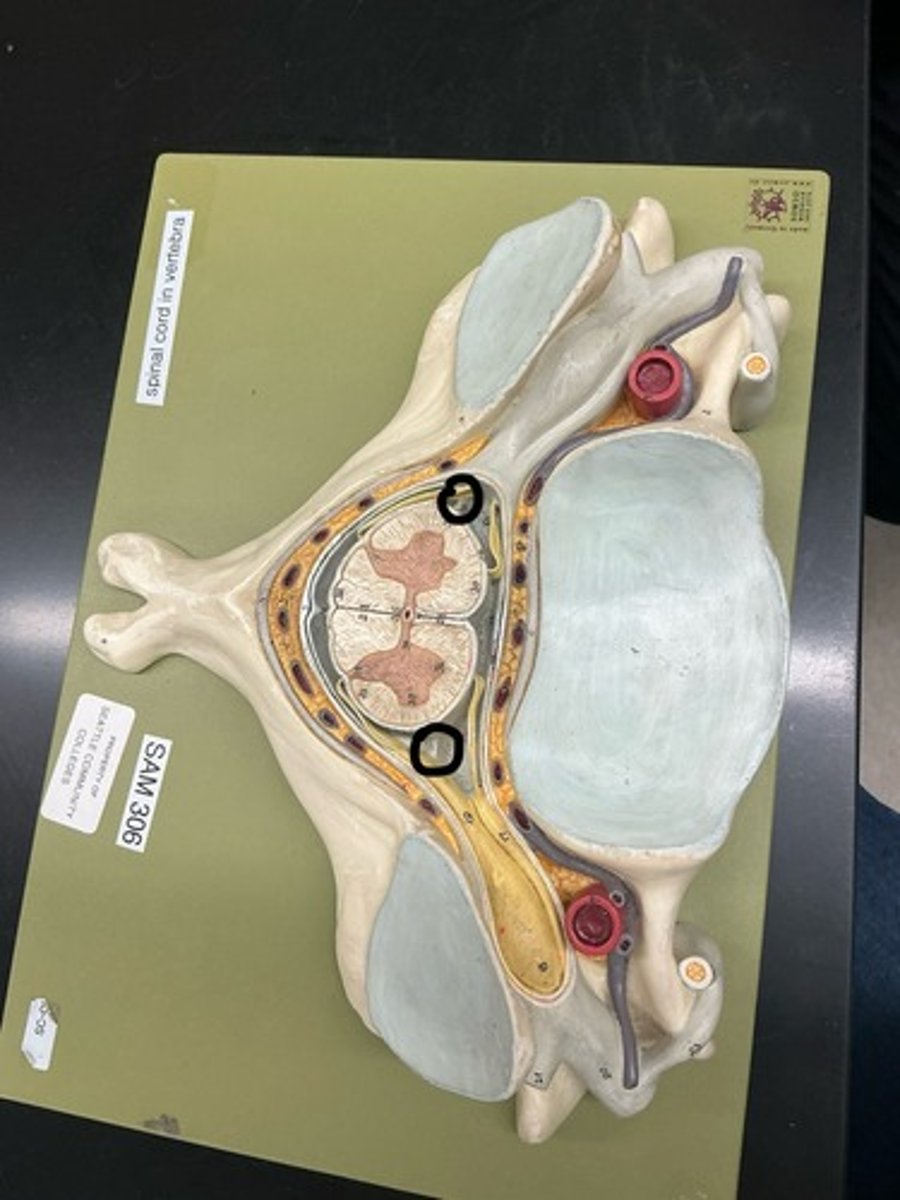
Anterior/ventral horn (somatic motor neurons)