History Final
1/98
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lt Col Barnes Class
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
Strategic Level
The highest level of war where national leaders set long-term goals, allocate resources, and determine why and under what conditions a nation goes to war. Focuses on achieving broad political and military end states.
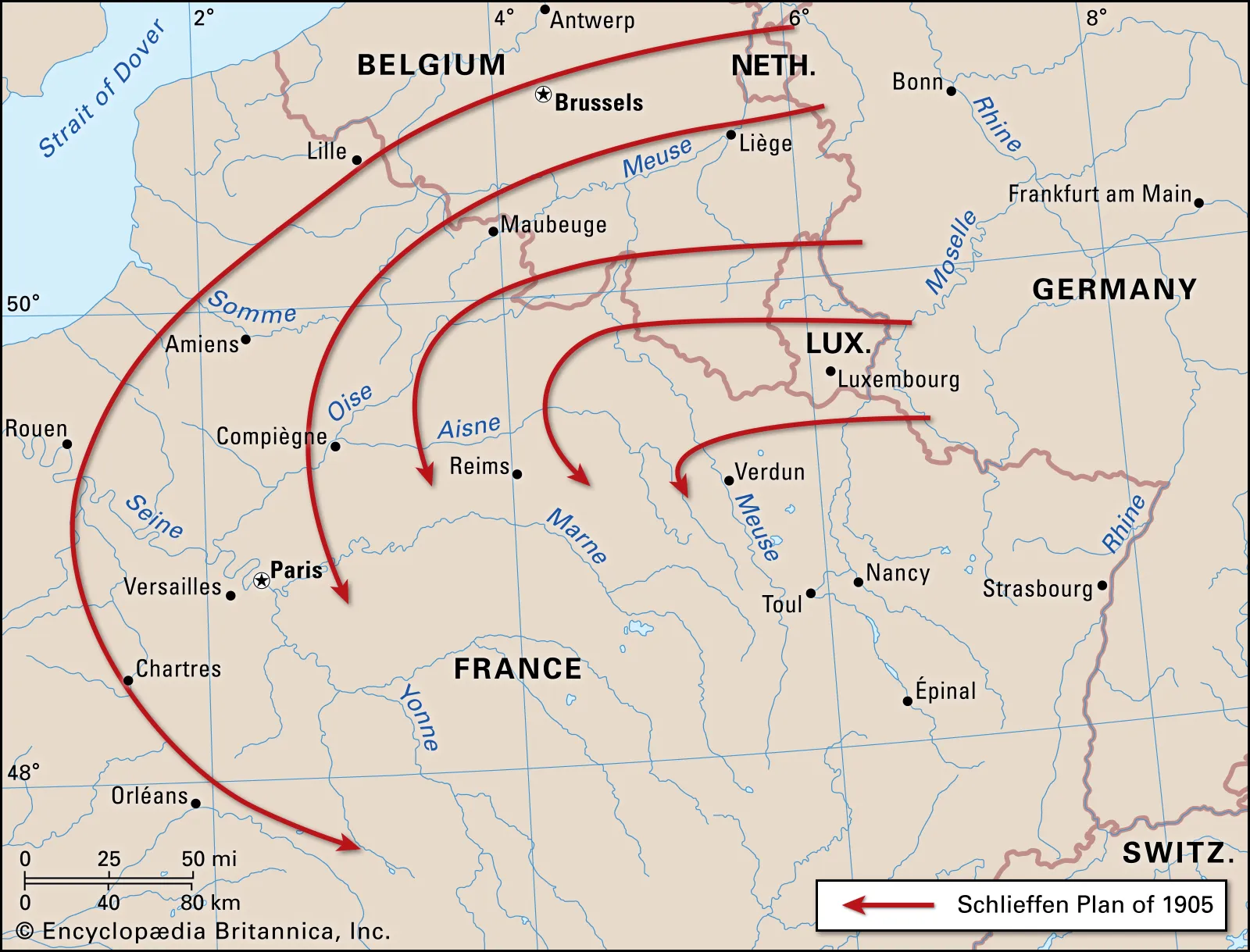
Schlieffen Plan
Germany’s pre-WWI plan to quickly defeat France by sweeping through Belgium, encircling Paris, and then turning east to fight Russia. Relied on rapid movement and overwhelming force but failed due to logistical issues and strong Allied resistance.
Adolf Hitler
Dictator of Nazi Germany whose strategic objectives—territorial expansion, racial ideology, and total war—drove Europe into WWII. He controlled Germany’s national strategy and directed major military decisions.

Joe Rochefort
U.S. naval intelligence officer whose cryptanalysis broke key Japanese codes before the Battle of Midway, allowing the U.S. to anticipate Japanese movements and win a decisive victory.

Mao Zedong
Leader of the Chinese Communist forces who used protracted warfare and guerrilla strategy to wear down opponents. Represents the strategic use of attrition and political mobilization to win long conflicts.

Al-Qaeda
A transnational terrorist organization whose strategy emphasizes asymmetric warfare—small, decentralized cells targeting political, economic, and symbolic structures to achieve ideological goals.

Operational Level
The level of war that links strategy to tactics. It focuses on campaigns, sequencing major operations, coordinating logistics, maneuver, movement of forces, and shaping battles to achieve strategic goals.
Helmuth von Moltke the Younger
German Chief of Staff in WWI who modified the Schlieffen Plan. His changes—weakening the right wing and strengthening forces in the east—contributed to operational failures in 1914.

Benito Mussolini
Italian fascist leader whose poor strategic decision-making and weak military structure led to repeated operational failures in WWII, requiring German intervention to stabilize Italy’s fronts.

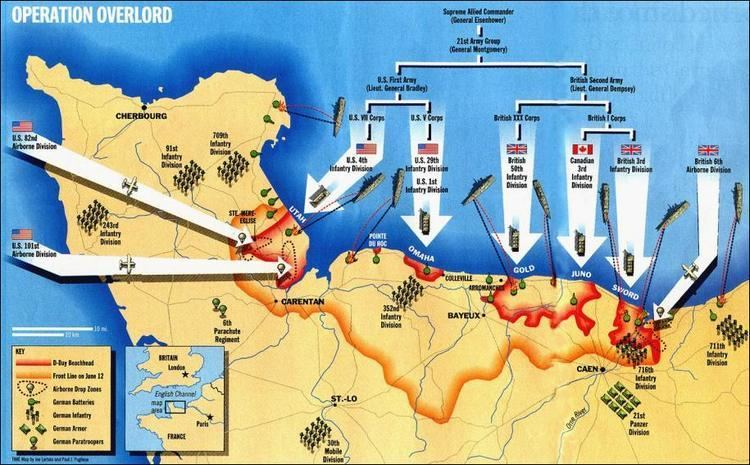
Operation Overlord
The Allied D-Day invasion of Nazi-occupied France (June 6, 1944). A massive operational campaign integrating land, air, and naval forces to open a Western front and weaken Germany.
Marshall Plan
A U.S. post-WWII economic recovery program aimed at stabilizing Europe. While not a battle plan, it served a strategic-operational purpose by preventing Soviet influence through economic strength.
Osama Bin Laden
Leader of Al-Qaeda who orchestrated 9/11. Represented the operational and strategic direction of a global terrorist network using asymmetric attacks to influence U.S. policy.

Tactical Level
The level of war focused on individual battles and engagements. It involves how units maneuver, fight, and apply force to achieve immediate, localized objectives that contribute to operational success.
Triple Entente
WWI alliance between France, Russia, and Britain, formed to counter Germany and the Triple Alliance. The alliance shaped strategic and operational coordination in WWI.
Hideki Tojo
Prime Minister of Japan during WWII who approved the attack on Pearl Harbor. Known for directing Japan’s wartime military strategy and expansion across the Pacific.

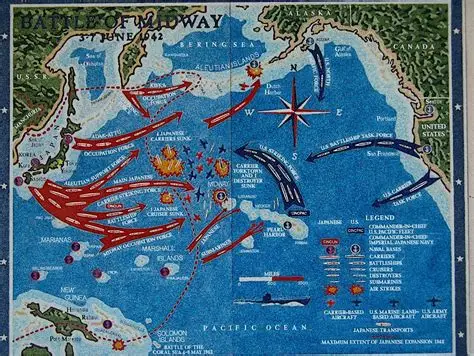
Battle of Midway
Turning point of the Pacific War (June 1942). U.S. codebreaking enabled a surprise attack that destroyed four Japanese carriers, shifting strategic initiative to the Allies.
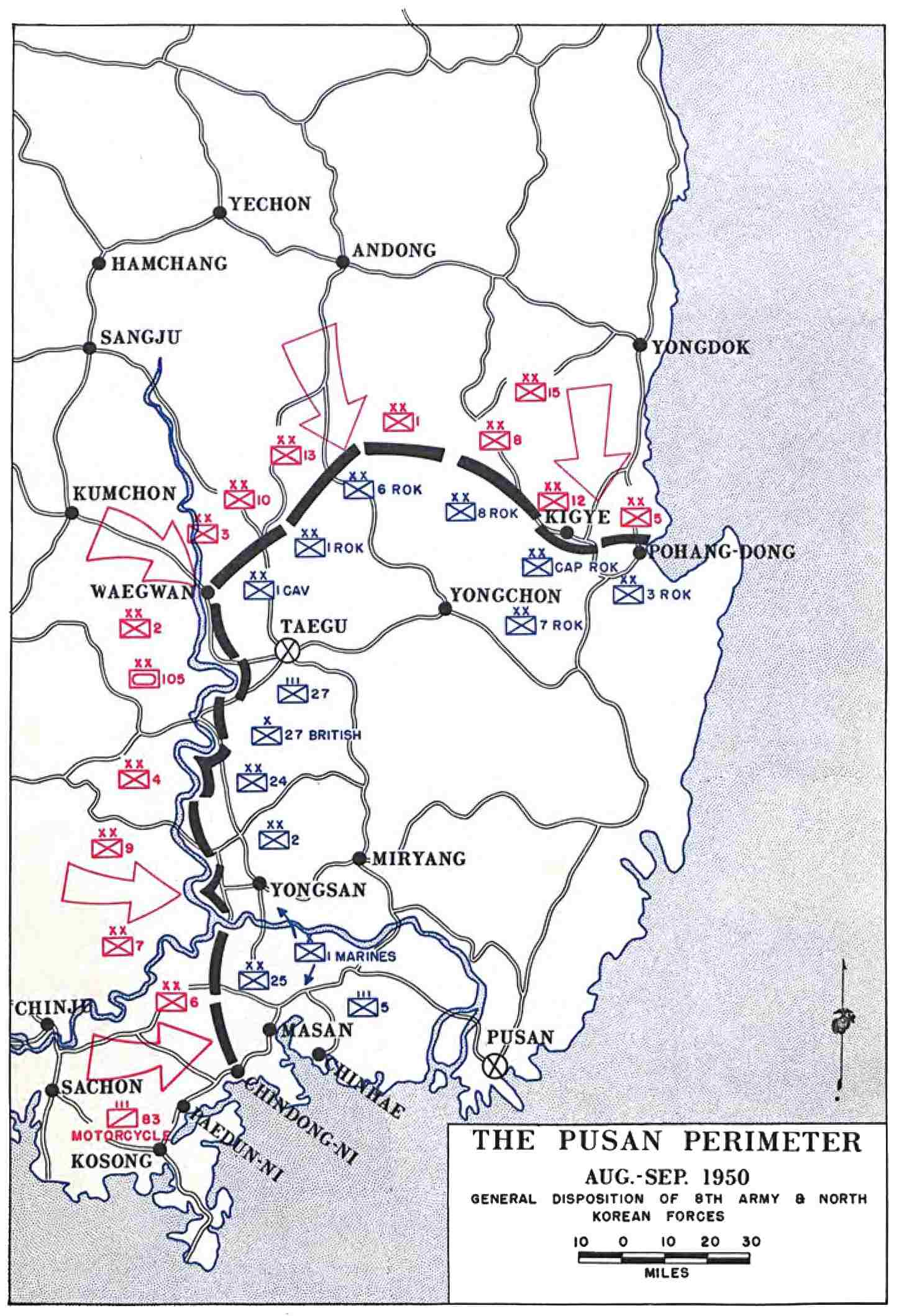
Pusan Perimeter
Defensive line held by UN and U.S. forces in the first months of the Korean War (1950). Successful defense prevented South Korea’s collapse and allowed for later offensive operations.
Taliban
Islamic fundamentalist movement that governed Afghanistan and provided sanctuary to Al-Qaeda. Known for guerrilla tactics and prolonged insurgency against U.S./NATO forces.

Center of Gravity (COG)
The source of a force’s strength—moral, physical, or organizational—that is essential for maintaining combat power. Destroying or neutralizing it disrupts enemy operations
Triple Alliance
WWI alliance of Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy (though Italy later defected). Formed as a counterbalance to the Triple Entente.
Billy Mitchell
U.S. airpower pioneer who argued that aircraft could be decisive in warfare. Demonstrated the power of air attack by sinking captured battleships; influenced the growth of the USAF.

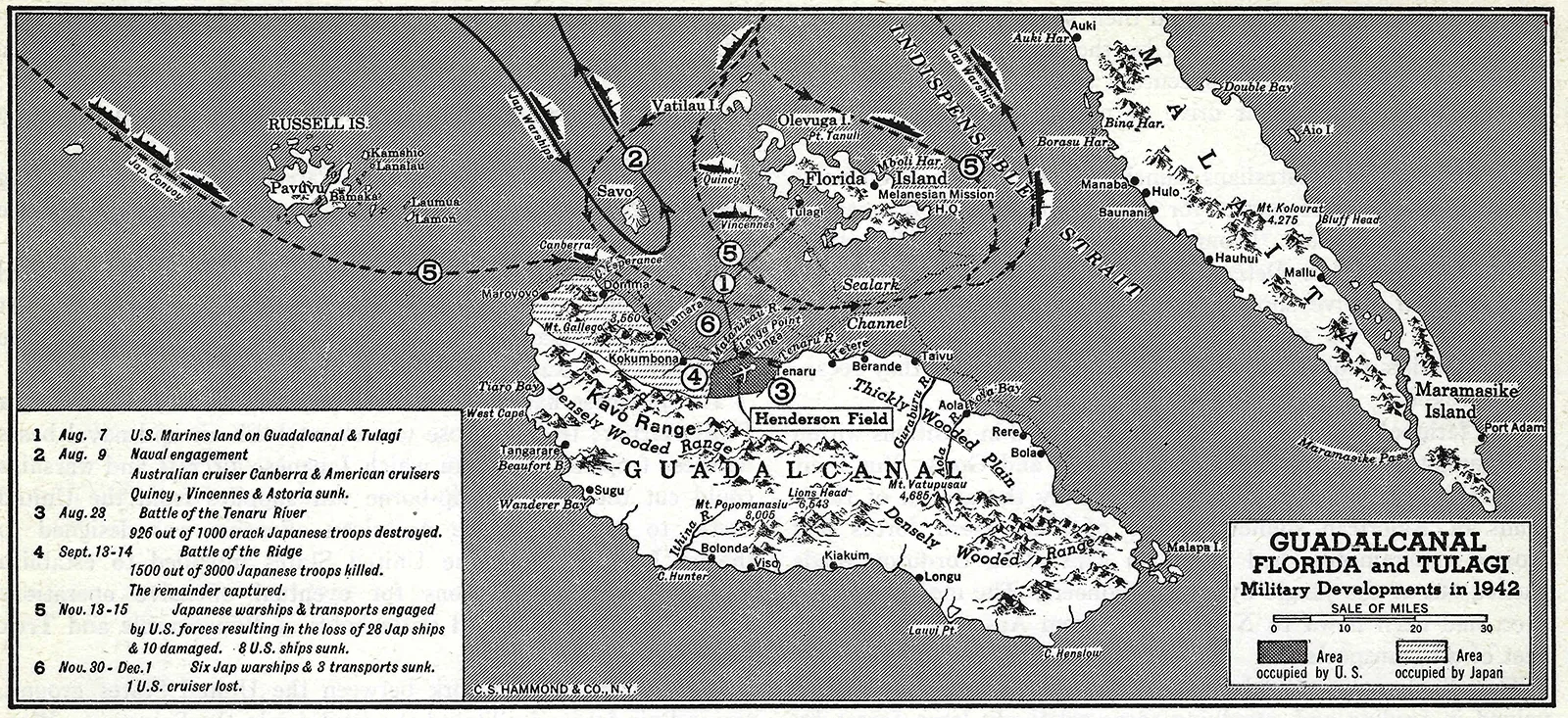
Battle of Guadalcanal
First major U.S. offensive in the Pacific (1942–43). A long, brutal campaign that stopped Japanese expansion and shifted momentum to the Allies.
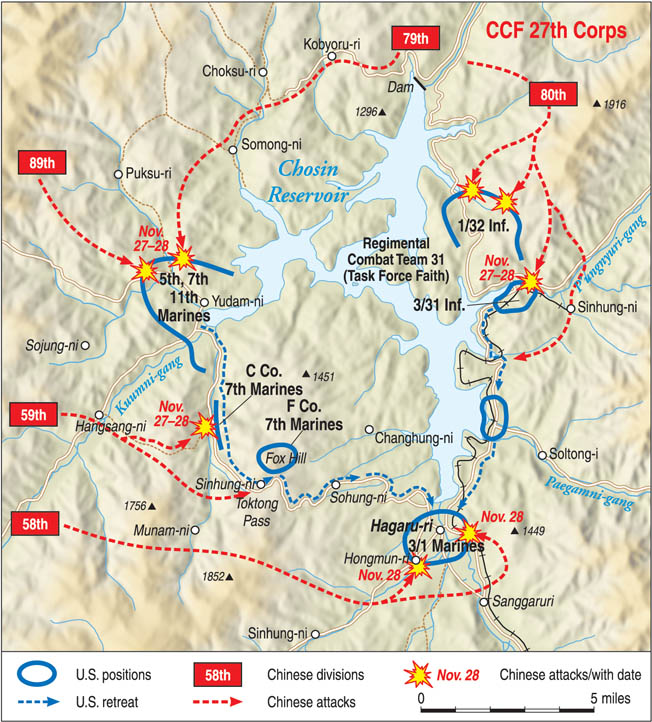
Chosin Reservoir
Brutal Korean War battle (1950) where U.S. Marines fought their way out of encirclement by Chinese forces in freezing conditions. Demonstrated discipline, logistics, and tactical resilience.
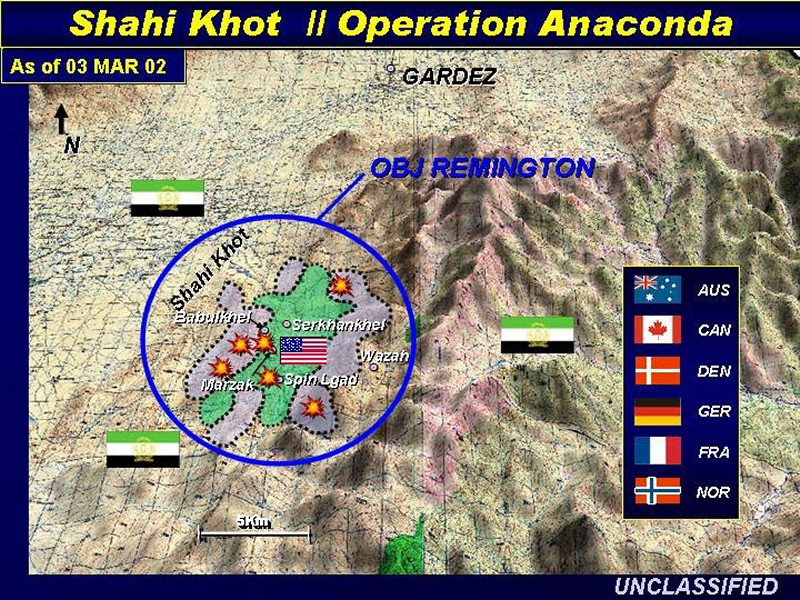
Operation Anaconda
Early Afghanistan War operation (2002) aimed at destroying Taliban and Al-Qaeda fighters in the Shah-i-Kot Valley. Revealed weaknesses in joint coordination but demonstrated evolving U.S. air-ground integration.
Attrition
A form of strategy focused on wearing down the enemy over time through continuous losses in manpower, material, and morale. Timeframe is long, targeting mainly military forces.
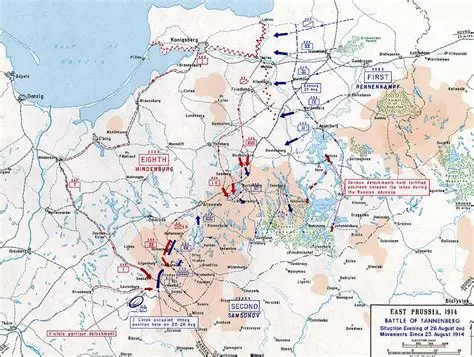
Battle of Tannenberg
WWI battle (1914) where Germany encircled and destroyed a larger Russian army. Demonstrated superior German mobility, coordination, and use of interior lines.
Giulio Douhet
Italian airpower theorist who argued that strategic bombing could break an enemy’s will by striking cities and industry. Influential in shaping early airpower doctrine.

George Kenney
Commander of Allied air forces in the Southwest Pacific in WWII. Known for innovation, close air support, and helping isolate Japanese forces through air interdiction.

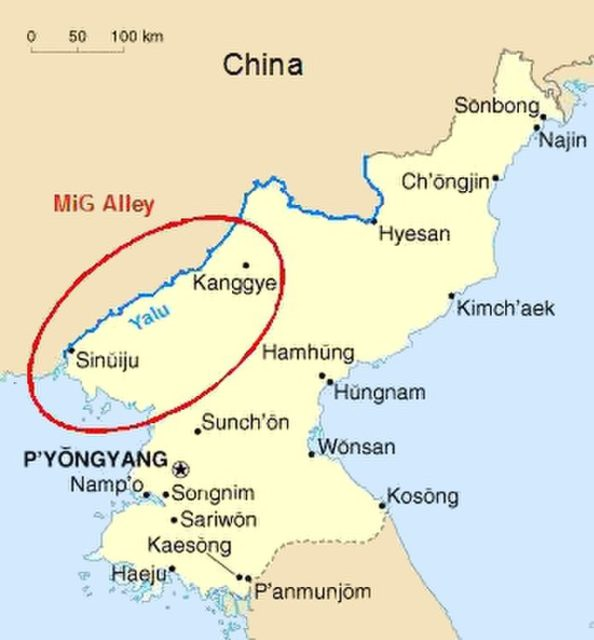
MiG Alley
Nickname for the northwestern region of North Korea where intense jet combat occurred between U.S. F-86 Sabres and Soviet-built MiG-15s during the Korean War.
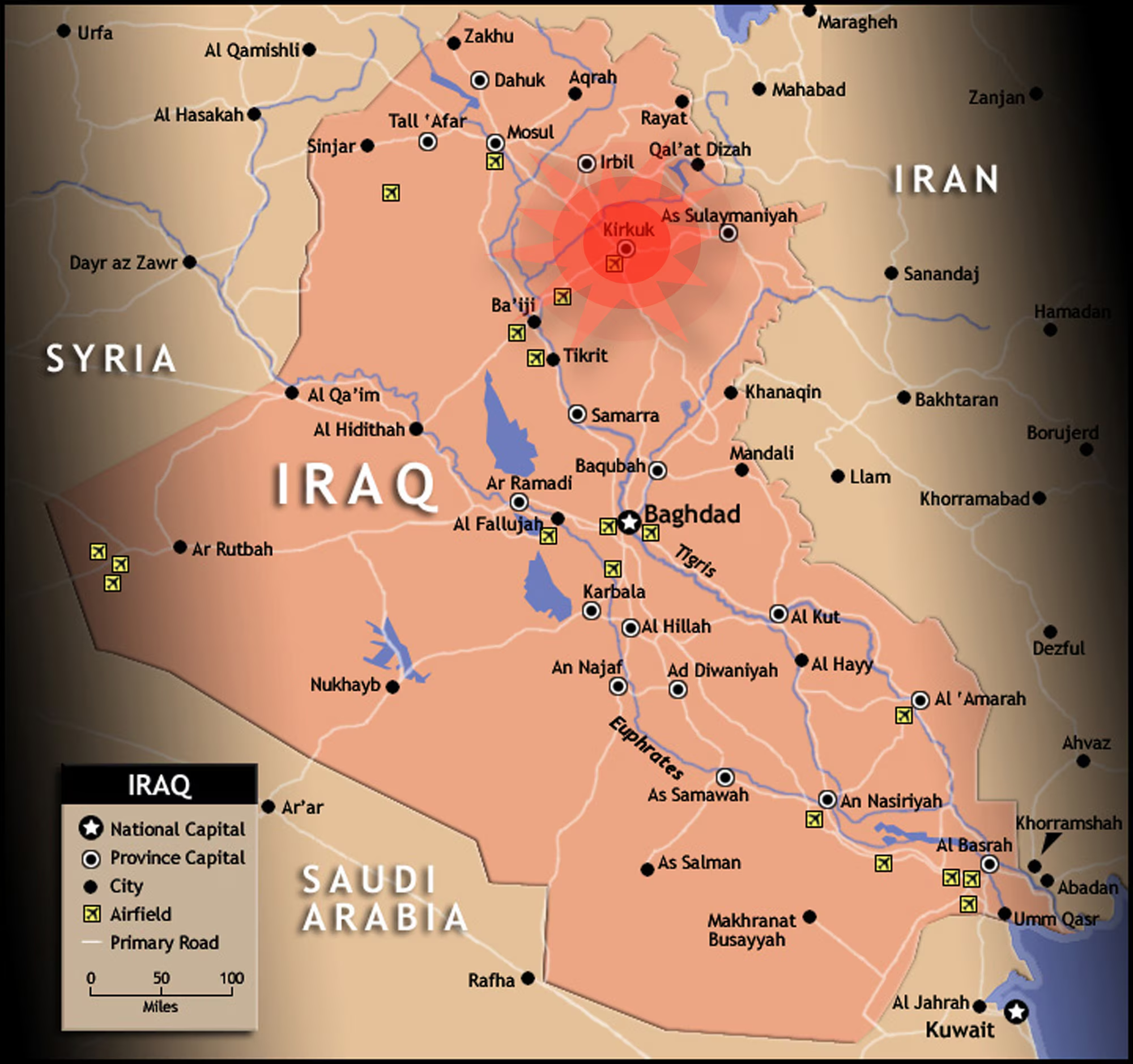
Operation Iraqi Freedom
U.S.-led invasion of Iraq (2003) aimed at overthrowing Saddam Hussein and eliminating supposed WMDs. Rapid initial success followed by prolonged insurgency.
Annihilation
A form of strategy seeking rapid, decisive destruction of an enemy’s forces—typically through overwhelming force in a short timeframe. Focuses primarily on military targets.
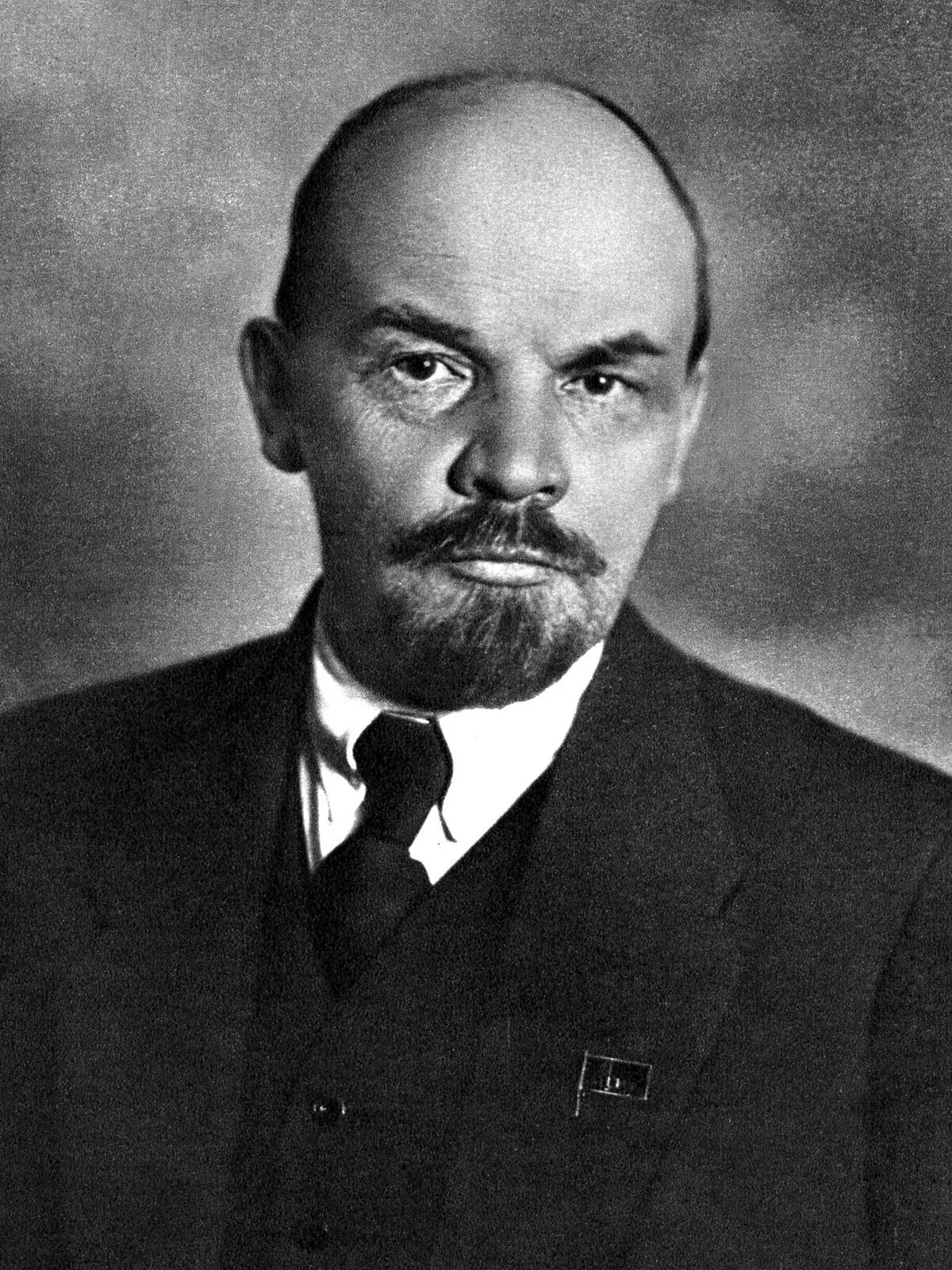
Vladimir Lenin
Leader of the Bolshevik Revolution. Pulled Russia out of WWI via the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk and promoted political/military revolution as a means of achieving power.

Sir Hugh Trenchard
Considered the father of the Royal Air Force. Advocated for offensive airpower and the idea that air forces should strike deep to maintain initiative.

Operation Downfall
Planned but never executed Allied invasion of Japan during WWII. Estimated massive casualties, ultimately avoided due to Japan’s surrender after atomic bombs.
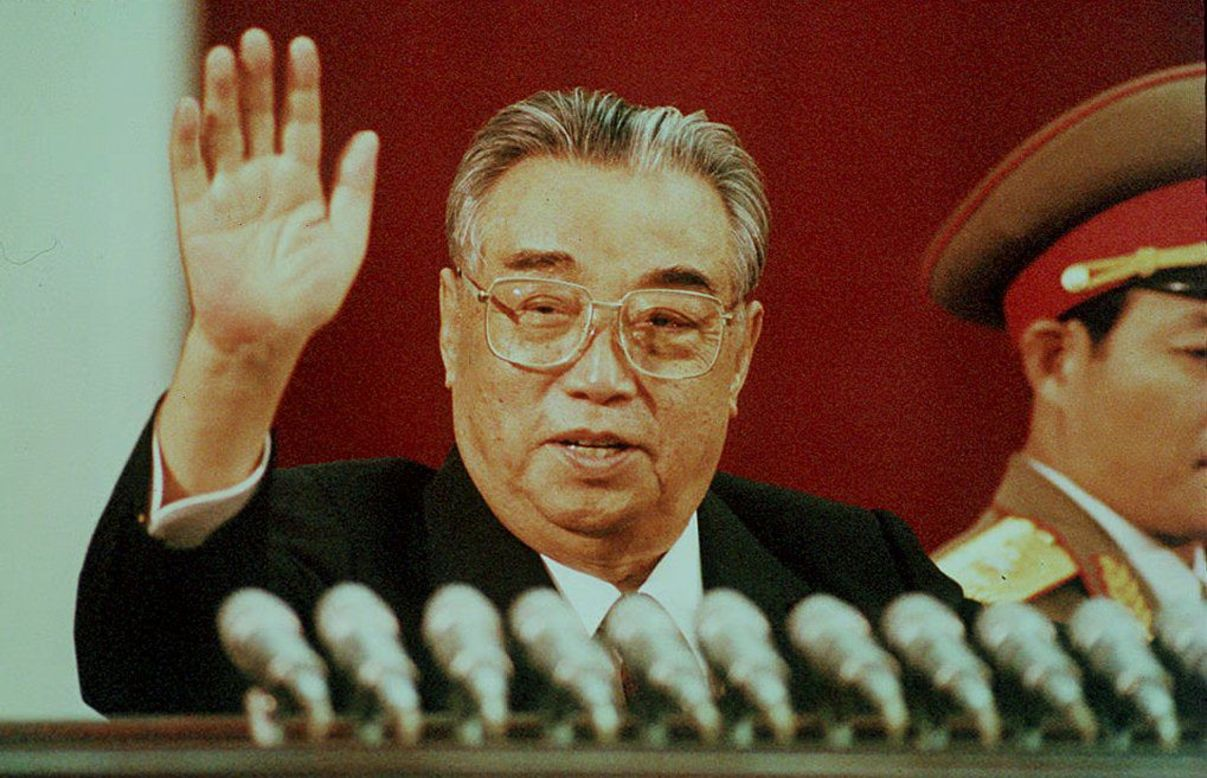
Kim Il-Sung
Founding leader of North Korea. Ordered the 1950 invasion of South Korea, which triggered the Korean War.

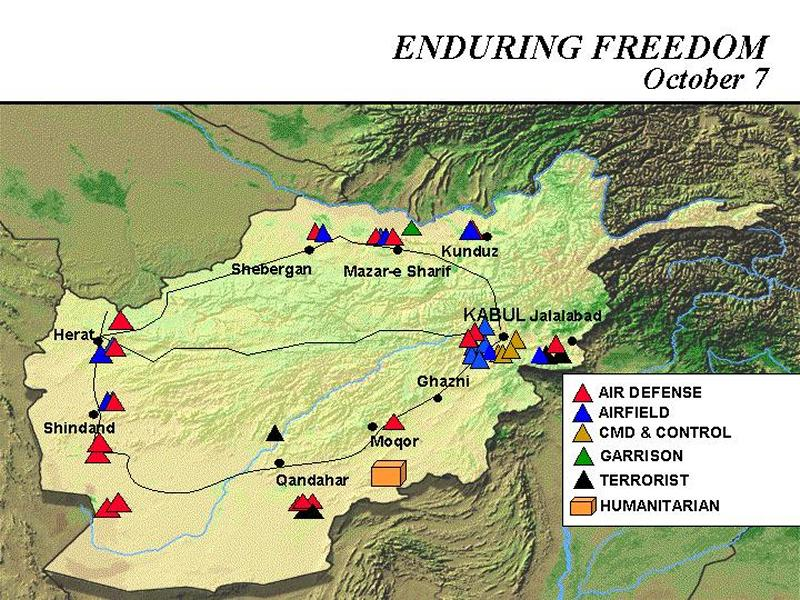
Operation Enduring Freedom
U.S.-led campaign in Afghanistan (2001–2014) following 9/11. Aimed to destroy Al-Qaeda and remove the Taliban from power.
Exhaustion
A form of strategy aimed at eroding an enemy’s society, economy, and internal stability rather than just military forces. Achieves victory by breaking national will over a long period.
Zimmerman Note
1917 German telegram proposing an alliance with Mexico against the U.S. Intercepted and decoded, contributing to U.S. entry into WWI.
Blitzkrieg
German “lightning war” doctrine using rapid, coordinated attacks by tanks, aircraft, and mechanized infantry to break enemy lines before they can react.
Hermann Goering
Commander of the German Luftwaffe in WWII. Oversaw early successes but later failures such as the Battle of Britain.

Syngman Rhee
First president of South Korea. His government was supported by the U.S. during the Korean War against North Korean and Chinese forces.

Surge
Refers to the 2007 increase in U.S. troop levels during the Iraq War. Improved security by changing counterinsurgency strategy and increasing presence on the ground.
Battle of the Somme
Massive WWI battle (1916) marked by weeklong artillery barrages and catastrophic casualties. Demonstrated the difficulty of attacking trench systems and led to tactical changes.
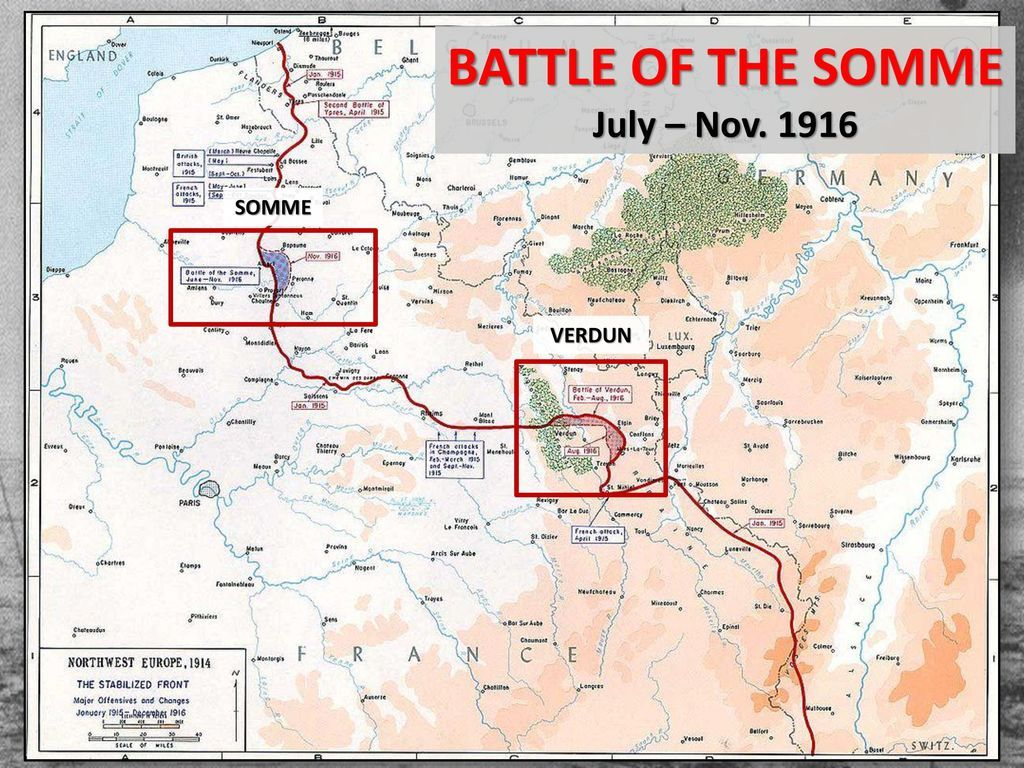
Dunkirk
1940 evacuation where Allied forces escaped encirclement by German armies in France. Saved over 300,000 troops, preserving the British Army.
Wernher von Braun
German rocket scientist who developed the V-2 rocket, later key figure in the U.S. space program and the Apollo missions.

David Petraeus
U.S. Army general who led the Iraq War Surge and heavily influenced modern counterinsurgency doctrine (COIN).

Otto von Bismarck
Prussian statesman who unified Germany through limited wars with Denmark, Austria, and France. Practiced “Realpolitik” and preferred limited war with limited ends.

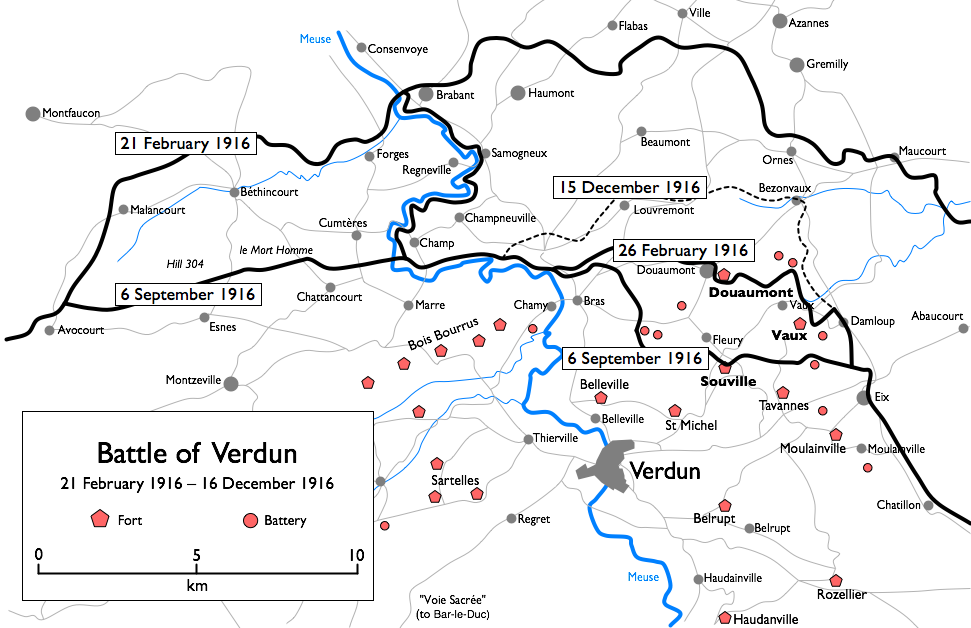
Battle of Verdun
Longest battle of WWI (1916). German goal was to “bleed France white.” Ultimately a French defensive victory, symbolizing national resolve and the horrors of attrition warfare.
Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact
1939 non-aggression pact between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union. Included secret agreements to divide Eastern Europe. Enabled Germany to invade Poland and start WWII.
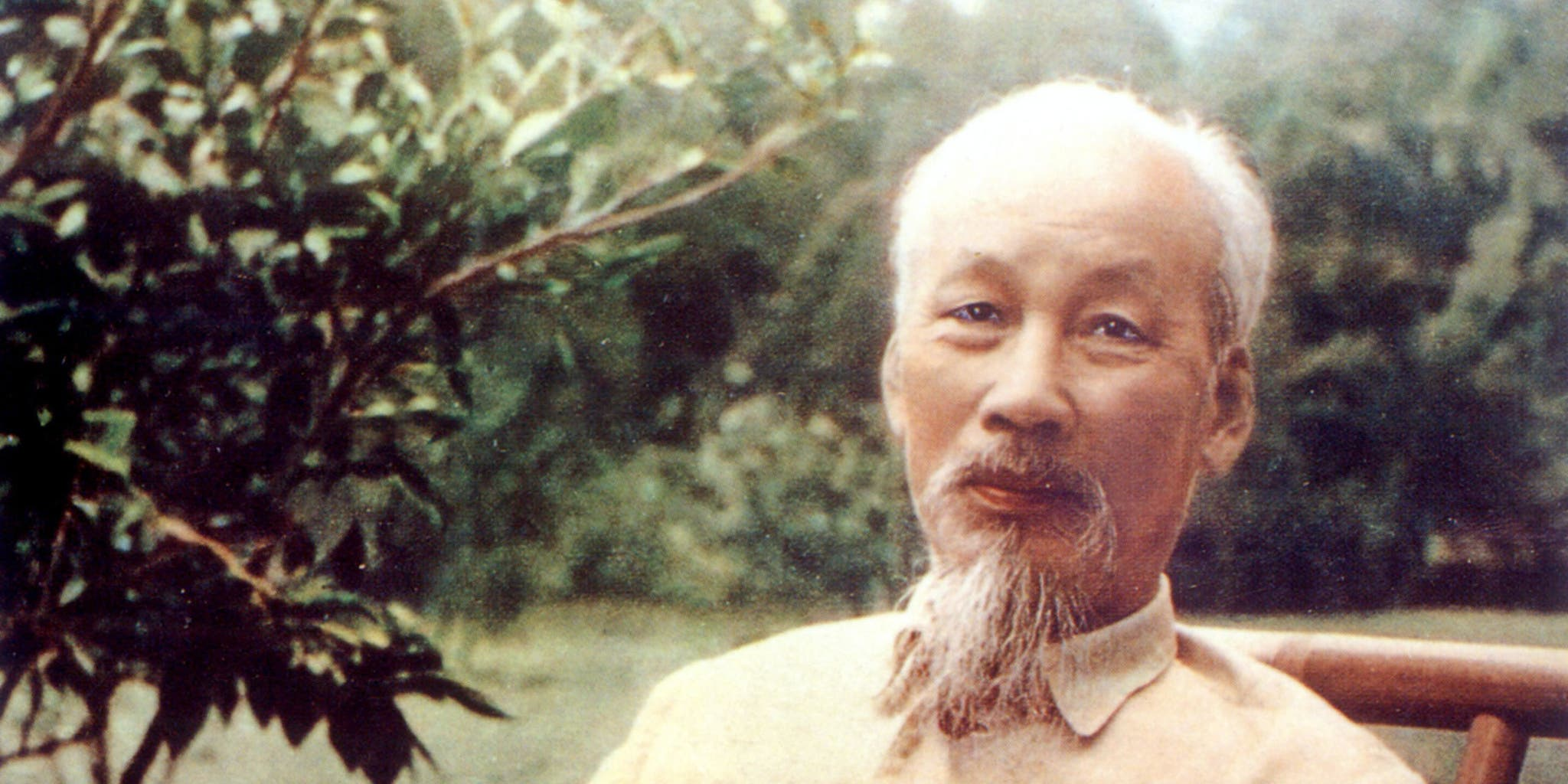
Ho Chi Minh
Leader of the Vietnamese communist movement (Viet Minh). Strategically combined nationalism and guerrilla warfare to defeat France, then the U.S.-backed South Vietnam.

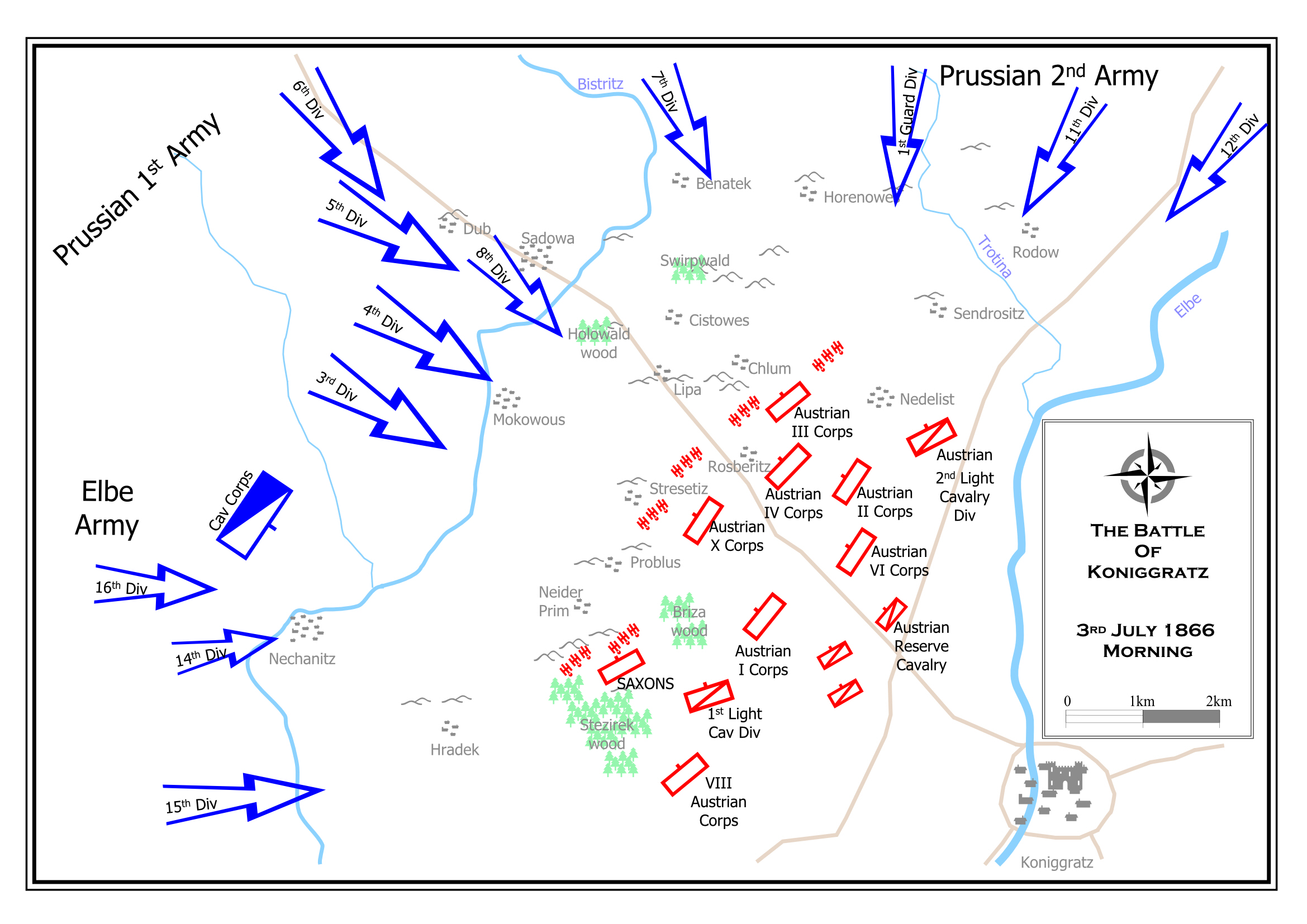
Battle of Königgrätz
Decisive 1866 Austro-Prussian War battle where Prussia used superior rail mobilization, staff work, and the needle gun to destroy Austrian forces. Paved the way for German unification.
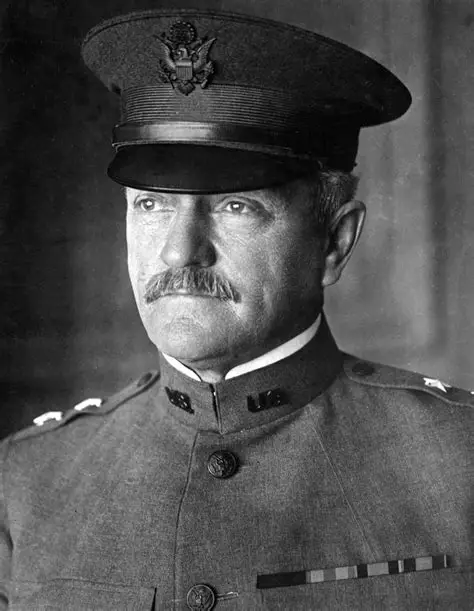
Gen John J. Pershing
Commander of the American Expeditionary Forces (AEF) in WWI. Insisted Americans fight as an independent force and organized the U.S. Army’s modern staff system.

Dowding System
British early-warning air defense network used in the Battle of Britain. Combined radar, observers, and centralized command to intercept German aircraft efficiently.

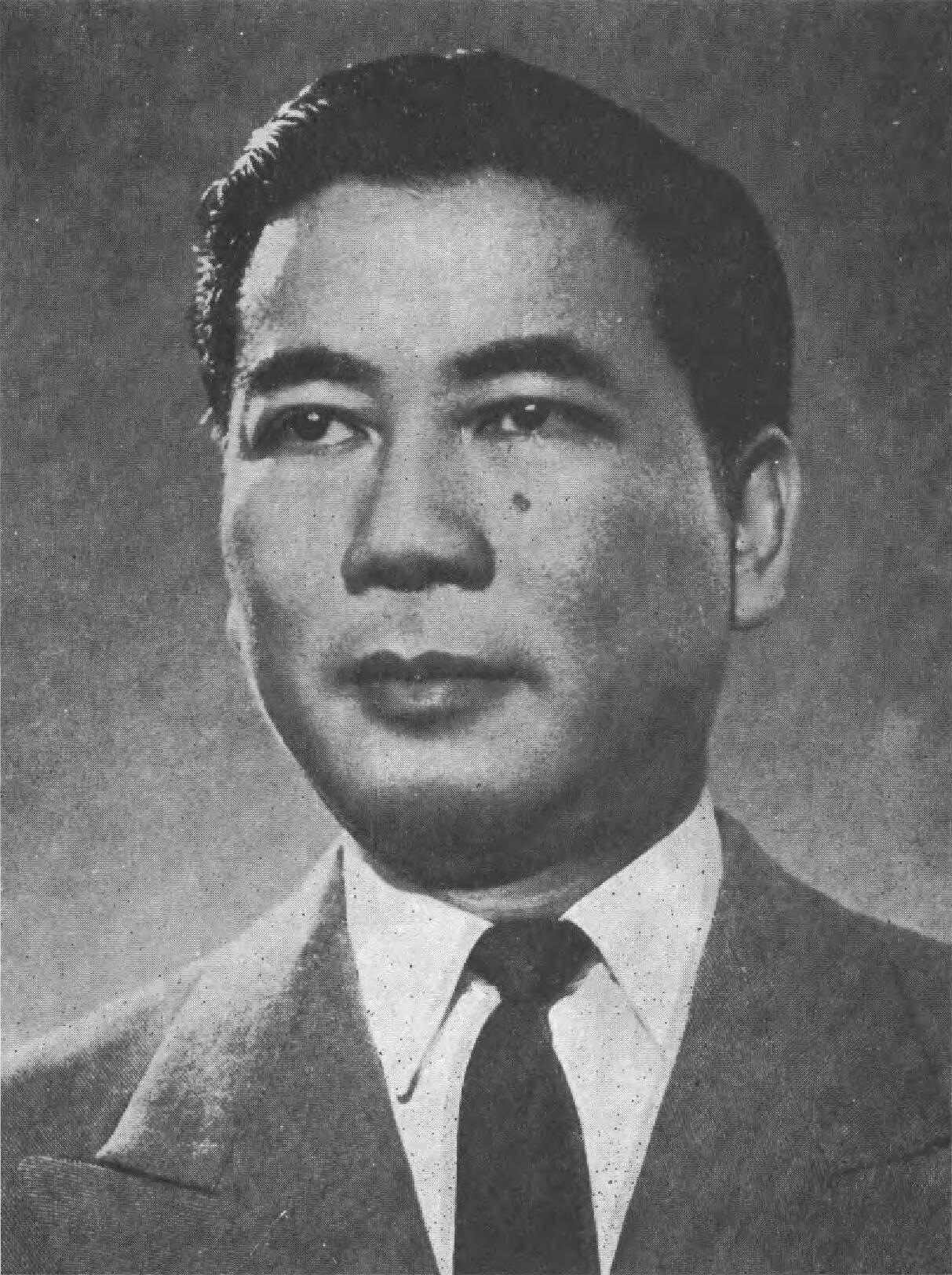
Ngo Dinh Diem
First president of South Vietnam. Anti-communist but authoritarian; his policies contributed to instability and strengthened the Vietcong insurgency.

Needle Gun
Prussian breech-loading rifle with high rate of fire (6 rounds/min). Major advantage in mid-19th-century wars, contributing to Prussian victories.

Brusilov Offensive
1916 Russian offensive that achieved major breakthroughs against Austria-Hungary. Ultimately stalled but inflicted huge casualties and destabilized the Central Powers.
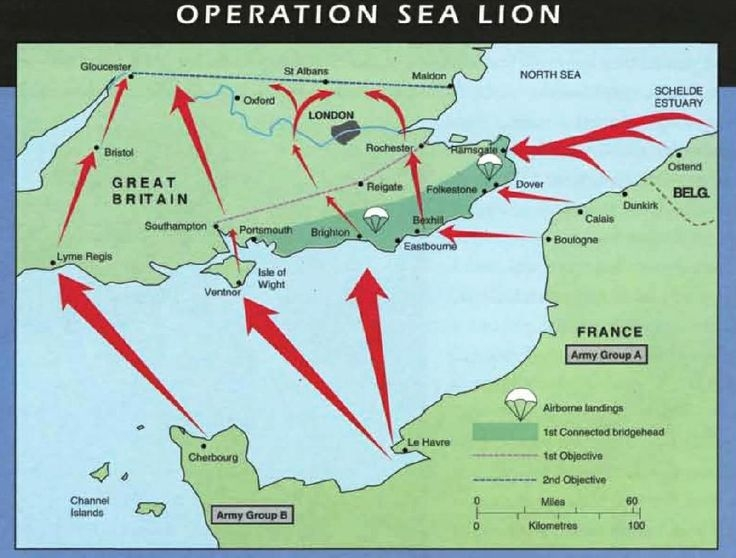
Operation Sea Lion
Germany’s planned invasion of Britain in 1940. Never executed due to Luftwaffe’s failure to win air superiority in the Battle of Britain.
Vietcong
Communist guerrilla force in South Vietnam. Used ambushes, tunnels, and political warfare to weaken South Vietnam and the U.S.

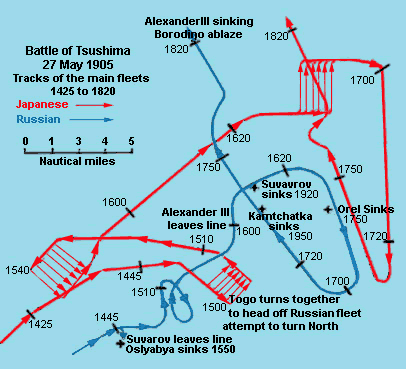
Battle of Tsushima
Decisive 1905 naval battle of the Russo-Japanese War. Japan annihilated the Russian fleet; demonstrated the importance of training, technology, and naval maneuver.
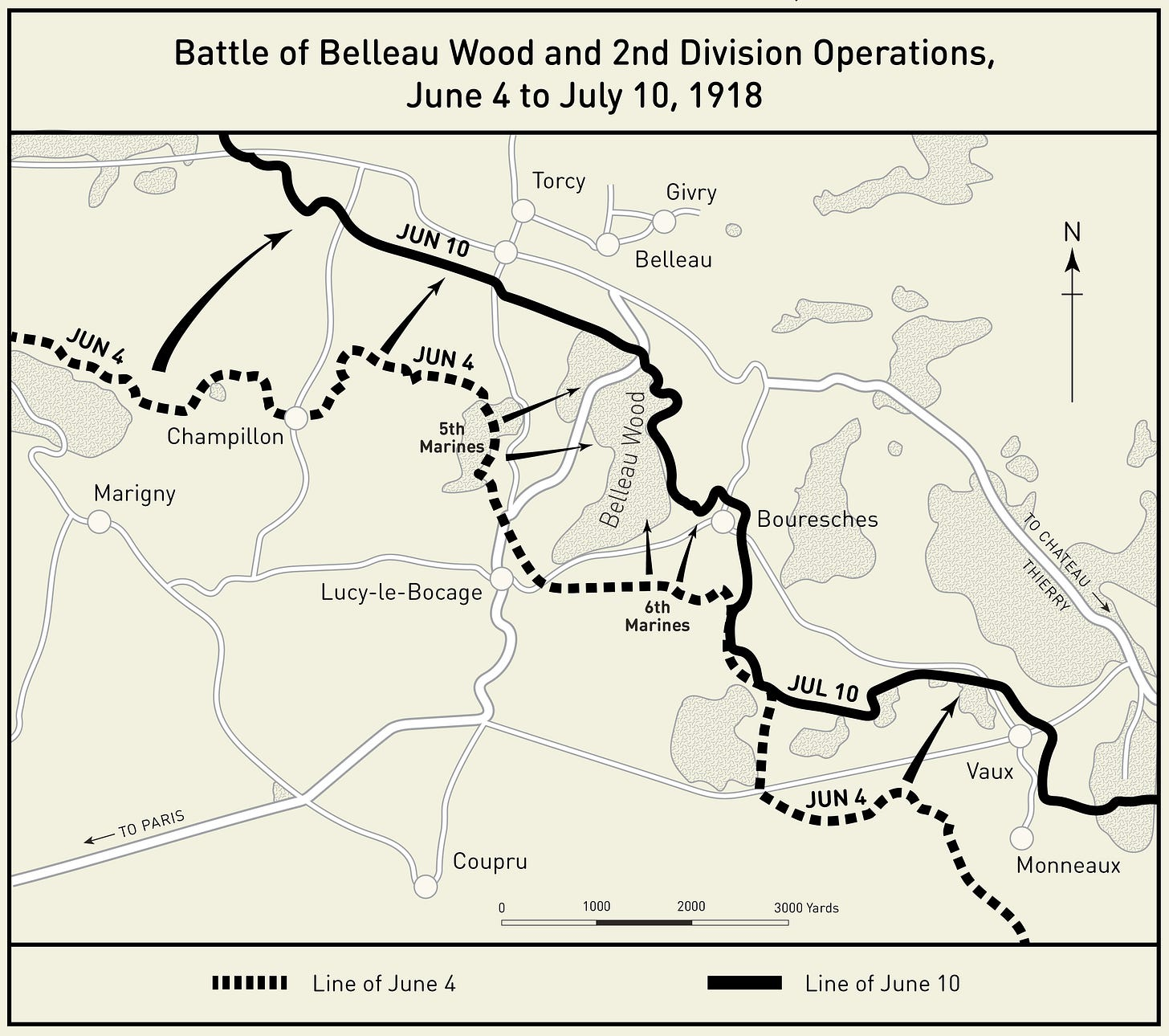
Battle of Belleau Wood
1918 WWI battle where U.S. Marines halted the German advance. Known for fierce close-quarters fighting; earned Marines the nickname “Devil Dogs.”
Air Marshal Sir Hugh Dowding
Commander of RAF Fighter Command during the Battle of Britain. Used the Dowding System to defeat the Luftwaffe and prevent a German invasion.

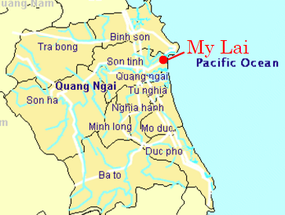
My Lai
1968 Vietnam War massacre of civilians by U.S. soldiers. Damaged U.S. credibility and intensified antiwar sentiment.
USS Maine
Battleship that exploded in Havana Harbor in 1898. Although the cause is disputed, its destruction helped spark the Spanish-American War.

Treaty of Versailles
1919 treaty ending WWI. Blamed Germany for the war, imposed huge reparations, restricted its military, and redrew borders.
Georgy Zhukov
Top Soviet general in WWII. Led defenses of Moscow and Stalingrad, and commanded the final assault on Berlin.

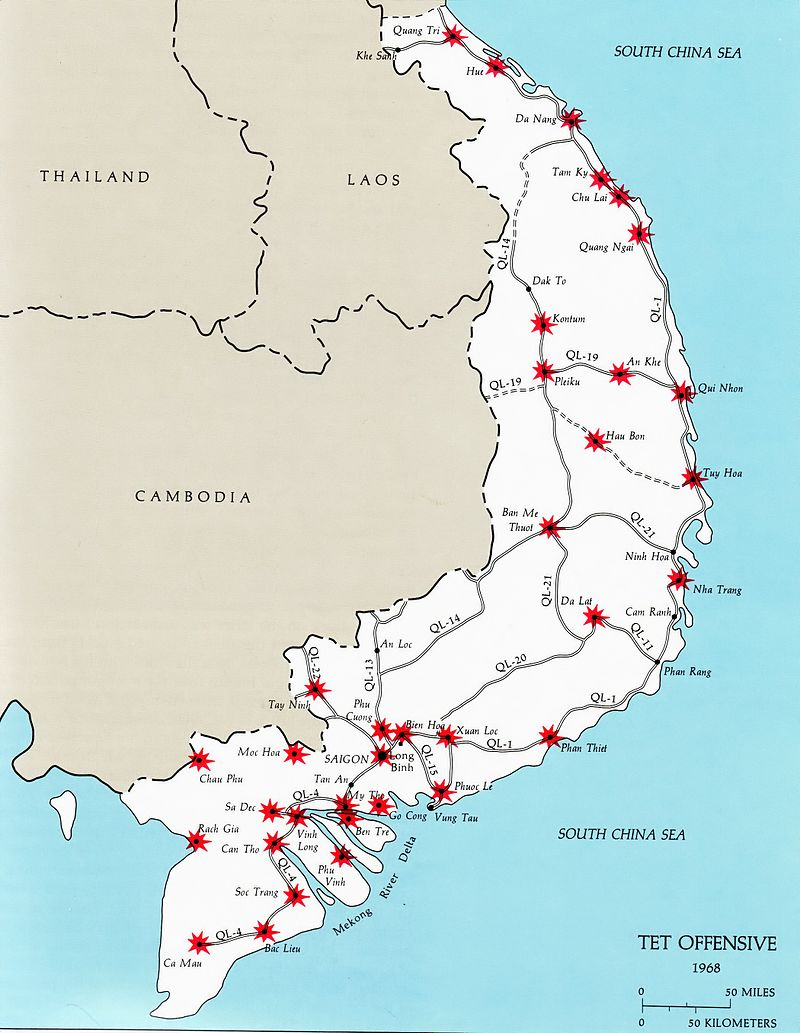
Tet Offensive
1968 Vietcong/North Vietnamese surprise offensive across South Vietnam. Militarily costly for the communists but strategically weakened U.S. public support.
Elihu Root
U.S. Secretary of War who reformed the Army after the Spanish-American War. Created the Army War College and established the General Staff system.

Attack
One of the fundamental missions of airpower: striking enemy forces, infrastructure, and key targets to achieve tactical and operational effects.
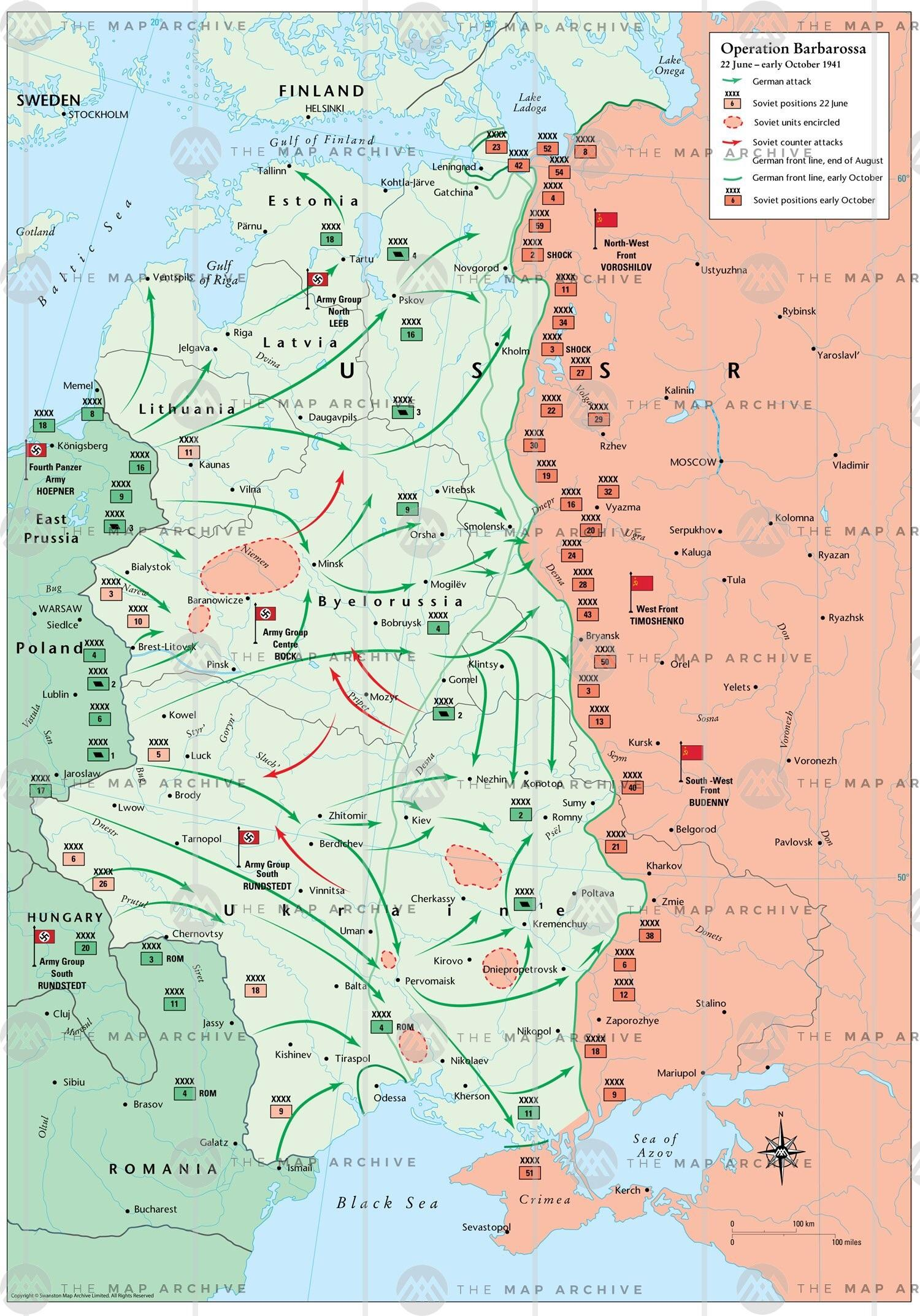
Operation Barbarossa
Germany’s 1941 invasion of the Soviet Union. Initially successful but ultimately failed due to logistics, weather, and Soviet resistance.
Vietnamization
U.S. strategy of turning combat responsibilities over to South Vietnamese forces while gradually withdrawing U.S. troops.
Alfred Thayer Mahan
American naval strategist who argued that sea power determines national strength. Influenced global naval expansion in the late 19th century.

Mobility
Airpower mission focused on moving troops, supplies, and equipment quickly across theaters to support operations.

Red Purge
Post-WWII political repression in Japan aimed at removing communists from government and society, influenced heavily by U.S. occupation forces.
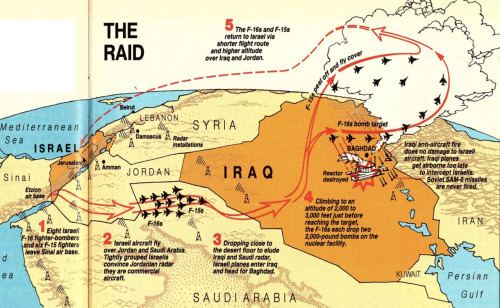
Operation Opera
1981 Israeli airstrike destroying Iraq’s Osirak nuclear reactor. Prevented Iraq from developing nuclear weapons.
General Staff Act of 1903
U.S. Army reform establishing the Chief of Staff system and creating a coordinated, professional military leadership structure.
Command of the Air
Airpower concept (Douhet) describing the ability to control the air domain and prevent enemy air operations while enabling friendly operations.
Jimmy Doolittle
U.S. aviator who led the 1942 Doolittle Raid on Japan. Boosted U.S. morale and demonstrated Japan’s vulnerability.

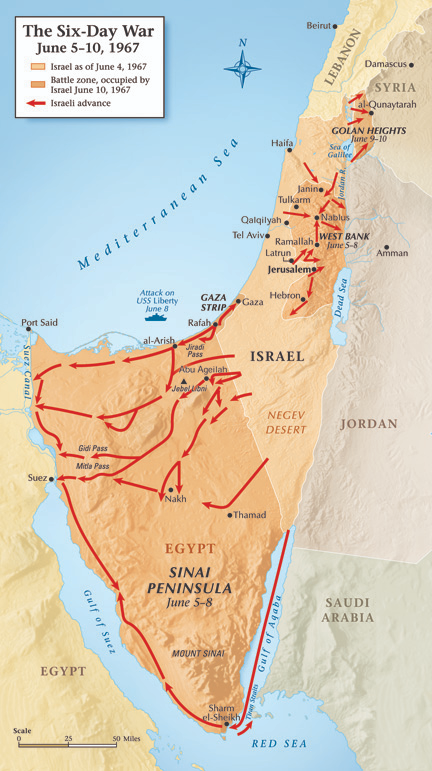
Six-Day War
1967 conflict where Israel fought Egypt, Syria, and Jordan, achieving rapid victory through preemptive airstrikes and armored maneuver.
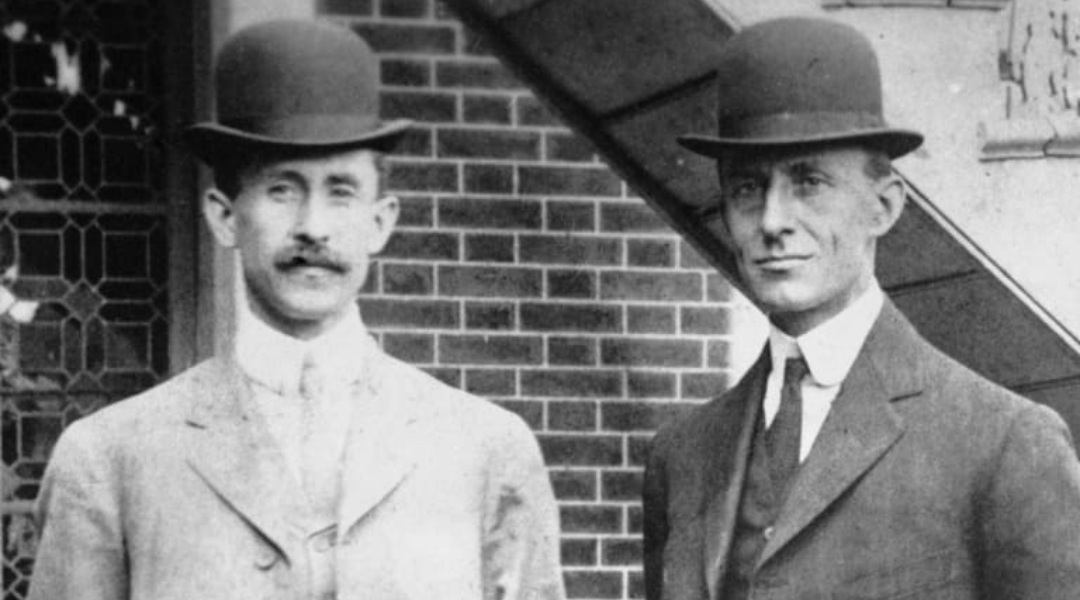
Wright Brothers
Inventors of the first practical airplane (1903). Their work initiated modern aviation and military airpower.

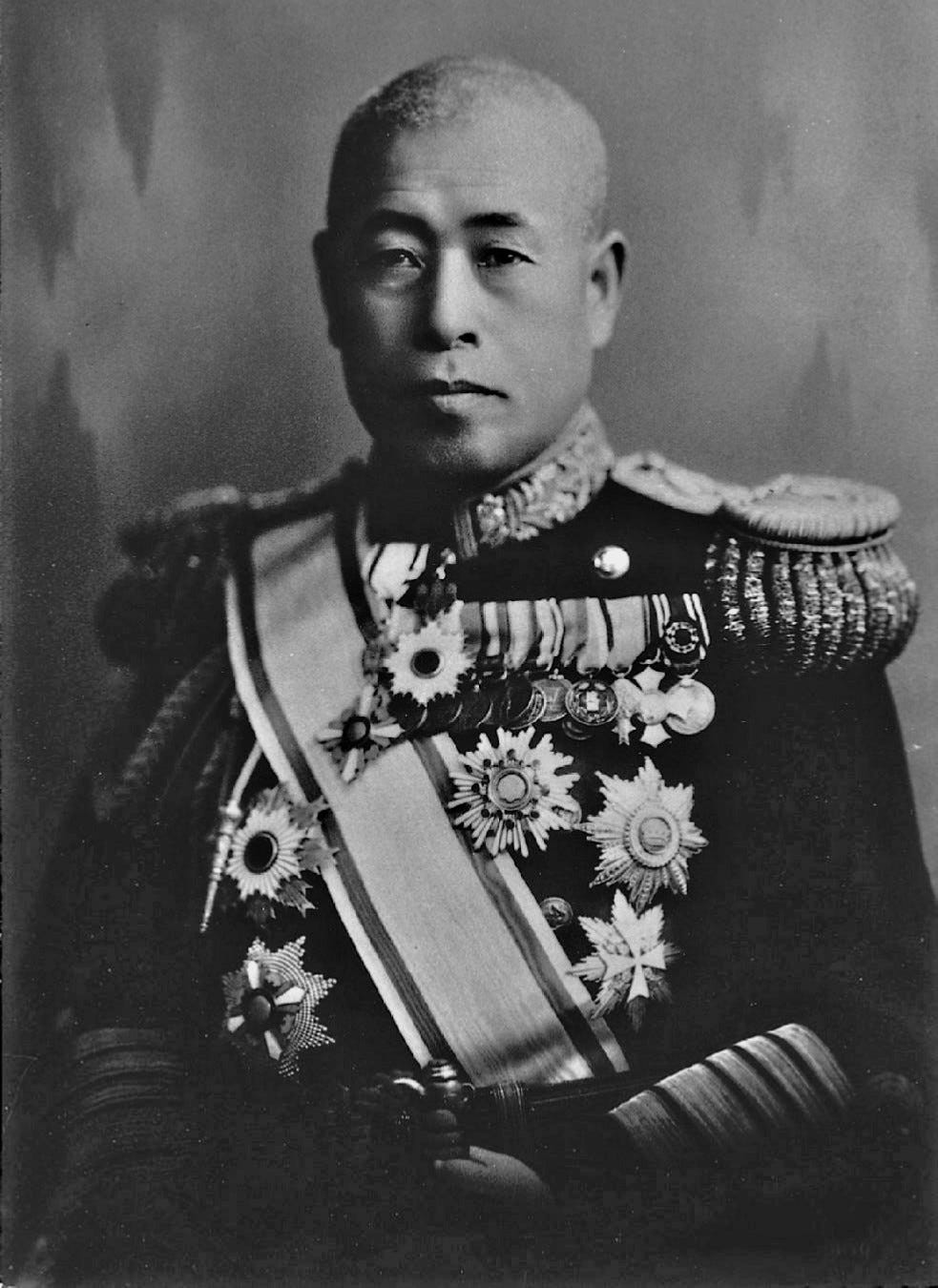
Isoroku Yamamoto
Commander of the Japanese Navy in WWII. Planned the Pearl Harbor attack and later lost naval superiority at Midway.

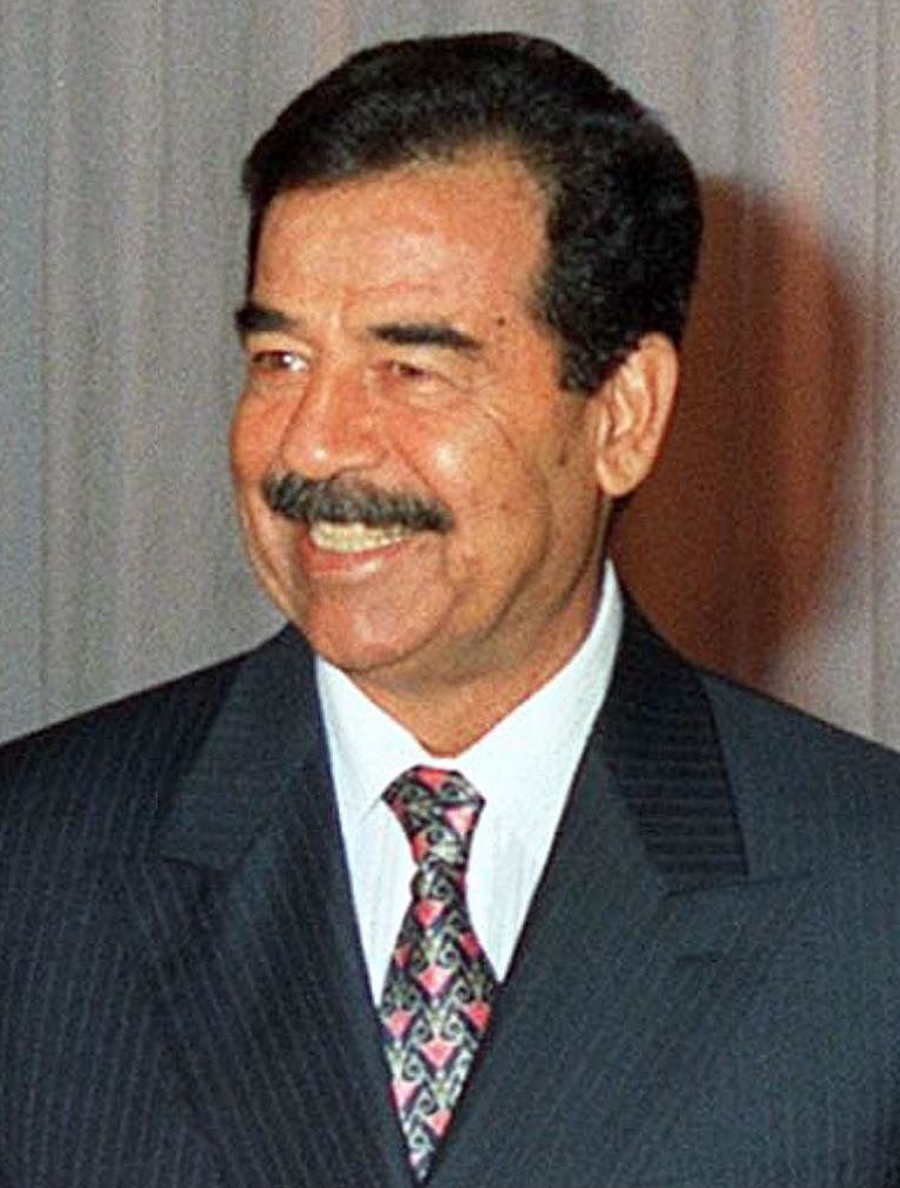
Saddam Hussein
Iraqi dictator whose invasion of Kuwait triggered the Gulf War. Later removed from power during Operation Iraqi Freedom.

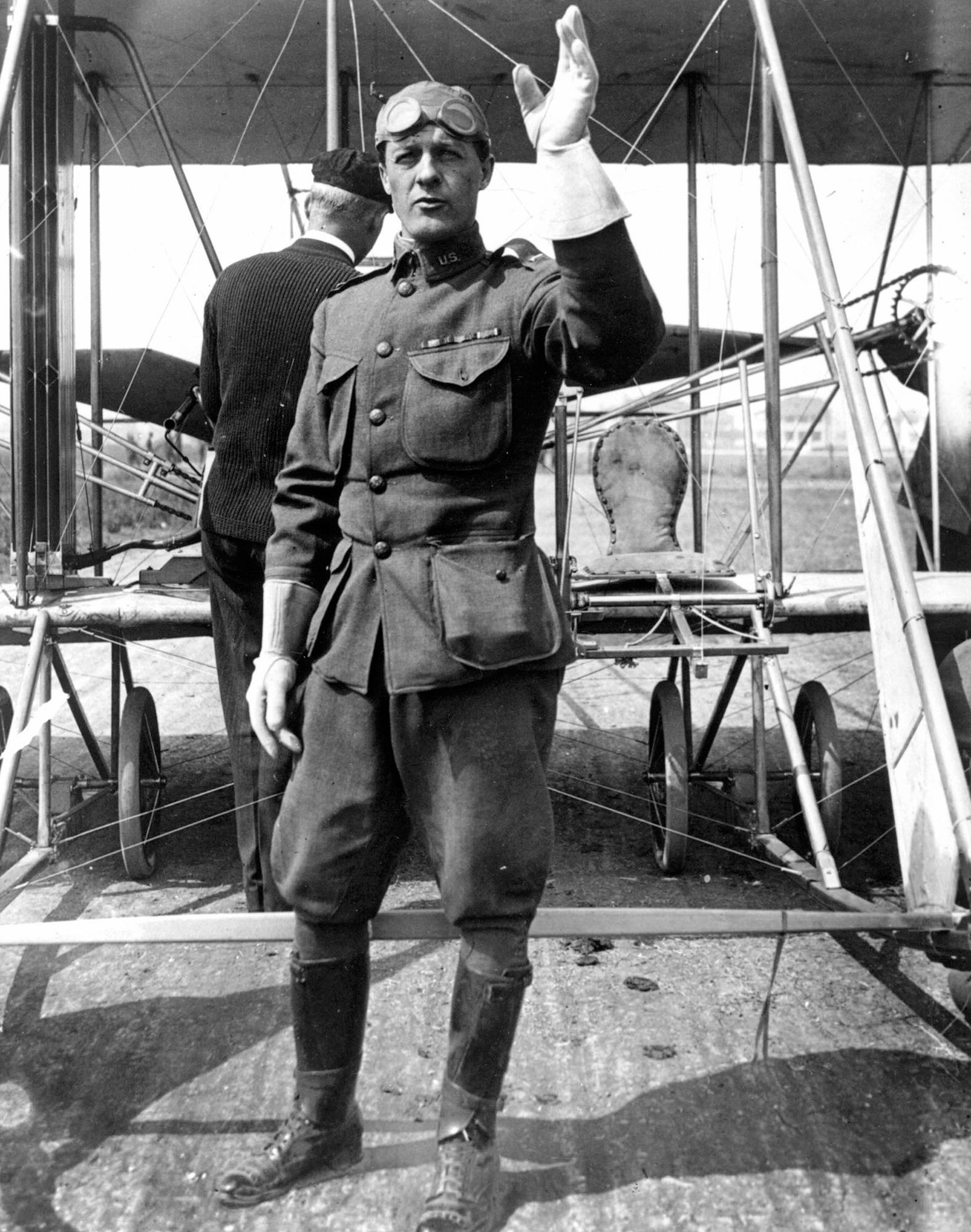
Benjamin Foulois
Early U.S. aviator who helped develop Army aviation and articulated early airpower missions: command of the air, ISR, attack, and mobility.

Erwin Rommel
German field marshal known as the “Desert Fox.” Skilled in maneuver warfare during the North African Campaign.

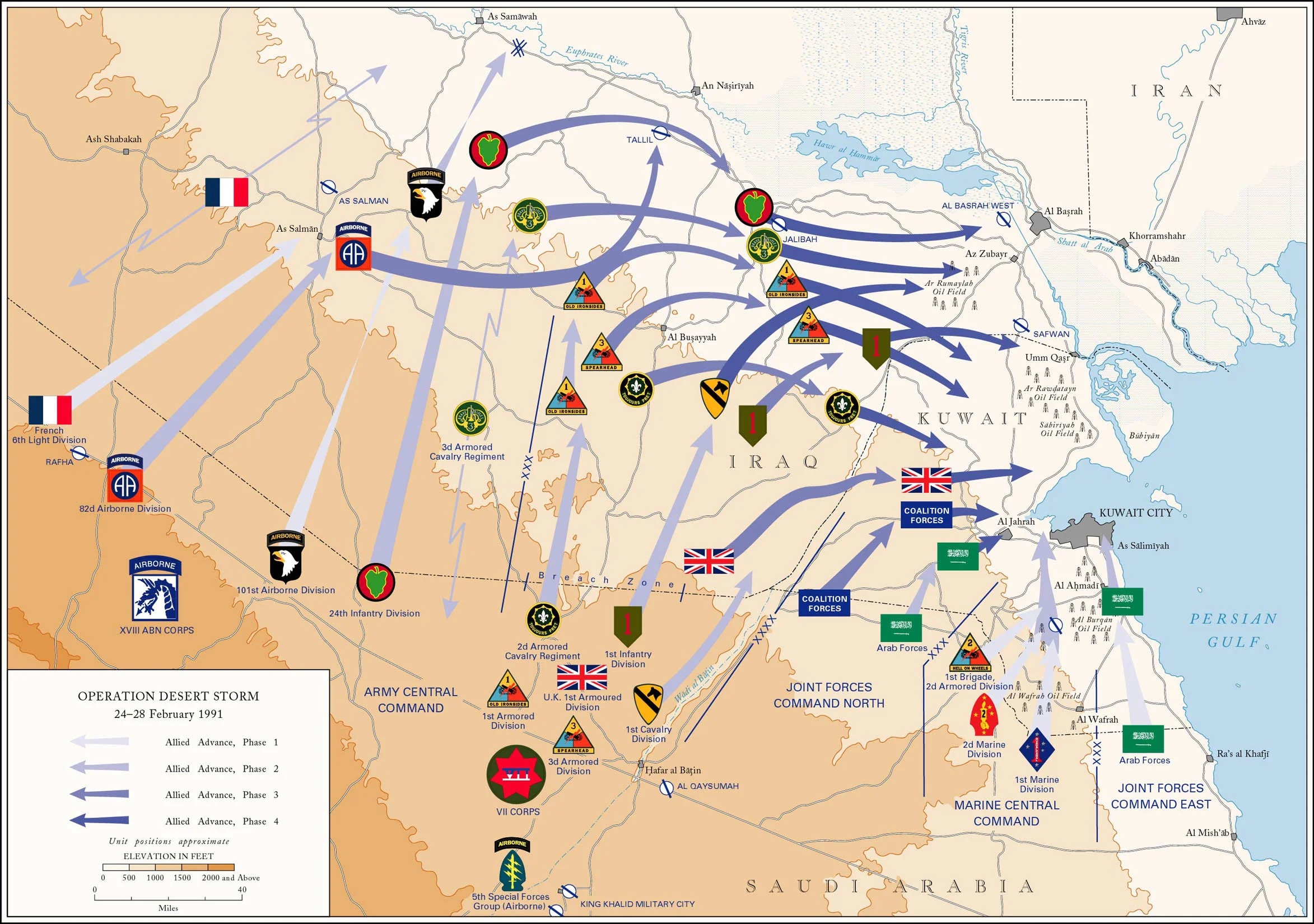
Norman Schwarzkopf
U.S. general who commanded Coalition forces in the Gulf War (Operation Desert Storm), known for rapid and decisive operations.

1st Aero Squadron
First U.S. military aviation unit. Used in the Punitive Expedition and early WWI for reconnaissance and communications.

Battle of the Atlantic
Longest WWII campaign. German U-boats attempted to cut Allied shipping; Allied technology and convoy systems eventually prevailed.
Operation Desert Shield/Storm
Desert Shield (1990): U.S. defense of Saudi Arabia after Iraq invaded Kuwait.
Desert Storm (1991): Coalition offensive that expelled Iraqi forces through air and ground operations.
ISR (Intelligence, Surveillance, Reconnaissance)
Airpower mission providing information on enemy positions, capabilities, and movements to support tactical and operational decisions.
Chester Nimitz
U.S. Pacific Fleet commander in WWII. Key architect of island-hopping strategy and victories at Midway and the Philippine Sea.

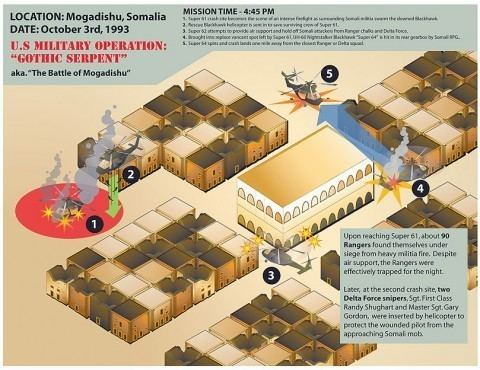
Operation GOTHIC SERPENT
1993 U.S. mission in Somalia to capture warlord lieutenants. Resulted in the Battle of Mogadishu (“Black Hawk Down”).
Objective
Principle of war requiring that every military action aim at a clearly defined and achievable goal.
Unity of Command
Ensuring all forces operate under one responsible commander to maintain coherence and effectiveness.
Mass
Concentrating combat power at the decisive point to achieve overwhelming force.
Offensive
Maintaining initiative by acting rather than reacting; striking the enemy to dictate tempo.
Maneuver
Using movement and positioning to place the enemy at a disadvantage and exploit weaknesses.
Economy of Force
Allocating minimum necessary combat power to secondary efforts to maximize resources at decisive points.
Security
Preventing the enemy from gaining unexpected advantage; protecting forces, information, and operations.
Surprise
Striking the enemy at a time or place they are unprepared for to maximize advantage.
Simplicity
Clear, uncomplicated plans and orders to reduce confusion and enhance execution.