hass rev
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:46 AM on 11/19/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
1
New cards
PRIMARY SOURCE
An original, first-hand piece of experience/information.
2
New cards
SECONDARY SOURCE
A second-hand piece of information.
3
New cards
BCE
Before Common Era
4
New cards
CE
Common Era
5
New cards
1882CE
19th Century
6
New cards
2021CE
21st Century
7
New cards
905CE
10th Century
8
New cards
60CE
7th Century
9
New cards
PHARAOH
- Considered a god-king.
- Had great wealth.
- Highest priest in the land.
- Had great wealth.
- Highest priest in the land.
10
New cards
VIZIER
- Second-in-command.
- Pharaoh's main adviser.
- Supervised other officials.
- Acted as a judge.
- Pharaoh's main adviser.
- Supervised other officials.
- Acted as a judge.
11
New cards
CHIEF PRIEST
- Represented the Pharaoh.
- Permitted to enter the inner temple.
- Responsible for the temple.
- Permitted to enter the inner temple.
- Responsible for the temple.
12
New cards
NOBLES
- Governed small regions.
- Collected taxes.
- Collected taxes.
13
New cards
PRIESTESSES
- Married to nobles and officials.
- Responsible for the care of the temple Goddess.
- Responsible for the care of the temple Goddess.
14
New cards
SCRIBES
- Could read and write.
- Recorded the decisions and orders of the Pharaoh.
- Kept records for the Vizier and the army.
- Recorded the decisions and orders of the Pharaoh.
- Kept records for the Vizier and the army.
15
New cards
SOLDIERS
- Professional, full-time soldiers.
16
New cards
MERCHANTS
- Traded goods from Egypt.
- Imported goods to Egypt.
- Imported goods to Egypt.
17
New cards
CRAFTSMAN
- Were skilled workers such as potters.
- Made goods for everyday use and for the temple.
- Made goods for everyday use and for the temple.
18
New cards
FARMERS
- Grew crops such as wheat and barley.
- Tended animals.
- Took on building work.
- Tended animals.
- Took on building work.
19
New cards
SLAVES
- Usually foreigners, captured in wars.
- Domestic servants, farmhands, or mineworkers.
- Some worked for the Pharaoh.
- Domestic servants, farmhands, or mineworkers.
- Some worked for the Pharaoh.
20
New cards
WHAT IS THE RIVER CALLED
The Nile River
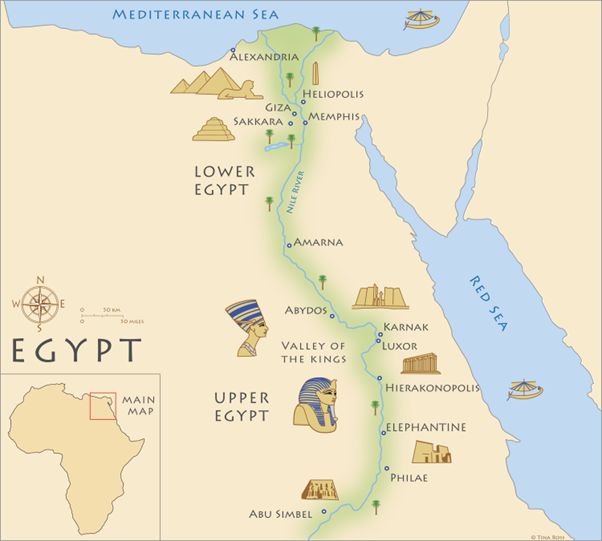
21
New cards
WHAT CONSISTS OF LOWER EGYPT
Memphis
Giza
Heliopolis
Giza
Heliopolis
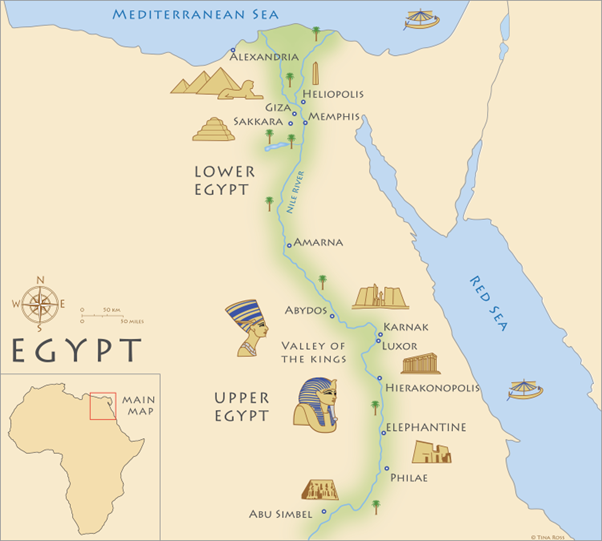
22
New cards
UPPER EGYPT
Valley of the Kings
Luxor
Philae
Luxor
Philae
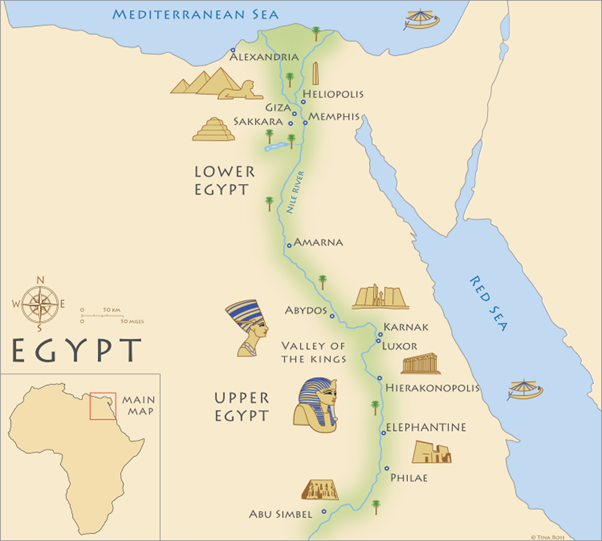
23
New cards
WHAT ARE THE SEAS
Mediterranean Sea
Red Sea
Red Sea
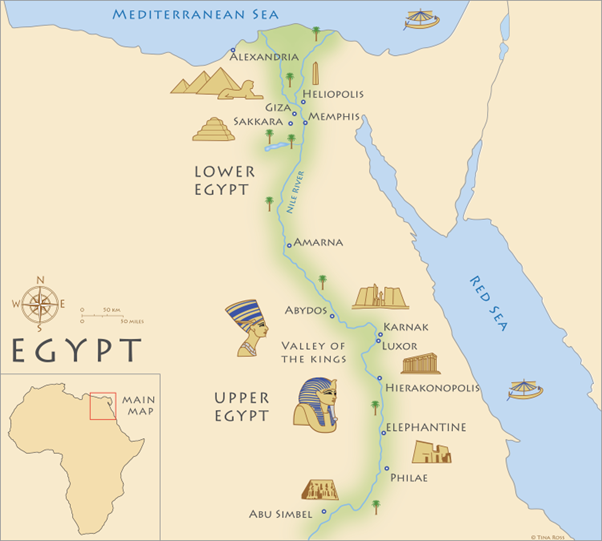
24
New cards
FIRST STEP INVOLVED IN MUMMIFICATION
The dead body is brought for mummification.
25
New cards
SECOND STEP
The body is washed.
26
New cards
THE THIRD STEP
The bodily organs are removed, whilst the heart is left in the body.
27
New cards
THE FOURTH STEP
The organs are dried, rubbed with oils and stored in jars who acts as a guardian for the organ within.
28
New cards
THE FIFTH STEP
The body is covered with salt for 70 days before being washed and smeared with oil.
29
New cards
THE SIXTH STEP
The body is wrapped with rolls of fine linen and prayers are read.
30
New cards
THE SEVENTH STEP
The mummy is painted with resin and wrapped with cloth.
31
New cards
THE EIGTH STEP
The mummy is placed in a coffin.
32
New cards
WHY IS MUMMIFICATION IMPORTANT
It was believed that this ritual is one of many needed to ensure a smooth journey into the afterlife.
33
New cards
WHAT ARE THE SEVEN CONCEPTS OF GEOGRAPHY (SPICESS)
Scale
Place
Interconnection
Change
Environment
Sustainability
Space
Place
Interconnection
Change
Environment
Sustainability
Space
34
New cards
WHAT ARE THE SEVEN CONTINENTS
North America, South America, Europe, Asia, Africa, Australia, Antarctica
35
New cards
FIRST STEP IN THE WATER CYCLE
Evaporation
36
New cards
WHAT IS EVAPORATION
Sun heats liquid water to vapour which rises into the atmosphere.
37
New cards
SECOND STEP
Transpiration
38
New cards
WHAT IS TRANSPIRATION
Evaporation of water from plant's pores, found in leaves and stems
39
New cards
THIRD STEP
Condensation
40
New cards
WHAT IS CONDENSATION
The evaporation in the air gets cold and changes back into liquid, forming clouds
41
New cards
FOURTH STEP
Precipitation
42
New cards
WHAT IS PRECIPITATION
The condensation in the clouds form to become heavier before falling as precipitation.
43
New cards
FIFTH STEP
Runoff
44
New cards
WHAT IS RUNOFF
Precipitation on ground returns to bodies of water.
45
New cards
SIXTH STEP
Infiltration
46
New cards
WHAT IS INFILTRATION
Water on the ground soaks into the soil and into the roots of plants.
47
New cards
DEFINE RENEWABLE
Resources that can replenish themselves over time if not used too quickly.
48
New cards
EXAMPLE OF RENEWABLE
Trees
49
New cards
DEFINE NON-RENEWABLE
Limited amounts that will run out if not managed correctly.
50
New cards
EXAMPLE OF NON-RENEWABLE
Diamonds, coal
51
New cards
DEFINE CONTINUOUS RESOURCES
Available in infinite amounts and will never run out.
52
New cards
EXAMPLE OF A CONTINOUS RESOURCE
Energy from the sun, wind
53
New cards
DEFINE LIVEABILITY
How suitable we think it is to live in a place and what we like about said place, depending on certain factors.
54
New cards
DEFINE FACTORS
Your own needs and wants, your age, income, background, lifestyle and values.
55
New cards
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN OBJECTIVE AND SUJECTIVE FACTORS
OBJECTIVE can be measured and expressed in numbers.
SUBJECTIVE is personal, emotional and spiritual.
SUBJECTIVE is personal, emotional and spiritual.
56
New cards
WHAT DOES BOLTSS STAND FOR
Border
Orientation
Legend
Title
Scale
Source
Orientation
Legend
Title
Scale
Source
57
New cards
BORDER
The border on a map
58
New cards
ORIENTATION
Shows directions on a map
59
New cards
LEGEND
Explains symbols used to represent features on a map.
60
New cards
TITLE
Names the place the map is representing.
61
New cards
SCALE
Represents the unit of length on a map and the length over the ground.
62
New cards
SOURCE
Where the information to create the map came from.
63
New cards
HOW IS WATER USED?
Relied on to drink, wash, cook, clean, grow food and produce electricity.
64
New cards
WATER SCARCITY
The lack of water resources to meet the demand.
65
New cards
HOW CAN WATER SCARCITY BE OVERCOME?
In Africa, it is solved by digging a water well, ensuring clean water.
66
New cards
DAMS
Barrier used to store bodies of water and create hydroelectric power.
67
New cards
DESALINATION
Treat seawater and remove the salt to make the water fresh.
68
New cards
GROUNDWATER RESERVES
A layer of rock that holds the water underground from water bores. The high-mineral water is best for industrial purposes.
69
New cards
RECYCLING AND TREATING WASTEWATER
Wastewater is piped to a treatment plant, purified before being released.
70
New cards
DEFINE WATER SUSTAINABILITY
Using water in a way that meets needs without compromising the ability to meet those needs in the future.
71
New cards
PERTH'S WATER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM -- FOR AND AGAINST
- Issue of scarcity has improved by 15 per cent per person in the last 30 years.
- Water is declining from surface and groundwater sources.
- Water is declining from surface and groundwater sources.