Organic Chemistry I
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Reagents and IR spec values
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
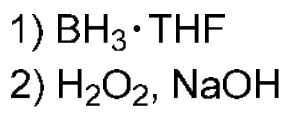
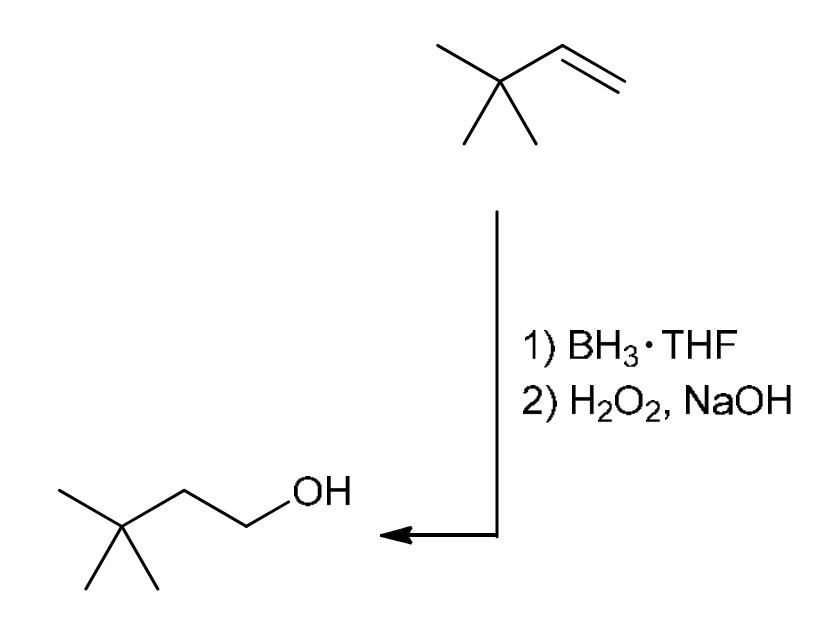
Hydroboration Oxidation
For Alkenes: Anti-Mark addition of H and OH, removing alkene bond and adding OH to the less sub C (Opposite of H3O+)
For Alkynes: Turns alkyne into an aldehyde
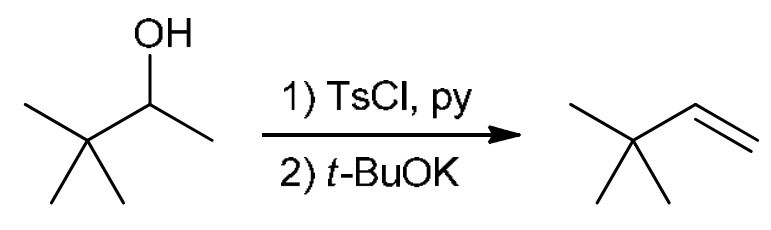
Nucleophilic substitution or elimination
Tosylate converts OH into OTs then t-BuOK (strong base) kicks it out to form an alkene in less sub C
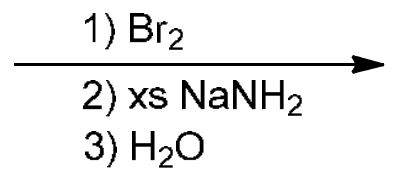
Brominating and alkyne synthesis
2 Br are added across the double bond, breaking it, then NaNH2 removing the 2 Br atoms and forming an alkyne
If only Br2, add two Br across the alkene, change stereochemistry if chiral centers present
NaNH2 (extending alkynes): attacks terminal H of alkyne to leave radicals (2 e-), where R-X (R is whatever you want to add onto the alkyne and X is Br, or I)
NaOH
Strong nucleophile and strong base (SN2 or E2), the OH attacks the carbon atom with a leaving group, and replaces it with OH
Use in SN2 if primary alkyl halide, use in E2 if secondary and tertiary
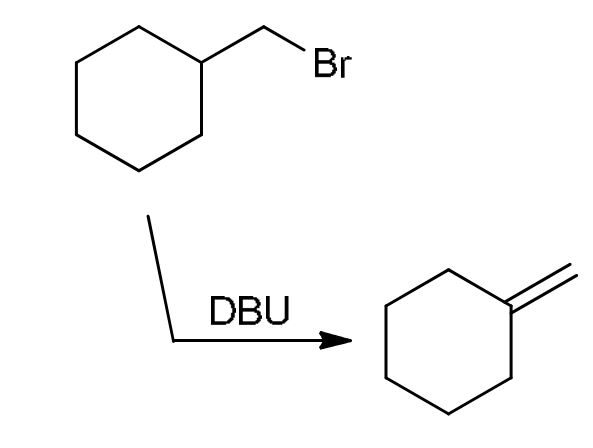
Dehydrogenation
DBU is a strong, bulky non-nucleophilic base that removes an H next to a leaving group, makes the halogen leave and form an alkene on less sub C
E2
Can use DBN, DBU and t-BuOK too
T-BuOK: removes beta H as leaving group leaves, forming C=C on less sub. alkene (Hofmann)
Syn-dihydroxylation
KMnO4 (cold/OH-/NaOH/aq/dilute): adds 2 OH across alkene bond (same side)
Opposite of RCOOOH (RCO3H) which adds 2 OH across alkene anti addition
→ Can cleave OH and turn into carbonyl (double bond O)
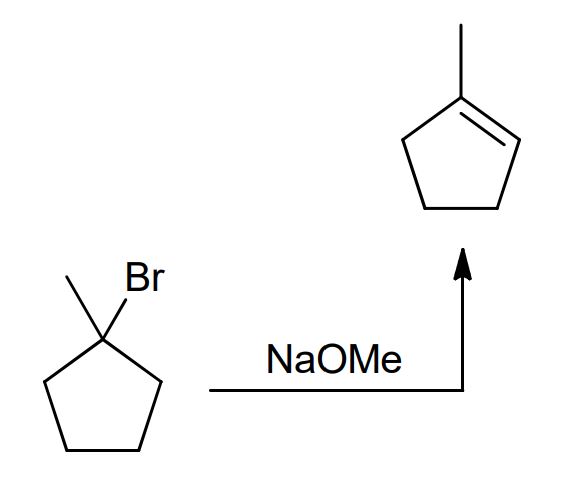
NaOMe and NaOEt
Strong nu and strong bases
NaOMe favors SN2: attacks the C with leaving group, group leaves
NAOEt (bulkier) favors E2 dehydrohalogenation: removes the H next to the leaving group and group leaves to form alkene bond on more sub C
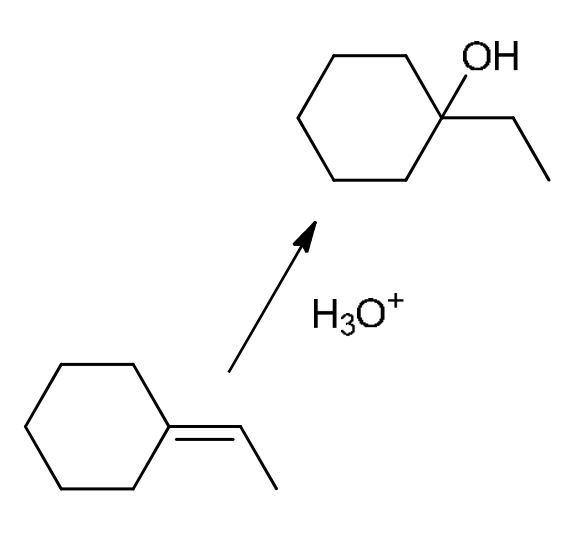
Acid-catalyzed hydration
Can use H3O+ or (dilute) H2SO4 (Don’t use when there could be a rearrangement)
Mark addition, alkene bond breaks, and OH is added to the more sub C (Opposite of BH3/THF with H2O2, NaOH)
Acid-catalyzed dehydration
E1 with H2SO4 (Δ/heat): O of OH attacks one H from H2SO4 to get H2O, H2O leaves, carbocation (do hydride or methyl shift is necessary), add alkene where most substituted (Zaitsev)
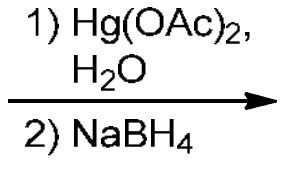
Oxymercuration-demercuration
Mark addition: Hg(OAc)2 and H2O adds Hg-OAc connected as a triangle with both sides of the alkene bond (double bond broken), then H2O attacks the more sub C to get OH, then NaBH4 replaces Hg-OAc with H on the less sub C.
Avoids rearrangement!!
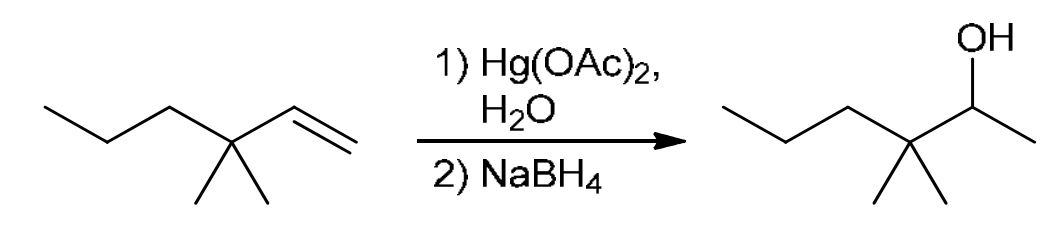
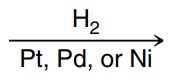
Catalytic hydrogenation
H2 (with Pd, Pt or Ni) (syn addition): alkene bond breaks and 2 H are added across the bond to the same side, no leaving group involved.
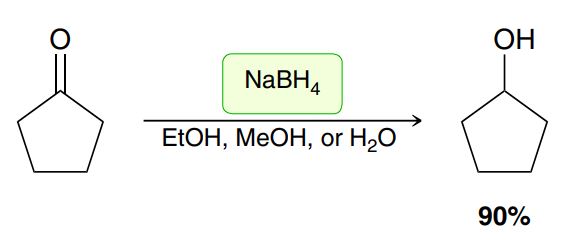
Reducing ketone or aldehyde into an alcohol
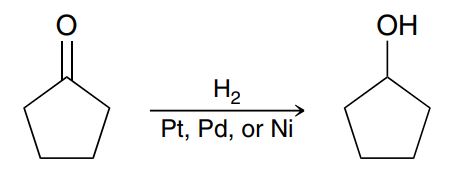
Hydride reduction (of a ketone or aldehyde)
NaBH4 adds an H- to the carbonyl carbon, alkene breaks, (EtOH, MeOH, or H₂O) adds an H to the Oxygen to form an OH (no leaving group involved) (a reducing like H3O+) (check for chiral centers → stereochemistry)
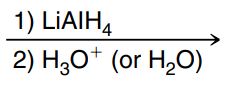
Hydride reduction (of a ketone, aldehyde, esters, carboxylic acids or amides)
LiAlH4 adds H- to the carbonyl C then H3O+ or H2O adds an H to the Oxygen to form an OH (no leaving group involved) NEED TO BE SEPARATE STEPS
When there is xs LiAlH4, eject any leaving groups (eg EtO-) before using LiAlH a 2nd time
Stronger than NaBH4, less selective (can reduce more groups)
Do not use when water, alcohol or acid (carboxylic acid COOH) is present
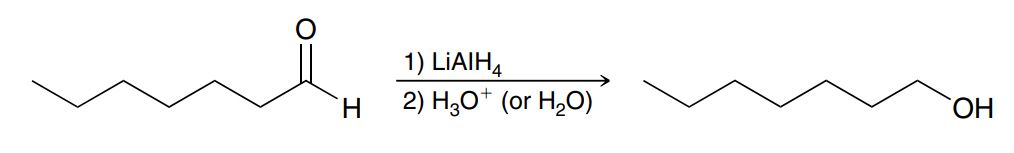
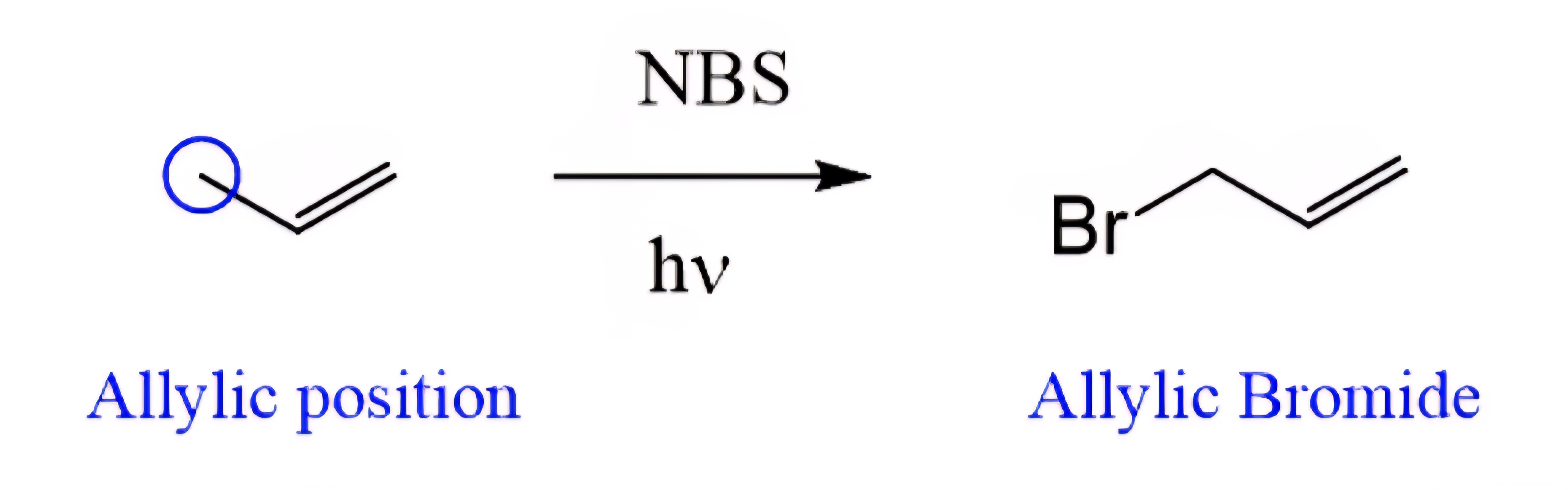
Allylic Bromination
An H on the allylic/benzylic carbon is replaced by Br, forming a C–Br bond and releasing HBr.
No addition
PCC
Turns primary OH into aldehyde and secondary OH into ketone
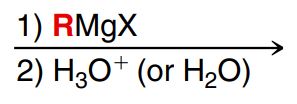
Reduction with Grignard reagent
Grignard reagent is formed by R-X and Mg, strong nu and strong base
R- attacks carbonyl C (R group attaches onto that C), C=O alkene bond breaks, H3O+ adds H to Oxygen to form an alcohol (no leaving group involved) (Similar to reduction with LiAlH4 or NaBH4)
MUST BE SEPARATE STEPS
A Grignard reagent will react with a ketone or aldehyde to produce alcohol (OH)
Examples: CH3MgBr/MeMgBr, EtMgBr, PhMgBr, any line bond structure attacked to MgBr
Making Grignard (R-X + Mg (with Et2O)): Start with an alkyl halide (Br, I or Cl) and add Mg with Et2O to get Grignard (R-Mg-X)
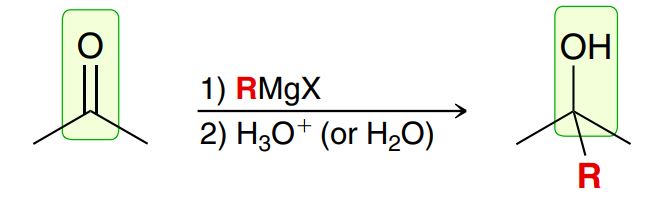
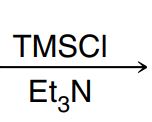
Protection of Grignard (and removal)
TMSCl with Et3N protects the OH group: O from OH attacks Si, Cl leaves, Et3N removes H from Oxygen and OH is converted into OTMS
Afterward, proceed with Grignard reagent: 1. Mg, 2. Ketone or aldehyde (with whatever needs to be added), 3. H3O+
Then use TBAF to remove TMS and replace O with OH
PBr3
Through SN2: Converts 1° and 2° OH into alkyl bromides: replaces OH with Br while avoiding carbocation rearrangement
Mechanism: O from OH attacks P, 1 Br breaks off and PBr2 attaches onto O, Br- attacks from backside of C attached to OPBr2, group leaves, Br attaches
Use when you want OH → Br for 1° and 2° alcohols

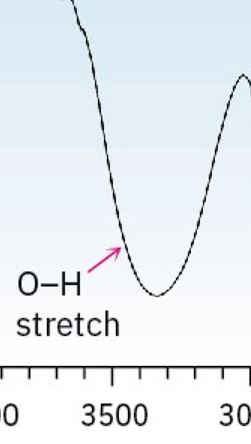
Alcohol
3200 - 3600 cm-1 (smooth long and broad curve, like a U)
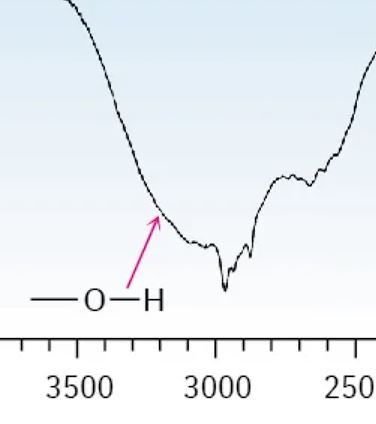
Carboxylic Acid
2200 - 3600 cm-1 (smooth going down, jagged at the bottom and up, very broad curve)
Amine (1st and 2nd degree)
1st degree (NH2): 3300 - 3500 cm-1 (Like small W)
2nd degree: 3350 - 3500 cm-1 (Like a V)

Alkyne Carbon with H
3300 cm-1 (like a V)
Alkene Carbon with H
3000 - 3100 cm-1 (like a V)
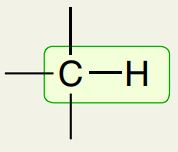
Alkane Carbon with H
2900 cm-1 (has jagged peaks)

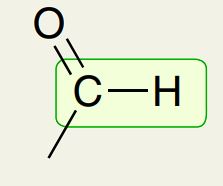
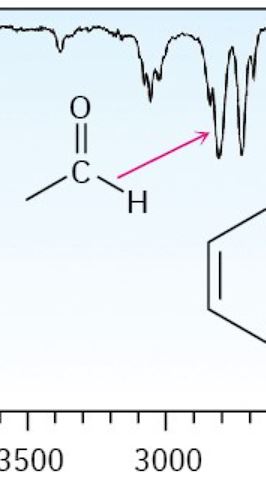
Aldehyde
2750 cm-1 (Like a W)
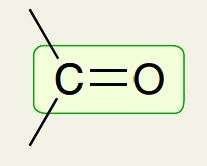
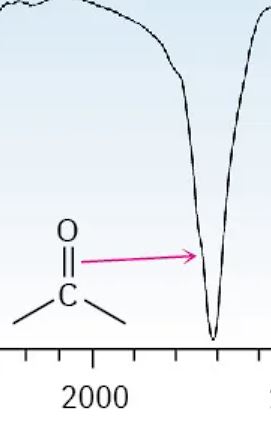
Ketone
1700-1820 cm-1 (like a V)
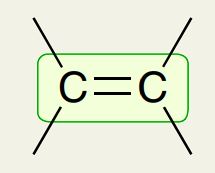
Alkene C=C bond
1600 - 1700 cm-1 (like a V)
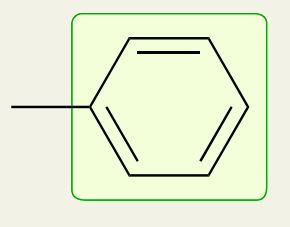
Benzene ring
~1600 cm-1
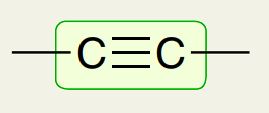
Alkyne Carbon bond
2100 - 2200 cm-1 (looks like a V)
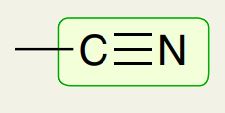
Alkyne Carbon with Nitrogen
2200 - 2300 cm-1 (looks like V)
CN- (25°C)
Strong nu (weak base), SN2: N attacks C attached to the leaving group, leaving group leaves, replaces its place
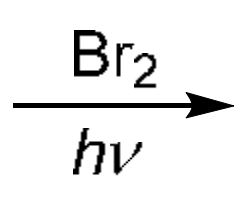
Bromination
Br2 homolytically split into two with a radical each, one Br radical combines with the first H radical to form HBr and the other Br radical combine with the 2nd H radical to form a bond where the H used to be (attaching Br there)
→ The H is from the most substituted C (3° usually for Br)
Br2 with H2O: Adds OH in most sub C of alkene (Mark) while adding Br anti to OH (one is on a wedge, and the other on dashes), makes enantiomer
→ Can also use NBS with H2O
xs Br2: For alkene: Adds twice across double bond (first addition is anti, second is simply added) (4 Br in total)
→ For alkyne: Same as alkene product
Br2 only with alkynes: Makes double bond with anti addition of 2 Br across it
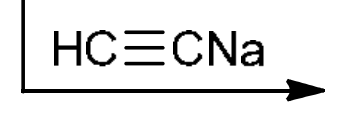
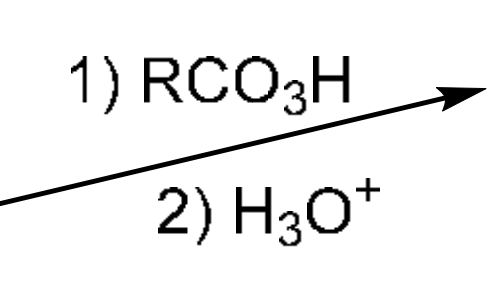
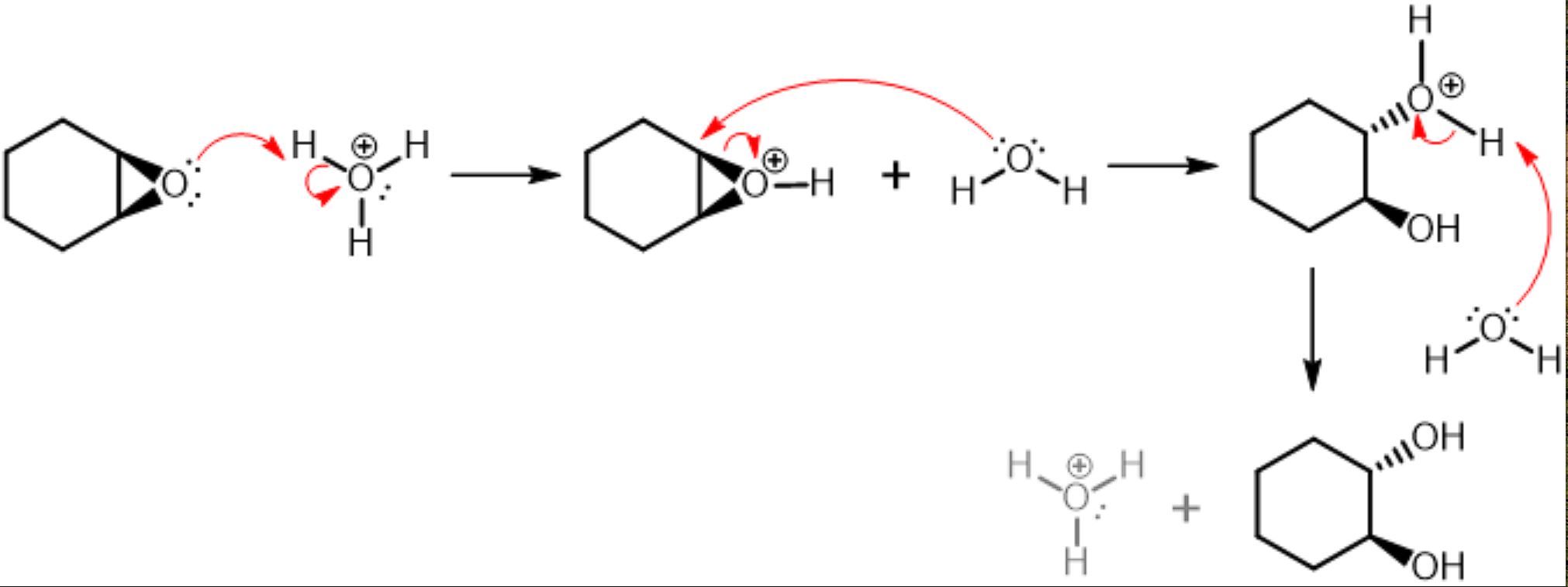
Anti dihydroxylation
RCO3H (RCOOOH) breaks alkene to attach an O on both Carbons to form a triangle with wedges, then the O attacks H3O, takes an H to become OH (still in triangle), then water attaches onto 1 C of the triangle (backside) so triangle breaks, and water is attached on dashes. Finally, another water deprotonate the water on dashes to get 2 OH (one on dashes, one on a wedge)
Opposite of KMnO4 (cold) which adds 2 OH across alkene syn addition
Ozonolysis
For Alkenes: O3 with DMS: Splits alkene in half, then attaches O on each split (gives aldehyde groups) (in steps)
→ To get carboxylic acids from alkene: O3 with H2O2
For Alkynes: O3 (only or H2O), creates carboxylic acid with CO2
Syn-addition of hydrogenation
(For alkynes only): H2 with Lindler’s catalyst: Adds 2 H’s across triple bond in syn addition (turns into alkene) (other substituents will bend opposite way)
Anti-addition of hydrogenation
(For alkynes only): Li or Na radicals with NH3 (liquid) to add H trans across the triple bond (turns into alkene)
Acid-catalyzed hydration (for alkynes)
H3O+ with H2O
2. HgSO4
Turns alkynes into ketones
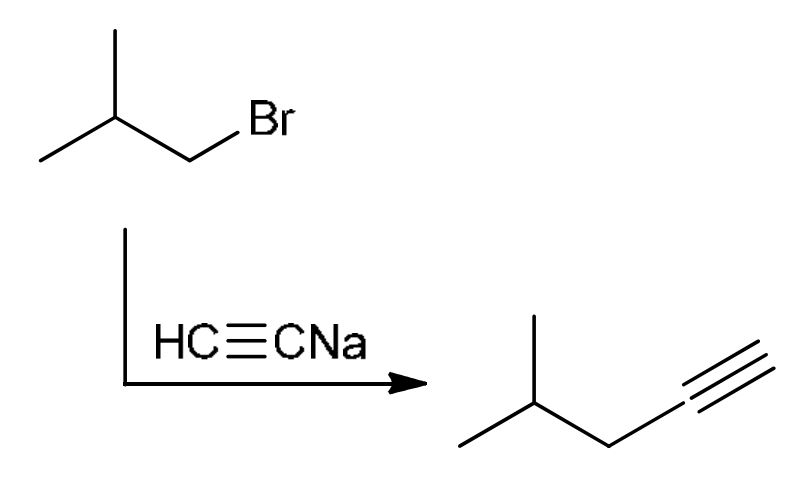
Alkylation of primary alkyl halides
HC≡CNa: strong base and strong nu: attacks the 1° alkyl halide (SN2), LG leaves, adds alkyne to the end of where LG left (Doesn’t work for 2° or 3°)
R2BH with H2O2, NaOH
More bulky, more controlled products: Same as BH3, THF with H2O2, NaOH: makes an anti mark OH (if with alkyne, makes into double bond with anti mark OH)