NEcon Week 5 - Dopamine Neurons
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
what is the difference between a reward and reinforcer?
reward > behaivoral definition the affective part is important
reinforcer > anything that increases liklihood of a behavior recurring regardless of whether it feels good\
example
positive reinforcer (adding something) > giving a child candyu after cleaning room
negative reinforcer (taking something away) > buckling seatbelt to stop the car from beeping; or a curse jar
what is criteria for rewards
1, strengthen the liklihood or frequency of behaivors that precede or leadup to them, via reinforcement learning mechanisms
rewards increase motivated behaivors like approach/seeking and consummatory(consumption) responses in the presence of reward-predictive cues
associated with feelings of pleasure or postive affective states
what is pavlovian conditioning?
what is classical conditioning?
what is instrumental conditioning
operant conditoning?
pavlovian conditioning = introduced in the 1920’s, Pavlov referred to this as conditional “reflexes”
classical conditioning = introduceed mid-20th century to distinguish from instrumental and operant conditionin
instrumental conditioning = introduced by Thorndike, idea that behavior is instrumental in producing an outcome, behavior is the instrument by which an organism gets a reeard
operant conditioning = introduced by Skinner, behavior operates on the environment and consequences shape future behavior
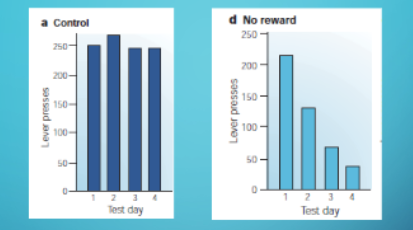
what do these graphs represent?
if u decrease delivering reward, animals gradual decrease the bahvior that would have led to reward, if you remove the reinforcer, the bahvior being reinforced decreases
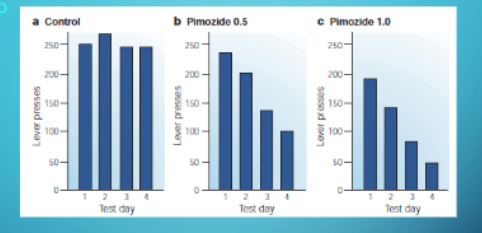
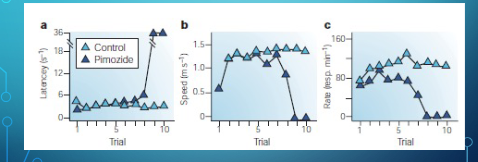
how does primozide impact behaivor?
primozide blocks dopamine D2 receptors in the brain, this blocks the rewarding effectiveness of the normally rewarding delivery of food.
food is devalued and it is no longer a reinforcer
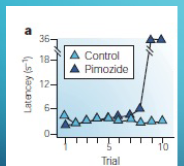
what is the effect of pimozide on lever pressing for lateral hypothalamus stimulation?
a classical experiment used to test Anhediona Hypothesis that dopamine bloackage (pimozide) impacts reward-seeking behavior inr ats
y = latency how long its takes rat so start pressing lever
x = trial number
pimozide animals are initially engaged and motivated in the task and start pressing the lever like control rats, around trial 8 they begin to slow down and eventually stop pressing altogether.
latency vs rate
Term | Meaning | What it Measures |
|---|---|---|
Latency | How long it takes the rat to start approaching or pressing the lever after the trial begins. | Motivation to initiate behavior |
Rate of pressing | How frequently the rat presses the lever once it starts. | Motivation to keep working for the reward |
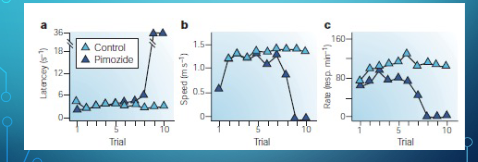
what did the anhediona lever pressing reveal about dopamine roll
speed and latency (how long it takes to start appraoching.) not quickly effected, but the rate of lever pressing is quickly impacted because pimozide animals decide quickly that lever pressing is not leading to a reward
If dopamine only caused pleasure (“liking”), then the rat should immediately lose interest once dopamine is blocked.
→ But that’s not what happens.Instead, the rats initially act as if they still expect the reward — but gradually lose the motivation to keep working for it.
→ This suggests dopamine is more about “wanting” or incentive motivation, not the pleasure itself.
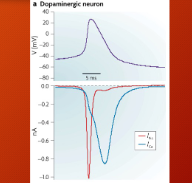
how do u know u are recroding dopamine neuron
neural recording = timing and waveform
broad action potentials are due to activation of calcium channels
low spontaneous frie rate (low and irregular spontaneous rates are 0.5-8.5 spikes/sec
can show location of electrode within dopamine brain regions
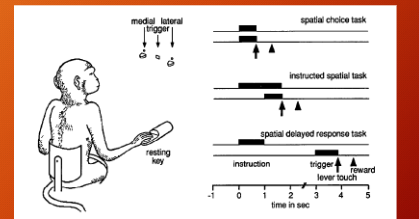
what was the monkey task in Schultz et al 1993)? - “response of monkey dopamine neurons to reward and conditioned stimuli during successive steps of learning a delayed resposne task.”
three lights - medial, lateral, trigger,
below the medial and latter light is a trigger, at the start of trial monkey sits with paw on resting key, instruction light comes on which cues either medial or lateral light, then trigger light comes on and monkey can reach for lever told by instruction light
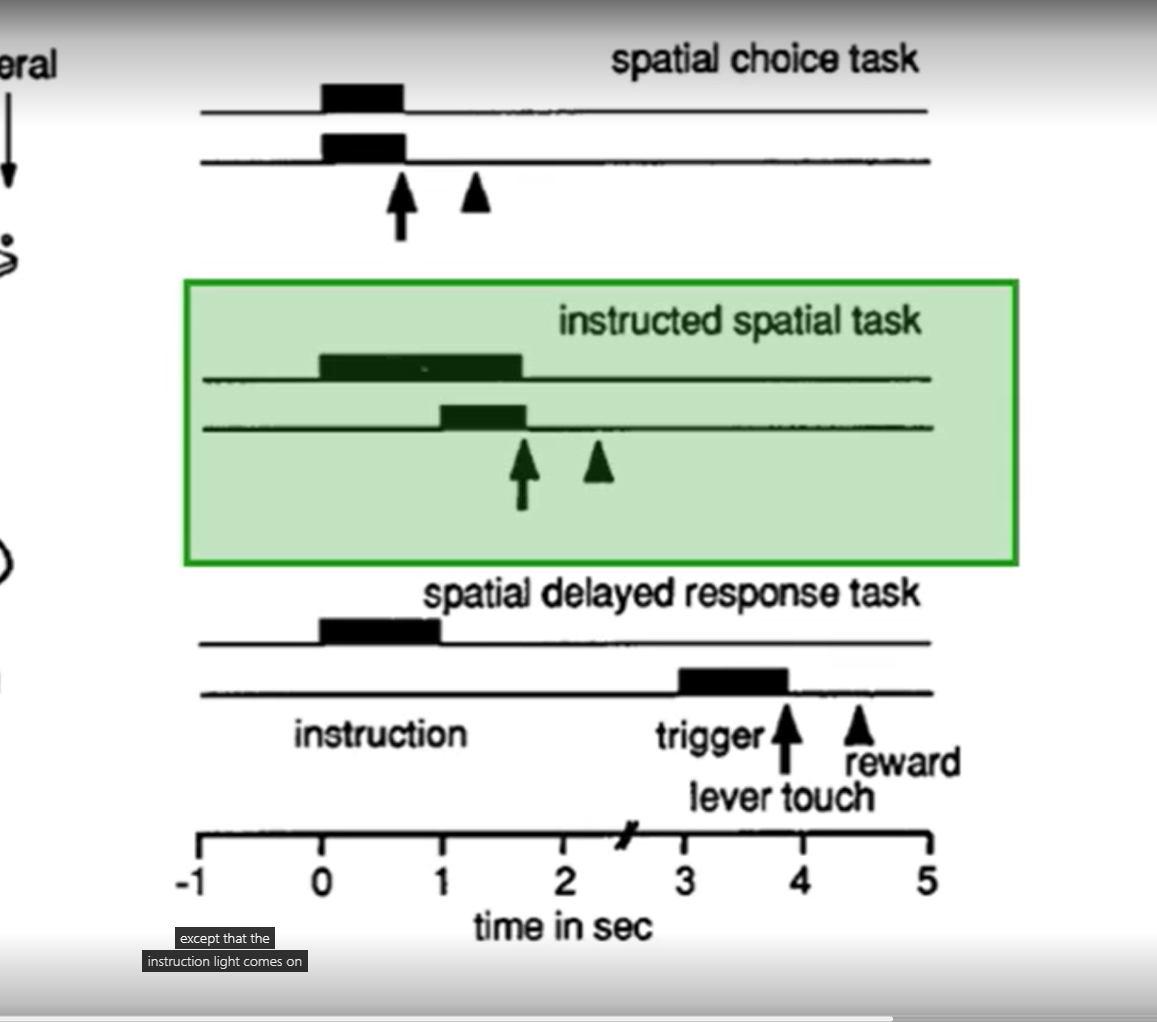
spatial choice task
instructed spatial task
spatial delayed response task
spatial choice task > instruction and trigger light come on same time monkey can grab immediately.
instructed spatial task > instruction light comes on then delay until trigger light comes on
spatial delayed response task > instruction light come on then go away, then trigger light comes on
spatial task mastered first, then instructed spatial task, and then delayed task
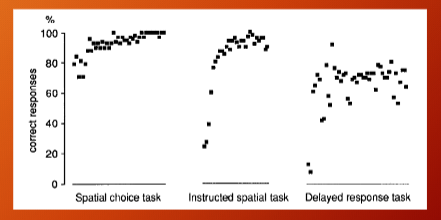
monkey task performance
monkey gets good enough and learning occurs.
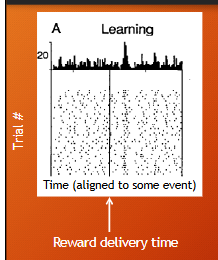
what is the peristimulus time histogram (PSTH)
what is raster plot
peristimulus time histogram (PSTH) > average # of action potentials at each time point
raster plot > each dot represents when an action occurs
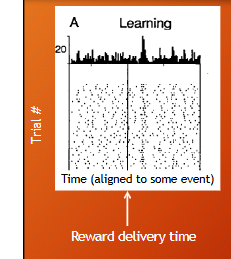
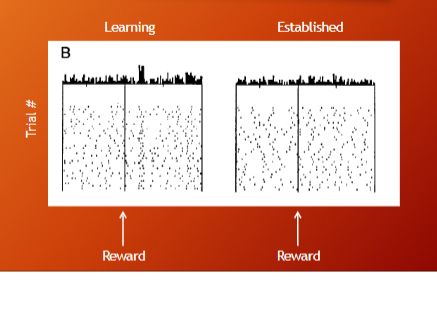
how was neuron data collected and what is the learning vs established phase?
researches recorded waveform of AP, time of AP, and time of stimulus presentations.
the left side of graph are AP before reward, and the right side is after the reward > raster plot > time 0 is when monkey pressed level/ event of interest > each dot is neuron response, when you average all the acption potentials before and after stimulus you get a peristimulus time histogram > shows us how neuron resposnes on single trial and averaged across all trials.
learning phase is when monkeys are not responding at their best, they are still learning task after they learn they are in established phase
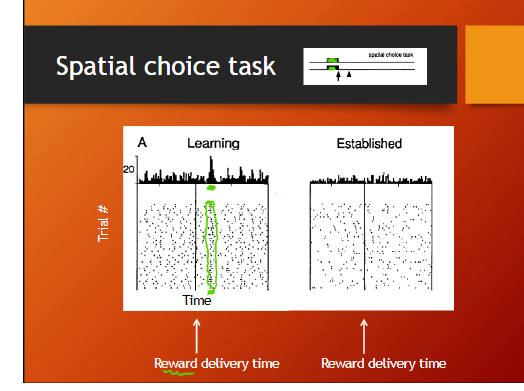
spatial choice task results
spatial task = instruction and trigger occur at same time
dopamine neurons response after the reward during learning, but during established phase dopamine neurons not responding
instructed spatial task
instructed spatial task = intruction light come on then a delay before trigger light come on
dopamine neurons active during learning but not established
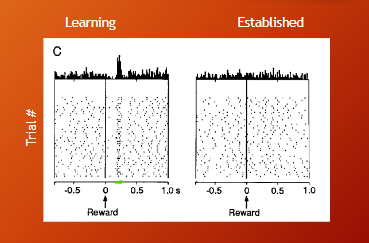
spatial delayed response task results
spatial delayed task = instruction light come on then off, after a delay trigger light come on
dopamine neurons active during learning but not established
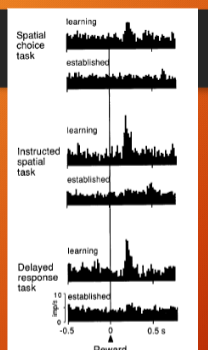
what does the populationa activity avg show?
there is response in dopamine neurons after reward in learning phase, but after monkey has learned the task the response goes away.
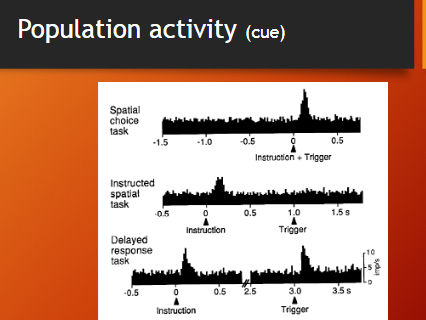
what does cue related activity show?
what was the point of splitting data analysis into medial and lateral cue
conclusion about dopamine neurons then
spatial choice task there is a response after the isntruction + trigger
instructed spatial task there is a response after the instruction comes on but not trigger (instruction cue turns on then a second later the trigger cue,
delayed response task there is response after instruction and after trigger pops up
——————
split it to see if response was diffrent based on location of trigger but dopamine neurons dont encode lever specific info
since the response varies based on when trigger cue shows up after instruction cue > dopamine neurons respond to reward during learning but reward responses dissapear after learning, dopamine neurons also respond to cues important for pulling the lever
what is a pure reward signal?
signal abstract information about objective economic value or utility of reward
signal should not be specific to what type of reward is it
should not reflect specific behavioral reactions necessary to obtain reward like where u have to reach to get it.
dopamine neurons are not pure reward signals, they respond to errors and also stop responding to reward once establlished learnin
describe dopamine neuron response during learning vs establised phase
what does it mean that dopamine neurons stop responding when monkey presses wrong lever after trigger?
dopamine neurons respond during learning after the reward when we are establishing value assocaition but not once its already established, they stop responding which indicates learning has occured >dopamine neurons respond during assocaitve learning but once the learning has occured they dont respond to reward itself only cue for the reward
when monkey presses wrong lever this is a negative reward prediction error, something unexpectadly negative happeended, worse outcome than expected.
based on these experimentas by Schultz et al 1993 when would dopamine neuron respond during palvalonian conditioning
palvalonian conditioning is the pairing food with a bell, dope neuron would respond when food presented, but after learning established dopamine neurosn dont respond to reward only to behaivorally relevant stimulus,
so after connection established and bell rung neurons respond to the bell alone and would stop activity if the food does not follow the bell.
Tobler et a. 2005 – Adaptive coding and reward value by dopamine neurons
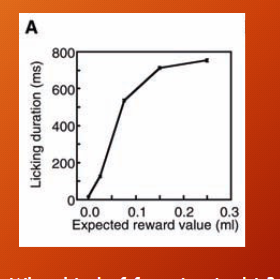
Presented one of five different stimuli to primates > each symbol is attached to some chosen expected value , The calculations below represent EV associated with each symbol (prob*value)
they tracked licking in anticipatoin duration based on stimulus presented, monkeys lick even before stimulus presented so we know when association with symbol and reward has been made. > continuous monotonic function
magnitude of dopamine respond coorelate with EV of stimuli, dopamine neurons respond to behaiovrally relevant stimuli and also EV of reward (respond diff based on how big drop of water was)
when symbol was followed by a lesser EV reward dopamine neurons stop responding, when symbol was followed a bigger EV reward there was excitation of dopamine neurons
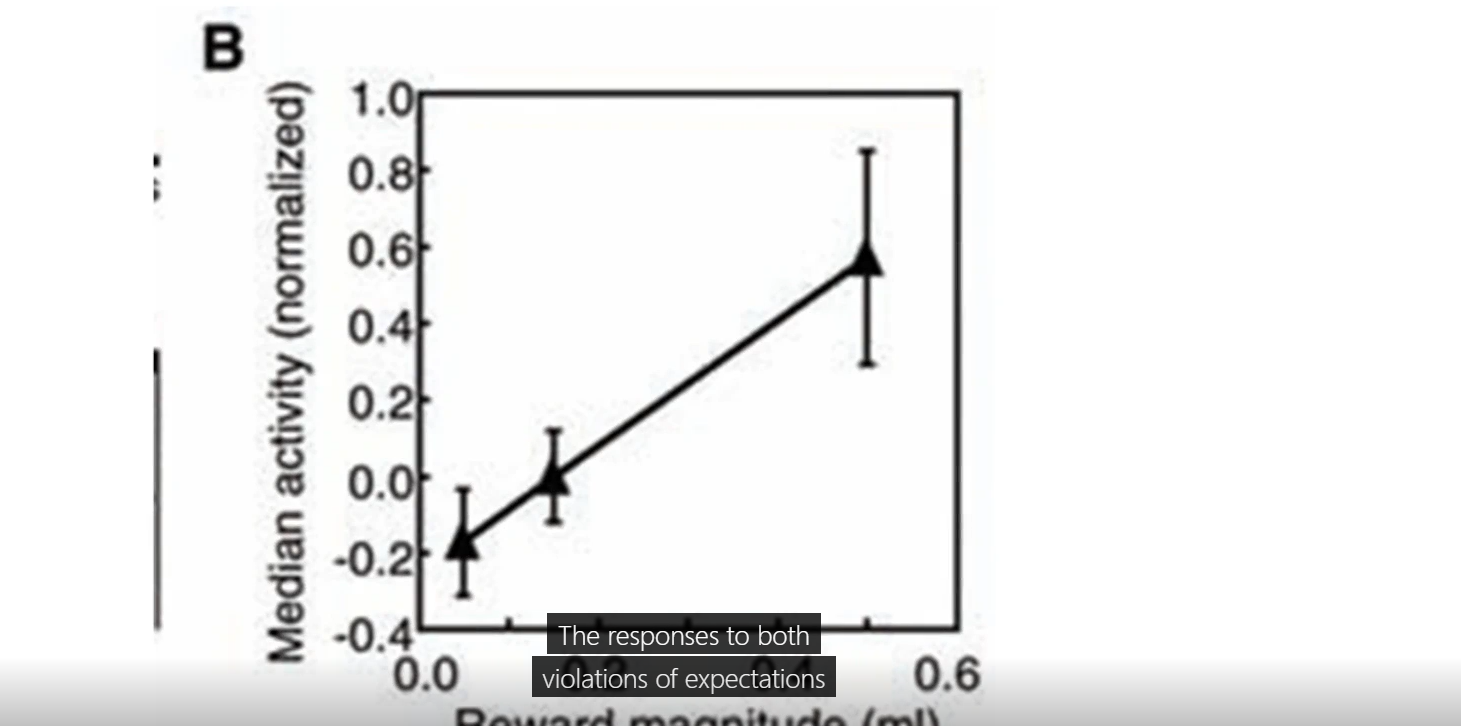
what does this figure show
when does representation in DA emerge
dopmaine neurons sensitive to violaition of expectations (when reward presented bigger more respond, when smaller less response.)
representation in DA neurons emerge at time of cue > this is assocaitiev learning
a cute lottery predicts 50% chance of 0.05ml
OR 50% chance of 0.15. what is EV of cue(lottery?)
how do dope neurons respond to either outcome?
0.025 + 0.075 = 0.10ml
when 0.05 ml reward given, we see deactivation cause 0.05 < 0.10 and 0.15 > 0.10 so exciation
individial neurons encode average reward expected and sensitive to violations from expected reward
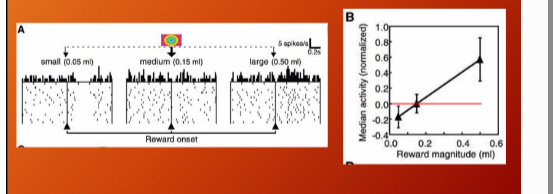
what is this graph showing in relation to Prospect Theory
when does assocaitive learning occur
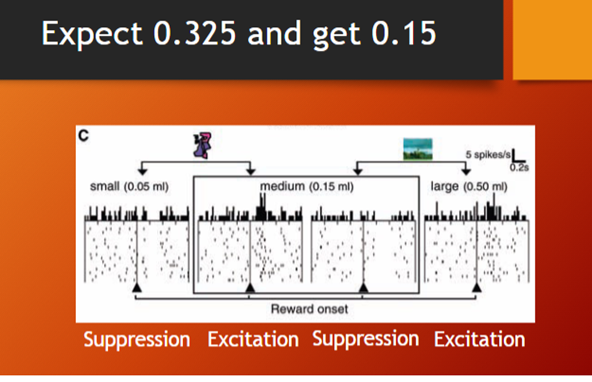
the same objective outcome, 0.15ml juice elicits a response from dopamine neurons that depends on the context> reference point has changed when we go from expecting smaller prize and getting medium one to then expecting medium response and getting a large one. even if EV dont change. similar to how there is a change in decision based on being in the gain frame (loss averse) or loss frame.(risk seeking)
associative learning > EV representation in dopamine neurons emerge at time of cue and violations of this EV will elicit a response from dope neurons at time of reward (reward prediction error)
Blocking - experiment that stems from learning theory
explain experiment by Leon Kamin 1968 (American pscychologist and leanring theroist) to test the hypothesis that violations of expectation drive assocative learning.
How do you know rat has formed association after stage 1?
rat 1. a light comes on and juice delivered, light and juice pairing repeated
you know the rat forms strong representation of light and juice pairing, rat spends alot of time by the well and also will run over to well as soon as the light turns on.
then present light + tone and present juice, repeat light-tone reward pairing and then move onto test phase > in test phase you present the tone in the conditionig chamber and look for behaivor that indicates rat shows associationg between tone and reward > result: typically no behaivor indicates an assocaition made
at the end of stage 1, rat made assocaited between light and reward, at stage 2 the tone is paired in with the light but the ligth has already been established as a predictive cue so there is on suprise or prediction violation when the reward is presented in stage 2, no violation of prediction = no learning
how do you re-work experiment such that learning of tone occurs
what is the phenomenon that rat 1 could not make association between the tone and food?
rat 2
stage 1: diff green light cue then present food, repeat pairing for assocaition
stage 2: use the light and tone from the original experiment with rat 1 and resent food, repeat for association
test phase: present the tone and see if representation has formed, the rat display behaivor that it has formed association between tone and food
blocking, rat 1’s association of the light and food was blocking association of tone and food in stage 2.
Homework 4
Schultz et al 1993 (medial, lateral, trigger lights experiment) say the lack of sustained activity during the delay period (between instruction and trigger) is because dope neurosn don’t encode what?
The authors conclude that that the transient response (short, bursts of activity during reward, behaiovr relevant cue, or attention grabbing event) are most likely related to what 2 processes?
Based on our last lecture, why might rats lever press for brain stimulation that activates dopamine neurons?
Dopamine neurons do not encode working memory, expectation of external stimuli, expectation of reward, or preparation of movement.
—
Basic attentional processes and motivational processes.
—
Dopamine neurons fire when the outcome is better than expected = reward prediction error. This signal teaches the brain that something rewarding occured. The rats may press the lever to activate dopamine neurons and it interprets that stimulation from the lever as an unexpected reward even if there was no reward. That stimulation of dopamine neurons is reinforcing an artificial reward signal.