New innovations Lecture 5
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Market research & Business analysis
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Cumulative Expenditures Curve
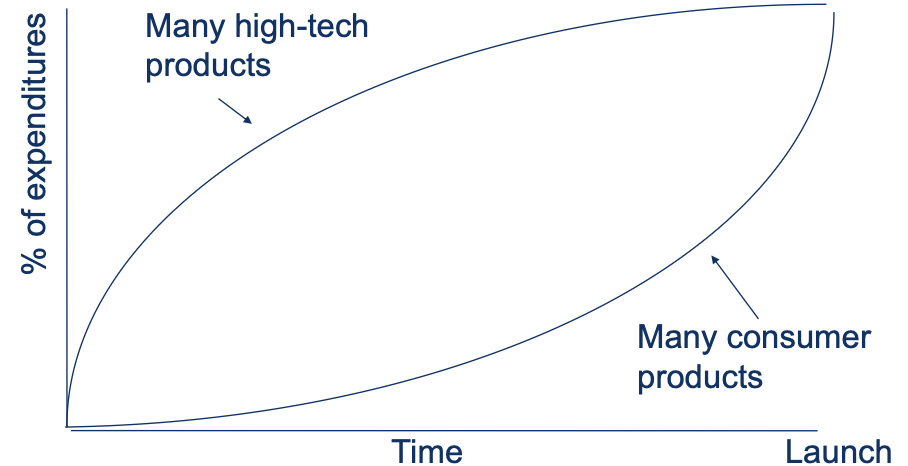
Many Ideas Are Eliminated Before
Concept Testing
⚫ PIC eliminates most new product ideas even
before they are developed into concepts.
⚫ Ideas of the following types are excluded:
– Ideas requiring technologies the firm does not have.
– Ideas to be sold to customers about whom the firm has no close knowledge.
– Ideas that offer too much (or too little) innovativeness.
– Ideas wrong on other dimensions: not low cost, too close to certain competitors, etc.
Market Analysis and Initial Reaction
⚫ Market analysis: in-depth study of market area that the PIC has selected for focus.
– Conducted immediately after PIC approval.
⚫ Initial reaction: preliminary, inexpensive assessment of concepts, which may be flowing very quickly at this point.
– Avoid “bazooka effect” (quickly blasting out concepts without forethought)
– Do not include idea source in initial reaction.
– Respect the “fragility of ideas” -- have more than a single person involved.
– Use more than pure intuition -- keep records and stay objective.
Suggested Questions for the Initial Reaction
⚫ Market Worth: what is the attractiveness of the new product to the targeted customer population?
⚫ Firm Worth: Is the new product project viewed
positively by management? Does this new product project enhance the firm’s competencies?
⚫ Competitive Insulation: Can the product’s
advantage be maintained against competitive etaliation?
Concept Testing Cautions and Concerns
⚫ If the prime benefit is a personal sense (aroma,
taste).
⚫ If the concept involves new art and entertainment.
⚫ If the concept embodies a new technology that
users cannot visualize.
⚫ If concept testing is mishandled by management, then blamed for product failure.
⚫ If customers simply do not know what problems
they have.
Some Key Issues in Concept Testing
⚫ Concept statement: narrative, drawing, model?
⚫ Respondent group: Lead users? Large users?
⚫ Response situation: Where? How?
⚫ Interviewing sequence: Believable?Important? Interesting? Would it work? What problems do they see? Would they buy?
⚫ Test procedure, change and implement, study findings.
Rolling Evaluation (or, "Everything is Tentative")
⚫ Project is assessed continuously (rather than a single Go/No Go decision)
⚫ Financial analysis also needs to be built up
continuously
⚫ Not enough data early on for complex financial
analyses
⚫ Run risk of killing off too many good ideas early
⚫ Marketing begins early in the process
⚫ Key: new product participants avoid "good/bad" mindsets, avoid premature closure
Potholes
⚫ Know what the really damaging problems are for your firm and focus on them when evaluating
concepts.
⚫ Example: Campbell Soup focuses on:
⚫ 1. Manufacturing Cost
⚫ 2. Taste
People
⚫ Proposal may be hard to stop once there is buy-
in on the concept.
⚫ Need tough demanding hurdles, especially late
in new products process.
⚫ Personal risk associated with new product
development.
⚫ Need system that protects developers and offers reassurance (if warranted).
Surrogates
⚫ Surrogate questions give clues to the real
answer.

The roles of product appearance for consumers perceived product value
⚫ Aesthetic - the pleasure derived from seeing the product
⚫ Symbolic - the choice of a specific product/brand may convey the kind of person a consumer is or wants to be
⚫ Functional - the utilitarian functions of a product
⚫ Ergonomic - the usability of a product
⚫ Attention-Drawing - the importance in gaining the consumers attention
⚫ Categorization - consumers may use the product appearance for categorization
Important aspects of appearance
⚫ Aesthetic:
– Products are used during many years
– Need also to fit with the environment of the product (e.g., in a house)
⚫ Symbolic:
– It fits directly with what you like and what you are. The product should correspond to your personality
– Buying a special product is often an emotional action: you buy because you like it.
NP Concepts though the Screening &
Protocol Process
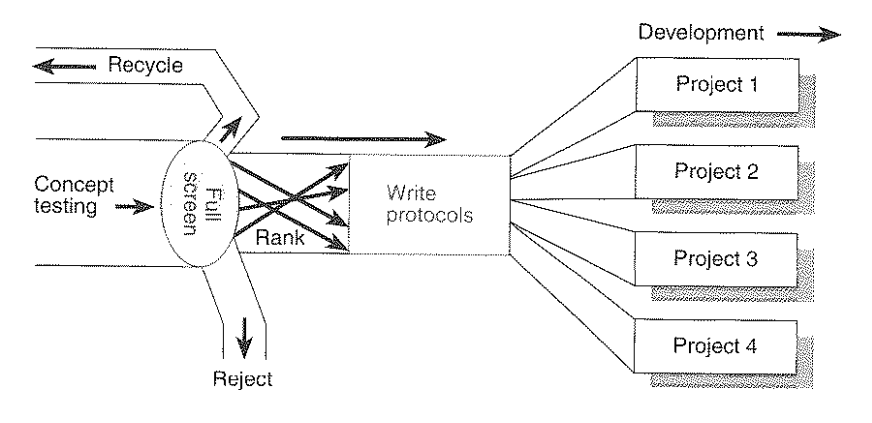
Project Evaluation – NewProd 3000
– ”A cross-functional group of experienced key persons evaluate your project on 30 factors which are critical to succes.
– Your project is benchmarked against the 2000 projects in our database.
– The program calculates the likelihood of success and provides a profile of the strengths and weaknesses of your project.
– The group makes a go/kill decision. In case of a go, the group also determine the actions needed to improve the likelihood of success for the new product.”
Empirical Screening Model
⚫ Eight Significant Factors
– Product superiority
– Overall firm/resource compatibility
– Market need, growth, and size
– Economic advantage of product to end user
– Technological resource compatibility
– Product scope (mass vs. narrow specialty)
– Market competitiveness (-)
– Newness to the firm (-)
Business analysis
Sales forecasting & Financial analysis!
An A-T-A-R Model of Innovation Diffusion
Profits = Units Sold x Profit Per Unit
Units Sold = Number of buying units
x % aware of product
x % who would try product if they can get it
x % to whom product is available
x % of triers who become repeat purchasers
x Number of units repeaters buy in a year
Profit Per Unit = Revenue per unit - cost per unit
The A-T-A-R Model: Definitions
⚫ Buying Unit: Purchase point (person or department/ buying center).
⚫ Aware: Has heard about the new product with some characteristic that differentiates it.
⚫ Trial: Usually means a purchase or consumption of the product.
⚫ Available: If the buyer wants to try the product, the effort to find it will be successful (expressed as a percentage).
⚫ Repeat: The product is bought at least once more, or (for durables) recommended to others.
A-T-A-R Model Application
10 million Number of owners of noise-cancelling headphones
x 40% Percent awareness after one year
x 20% Percent of "aware" owners who will try product
x 70% Percent availability at electronics retailers
x 20% Percent who will buy a second unit (repeat)
x 50 Euro Price per unit minus trade margins and discounts;
(100 Euro) minus unit cost at the intended volume
(50 Euro)
= 5,600,000 Euro Profit
Points to Note About A-T-A-R Model
1. Each factor is subject to estimation. Estimates improve with each step in the development phase.
2. Inadequate profit forecast can be improved
by changing factors. If profit forecast is inadequate, look at each factor and see which can be improved, and at what cost.
Bass Model - Forecast of
Product Diffusion
BASS formula - explanation
⚫ Based on Roger’s Diffusion of Innovation.
⚫ Mostly used on durable goods like television, coffee makers, irons etc.
⚫ Estimates the sales at a given time depending on factors:
– p: Initial trial probability (often around 0,04)
– q: Diffusion rate (often around 0,3)
– m: total number of potential buyers
– Y(t): total number of purchases by time t.
⚫ You can then calculate the time needed to reach the sales peak, as well as the sales peak itself.
Calculating New Product’s Required Rate of Return
Computer-Aided Design (CAD)
⚫ Greatly accelerates the design step and allows
assessment of multiple possible designs without
building expensive prototypes.
⚫ Design for Manufacturability (DFM): search for ways to minimize manufacturing costs.
⚫ Design for Assembly (DFA): search for
ways to ease assembly and manufacture
Some of the Uses of CAD in Auto Industry
⚫ Determining fit of subassemblies:
– does the radio/CD/Navigation player protrude too far into the engine area?
⚫ Do all the pieces fit together perfectly?
– Facilitating “decking” of cars (attaching the powertrain to the upper body):
⚫ Can we modify any aspects?
⚫ Crashworthiness of the car’s design to improve its ability to protect the passengers in a crash?
Recent Developments in CAD/CAE
⚫ Stereolithography (rapid prototyping)
⚫ Mechanical computer-aided engineering (MCAE)
(Computer Aided Design & Computer Aided Engineering