Prokaryotic Cells
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Prokaryote
simple, single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles
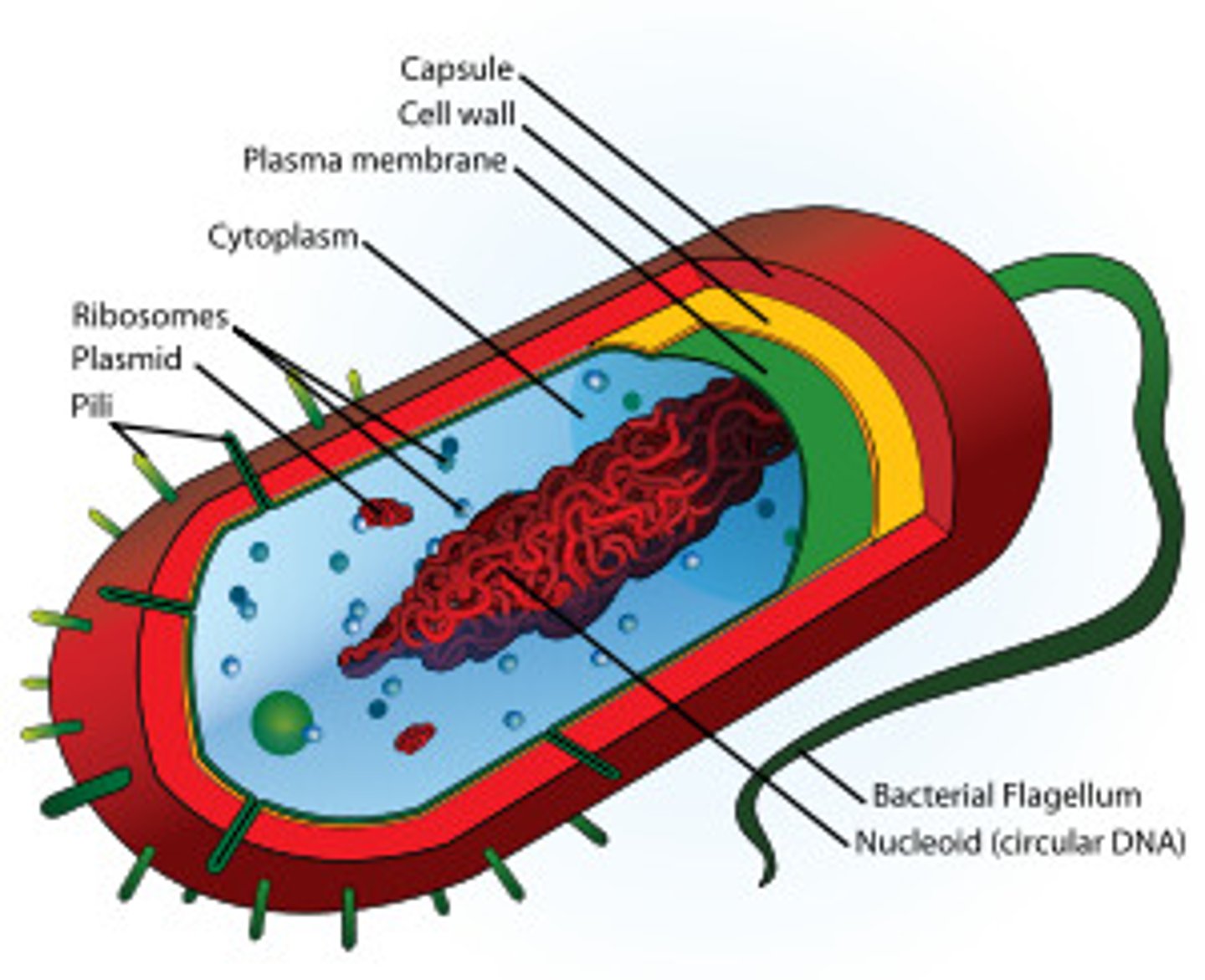
Plasma membrane
controls the movement of materials into and out of the cell
Cell wall
protects and maintains the shape of the cell / provides rigidity and strength / prevents over-expansion when water enters the cell
Pili
attachment / adhesion and used to transfer DNA from one cell to another
Flagella
allow motility / locomotion
Ribosomes
involved in protein synthesis (this process is called translation)
Nucleoid region
Contains naked DNA (genetic material of the cell) and is involved with cell control and reproduction
Plasmid
Circular DNA
Cytoplasm
Fluid that fills the cell; Contains ribosomes, enzymes, and other important molecules
Peptidoglycan
Material used to form the cell wall (in contrast to the cellulose used to form a eukaryotic plant cell wall)
Binary fission
Means by which prokaryotic cells divide - DNA is copied and the cell divides into two genetically identical daughter cells
Example of a prokaryote
Bacterium