[D.1] FLOOR COVERINGS
1/183
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
184 Terms
Carpet
Used as floor covering. It provides floors with both visual and textural softness, resilience, and warmth in a wide range of colors and patterns. It absorbs sounds, reduces impact noise, and provides a comfortable and safe surface to walk on and is fairly easy to maintain.
Carpita
The term carpet comes from this Old Italian term, meaning to pluck
Wool
Types of Natural Fibers
Used for centuries in the manufacturing of carpet. It is still the standard against which other carpet fibers are judged. It is generally the most expensive carpet fiber and is commonly used in woven carpets.
Wool
Types of Natural Fibers
Its outer layer is scaly, which diffuses light, thus hiding soil. When exposed to flame, wool chars, rather than melting like most synthetic fibers, making it naturally flame resistant.
New Zealand Wool
Characteristics of Wool from Different Countries
wool absorbs dye easily, colors with great clarity and uniformity, staple are lustrous and tough, and color is almost white
Argentinean Wool
Characteristics of Wool from Different Countries
noted for its gloss and sheen with natural resistance to soiling; not as white as New Zealand Wool
Indian Wool
Characteristics of Wool from Different Countries
crush resistant wool
Iraqi Wool
Characteristics of Wool from Different Countries
among the most luxurious and costly of wool; high abrasion resistance and durability
Scottish Wool
Characteristics of Wool from Different Countries
Scottish black face sheep bear finest of all carpet wool with stapes as long as 15 inches
Sisal
Types of Natural Fibers
Light cream or oatmeal in color; It is a strong, woody fiber produced from the leaves of the agave plant. Used mostly in twine, rugs, floor mats, ad rope.
Sisal
Types of Natural Fibers
It has a rough texture, is stiff, and inflexible. It tends to stain and crush easily, but is still stronger and more durable than any natural fiber.
Scratch Rush
This is another term for Sisal
Maize
Types of Natural Fibers
made from corn husks
Coir
Types of Natural Fibers
Strong and flexible hair like fiber from coconut shells. It is tough, does not pill, can withstand a great deal of abrasion, is highly rot resistant, and is proven to be unfriendly to insects.
Coconut Plush
What is another term for Coir?
Cotton
Types of Natural Fibers
Softer than wool but less durable; does not resist stains and also absorbs moisture
Jute
Types of Natural Fibers
Softest of all natural fibers; May fade or darken in color when exposed to sunlight, and its fiber disintegrates with prolonged exposure to moisture
Nylon
Types of Synthetics or Man-made Fibers
Most popular carpet fiber used today; It is versatile, and easy to maintain and clean, and withstands heavy foot traffic. It is the most widely used man-made fiber and is often combine with wool for durability
Acrylic
Types of Synthetics or Man-made Fibers
One of the first synthetic fibers to be used successfully in the production of carpet. It is always used as a staple fiber and has many of the characteristics of wool and has the lowest static build-up factor. It is highly resistant to sunlight, stains, and mildew. Used in bath mats and rugs.
Modacrylic
Types of Synthetics or Man-made Fibers
Has better heat retention and is flame resistant compared to acrylic
Polyester
Types of Synthetics or Man-made Fibers
Soft and luxurious; It is strong, durable with high abrasion resistance. Dyes well, and has low static build-up factor. Used for residential carpet applications as shags and random sheared carpet
Polypropylene Olefin
Types of Synthetics or Man-made Fibers
Newest and most economical. Comparable to nylon in durability, strength, and wear resistance. It is the lightest commercial carpet almost completely free of static build-up.
Polypropylene Olefin
Types of Synthetics or Man-made Fibers
Used in outdoor carpeting. Most resistant synthetic fiber because it repels water and impervious to stains, and is less expensive than other fibers
Acetate
Types of Synthetics or Man-made Fibers
Made from cellulose obtained from wood pulp or cotton linters. These fibers are often used in carpets because they can mimic the look and feel of natural fibers like silk, wool, or cotton at a lower cost
Acetate
Types of Synthetics or Man-made Fibers
Brand names such as Avisco, Celaire, Cromspun, Estron
Azlon
Types of Synthetics or Man-made Fibers
Created from protein-based polymers, often derived from natural sources such as soybean protein or milk casein. These fibers are sometimes used in textiles, including carpets, as an alternative to traditional synthetic fibers like nylon or polyester
Azlon
Types of Synthetics or Man-made Fibers
Brands like Vicara
Rayon
Types of Synthetics or Man-made Fibers
A semi-synthetic fiber made from natural cellulose, usually derived from wood pulp; offers a soft and luxurious feel, similar to natural fibers like silk, making it an attractive choice for certain carpet styles but may not be as durable as other synthetic fibers
Rayon
Types of Synthetics or Man-made Fibers
Brands like Avicolor, Avicron, Avsio, Corval, Fibro, Kolorbon, Skybloom, Skyloft, Soluran, Spunvis, Staylux, Tufton
Saran
Types of Synthetics or Man-made Fibers
Brands like Rovana and Saran
Saran
Types of Synthetics or Man-made Fibers
Developed by the Dow Chemical Company in the mid-20th century; It is a polymer made from vinyl chloride, a type of plastic known for their resistance to moisture, chemicals, and sunlight, making them suitable for a variety of applications
Triacetate
Types of Synthetics or Man-made Fibers
Brands like Arnel
Triacetate
Types of Synthetics or Man-made Fibers
Derived from cellulose, typically obtained from wood pulp or cotton linters; Formed through a chemical process in which cellulose is treated with acetic acid and acetic anhydride
Blend
Types of Synthetics or Man-made Fibers
Combinations of two or more fibers into a single carpet yarn, with each yarn lending to the other its dominant characteristic
Face
Parts of a Carpet
Composed of the pile. The upright ends of yarn whether cut or looped; Forms the wearing surface of carpet or rugs
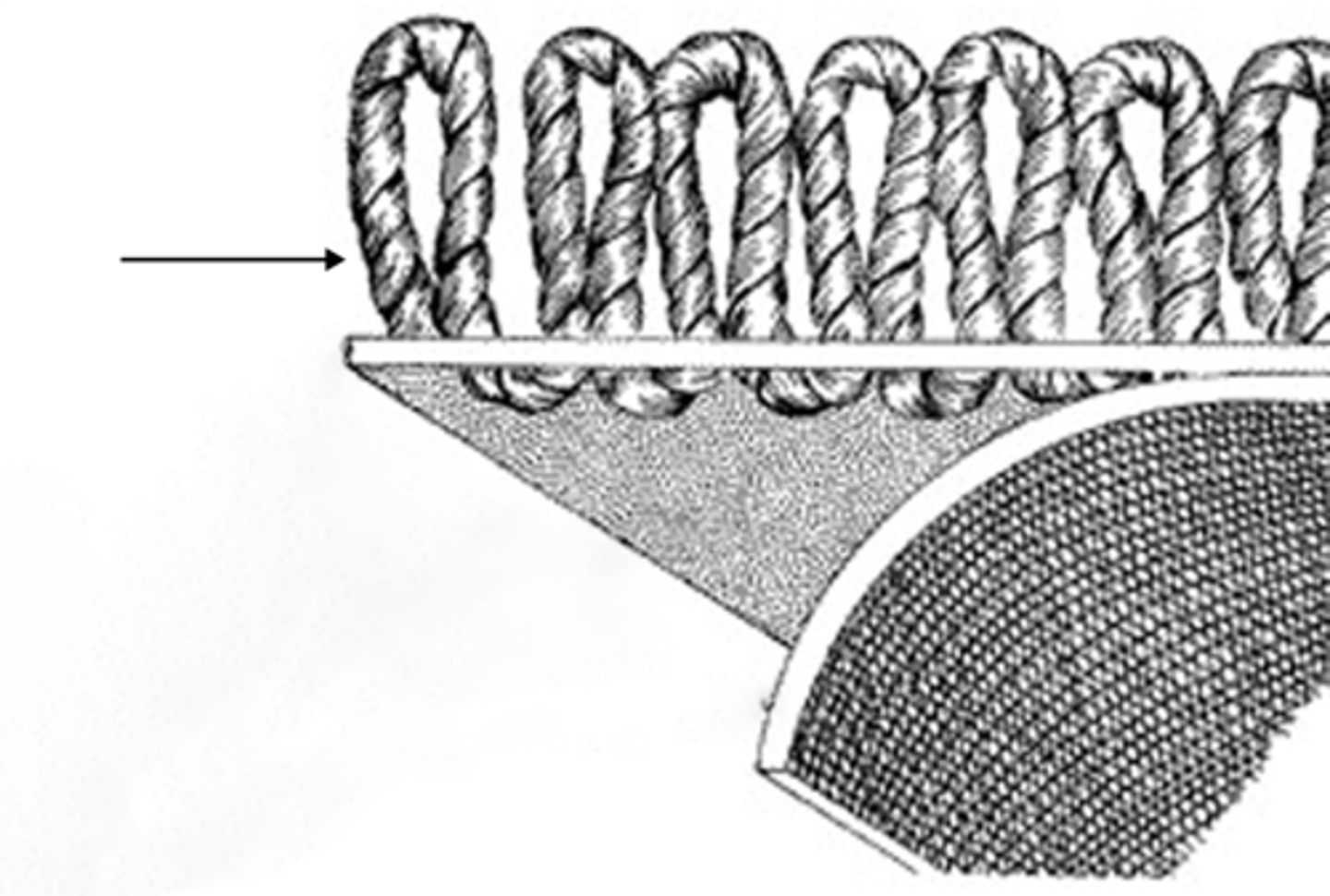
Primary backing
Parts of a Carpet
a ground on which to hook the yarns. The foundation is the canvas on which the yarns are woven
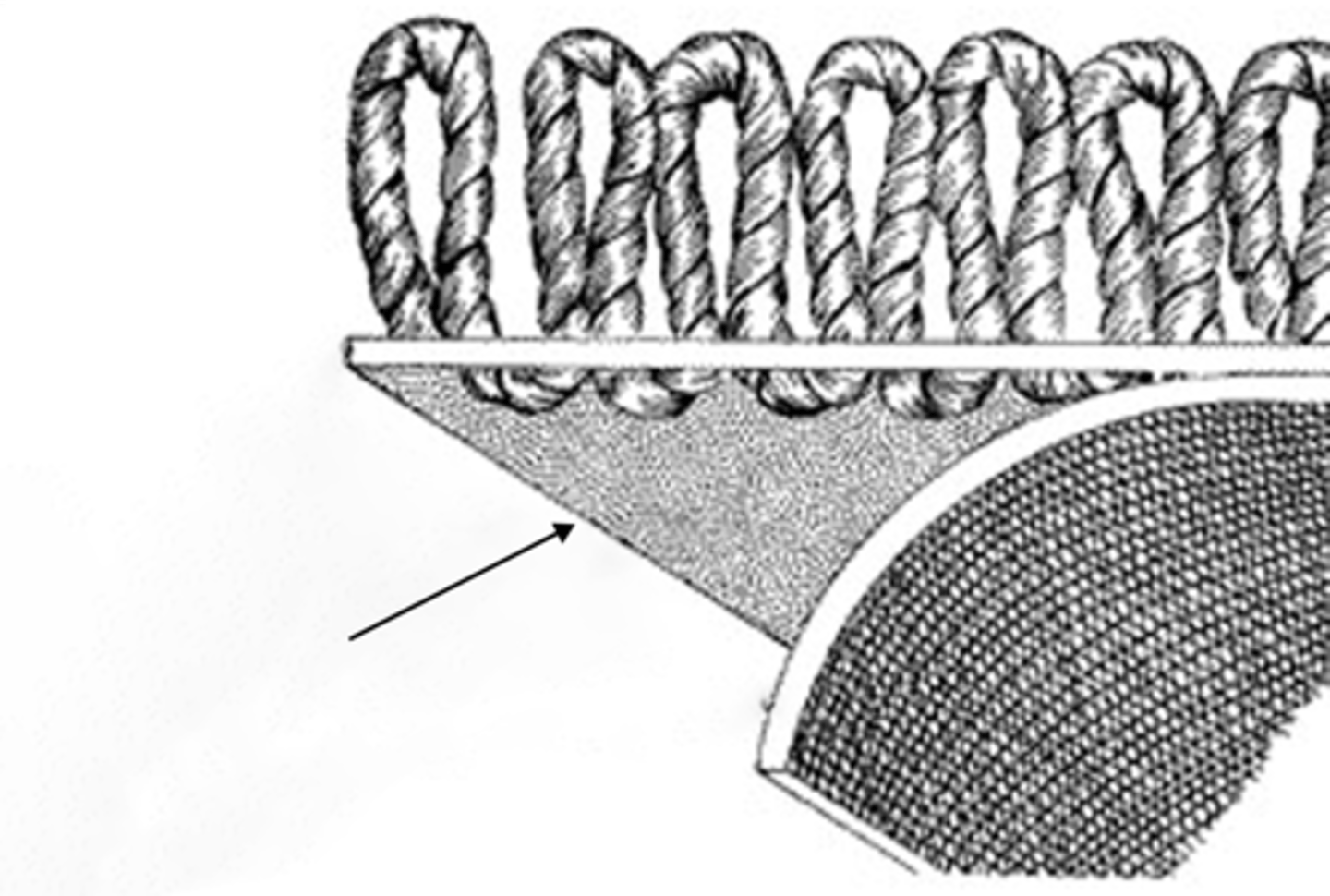
Latex
Parts of a Carpet
To glue on the roots of the yarns onto the cotton canvas backing on which they are woven; Provides superior tuft lock and resilience in stretching, especially for wall-to-wall installations
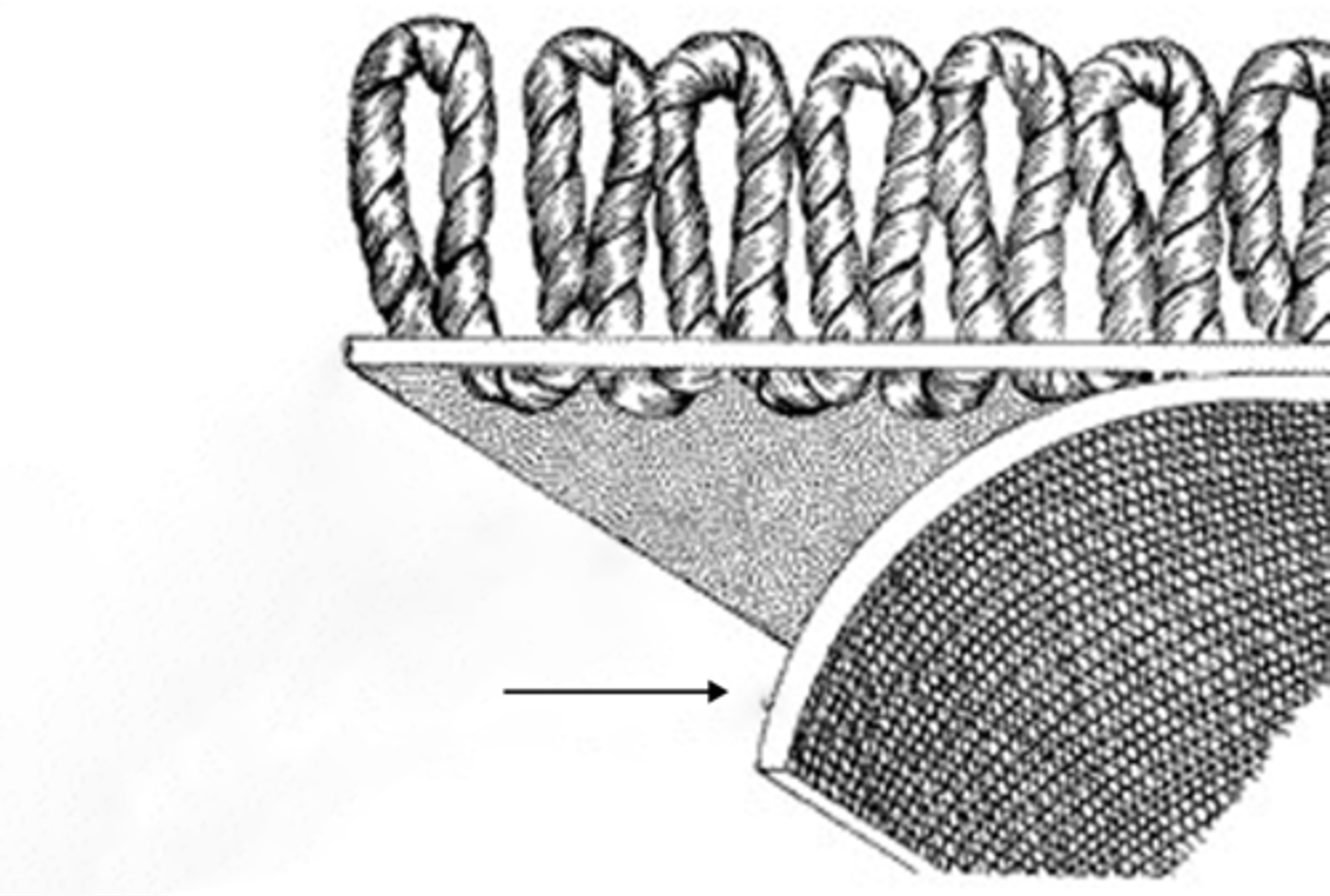
Secondary backing
Parts of a Carpet
Carpet pads; Bonded to the primary backing in the latexing stage. Either Jute (stable and heat resistant but tends to shrink when wet and can stain the carpet face) or Polypropylene (moisture resistant)
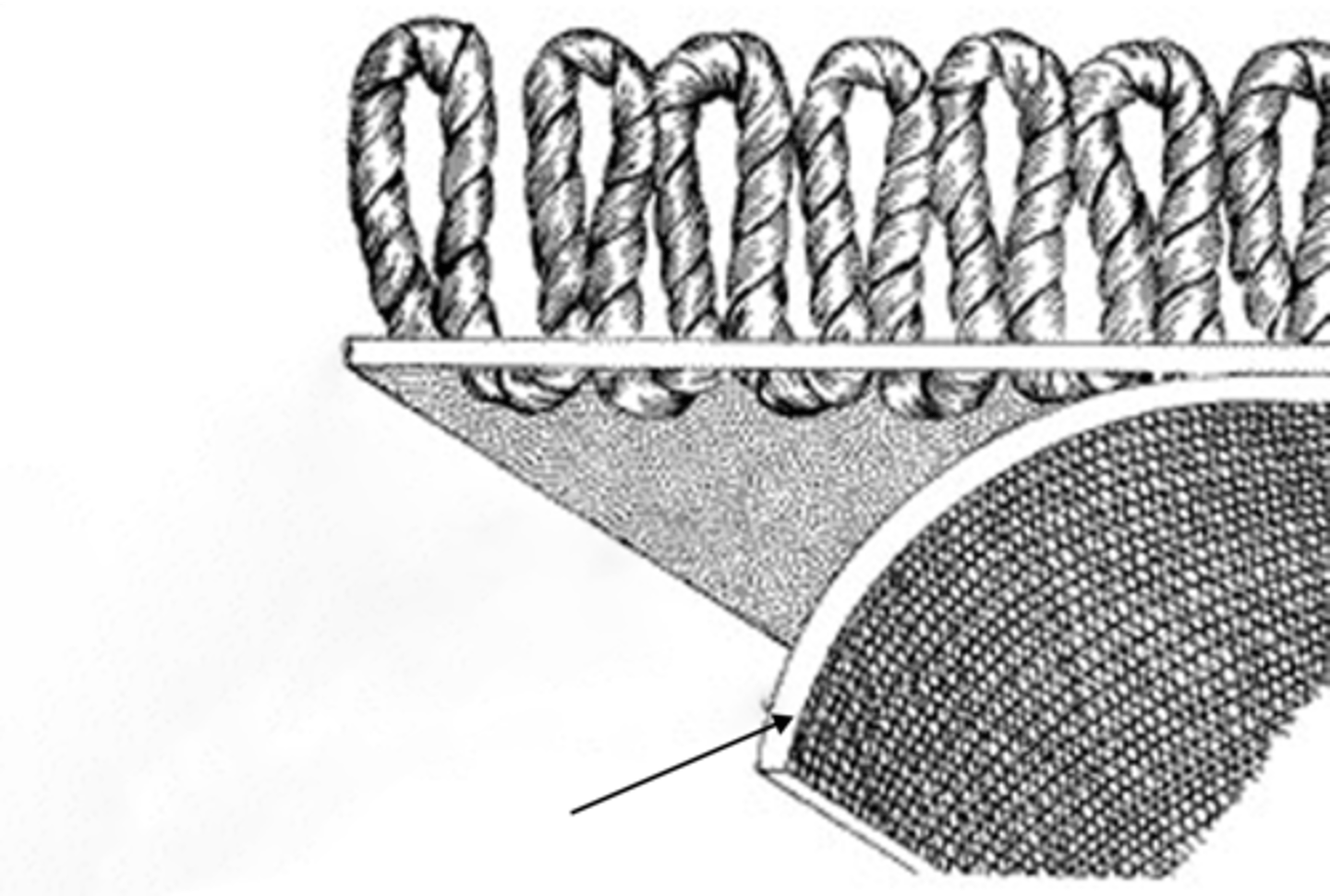
Tufting
Methods of Manufacturing Carpets
Far less expensive and faster to produce than woven carpet. It enabled to mass production of an affordably priced textile floor covering
Tufting
Methods of Manufacturing Carpets
Constructed by punching tufts of yarns into a backing. Yarns are threaded through hundreds of individual needles on a device that extends the entire width of the finished carpet
Tufting
Methods of Manufacturing Carpets
he needles are forced through a loosely woven or non-woven primary backing material, which forms the loops or tufts. Adhesive is added to hold the loops in place and then a secondary backing
Weaving
Methods of Manufacturing Carpets
Traditional way of making carpet on a loom. Produced by intertwining the surface pile and the backing simultaneously into an integrated whole.
Weaving
Methods of Manufacturing Carpets
This produces heavy, dimensionally stable, and strong carpets and does not require a secondary backing. It is a slower, more labor-intensive process than tufting and is more expensive
Velvet
Three Basic Types of Weaving
Least complex weaving method and the most inexpensive. Produces solid color carpets and is made on looms similar to Wilton looms, but without the Jacquard mechanism. All yarn in this type appears on the back of the carpet.
Wilton
Three Basic Types of Weaving
Named after a town in England. Constructed on a modified Jacquard loom. Used to produce carpet of more than one color with as many as 5 colors possible. It is thick and heavy because yarn of every color used is carried beneath the pile surface
Axminster
Three Basic Types of Weaving
Inspired by European and Oriental patterns. Combinations of patterns and colors are virtually limitless, because the colored yarns are inserted individually. It is intricate, multi-colored patterns and a backing heavily ribbed, and can only be rolled lengthwise. Tends to stretch quite a bit in length and very little in width.
Velvet, Wilton, Axmister
What are the three basic types of weaving processes?
Knitting
Methods of Manufacturing Carpets
Similar to woven carpet because pile and backing are made in a single operation. Uses 3 sets of needles to loop the pile backing yarn and the stitching yarns together. Latex is given to the back for additional strength and body.
Knitting
Methods of Manufacturing Carpets
Known for their plush piles because there is more yarn in the wear surface than tufted carpets. Has a tendency to stretch, especially on the diagonal, and is difficult to seam during installation.
Needlepunched Carpet
Methods of Manufacturing Carpets
Fibers, usually acrylic or polypropylene are punched into a web of synthetic fiber to form a homogenized layer of fiber. Put under heavy compression to form the characteristic of fabric
Flocked Carpet
Methods of Manufacturing Carpets
Uses an electrostatic method. Fibers are electro-statically treated and sprayed onto an electrically charged backing sheet which has been treated with adhesive
Pile Density
Factors to Consider in Carpet Construction
Weight of pile yarn in a given volume of carpet face
Gauge
Widthwise Density Measurement
distance between the needles in tufted carpets
Pitch
Widthwise Density Measurement
number of ends in a woven carpet
Stitch Rate
Lengthwise Density Measurement
Defines the number of times per inch a stitch occurs in tufted carpets. The number of times an individual needle inserts a tuft into the primary backing as the primary backing moves one inch through tufting machines; Also called Stitches per Inch
Rows/Wires
Number of ends per inch lengthwise
Pile Height
Lengthwise Density Measurement
length of the tuft from the primary backing to the tip
Face Weight
Factors to Consider in Carpet Construction
Weight of the pile yarn stated in ounces per square yard of carpet. Describes the amount of yarn in the wear surface of the carpet
Total Weight
Factors to Consider in Carpet Construction
Includes the face weight and the weight of backing materials, finishes, and coatings
Yarn Weight
Factors to Consider in Carpet Construction
indicates the fineness or coarseness of the finished yarn
Woolen Count
Factors to Consider in Carpet Construction
number of running yards in one ounce on finished yarn
Denier
Factors to Consider in Carpet Construction
measurement of weight in grams of a standard 900m length of yarn
Ply
Factors to Consider in Carpet Construction
affects color, surface texture, and feel underfoot. The number of strands of a single yarn twisted together to form one pile yarn
Twist Level
Factors to Consider in Carpet Construction
products with higher twist levels have the tendency to hold their original appearance longer than lower twist products
Cut Pile, Loop Pile, Loop and Cut Pile
What are the three major categories of carpet textures?
Cut Pile
Textures of Carpets
cutting each loop of pile and produces wide range of textures
Cut Pile Plush
Types of Cut Pile
Smooth cut pile; The cut ends of the yarn blend with each other for a consistent surface appearance. Has a luxurious look and feel but is subject to shading and shows foot marks
Saxony Plush
Types of Cut Pile
texture between cut pile plush and cut pile shag. Makes use of thicket yarns and has a twisted yarn, which gives definition to each tuft. Made with heat-set yarn usually in a dense, low-pile construction
Twist/Frieze
Types of Cut Pile
made from yarns that have been tightly twisted and the twist set by a special heating treatment that imparts a grainy appearance. Has a heavier, rougher texture than cut pile plush. Made in solid color or multi-tone effects and it hides dirt well
Shag
Types of Cut Pile
multi-directional, high pile twist, giving an attractive, informal look. Has a heavily textured surface created by the long twisting yarns
Loop Pile
Textures of Carpets
weaving, tufting, or knitting the pile yarn into loops. Left uncut and is called Round Wire. Tougher and more easily maintained than cut pile, but is less versatile in color and pattern
Level Loop Pile
Types of Loop Pile
made of uniform uncut loops which are of the same height. Very sturdy and offers little textural variation. Has a pebbled surface texture that conceals soilage and hides footprints and other indentations. Used for heavy traffic areas and commercial installations
Multilevel Loop
Types of Loop Pile
made of different pile heights, all uncut loops. Gives a dimensional character to the carpet. Capable of producing sculptured patterns
Loop and Cut Pile
Textures of Carpets
adds a degree of warmth to an all-loop pile. Can be produced in tufted and woven constructions
Level Type Shear
Types of Loop and Cut Pile
some of the loops are cut and some remain uncut. Adds interest to colors and gives a desirable pattern effect
Random Shear loops
Types of Loop and Cut Pile
are sheared to different heights, forming a pattern that can be definite or irregular. Produces tonal contrast between the cut and uncut loops of varying heights
Carving
Sculptured Textures
incising a design into a carpet or rug which has already been woven
Hairline Carving
Types of Carving Sculptured Textures
used between colors in a multicolor design rug in order to accentuate and give a design some dimension
Recessing
Sculptured Textures
weaving a design into a low level rather than shearing down or carving it into the carpet
Embossing
Sculptured Textures
weaving a design in a higher level
Beveling
Sculptured Textures
rounding off the parts of a carpet that have already been carved, recessed, or embossed
Stock Dyeing
Methods of Coloring
dye is applied to the synthetic fibers before they are extruded or spun into yarn. This means that the color is integrated throughout the entire fiber, providing uniform coloration
Carpet Coloring
Accomplished by predyeing the carpet fibers before the carpet is manufactures or postdyeing the finished piece of carpet
Skein Dyeing
Methods of Coloring
also known as Yarn Dyeing; involves dyeing the yarn after it has been spun from the fiber but before it is woven or tufted into carpet. The yarn is typically wound onto skeins or cones and then immersed in a dye bath to apply the color
Solution Dyeing
Methods of Coloring
the color pigment is added to the polymer solution before it is extruded into fibers. This means that the color is an inherent part of the fiber itself, providing excellent colorfastness and resistance to fading, even in harsh environments
Piece Dyeing
Methods of Coloring
method in which the entire carpet, typically in the form of a large roll or "piece," is dyed after it has been tufted or woven. In this process, the carpet is passed through a dye bath or sprayed with dye to apply the color evenly across the entire surface
Jig Dyeing
Types of Piece Dyeing
carpet or fabric is wound onto a perforated roller known as a jig. The jig then moves through a dye bath, where the dye is forced through the fabric using pressure or vacuum
Winch, Real, or Back Dyeing
Types of Piece Dyeing
involves immersing the carpet or fabric in a dye bath contained within a large cylindrical vessel known as a winch, reel, or beck. The carpet or fabric is wound onto a reel or placed on a winch, which is then submerged and agitated in the dye bath
Open Beck Dyeing
Types of Jig Dyeing
produces 1000 yards of dyed carpet. Carpet ends are attached to form a large loop, which is submerged in a dye vat
Jet Beck Dyeing
Types of Jig Dyeing
has a very consistent level of color. Carpet is sewn together end to end, forming a continuous loop places in a large circular tubes called jet becks
Pad Dyeing
Types of Piece Dyeing
continuous dyeing process where the dye is applied to the carpet or fabric using a padded roller or applicator. The carpet or fabric passes through a dye bath, and the dye is transferred onto the surface using pressure
Differential
Methods of Coloring
Also known as Cross-Dyeing; dyeing technique used in textiles, including carpets, to achieve multicolor effects. In this process, different fibers or yarns within the same fabric or carpet are dyed with different types of dyes or different colors, resulting in a fabric with distinct color variations
Space Dyeing
Methods of Coloring
different colors are printed along the length of the yarn before it is manufactured into carpet, with different color baths for each of the yarns
Resist Dyeing
Methods of Coloring
yarn is treated to resist additional dyes. It produces no discernible pattern and used for shading only
Continuous Dyeing
Methods of Coloring
dyeing carpet in a continuous production line, rather than piece-dyeing separate lots
Package Dyeing
Methods of Coloring
spun yarns are wound on large perforated forms. Under heat or pressure, dyes are forced through the perforation and onto the yarn
Random Multicolor Dyeing
Methods of Coloring
achieved with a random dye application or a TAK random pattern machine which disperses regulated amounts of dye on carpet that is already dyes a single ground color or even on undyed goods
Printing
Patterns are applied to carpet after it is manufactured. Simulates the intricate patterns of woven carpet at a much lower cost
Screen Printing
Types of Printing
flat templates, or screens, through which dyes are forced to form finished pattern on the carpet pile
Deep dye Printing
Types of Printing
electrostatic charge forces the pre-metallized dyes used in this process deep into the pile. Puts down all the colors in the design at the same time