Visual Fields I
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Define the visual field
extent of space in which objects are visible to an eye in a given position
Approximate monocular visual field size
100° temporal
60° nasal → nose in the way so less
60° superior → brows in the way
75° inferiorly
What is the size of the binocular field approximately
120° horizontally
Why do we measure the visual field?
visual field determined by our retina + connectivity between retina and brain
VF can tell us about abnormalities or damage in the visual system along this pathway
can help pinpoint exactly where along pathway problem lies
What is the purpose of measuring the visual field?
detection of abnormalities in visual function
locating site of abnormality
monitoring disease progression
What is discrimination threshold?
tells us when patient just able to detect that stimulus luminance is different from background luminance → contrast perception task
our ability to discriminate between different light intensities can get worse with disease
e.g if background luminance L → 400 units , smallest change we can detect is 50 units
50/400 =0.125
What does a smaller threshold value indicate?
more sensitive patient is to small changes in luminance
What is sensitivity?
The reciprocal of threshold value
1/Threshold
How is stimulus intensity expressed?
In decibels (dB) on a logarithmic scale
What do higher dB values represent?
Dimmer (less intense) lights and higher sensitivity
33dB average in young patient → good
Can dB values be compared across machines?
No, because background luminance and max intensity of bulbs in machine differ (varies between manufacturers)
What is the Method of limits - determine threshold?
in ascending method of limits luminance of stimulus gradually increased → patient reports when they first detect the stimulus (against the background)
difference between luminance level of stimulus& background luminance gives threshold
What is the Descending method of limits?
Stimulus brightness decreases until no longer seen
threshold can also be calculated as avg of both ascending + descending values
Staircase method for determining threshold
luminance increased in steps until patient reports that they can see it
then luminance decreased again until they report that stimulus can no longer be seen
it is then increased/decreased in increasingly smaller increments until each change in luminance gives reversal (bracketing technique)
threshold avg between last few reversals
Psychometric function to determine threshold?
stimuli presented at dif intensities + patient reports when they can see stimulus
curve can be plotted showing dif stimulus intensities in dB (x axis) against % of times patient reports that they saw stimulus (y axis)
when they could see stimulus 50% of time , corresponding value taken as threshold
very time consuming
What is the Hill (island) of vision?
higher the hill, more sensitive that part of retina is
fovea = most sensitive
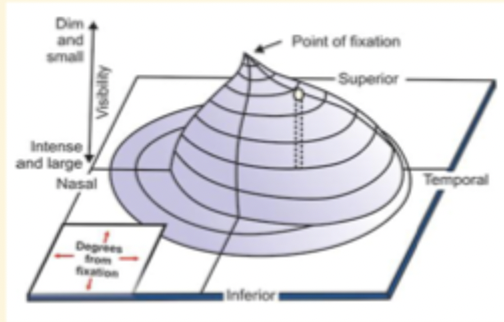
What does width of hill represent and the height?
width → Extent of the visual field
height → sensitivity of vision at various location within the field
Retinitis pigmentosa can constrict VF (tunnel vision) we might want to measure extent of px’s visual field
Define kinetic perimetry?
Uses moving stimuli to plot the full extent of the visual field
not good at sensitivity so not good for glaucoma etc
measured on Octopus 900 machine or Goldmann perimeter
What is the Goldmann perimeter?
Maps entire visual field with dif targets → lights varying in size + brightness
time consuming
What is the Goldmann Field plot?
different targets plotted in different colours
larger brighter targets more easily detected than small dim ones
blind spot drawn in black
Goldmann target size and intensity range
target size → 0 (0.0625mm2 to V 64mm2)
target intensity 1a (19dB (dimmest) to 4e 0dB (brightest)
quite time consuming
What is automated static perimetry?
Uses stationary stimuli flashed at a different number of locations within patient VF
done on automated machine unlike Goldmann
tests categorised as threshold or suprathreshold
Main use of automated static perimetry
useful for measuring patients threshold or detecting localised scotoma
tests can be categorised as threshold or supra threshold
what are the common machines of automated static perimetry?
Humphrey Visual field analyser (Zeiss)
Henson (Elektron Eye Technology)
Octopus (Haag Streit)
Advantages of automated perimetry
Standardised, sensitive, good for monitoring disease.
What is the 30-2 test pattern?
stimuli presented to 76 different locations (76 points)
extends out to 30° from fixation
stimuli 6° apart
2 in the name refers to fact that stimulus offset from vertical + horizontal midline by 3°
What is the 24-2 test pattern?
54 locations
extends out to 21° in all directions except NASALLY where it goes out to 27°
→ early glaucomatous field loss can occur in nasal region
Why are points offset from midlines?
helps interpreting & diagnosing field loss
What is a Threshold test?
plot px exact threshold at various locations
useful for detecting or monitoring subtle changes such as in early disease
typically takes 3-5 mins per eye to do full threshold test
What is the Disadvantage of threshold tests?
time consuming
on Humphrey VFA the full threshold method employs a staircase at each location
What is the Humphrey threshold algorithm ?
predicts px threshold based on knowledge of a normal VF
SITA
Octopus threshold algorithm
TOP
What is the Henson threshold algorithm?
ZATA
What is the Suprathreshold test (single stimulus)?
use age-matched normal values as starting point + then present stimuli which are several decibels brighter
assumption is that all stimulus will be above the px threshold (easily seen) and someone with a normal field will get a full score
quicker and not as difficult for px as most lights can be easily detected
Main use of suprathreshold tests
Screening tool
if field abnormal can be very time consuming as machine goes on to plot exact threshold of each missed point → not using speedy algorithm
Limitation of suprathreshold tests
May miss subtle defects
What is the Multiple stimulus suprathreshold test?
initially determines rough threshold for px, then presents subsequent stimuli several dB above threshold
presents between 1-4 stimuli simultaneously at different locations
px must state how many lights seen on each presentation
any miss points →determined using clock face analogy , examiner then indicates missed stimuli on printout
quick screening tool
What is the 10-2 test?
concentrates on MACULAR REGION
Testing out to 10°
stimulus spacing of 2°
tests 68 locations in total → can see what part of macula affected
why is the 10-2 specialist test helpful?
mapping out CENTRAL defects
end stage disease where only a small island of vision is remaining → 24-2 would take very long time to complete
What is the Estermann test (specialist test)
Binocular suprathreshold test often used to determine px legality to drive → DVLA may request
tests 120 points at 10dB (fairly bright stimuli)
spans ~150°horizontally and 90° vertically