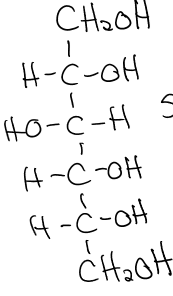exam 3
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
some enzymes, carbs, nucleic acids, and nucleotides
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
general mechanism of chymotrypsin
protein enters
this is what we want to break down in the stomach
Ser attacks protein → oxyanion forms → oxyanion hole (from enzyme backbone) stabilizes oxyanion
carbonyl is reformed int he oxyanion
carbonyl reforms → N-H bonds → 1st product leaves (R-NH2)
water enters the active site
water bonds to substrate → serine reforms → rest of peptide leaves (carboxylic acid)
regulatory enzymes
catalytic activity increases/decreases in response to certain signals
activities of regulatory enzymes are modulated through:
allosteric enzymes
reversible covalent modification
binding of separate regulatory proteins
removal of peptide segments by proteolytic cleavage
how do allosteric enzymes function?
function through reversible, noncovalent binding of regulatory compounds called allosteric modulators / effectors
adding a group that makes a change to the protein
what do allosteric enzymes do in response to modulator binding?
undergo conformational changes
what type of conformational changes can allosteric enzymes undergo?
homotrophic: regulation in which the substrate and modulator are identical
heterotrophic: regulation in which the modulator is a mlcl other than the substrate
what does a michaelis-menten graph of allosteric enzymes look like?
sigmoid curve
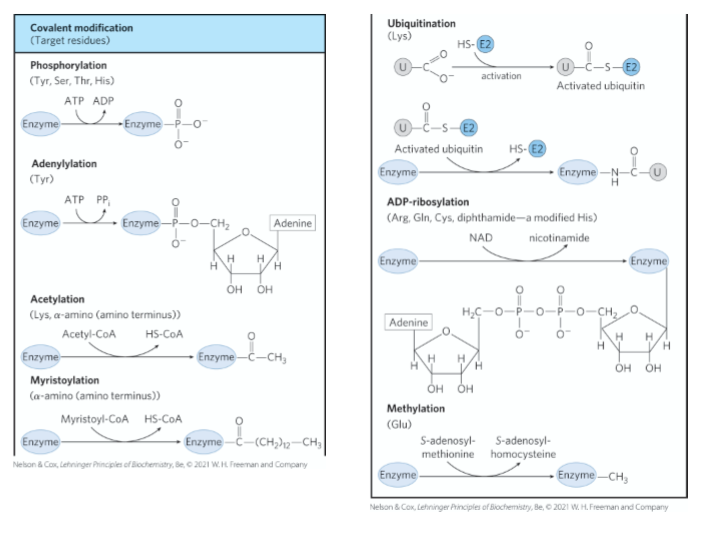
reversible covalent modification
a method of enzyme regulation
a small chemical group is added to / removed from a protein thus causing a temporary change in its structure + function
examples of reversible covalent modification
phosphorylation (ATP→ ADP)
acetylation (acetyl-CoA → HS-CoA)
proteolytic cleavage (of an enzyme precursor)
method of enzyme regulation
process in which a protein is broken down into smaller peptides / AA by enzymes called proteases
proteolytic cleavage of an enzyme precursor: examples of precursors
zymogen: inactive precursor that is cleaved to form an active protease enzyme
proprotein / proenzyme: precursors that are cleaved to form other proteins
what is the configuration of sugars based off of?
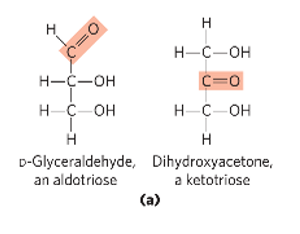
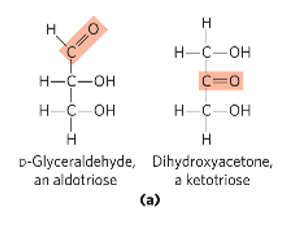
D-glyceraldehyde
structure of D-glyceraldehyde
aka aldose
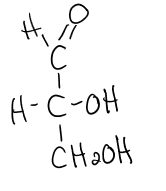
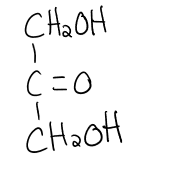
structure of dihydroxyacetone
aka ketose
structure of D-glucose
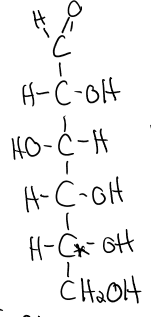
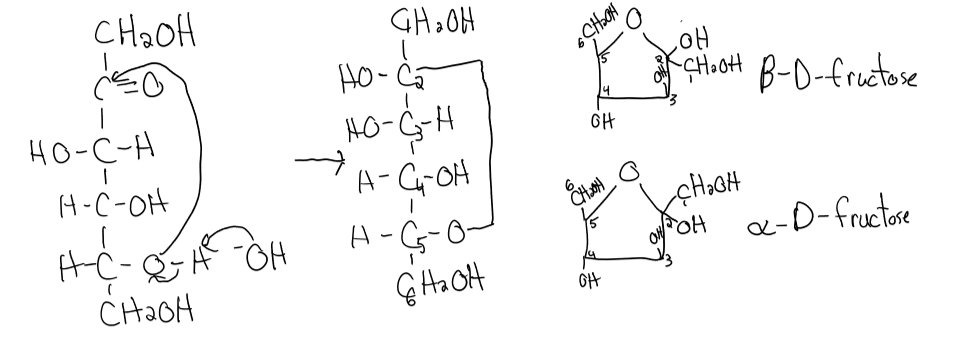
structure of fructose
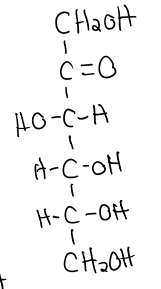
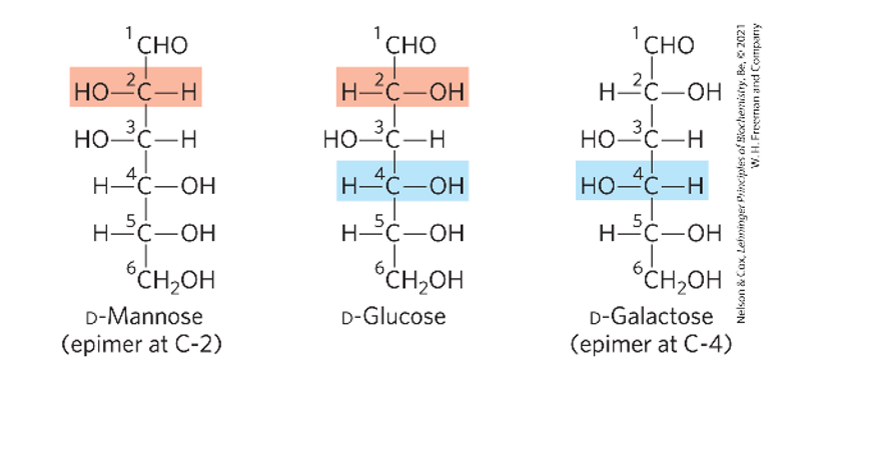
structure of mannose
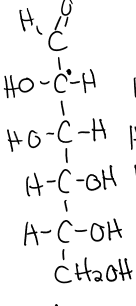
structure of galactose
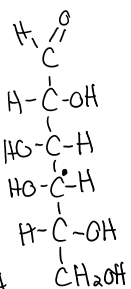
structure of ribose
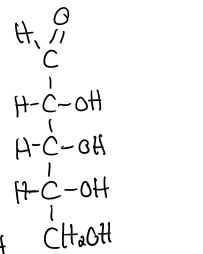
glucose function
blood sugar used for energy
fructose
fruit sugar
mannose
important for human metabolism, glycosylates proteins
epimer of glucose @ C2
galactose
component of milk sugar
epimer of glucose @ C4
ribose function
RNA
deoxyribose for DNA
hemiacetal formation
aldehyde + alcohol → pyranose ring
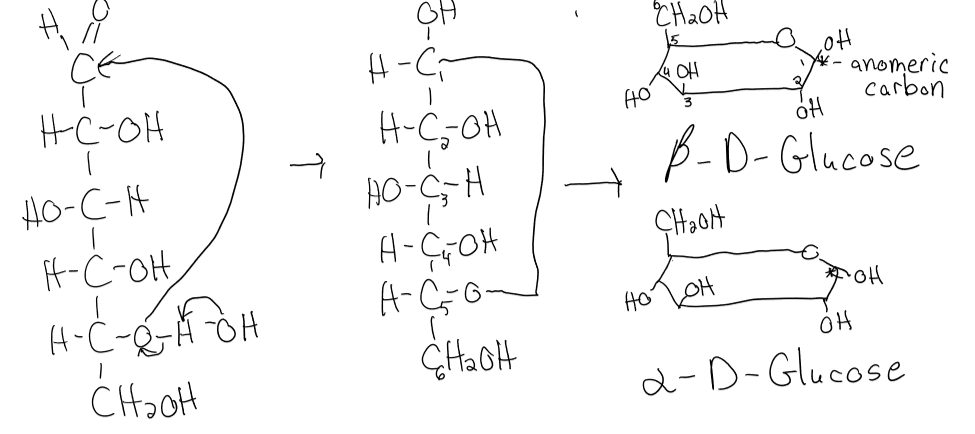
hemiketal formation
ketone + alcohol → furanose ring
hayworth structure rules
if OH group is on R in fisher → is down (axial) on hayworth structure
if OH group is on L in fisher → is up (equatorial) on hayworth structure
anomeric carbon: C in cyclic sugar that was formally the carbonyl carbon in the open-chain form
alpha structure of hayworth: OH group on anomeric carbon + CH2OH group on C6 point in OPPOSITE directions
beta structure of hayworth: groups both point in same direction
aldose
carbonyl group at the end of the C chain (in an aldehyde group)
ketose
carbonyl group that is at any other position than the end (in a ketone group)
how to number carbons on a sugar?
start at the end of the chain near the carbonyl group
epimers
2 sugars that differ only in the configuration around 1 C atom
pyranose
6C ring
form when the hydroxyl group at C6 reacts w the keto group at C2
furanose
5C ring
form when the hydroxyl group at C5 reacts w the keto group at C2
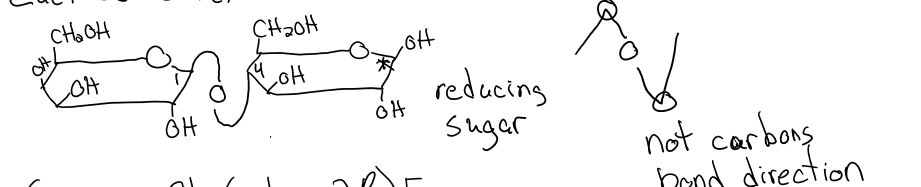
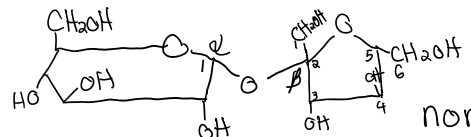
maltose
glucose (a1 → a4) glucose
reducing
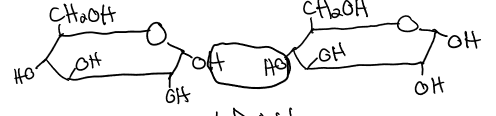
lactose
galactose (B1 →B4) glucose
reducing sugar
sucrose
glucose (a1 → B2) fructose
nonreducing sugar
what does the oxidation of glucose on C1 form?
gluconic acid
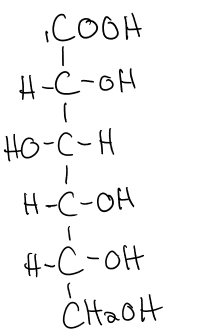
gluconic acid structure
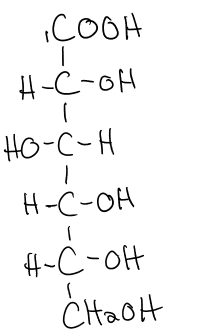
what does the oxidation of glucose on C6 form?
glucuronic acid
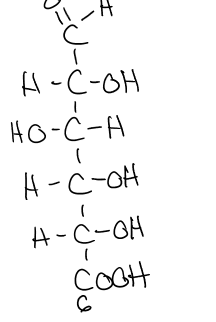
glucuronic acid structure
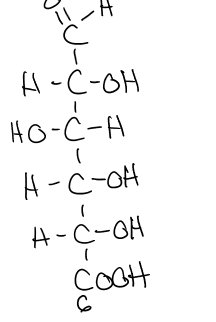
what does the reduction of glucose form?
sorbitol
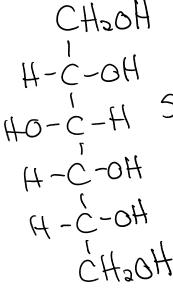
sorbitol structure