KIN 360--Exam 3: Practice Questions
4.5(8)
Card Sorting
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:31 PM on 4/24/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
1
New cards
what type of joint is the humeroulnar joint?
ginglymus
2
New cards
what type of joint is the humeroradial joint?
enarthrodial
3
New cards
what limits the rotation of the radius in the humeroradial joint?
annular ligament
4
New cards
what type of joint is the elbow?
ginglymus
5
New cards
when standing in AP, what is the angle of the forearm relative to the humerus called?
carrying angle
6
New cards
what is an exaggerated carrying angle called?
cubitis valgus
7
New cards
who has a naturally larger carrying angle: men or women?
women
8
New cards
why do women have a larger carrying angle?
narrower shoulders and a broader pelvis
9
New cards
what movements cause the carrying angle to disappear?
flexion and pronation
10
New cards
True or False: Elbow flexion is greater in pronation rather than supination.
False. It is larger in supination.
11
New cards
True or False: The proximal radioulnar joint is a trochoid type joint.
True
12
New cards
Multiple Choice: The distal radioulnar joint is which type?
\-enarthrodial
\-ginglymus
\-trochoid
\-condyloid
\-enarthrodial
\-ginglymus
\-trochoid
\-condyloid
trochoid
13
New cards
what three carpal bones make up the radiocarpal joint?
navicular, lunate, and triquetral
14
New cards
True or False: The MCP of the four fingers and the MCP of the thumb are the same type of joint.
False
15
New cards
what type of joint is the MCP of the four fingers?
condyloid
16
New cards
what type of joint is the MCP of the thumb?
ginglymus
17
New cards
True or False: You cannot abduct your fingers when they are already fully flexed.
true
18
New cards
what type of joint are the interphalangeal joints of the fingers and thumb?
ginglymus
19
New cards
Multiple Choice: What type of joint is the carpometacarpal joint of the thumb?
\-condyloid
\-trochoid
\-ginglymus
\-saddle
\-condyloid
\-trochoid
\-ginglymus
\-saddle
saddle
20
New cards
True or False: opposition of the thumb is the combination of adduction and flexion.
False. Abduction and hyperflexion.
21
New cards
at what joint of the thumb does opposition occur?
carpometacarpal
22
New cards
what bones make up the carpometacarpal joint of the thumb?
trapezium and the first metacarpal
23
New cards
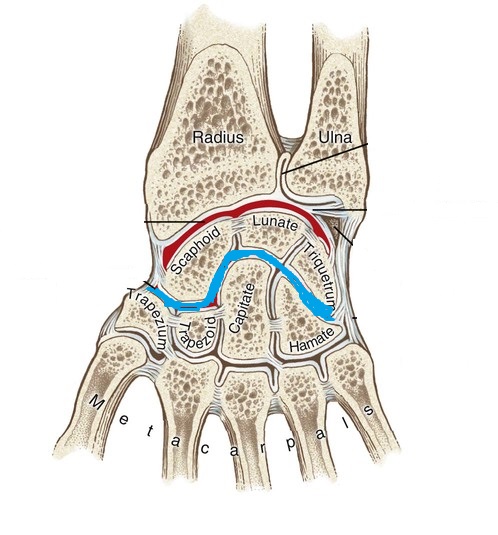
what is the articulation between the four carpal bones in the proximal row with the four in the distal row? (blue line)
midcarpal joint
24
New cards
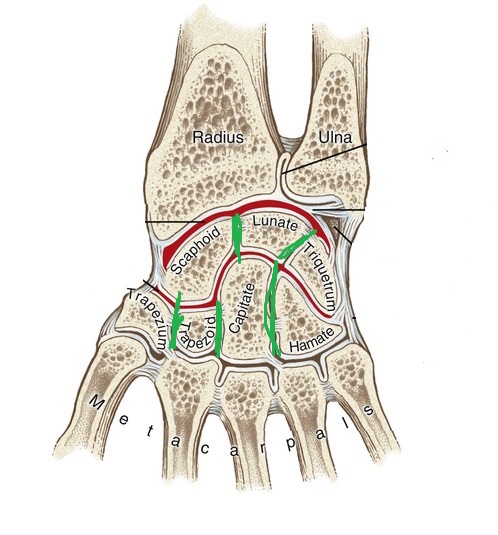
what are the articulations between the adjacent carpal bones within either row (proximal or distal)? (green lines)
intercarpal joint
25
New cards
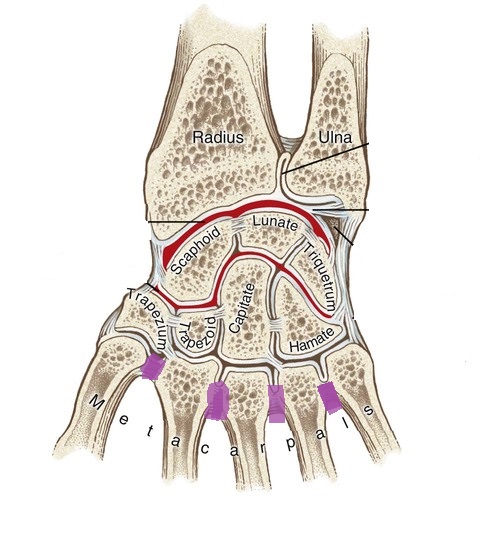
what are the articulations between the bases of the metacarpal bones of the four fingers? (purple lines)
intermetacarpal joints
26
New cards
what muscles prevents complete flexion of the wrist and fingers simultaneously? (hint: the one that causes pain when you do this)
extensor digitorum
27
New cards
True or False: maximal wrist action requires either flexed or extended fingers.
False. It requires relaxed fingers.
28
New cards
True or False: maximal finger action requires a relaxed wrist.
False. It requires a rigid wrist.
29
New cards
what 3 bones make up the acetabulum?
ilium, ischium, and pubis
30
New cards
what is the gap found in the lower aspect of the acetabulum called?
acetabular notch
31
New cards
True or False: The entire acetabulum is lined with hyaline cartilage.
True
32
New cards
True or False: This hyaline cartilage that lines the acetabulum is thicker inferiorly rather than superiorly.
False. It is thicker superiorly than it is inferiorly.
33
New cards
what makes up the glenoid labrum and covers the hyaline cartilage?
fibrocartilage
34
New cards
the head of the femur is completely covered in hyaline cartilage except where?
fovea capitis
35
New cards
what 3 factors contribute to the stability of the hip joint?
the spherical head of the femur, the deep socket, and the low atmospheric pressure within the socket
36
New cards
there are two hip bones that make up the pelvic girdle. these hip bones are the combination of what three bones?
ilium, ischium, and pubis
37
New cards
when do the components of the hip bones (the ilium, ischium, and pubis) become fully fused together?
puberty
38
New cards
what bone is the pelvic girdle attached to and what is the articulation between them called?
sacrum; sacroiliac articulation
39
New cards
what type of joint is the sacroiliac articulation?
diarthrodial
40
New cards
True or False: Voluntary movement is possible at the sacroiliac articulations
False
41
New cards
movement of the pelvis in the sagittal plane about a lateral axis so that the pubis symphysis turns downward and the posterior surface of the sacrum turns upward
forward tilt
42
New cards
what movement of the hip and of the spine create forward tilt of the pelvis?
hip flexion and spinal extension
43
New cards
a rotation of the pelvis in the sagittal plane about a lateral axis so that the pubis symphysis moves forward-upward and the posterior surface of the sacrum turns downward
backward tilt
44
New cards
True or False: The movements of the hip and spine that are required to create backward tilt of the pelvis are hip extension and spine flexion.
true
45
New cards
a rotation of the pelvis in the frontal plane about an antero-posterior axis so that one iliac crest is lowered and the other raised
lateral tilt
46
New cards
a rotation of the pelvis in the transverse (horizontal) plane about a vertical axis; the movement is named in terms of the direction toward which the front of the pelvis turns
rotation/lateral twist
47
New cards
true or false: turning your hips to the right would create a right rotation or right lateral twist of the pelvis.
true
48
New cards
True or False: The iliacus and psoas muscles only contribute to part of the motion of doing a sit-up from a supine position, aka flexion.
false